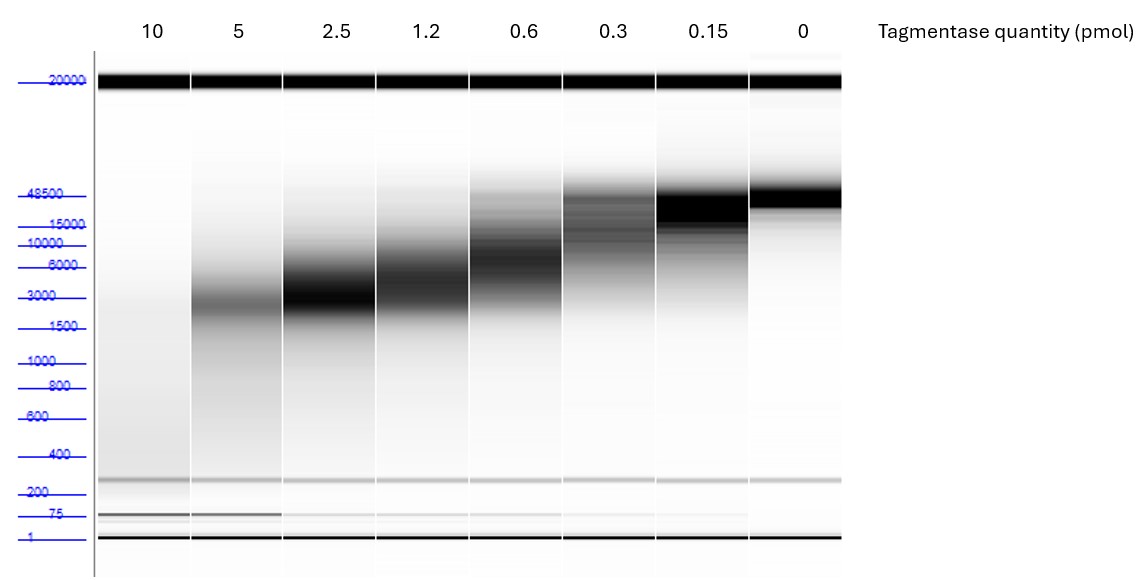
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: Tagmentase (Tn5 transposase) - unloaded (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C01070010-10). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Protocol for mapping insertion sites of Tol2 transgenes in zebrafish using TransTag
Wei, Xiaolu et al.
A valuable and widely utilized approach to study gene regulatory networks is through transgenic lines. However, detailed information of transgene insertion sites is often not available, complicating the interpretation of experimental results involving transgenes. Here, we present a protocol for mapping the inserti... |
Human iPSCs-based modeling unveils SETBP1 as a driver of chromatin rewiring in GATA2 deficiency
Pera, Joan et al.
Patients with GATA2 deficiency are predisposed to developing myelodysplastic neoplasms (MDS), which can progress to acute myeloid leukemia. This progression is often associated with cytogenetic and somatic alterations. Mutations in SETBP1 and ASXL1 genes are recurrently observed in GATA2 patients, although their... |
Single-cell, multi-region profiling of the macaque brain across the lifespan
Yang, Wei et al.
Brain aging is a complex process with profound health and societal consequences. However, the molecular and cellular pathways that govern its temporal progression–along with any cell type-, region-, and sex-specific heterogeneity in such progression–remain poorly defined. Here, we present a transcripto... |
The brain neurovascular epigenome and its association with dementia
Ziegler, Kevin Chris et al.
Cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) is frequently comorbid with Alzheimer's disease (AD), and brain endothelial cells (BECs) express genes associated with AD genetic risk. However, the epigenome of neurovascular cells and its intersection with genetic risk remain unexplored. Here, we generated gene regulomes for h... |
Global Mapping of Combinatorial Chromatin Regulatory Events Using Hi-Plex CUT&Tag
Liao, Yuan et al.
Epigenetic modulators, transcription factors, and chromatin-associated proteins collaboratively regulate essential genomic functions, such as transcription, repression, and DNA damage repair. However, the intricate cross-talk or the interaction between these chromatin regulatory factors (CRFs) remains poorly under... |
Epigenomic Heterogeneity of Non-Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Uncovered by Single nucleus and Spatial ATAC Profiling
Wang, Dejiang et al.
Non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (NF-PanNETs) account for the majority of neuroendocrine neoplasms arising in the pancreas and exhibit substantial clinical and biological heterogeneity, yet their epigenetic regulation and spatial architecture remain poorly understood. Here, we present an integrati... |
Spatial joint profiling of DNA methylome and transcriptome in tissues
Lee, Chin Nien et al.
The spatial resolution of omics analyses is fundamental to understanding tissue biology1-3. The capacity to spatially profile DNA methylation, which is a canonical epigenetic mark extensively implicated in transcriptional regulation4,5, is lacking. Here we introduce a method for whole-genome spatial co-profiling... |
Charting the Multi-level Molecular Response to Palbociclib in ER-Positive Breast Cancer
Kavalipati, Archishma et al.
The addition of CDK4/6 inhibitors to endocrine therapy has significantly improved outcomes in HR+/HER2-breast cancer. However, variable patient responses and acquired resistance remain a clinical challenge. We therefore defined the comprehensive molecular response to palbociclib, the most clinically used CDK4/6 ... |
Beyond the Cut: Long-read sequencing reveals complex genomic and transcriptomic changes in AAV-CRISPR therapy for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Jia, Mary S et al.
Adeno associated virus (AAV)-mediated delivery of CRISPR associated nucleases (AAV-CRISPR) is a promising solution to treat genetic diseases such as Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) and is now in early clinical trials. However, genotoxicity and immunogenicity concerns have hindered clinical translation. Due to the ... |
TransTag enables simple and efficient transgene mapping in zebrafish via tagmentation
Meng, Fanju W et al.
Zebrafish has become a preeminent model for developmental biology research, largely due to the ease of transgenesis. Despite widespread usage of transgenic lines, mapping of transgene insertion sites is rare, which raises complications involving potential local chromatin influences on transgene expression, off-targe... |
Spatial profiling of chromatin accessibility in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues
Guo, Pengfei et al.
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples represent a vast, untapped resource for epigenomic research, yet molecular tools for deep analysis of these specimens remain limited. We introduce spatial FFPE-ATAC-seq, an approach for in situ profiling chromatin accessibility within archived tissues. This approach ... |
RSK1-driven TRIM28/E2F1 feedback loop promotes castration-resistant prostate cancer progression
Kim, Miyeong et al.
Castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) marks the advanced and lethal stage of prostate cancer (PCa). TRIM28, also known as KAP1, is a transcriptional regulator recently shown to promote CRPC cell proliferation and xenograft tumor growth. Nonetheless, knowledge gaps persist regarding the mechanisms underlying ... |
Spatial epigenomic niches underlie glioblastoma cell state plasticity
Kint, Sam et al.
IDH-wildtype glioblastoma (GBM) is an aggressive brain tumor with poor survival and few therapeutic options. Transcriptionally-defined cell states coexist in GBM and occupy defined regions of the tumor. Evidence indicates that GBM cell states are plastic, but it remains unclear if they are determined by the underl... |
Unified molecular approach for spatial epigenome, transcriptome, and cell lineages
Huang, YH., et al.
Spatial epigenomics and multiomics can provide fine-grained insights into cellular states but their widespread adoption is limited by the requirement for bespoke slides and capture chemistries for each data modality. Here, we present SPatial assay for Accessible chromatin, Cell lineages, and gene Expression with seq... |
Single cell multi-omic whole genome sequencing and chromatin accessibility profiling reveals genome-epigenome coevolution in colorectal cancer
Mossner, Maximilian et al.
Epigenetic alterations co-evolve with genetic mutations to drive carcinogenesis and treatment response. Resolving genome-epigenome coevolution requires accurate multi-omic single cell measurement. Here we develop a new technology called “double ATAC” (dATAC) for high-throughput, high-quality, concurren... |
Embryo-scale single-cell chemical transcriptomics reveals dependencies between cell types and signaling pathways
Barkan, E., et al.
Summary
Organogenesis is a highly organized process that is conserved across vertebrates and is heavily dependent on intercellular signaling to achieve cell type identity. We lack a comprehensive understanding of how developing cell types in each organ and tissue depend on developmental signaling pathways. To addre... |
Spatial transcriptomic imaging of an intact organism using volumetric DNA microscopy
Qian, N., Weinstein, J.A.
Lymphatic, nervous and tumor tissues exhibit complex physiology arising from three-dimensional interactions within genetically unique microenvironments. Here we develop a technology capable of volumetrically imaging transcriptomes, genotypes and morphologies in a single measurement, without relying on prior knowledg... |
Spatially resolved genome-wide joint profiling of epigenome and transcriptome with spatial-ATAC-RNA-seq and spatial-CUT&Tag-RNA-seq
Haikuo Li et al.
The epigenome of a cell is tightly correlated with gene transcription, which controls cell identity and diverse biological activities. Recent advances in spatial technologies have improved our understanding of tissue heterogeneity by analyzing transcriptomics or epigenomics with spatial information preserved, but ha... |
Multi-step genomics on single cells and live cultures in sub-nanoliter capsules
Mazelis I, et al.
Abstract
Single-cell genomics encompasses a set of methods whereby hundreds to millions of cells are individually subjected to multiplexed assays including sequencing DNA, chromatin accessibility or modification, RNA, or combinations thereof 1,2. These methods enable unbiased, systematic discovery of cellular ... |
Recurrent patterns of widespread neuronal genomic damage shared by major neurodegenerative disorders
Zinan Zhou et al.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), frontotemporal dementia (FTD), and Alzheimer's disease (AD) are common neurodegenerative disorders for which the mechanisms driving neuronal death remain unclear. Single-cell whole-genome sequencing of 429 neurons from three C9ORF72 ALS, six C9ORF72 FTD, seven AD, and twenty-thre... |
Diverse somatic genomic alterations in single neurons in chronic traumatic encephalopathy
Guanlan Dong et al.
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a neurodegenerative disease that is linked to exposure to repetitive head impacts (RHI), yet little is known about its pathogenesis. Applying two single-cell whole-genome sequencing methods to hundreds of neurons from prefrontal cortex of 15 individuals with CTE, and 4 with ... |
Combinatorial mapping of E3 ubiquitin ligases to their target substrates
Chase C. Suiter et al.
Highlights
Developed a combinatorial assay to test E3-substrate interactions at scale
Identified known and unknown E3-substrate relationships across three screens
Assessment of in silico models points to scalable computational substrate discovery
Computed models of E3-... |
Minimization of gene editing off-target effects by tissue restriction of expression
Nam-Gyun Kim et al.
Therapeutic in vivo gene editing with highly specific nucleases has the potential to revolutionize treatment for a wide range of human diseases, including genetic disorders and latent viral infections like herpes simplex virus (HSV). However, challenges regarding specificity, efficiency, delivery, and safe... |
Cells transit through a quiescent-like state to convert to neurons at high rates
A. Beitz et al.
While transcription factors (TFs) provide essential cues for directing and redirecting cell fate, TFs alone are insufficient to drive cells to adopt alternative fates. Rather, transcription factors rely on receptive cell states to induce novel identities. Cell state emerges from and is shaped by cellular history and... |
Enhancing single-cell ATAC sequencing with formaldehyde fixation, cryopreservation, and multiplexing for flexible analysis
Tobias Hohl et al.
The assay for transposase-accessible chromatin using sequencing (ATAC-seq) revolutionized the field of epigenetics since its emergence by providing a means to uncover chromatin dynamics and other factors affecting gene expression. The development of single-cell (sc) applications in recent years led to an even deeper... |
Engineered PsCas9 enables therapeutic genome editing in mouse liver with lipid nanoparticles
Dmitrii Degtev et al.
Clinical implementation of therapeutic genome editing relies on efficient in vivo delivery and the safety of CRISPR-Cas tools. Previously, we identified PsCas9 as a Type II-B family enzyme capable of editing mouse liver genome upon adenoviral delivery without detectable off-targets and reduced chromosomal translocat... |
AistSeq: An In-House Tn5-Based Plasmid Sequencing Platform Using A Compact Benchtop Sequencer
Hayato Suzuki et al.
Sequence verification of plasmids is a fundamental process in synthetic biology. For plasmid sequence verification using next-generation sequencing (NGS) library preparation, Tn5 transposase is widely used. Streamlined sequencing workflow for laboratory-scale applications is important; however, recombinant Tn5 produ... |
Rational design of peak calling parameters for TIP-seq based on pA-Tn5 insertion patterns improves predictive power
Thomas Roberts et al.
Epigenomic profiling provides insights into the regulatory mechanisms that govern gene expression. At a fundamental level, these mechanisms are determined by proteins that bind the DNA or modify the chromatin. Techniques such as ChIP-seq and CUT&Tag have been instrumental in mapping the binding sites of such pro... |
Multiplex, single-cell CRISPRa screening for cell type specific regulatory elements
Florence M. Chardon et al.
CRISPR-based gene activation (CRISPRa) is a strategy for upregulating gene expression by targeting promoters or enhancers in a tissue/cell-type specific manner. Here, we describe an experimental framework that combines highly multiplexed perturbations with single-cell RNA sequencing (sc-RNA-seq) to identify cell-typ... |
Auto-expansion of in vivo HDAd-transduced hematopoietic stem cells by constitutive expression of tHMGA2
Wang H. et al.
We developed an in vivo hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) gene therapy approach that does not require cell transplantation. To achieve therapeutically relevant numbers of corrected cells, we constructed HSC-tropic HDAd5/35++ vectors expressing a 3′ UTR truncated HMGA2 gene and a GFP reporter gene. A... |
Single cell genome and epigenome co-profiling reveals hardwiring and plasticity in breast cancer
Kaile Wang et al.
Understanding the impact of genetic alterations on epigenomic phenotypes during breast cancer progression is challenging with unimodal measurements. Here, we report wellDA-seq, the first high-genomic resolution, high-throughput method that can simultaneously measure the whole genome and chromatin accessibility profi... |
Precision and efficacy of RNA-guided DNA integration in high-expressing muscle loci
Made Harumi Padmaswari et al.
Gene replacement therapies primarily rely on adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors for transgene expression. However, episomal expression can decline over time due to vector loss or epigenetic silencing. CRISPR-based integration methods offer promise for long-term transgene insertion. While the development of transge... |
Detection of genome structural variation in normal cells and tissues by single molecule sequencing
Heid J. et al.
Detecting somatic mutations in normal cells and tissues is notoriously challenging due to their low abundance, orders of magnitude below the sequencing error rate. While several techniques, such as single-cell and single-molecule sequencing, have been developed to identify somatic mutations, they are insufficient fo... |
Technical considerations for cost-effective transposon directed insertion-site sequencing (TraDIS)
Kyono Y. et al.
Transposon directed insertion-site sequencing (TraDIS), a variant of transposon insertion sequencing commonly known as Tn-Seq, is a high-throughput assay that defines essential bacterial genes across diverse growth conditions. However, the variability between laboratory environments often requires laborious, time-co... |
MED1 IDR acetylation reorganizes the transcription preinitiation complex, rewires 3D chromatin interactions and reprograms gene expression
Ran Lin et al.
With our current appreciation of the complexity of eukaryotic transcription, whose dysregulation drives diseases including cancer, it is becoming apparent that identification of key events coordinating multiple aspects of transcriptional regulation is of special importance. To elucidate how assembly of RNA polymeras... |
Plasticity-induced repression of Irf6 underlies acquired resistance to cancer immunotherapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Kim IK et al.
Acquired resistance to immunotherapy remains a critical yet incompletely understood biological mechanism. Here, using a mouse model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) to study tumor relapse following immunotherapy-induced responses, we find that resistance is reproducibly associated with an epithelial-to-mes... |
CompDuplex: Accurate detection of somatic mutations by duplex-seq with comprehensive genome coverage
Muchun Niu et al.
Somatic mutations continuously accumulate in the human genome, posing vulnerabilities towards aging and increased risk of various diseases. However, accurate detection of somatic mutations at the whole genome scale is still challenging. By tagging and independently sequencing the two complementar... |
Integrative functional genomic analyses identify genetic variants influencing skin pigmentation in Africans
Yuanqing Feng et al.
Skin color is highly variable in Africans, yet little is known about the underlying molecular mechanism. Here we applied massively parallel reporter assays to screen 1,157 candidate variants influencing skin pigmentation in Africans and identified 165 single-nucleotide polymorphisms showing differential regulatory a... |
High-capacity sample multiplexing for single cell chromatin accessibility profiling
Gregory T. Booth et al.
Single-cell chromatin accessibility has emerged as a powerful means of understanding the epigenetic landscape of diverse tissues and cell types, but profiling cells from many independent specimens is challenging and costly. Here we describe a novel approach, sciPlex-ATAC-seq, which uses unmodified DNA oligos as samp... |
A Type II-B Cas9 nuclease with minimized off-targets and reduced chromosomal translocations in vivo
Bestas B. et al.
Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9 (SpCas9) and derived enzymes are widely used as genome editors, but their promiscuous nuclease activity often induces undesired mutations and chromosomal rearrangements. Several strategies for mapping off-target effects have emerged, but they suffer from limited sensitivity. To i... |
Combined Analysis of mRNA Expression and Open Chromatin in Microglia
Scholz R.et al.
The advance of single-cell RNA-sequencing technologies in the past years has enabled unprecedented insights into the complexity and heterogeneity of microglial cell states in the homeostatic and diseased brain. This includes rather complex proteomic, metabolomic, morphological, transcriptomic, and epigenetic adaptat... |
Volumetric imaging of an intact organism by a distributed molecular network
Nianchao Qian and Joshua A Weinstein
Lymphatic, nervous, and tumoral tissues, among others, exhibit physiology that emerges from three-dimensional interactions between genetically unique cells. A technology capable of volumetrically imaging transcriptomes, genotypes, and morphologies in a single de novo measurement would therefore provide a critical vi... |
CXCR4 signaling strength regulates hematopoietic multipotent progenitor fate through extrinsic and intrinsic mechanisms
Vincent Rondeau et al.
How cell-extrinsic niche-related and cell-intrinsic cues drive lineage specification of hematopoietic multipotent progenitors (MPPs) in the bone marrow (BM) is partly understood. We show that CXCR4 signaling strength regulates localization and fate of MPPs. In mice phenocopying the BM myeloid skewing of patients wit... |
Spatial epigenome-transcriptome co-profiling of mammalian tissues.
Zhang D. et al.
Emerging spatial technologies, including spatial transcriptomics and spatial epigenomics, are becoming powerful tools for profiling of cellular states in the tissue context. However, current methods capture only one layer of omics information at a time, precluding the possibility of examining the mechanistic relatio... |
Analyzing genomic and epigenetic profiles in single cells by hybridtransposase (scGET-seq).
Cittaro D. et al.
scGET-seq simultaneously profiles euchromatin and heterochromatin. scGET-seq exploits the concurrent action of transposase Tn5 and its hybrid form TnH, which targets H3K9me3 domains. Here we present a step-by-step protocol to profile single cells by scGET-seq using a 10× Chromium Controller. We describ... |
Imaging Chromatin Accessibility by Assay ofTransposase-Accessible Chromatin with Visualization.
Miyanari Yusuke
Chromatin accessibility is one of the fundamental structures regulating genome functions including transcription and DNA repair. Recent technological advantages to analyze chromatin accessibility begun to explore the dynamics of local chromatin structures. Here I describe protocols for Assay of Transposase-Accessibl... |
Mouse kidney nuclear isolation and library preparation for single-cell combinatorial indexing RNA sequencing
Li Haikuo and Humphreys Benjamin D.
Single-cell combinatorial indexing RNA sequencing (sci-RNA-seq3) enables high-throughput single-nucleus transcriptomic profiling of multiple samples in one experiment. Here, we describe an optimized protocol of mouse kidney nuclei isolation and sci-RNA-seq3 library preparation. The use of a dounce tissue homogenizer... |
Optimized single-nucleus transcriptional profiling by combinatorialindexing.
Martin Beth K et al.
Single-cell combinatorial indexing RNA sequencing (sci-RNA-seq) is a powerful method for recovering gene expression data from an exponentially scalable number of individual cells or nuclei. However, sci-RNA-seq is a complex protocol that has historically exhibited variable performance on different tissues, as well a... |
Spatial profiling of chromatin accessibility in mouse and human tissues
Yanxiang Deng et al.
Cellular function in tissue is dependent on the local environment, requiring new methods for spatial mapping of biomolecules and cells in the tissue context1. The emergence of spatial transcriptomics has enabled genome-scale gene expression mapping2,3,4,5, but the ability to capture spatial epigenetic informati... |
Spatially resolved epigenome-transcriptome co-profiling of mammalian tissues at the cellular level
Fan Rong et al.
Emerging spatial technologies including spatial transcriptomics and spatial epigenomics are becoming powerful tools for profiling cellular states in the tissue context. However, current methods capture only one layer of omics information at a time precluding the possibility to examine the mechanistic relationship ac... |
Reverse-transcribed SARS-CoV-2 RNA can integrate into the genome of cultured human cells and can be expressed in patient-derived tissues
Liguo Zhang et al.
Prolonged detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA and recurrence of PCR-positive tests have been widely reported in patients after recovery from COVID-19, but some of these patients do not appear to shed infectious virus. We investigated the possibility that SARS-CoV-2 RNAs can ... |
T-RHEX-RNAseq – A tagmentation-based, rRNA blocked, randomhexamer primed RNAseq method for generating stranded RNAseq librariesdirectly from very low numbers of lysed cells
Gustafsson Charlotte et al.
Background: RNA sequencing has become the mainstay for studies of gene expression. Still, analysis of rare cells with random hexamer priming – to allow analysis of a broader range of transcripts – remains challenging. Results: We here describe a tagmentation-based, rRNA blocked, random hexamer primed RNA... |