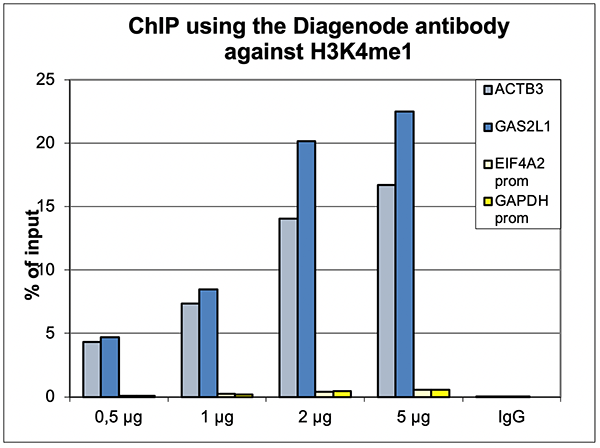
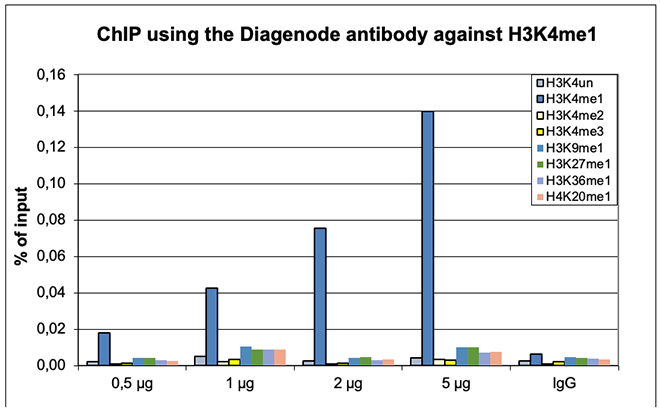
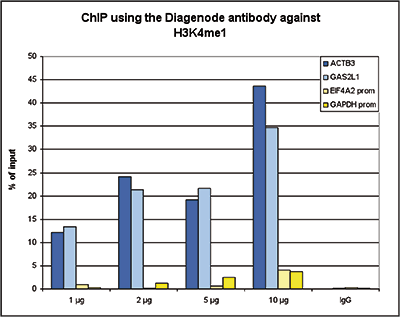
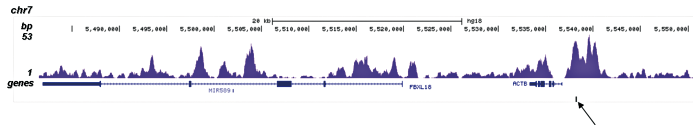
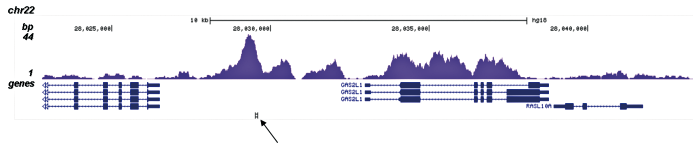
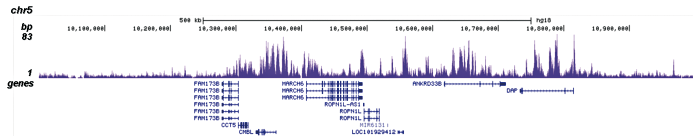
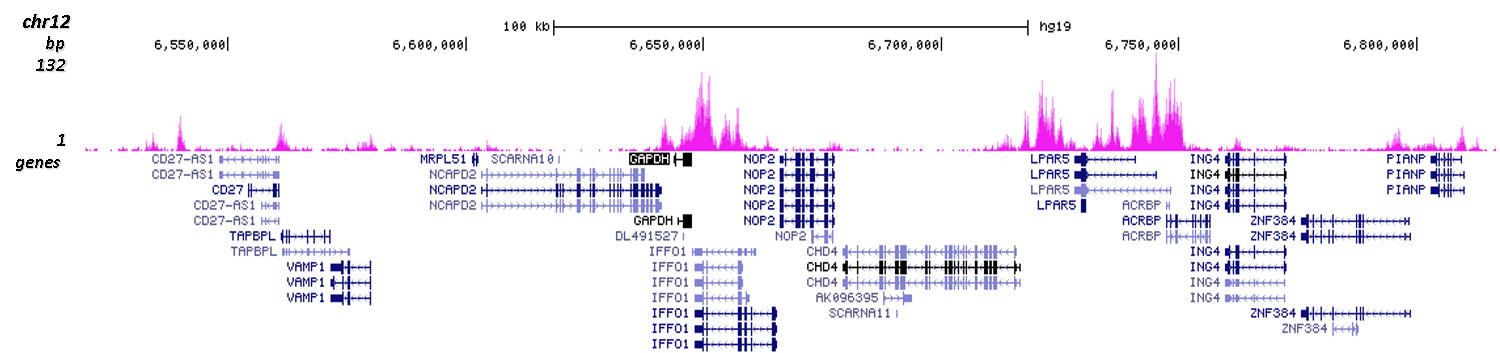
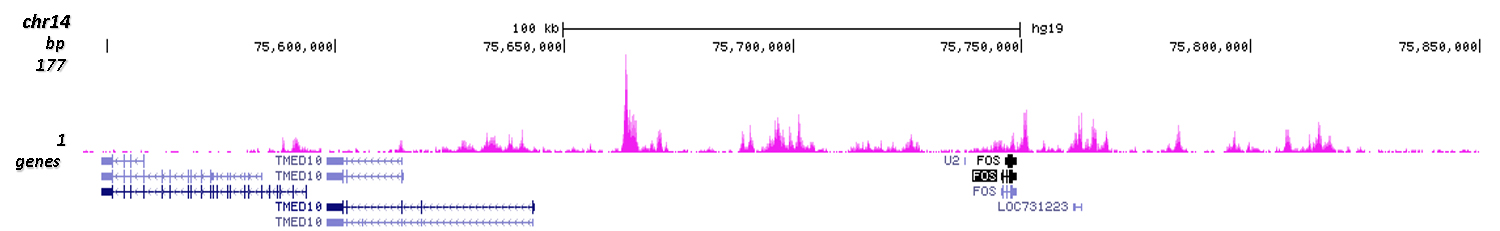
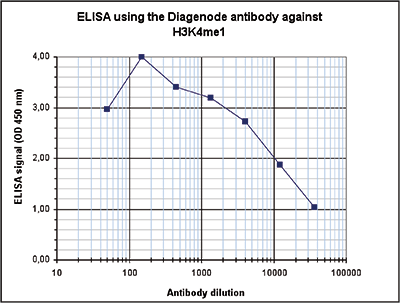
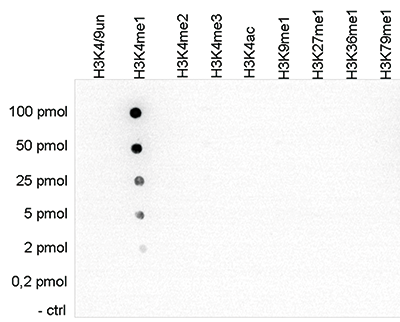
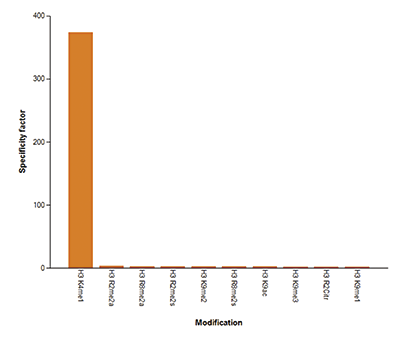
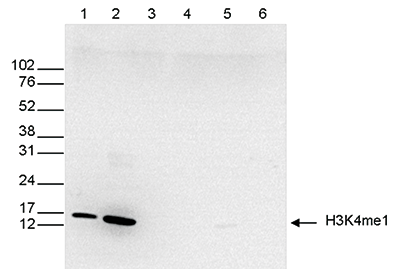
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K4me1 Antibody (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410194 Lot# A1862D). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
CRISPR-based precise methylation of specific FUT8 promoter regions allows isolation of CHO cells with a fine-tuned glycoprofile
Jiménez Lancho, Víctor et al.
A major advantage of producing therapeutic proteins in mammalian cells is their ability to tailor proteins with human-like posttranslational modifications such as glycosylation, which ultimately defines aspects like stability, protein folding or immunogenicity. However, producing therapeutic proteins with a consis... |
Lysine-specific demethylase 1 regulates hematopoietic stem cell expansion and myeloid cell differentiation
Staehle, Hans Felix et al.
The lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) regulates hematopoietic stem cell differentiation and has been identified as a therapeutic target in hematological disorders. LSD1 demethylates mono and dimethylated histones 3 at lysine 4 and 9. In addition, it acts as a scaffold for the formation of chromatin-modifying ... |
Chromatin environment-dependent effects of DOT1L on gene expression in male germ cells
Manon Coulée et al.
The H3K79 methyltransferase DOT1L is essential for multiple aspects of mammalian development where it has been shown to regulate gene expression. Here, by producing and integrating epigenomic and spike-in RNA-seq data, we decipher the molecular role of DOT1L during mouse spermatogenesis and show that it has opposite... |
Trithorax regulates long-term memory in Drosophila through epigenetic maintenance of mushroom body metabolic state and translation capacity
Nicholas Raun et al.
The role of epigenetics and chromatin in the maintenance of postmitotic neuronal cell identities is not well understood. Here, we show that the histone methyltransferase Trithorax (Trx) is required in postmitotic memory neurons of the Drosophila mushroom body (MB) to enable their capacity for long-term mem... |
Interferon-gamma rescues FK506 dampened dendritic cell calcineurin-dependent responses to Aspergillus fumigatus via Stat3 to Stat1 switching
Amit Adlakha et al.
IScience Highlights
Calcineurin inhibitors block DC maturation in response to A. fumigatus
Lack of DC maturation impairs Th1 polarization in response to A. fumigatus
Interferon-γ restores maturation, promotes Th1 polarization and fungal killing
ChIPseq reveals in... |
Systematic prioritization of functional variants and effector genes underlying colorectal cancer risk
Law P.J. et al.
Genome-wide association studies of colorectal cancer (CRC) have identified 170 autosomal risk loci. However, for most of these, the functional variants and their target genes are unknown. Here, we perform statistical fine-mapping incorporating tissue-specific epigenetic annotations and massively parallel reporter as... |
RNA sequestration in P-bodies sustains myeloid leukaemia
Srikanth Kodali et al.
Post-transcriptional mechanisms are fundamental safeguards of progenitor cell identity and are often dysregulated in cancer. Here, we identified regulators of P-bodies as crucial vulnerabilities in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) through genome-wide CRISPR screens in normal and malignant haematopoietic progenitors. We... |
A multiomic atlas of the aging hippocampus reveals molecular changes in response to environmental enrichment
Perez R. F. at al.
Aging involves the deterioration of organismal function, leading to the emergence of multiple pathologies. Environmental stimuli, including lifestyle, can influence the trajectory of this process and may be used as tools in the pursuit of healthy aging. To evaluate the role of epigenetic mechanisms in this context, ... |
Alterations in the hepatocyte epigenetic landscape in steatosis.
Maji Ranjan K. et al.
Fatty liver disease or the accumulation of fat in the liver, has been reported to affect the global population. This comes with an increased risk for the development of fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Yet, little is known about the effects of a diet containing high fat and alcohol towards epigenet... |
Comprehensive epigenomic profiling reveals the extent of disease-specificchromatin states and informs target discovery in ankylosing spondylitis
Brown A.C. et al.
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a common, highly heritable inflammatory arthritis characterized by enthesitis of the spine and sacroiliac joints. Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have revealed more than 100 genetic associations whose functional effects remain largely unresolved. Here, we present a comprehensiv... |
DNA dioxygenases Tet2/3 regulate gene promoter accessibility andchromatin topology in lineage-specific loci to control epithelialdifferentiation.
Chen G-D et al.
Execution of lineage-specific differentiation programs requires tight coordination between many regulators including Ten-eleven translocation (TET) family enzymes, catalyzing 5-methylcytosine oxidation in DNA. Here, by using --driven ablation of genes in skin epithelial cells, we demonstrate that ablation of results... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple Myeloma
Elina Alaterre et al.
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have been widely used to understand themolecular processes that drive MM biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape of MM wouldadvance our un... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple
Myeloma
Alaterre, Elina and Ovejero, Sara and Herviou, Laurie and de
Boussac, Hugues and Papadopoulos, Giorgio and Kulis, Marta and
Boireau, Stéphanie and Robert, Nicolas and Requirand, Guilhem
and Bruyer, Angélique and Cartron, Guillaume and Vincent,
Laure and M
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have
been widely used to understand the molecular processes that drive MM
biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,
progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the
epigenetic landscape of MM would advance our... |
Epromoters function as a hub to recruit key transcription factorsrequired for the inflammatory response
Santiago-Algarra D. et al.
Gene expression is controlled by the involvement of gene-proximal (promoters) and distal (enhancers) regulatory elements. Our previous results demonstrated that a subset of gene promoters, termed Epromoters, work as bona fide enhancers and regulate distal gene expression. Here, we hypothesized that Epromoters play a... |
p300 suppresses the transition of myelodysplastic syndromes to acutemyeloid leukemia
Man Na et al.
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) malignancies characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis and an increased risk of leukemia transformation. Epigenetic regulators are recurrently mutated in MDS, directly implicating epigenetic dysregulation in MDS pathogenesis. Here, we... |
Epigenetic control of region-specific transcriptional programs in mousecerebellar and cortical astrocytes.
Welle Anna et al.
Astrocytes from the cerebral cortex (CTX) and cerebellum (CB) share basic molecular programs, but also form distinct spatial and functional subtypes. The regulatory epigenetic layers controlling such regional diversity have not been comprehensively investigated so far. Here, we present an integrated epigenome analys... |
Lasp1 regulates adherens junction dynamics and fibroblast transformationin destructive arthritis
Beckmann D. et al.
The LIM and SH3 domain protein 1 (Lasp1) was originally cloned from metastatic breast cancer and characterised as an adaptor molecule associated with tumourigenesis and cancer cell invasion. However, the regulation of Lasp1 and its function in the aggressive transformation of cells is unclear. Here we use integrativ... |
Sarcomere function activates a p53-dependent DNA damage response that promotes polyploidization and limits in vivo cell engraftment.
Pettinato, Anthony M. et al.
Human cardiac regeneration is limited by low cardiomyocyte replicative rates and progressive polyploidization by unclear mechanisms. To study this process, we engineer a human cardiomyocyte model to track replication and polyploidization using fluorescently tagged cyclin B1 and cardiac troponin T. Using time-lapse i... |
GATA6 defines endoderm fate by controlling chromatin accessibility duringdifferentiation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells
Heslop J. A. et al.
SUMMARY In addition to driving specific gene expression profiles, transcriptional regulators are becoming increasingly recognized for their capacity to modulate chromatin structure. GATA6 is essential for the formation of definitive endoderm; however, the molecular basis defining the importance of GATA6 to endoderm ... |
Androgen and glucocorticoid receptor direct distinct transcriptionalprograms by receptor-specific and shared DNA binding sites.
Kulik, Marina et al.
The glucocorticoid (GR) and androgen (AR) receptors execute unique functions in vivo, yet have nearly identical DNA binding specificities. To identify mechanisms that facilitate functional diversification among these transcription factor paralogs, we studied them in an equivalent cellular context. Analysis of chroma... |
Epigenomic landscape of human colorectal cancer unveils an aberrant core ofpan-cancer enhancers orchestrated by YAP/TAZ.
Della Chiara, Giulia et al.
Cancer is characterized by pervasive epigenetic alterations with enhancer dysfunction orchestrating the aberrant cancer transcriptional programs and transcriptional dependencies. Here, we epigenetically characterize human colorectal cancer (CRC) using de novo chromatin state discovery on a library of different patie... |
Epigenomic tensor predicts disease subtypes and reveals constrained tumorevolution.
Leistico, Jacob R et al.
Understanding the epigenomic evolution and specificity of disease subtypes from complex patient data remains a major biomedical problem. We here present DeCET (decomposition and classification of epigenomic tensors), an integrative computational approach for simultaneously analyzing hierarchical heterogeneous data, ... |
Restricted nucleation and piRNA-mediated establishment of heterochromatinduring embryogenesis in Drosophila miranda
Wei, K. et al.
Heterochromatin is a key architectural feature of eukaryotic genomes, crucial for silencing of repetitive elements and maintaining genome stability. Heterochromatin shows stereotypical enrichment patterns around centromeres and repetitive sequences, but the molecular details of how heterochromatin is established dur... |
Environmental enrichment induces epigenomic and genome organization changesrelevant for cognitive function
Espeso-Gil, S. et al.
In early development, the environment triggers mnemonic epigenomic programs resulting in memory and learning experiences to confer cognitive phenotypes into adulthood. To uncover how environmental stimulation impacts the epigenome and genome organization, we used the paradigm of environmental enrichment (EE) in youn... |
Kmt2c mutations enhance HSC self-renewal capacity and convey a selectiveadvantage after chemotherapy.
Chen, Ran et al.
The myeloid tumor suppressor KMT2C is recurrently deleted in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML), particularly therapy-related MDS/AML (t-MDS/t-AML), as part of larger chromosome 7 deletions. Here, we show that KMT2C deletions convey a selective advantage to hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs... |
The glucocorticoid receptor recruits the COMPASS complex to regulateinflammatory transcription at macrophage enhancers.
Greulich, Franziska et al.
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are effective anti-inflammatory drugs; yet, their mechanisms of action are poorly understood. GCs bind to the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), a ligand-gated transcription factor controlling gene expression in numerous cell types. Here, we characterize GR's protein interactome and find the SETD1A ... |
Analysis of Histone Modifications in Rodent Pancreatic Islets by Native Chromatin Immunoprecipitation.
Sandovici I, Nicholas LM, O'Neill LP
The islets of Langerhans are clusters of cells dispersed throughout the pancreas that produce several hormones essential for controlling a variety of metabolic processes, including glucose homeostasis and lipid metabolism. Studying the transcriptional control of pancreatic islet cells has important implications for ... |
Changes in H3K27ac at Gene Regulatory Regions in Porcine AlveolarMacrophages Following LPS or PolyIC Exposure.
Herrera-Uribe, Juber and Liu, Haibo and Byrne, Kristen A and Bond, Zahra Fand Loving, Crystal L and Tuggle, Christopher K
Changes in chromatin structure, especially in histone modifications (HMs), linked with chromatin accessibility for transcription machinery, are considered to play significant roles in transcriptional regulation. Alveolar macrophages (AM) are important immune cells for protection against pulmonary pathogens, and must... |
Charting the cis-regulome of activated B cells by coupling structural and functional genomics.
Chaudhri VK, Dienger-Stambaugh K, Wu Z, Shrestha M, Singh H
Cis-regulomes underlying immune-cell-specific genomic states have been extensively analyzed by structure-based chromatin profiling. By coupling such approaches with a high-throughput enhancer screen (self-transcribing active regulatory region sequencing (STARR-seq)), we assembled a functional cis-regulome for lipopo... |
Functionally Annotating Regulatory Elements in the Equine Genome Using Histone Mark ChIP-Seq.
Kingsley NB, Kern C, Creppe C, Hales EN, Zhou H, Kalbfleisch TS, MacLeod JN, Petersen JL, Finno CJ, Bellone RR
One of the primary aims of the Functional Annotation of ANimal Genomes (FAANG) initiative is to characterize tissue-specific regulation within animal genomes. To this end, we used chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-Seq) to map four histone modifications (H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27ac, and H3K27me... |
H3K4me1 Supports Memory-like NK Cells Induced by Systemic Inflammation.
Rasid O, Chevalier C, Camarasa TM, Fitting C, Cavaillon JM, Hamon MA
Natural killer (NK) cells are unique players in innate immunity and, as such, an attractive target for immunotherapy. NK cells display immune memory properties in certain models, but the long-term status of NK cells following systemic inflammation is unknown. Here we show that following LPS-induced endotoxemia in mi... |
MicroRNA-708 is a novel regulator of the Hoxa9 program in myeloid cells.
Schneider E, Pochert N, Ruess C, MacPhee L, Escano L, Miller C, Krowiorz K, Delsing Malmberg E, Heravi-Moussavi A, Lorzadeh A, Ashouri A, Grasedieck S, Sperb N, Kumar Kopparapu P, Iben S, Staffas A, Xiang P, Rösler R, Kanduri M, Larsson E, Fogelstrand L,
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are commonly deregulated in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), affecting critical genes not only through direct targeting, but also through modulation of downstream effectors. Homeobox (Hox) genes balance self-renewal, proliferation, cell death, and differentiation in many tissues and aberrant Hox gene... |
TET2 Regulates the Neuroinflammatory Response in Microglia.
Carrillo-Jimenez A, Deniz Ö, Niklison-Chirou MV, Ruiz R, Bezerra-Salomão K, Stratoulias V, Amouroux R, Yip PK, Vilalta A, Cheray M, Scott-Egerton AM, Rivas E, Tayara K, García-Domínguez I, Garcia-Revilla J, Fernandez-Martin JC, Espinosa-Oliva AM, Shen X,
Epigenomic mechanisms regulate distinct aspects of the inflammatory response in immune cells. Despite the central role for microglia in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration, little is known about their epigenomic regulation of the inflammatory response. Here, we show that Ten-eleven translocation 2 (TET2) methylc... |
β-Glucan-Induced Trained Immunity Protects against Leishmania braziliensis Infection: a Crucial Role for IL-32.
Dos Santos JC, Barroso de Figueiredo AM, Teodoro Silva MV, Cirovic B, de Bree LCJ, Damen MSMA, Moorlag SJCFM, Gomes RS, Helsen MM, Oosting M, Keating ST, Schlitzer A, Netea MG, Ribeiro-Dias F, Joosten LAB
American tegumentary leishmaniasis is a vector-borne parasitic disease caused by Leishmania protozoans. Innate immune cells undergo long-term functional reprogramming in response to infection or Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccination via a process called trained immunity, conferring non-specific protectio... |
Reactivation of super-enhancers by KLF4 in human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Tsompana M, Gluck C, Sethi I, Joshi I, Bard J, Nowak NJ, Sinha S, Buck MJ
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a disease of significant morbidity and mortality and rarely diagnosed in early stages. Despite extensive genetic and genomic characterization, targeted therapeutics and diagnostic markers of HNSCC are lacking due to the inherent heterogeneity and complexity of the dis... |
Development and epigenetic plasticity of murine Müller glia.
Dvoriantchikova G, Seemungal RJ, Ivanov D
The ability to regenerate the entire retina and restore lost sight after injury is found in some species and relies mostly on the epigenetic plasticity of Müller glia. To understand the role of mammalian Müller glia as a source of progenitors for retinal regeneration, we investigated changes in gene expres... |
The alarmin S100A9 hampers osteoclast differentiation from human circulating precursors by reducing the expression of RANK.
Di Ceglie I, Blom AB, Davar R, Logie C, Martens JHA, Habibi E, Böttcher LM, Roth J, Vogl T, Goodyear CS, van der Kraan PM, van Lent PL, van den Bosch MH
The alarmin S100A8/A9 is implicated in sterile inflammation-induced bone resorption and has been shown to increase the bone-resorptive capacity of mature osteoclasts. Here, we investigated the effects of S100A9 on osteoclast differentiation from human CD14 circulating precursors. Hereto, human CD14 monocytes were is... |
Bromodomain inhibition of the coactivators CBP/EP300 facilitate cellular reprogramming.
Ebrahimi A, Sevinç K, Gürhan Sevinç G, Cribbs AP, Philpott M, Uyulur F, Morova T, Dunford JE, Göklemez S, Arı Ş, Oppermann U, Önder TT
Silencing of the somatic cell type-specific genes is a critical yet poorly understood step in reprogramming. To uncover pathways that maintain cell identity, we performed a reprogramming screen using inhibitors of chromatin factors. Here, we identify acetyl-lysine competitive inhibitors targeting the bromodomains of... |
ChIP-seq of plasma cell-free nucleosomes identifies cell-of-origin geneexpression programs
Sadeh, Ronen and Sharkia, Israa and Fialkoff, Gavriel and Rahat, Ayelet andGutin, Jenia and Chappleboim, Alon and Nitzan, Mor and Fox-Fisher, Ilanaand Neiman, Daniel and Meler, Guy and Kamari, Zahala and Yaish, Dayana andPeretz, Tamar and Hubert, Ayala
Blood cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is derived from fragmented chromatin in dying cells. As such, it remains associated with histones that may retain the covalent modifications present in the cell of origin. Until now this rich epigenetic information carried by cell-free nucleosomes has not been explored at the genome level... |
Long intergenic non-coding RNAs regulate human lung fibroblast function: Implications for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Hadjicharalambous MR, Roux BT, Csomor E, Feghali-Bostwick CA, Murray LA, Clarke DL, Lindsay MA
Phenotypic changes in lung fibroblasts are believed to contribute to the development of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF), a progressive and fatal lung disease. Long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) have been identified as novel regulators of gene expression and protein activity. In non-stimulated cells, we o... |
Extensive Recovery of Embryonic Enhancer and Gene Memory Stored in Hypomethylated Enhancer DNA.
Jadhav U, Cavazza A, Banerjee KK, Xie H, O'Neill NK, Saenz-Vash V, Herbert Z, Madha S, Orkin SH, Zhai H, Shivdasani RA
Developing and adult tissues use different cis-regulatory elements. Although DNA at some decommissioned embryonic enhancers is hypomethylated in adult cells, it is unknown whether this putative epigenetic memory is complete and recoverable. We find that, in adult mouse cells, hypomethylated CpG dinucleotides preserv... |
The epigenetic basis for the impaired ability of adult murine retinal pigment epithelium cells to regenerate retinal tissue.
Dvoriantchikova G, Seemungal RJ, Ivanov D
The epigenetic plasticity of amphibian retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) allows them to regenerate the entire retina, a trait known to be absent in mammals. In this study, we investigated the epigenetic plasticity of adult murine RPE to identify possible mechanisms that prevent mammalian RPE from regenerating retinal... |
Chromatin-Based Classification of Genetically Heterogeneous AMLs into Two Distinct Subtypes with Diverse Stemness Phenotypes.
Yi G, Wierenga ATJ, Petraglia F, Narang P, Janssen-Megens EM, Mandoli A, Merkel A, Berentsen K, Kim B, Matarese F, Singh AA, Habibi E, Prange KHM, Mulder AB, Jansen JH, Clarke L, Heath S, van der Reijden BA, Flicek P, Yaspo ML, Gut I, Bock C, Schuringa JJ
Global investigation of histone marks in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains limited. Analyses of 38 AML samples through integrated transcriptional and chromatin mark analysis exposes 2 major subtypes. One subtype is dominated by patients with NPM1 mutations or MLL-fusion genes, shows activation of the regulat... |
The Wnt-Driven Mll1 Epigenome Regulates Salivary Gland and Head and Neck Cancer.
Zhu Q, Fang L, Heuberger J, Kranz A, Schipper J, Scheckenbach K, Vidal RO, Sunaga-Franze DY, Müller M, Wulf-Goldenberg A, Sauer S, Birchmeier W
We identified a regulatory system that acts downstream of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in salivary gland and head and neck carcinomas. We show in a mouse tumor model of K14-Cre-induced Wnt/β-catenin gain-of-function and Bmpr1a loss-of-function mutations that tumor-propagating cells exhibit increased Mll1 activi... |
MIWI2 targets RNAs transcribed from piRNA-dependent regions to drive DNA methylation in mouse prospermatogonia.
Watanabe T, Cui X, Yuan Z, Qi H, Lin H
Argonaute/Piwi proteins can regulate gene expression via RNA degradation and translational regulation using small RNAs as guides. They also promote the establishment of suppressive epigenetic marks on repeat sequences in diverse organisms. In mice, the nuclear Piwi protein MIWI2 and Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) ar... |
Mapping molecular landmarks of human skeletal ontogeny and pluripotent stem cell-derived articular chondrocytes.
Ferguson GB, Van Handel B, Bay M, Fiziev P, Org T, Lee S, Shkhyan R, Banks NW, Scheinberg M, Wu L, Saitta B, Elphingstone J, Larson AN, Riester SM, Pyle AD, Bernthal NM, Mikkola HK, Ernst J, van Wijnen AJ, Bonaguidi M, Evseenko D
Tissue-specific gene expression defines cellular identity and function, but knowledge of early human development is limited, hampering application of cell-based therapies. Here we profiled 5 distinct cell types at a single fetal stage, as well as chondrocytes at 4 stages in vivo and 2 stages during in vitro differen... |
The reference epigenome and regulatory chromatin landscape of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Beekman R. et al.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a frequent hematological neoplasm in which underlying epigenetic alterations are only partially understood. Here, we analyze the reference epigenome of seven primary CLLs and the regulatory chromatin landscape of 107 primary cases in the context of normal B cell differentiation.... |
UTX-mediated enhancer and chromatin remodeling suppresses myeloid leukemogenesis through noncatalytic inverse regulation of ETS and GATA programs.
Gozdecka M, Meduri E, Mazan M, Tzelepis K, Dudek M, Knights AJ, Pardo M, Yu L, Choudhary JS, Metzakopian E, Iyer V, Yun H, Park N, Varela I, Bautista R, Collord G, Dovey O, Garyfallos DA, De Braekeleer E, Kondo S, Cooper J, Göttgens B, Bullinger L, Northc
The histone H3 Lys27-specific demethylase UTX (or KDM6A) is targeted by loss-of-function mutations in multiple cancers. Here, we demonstrate that UTX suppresses myeloid leukemogenesis through noncatalytic functions, a property shared with its catalytically inactive Y-chromosome paralog, UTY (or KDM6C). In keeping wi... |
Micro-ribonucleic acid-155 is a direct target of Meis1, but not a driver in acute myeloid leukemia
Schneider E. et al.
Micro-ribonucleic acid-155 (miR-155) is one of the first described oncogenic miRNAs. Although multiple direct targets of miR-155 have been identified, it is not clear how it contributes to the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia. We found miR-155 to be a direct target of Meis1 in murine Hoxa9/Meis1 induced acute ... |
BRACHYURY directs histone acetylation to target loci during mesoderm development.
Beisaw A. et al.
T-box transcription factors play essential roles in multiple aspects of vertebrate development. Here, we show that cooperative function of BRACHYURY (T) with histone-modifying enzymes is essential for mouse embryogenesis. A single point mutation (TY88A) results in decreased histone 3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) ... |
Genetic Predisposition to Multiple Myeloma at 5q15 Is Mediated by an ELL2 Enhancer Polymorphism
Li N. et al.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignancy of plasma cells. Genome-wide association studies have shown that variation at 5q15 influences MM risk. Here, we have sought to decipher the causal variant at 5q15 and the mechanism by which it influences tumorigenesis. We show that rs6877329 G > C resides in a predicted ... |
Chromosome contacts in activated T cells identify autoimmune disease candidate genes
Burren OS et al.
BACKGROUND:
Autoimmune disease-associated variants are preferentially found in regulatory regions in immune cells, particularly CD4+ T cells. Linking such regulatory regions to gene promoters in disease-relevant cell contexts facilitates identification of candidate disease genes.
RESULTS:
Within 4 h, act... |
Platelet function is modified by common sequence variation in megakaryocyte super enhancers
Petersen R. et al.
Linking non-coding genetic variants associated with the risk of diseases or disease-relevant traits to target genes is a crucial step to realize GWAS potential in the introduction of precision medicine. Here we set out to determine the mechanisms underpinning variant association with platelet quantitative traits usi... |
Dynamic Reorganization of Chromatin Accessibility Signatures during Dedifferentiation of Secretory Precursors into Lgr5+ Intestinal Stem Cells
Jadhav U. et al.
Replicating Lgr5+ stem cells and quiescent Bmi1+ cells behave as intestinal stem cells (ISCs) in vivo. Disrupting Lgr5+ ISCs triggers epithelial renewal from Bmi1+ cells, from secretory or absorptive progenitors, and from Paneth cell precursors, revealing a high degree of plasticity within intestinal crypts. He... |
Evolutionary re-wiring of p63 and the epigenomic regulatory landscape in keratinocytes and its potential implications on species-specific gene expression and phenotypes
Sethi I. et al.
Although epidermal keratinocyte development and differentiation proceeds in similar fashion between humans and mice, evolutionary pressures have also wrought significant species-specific physiological differences. These differences between species could arise in part, by the rewiring of regulatory network due to cha... |
DNA methylation heterogeneity defines a disease spectrum in Ewing sarcoma
Sheffield N.C. et al.
Developmental tumors in children and young adults carry few genetic alterations, yet they have diverse clinical presentation. Focusing on Ewing sarcoma, we sought to establish the prevalence and characteristics of epigenetic heterogeneity in genetically homogeneous cancers. We performed genome-scale DNA methylation ... |
Genetic Drivers of Epigenetic and Transcriptional Variation in Human Immune Cells
Chen L. et al.
Characterizing the multifaceted contribution of genetic and epigenetic factors to disease phenotypes is a major challenge in human genetics and medicine. We carried out high-resolution genetic, epigenetic, and transcriptomic profiling in three major human immune cell types (CD14+ monocytes, CD16+ neutrophils, ... |
The Hematopoietic Transcription Factors RUNX1 and ERG Prevent AML1-ETO Oncogene Overexpression and Onset of the Apoptosis Program in t(8;21) AMLs
Mandoli A. et al.
The t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia (AML)-associated oncoprotein AML1-ETO disrupts normal hematopoietic differentiation. Here, we have investigated its effects on the transcriptome and epigenome in t(8,21) patient cells. AML1-ETO binding was found at promoter regions of active genes with high levels of histone acetyl... |
Iterative Fragmentation Improves the Detection of ChIP-seq Peaks for Inactive Histone Marks
Laczik M. et al.
As chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) sequencing is becoming the dominant technique for studying chromatin modifications, new protocols surface to improve the method. Bioinformatics is also essential to analyze and understand the results, and precise analysis helps us to identify the effects of protocol optimizati... |
Neonatal monocytes exhibit a unique histone modification landscape
Bermick JR et al.
Background
Neonates have dampened expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and difficulty clearing pathogens. This makes them uniquely susceptible to infections, but the factors regulating neonatal-specific immune responses are poorly understood. Epigenetics, including histone modifications, can activate or silen... |
Epigenetic dynamics of monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation
Wallner S et al.
BACKGROUND:
Monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation involves major biochemical and structural changes. In order to elucidate the role of gene regulatory changes during this process, we used high-throughput sequencing to analyze the complete transcriptome and epigenome of human monocytes that were differentiated in... |
Chromatin accessibility maps of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia identify subtype-specific epigenome signatures and transcription regulatory networks
Rendeiro AF et al.
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) is characterized by substantial clinical heterogeneity, despite relatively few genetic alterations. To provide a basis for studying epigenome deregulation in CLL, here we present genome-wide chromatin accessibility maps for 88 CLL samples from 55 patients measured by the ATAC-seq ... |
Chromatin immunoprecipitation from fixed clinical tissues reveals tumor-specific enhancer profiles.
Cejas P et al.
Extensive cross-linking introduced during routine tissue fixation of clinical pathology specimens severely hampers chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by next-generation sequencing (ChIP-seq) analysis from archived tissue samples. This limits the ability to study the epigenomes of valuable, clinically annotated t... |
Comprehensive genome and epigenome characterization of CHO cells in response to evolutionary pressures and over time
Feichtinger J, Hernández I, Fischer C, Hanscho M, Auer N, Hackl M, Jadhav V, Baumann M, Krempl PM, Schmidl C, Farlik M, Schuster M, Merkel A, Sommer A, Heath S, Rico D, Bock C, Thallinger GG, Borth N
The most striking characteristic of CHO cells is their adaptability, which enables efficient production of proteins as well as growth under a variety of culture conditions, but also results in genomic and phenotypic instability. To investigate the relative contribution of genomic and epigenetic modifications towards... |
KMT2D regulates specific programs in heart development via histone H3 lysine 4 di-methylation
Ang SY et al.
KMT2D, which encodes a histone H3K4 methyltransferase, has been implicated in human congenital heart disease in the context of Kabuki syndrome. However, its role in heart development is not understood. Here, we demonstrate a requirement for KMT2D in cardiac precursors and cardiomyocytes during cardiogenesis in mice.... |
MLL-Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemias Activate BCL-2 through H3K79 Methylation and Are Sensitive to the BCL-2-Specific Antagonist ABT-199
Benito JM et al.
Targeted therapies designed to exploit specific molecular pathways in aggressive cancers are an exciting area of current research. Mixed Lineage Leukemia (MLL) mutations such as the t(4;11) translocation cause aggressive leukemias that are refractory to conventional treatment. The t(4;11) translocation produces an M... |
Glucocorticoid receptor and nuclear factor kappa-b affect three-dimensional chromatin organization
Kuznetsova T et al.
BACKGROUND:
The impact of signal-dependent transcription factors, such as glucocorticoid receptor and nuclear factor kappa-b, on the three-dimensional organization of chromatin remains a topic of discussion. The possible scenarios range from remodeling of higher order chromatin architecture by activated transcrip... |
Cell-Cycle-Dependent Reconfiguration of the DNA Methylome during Terminal Differentiation of Human B Cells into Plasma Cells
Caron G et al.
Molecular mechanisms underlying terminal differentiation of B cells into plasma cells are major determinants of adaptive immunity but remain only partially understood. Here we present the transcriptional and epigenomic landscapes of cell subsets arising from activation of human naive B cells and differentiation into... |
Non-coding recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.
Xose S. Puente, Silvia Beà, Rafael Valdés-Mas, Neus Villamor, Jesús Gutiérrez-Abril et al.
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) is a frequent disease in which the genetic alterations determining the clinicobiological behaviour are not fully understood. Here we describe a comprehensive evaluation of the genomic landscape of 452 CLL cases and 54 patients with monoclonal B-lymphocytosis, a precursor disorder.... |
Human disease modeling reveals integrated transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms of NOTCH1 haploinsufficiency.
Theodoris CV, Li M, White MP, Liu L, He D, Pollard KS, Bruneau BG, Srivastava D
The mechanisms by which transcription factor haploinsufficiency alters the epigenetic and transcriptional landscape in human cells to cause disease are unknown. Here, we utilized human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived endothelial cells (ECs) to show that heterozygous nonsense mutations in NOTCH1 that cau... |
Epigenome mapping reveals distinct modes of gene regulation and widespread enhancer reprogramming by the oncogenic fusion protein EWS-FLI1.
Tomazou EM, Sheffield NC, Schmidl C, Schuster M, Schönegger A, Datlinger P, Kubicek S, Bock C, Kovar H
Transcription factor fusion proteins can transform cells by inducing global changes of the transcriptome, often creating a state of oncogene addiction. Here, we investigate the role of epigenetic mechanisms in this process, focusing on Ewing sarcoma cells that are dependent on the EWS-FLI1 fusion protein. We establi... |