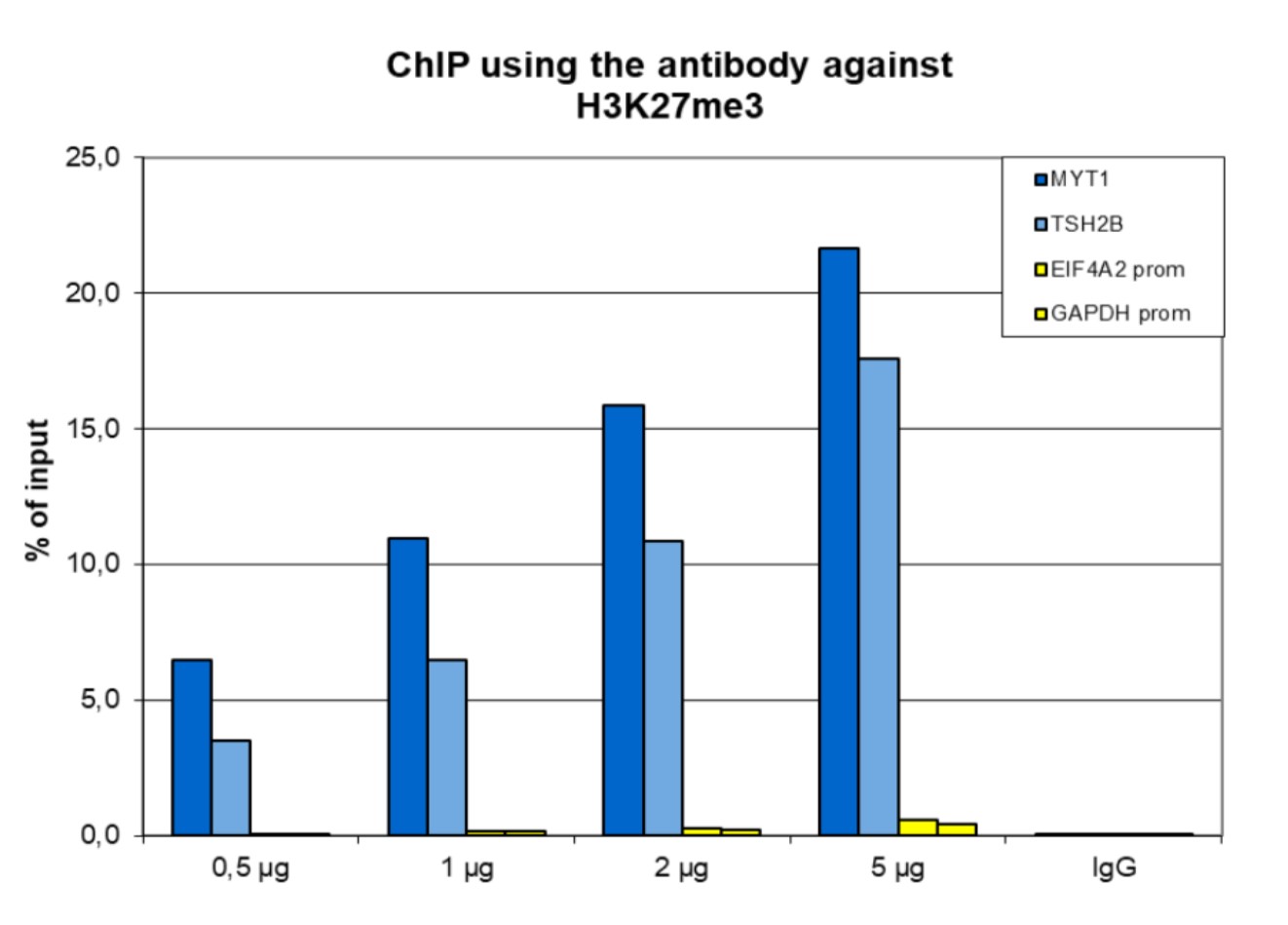
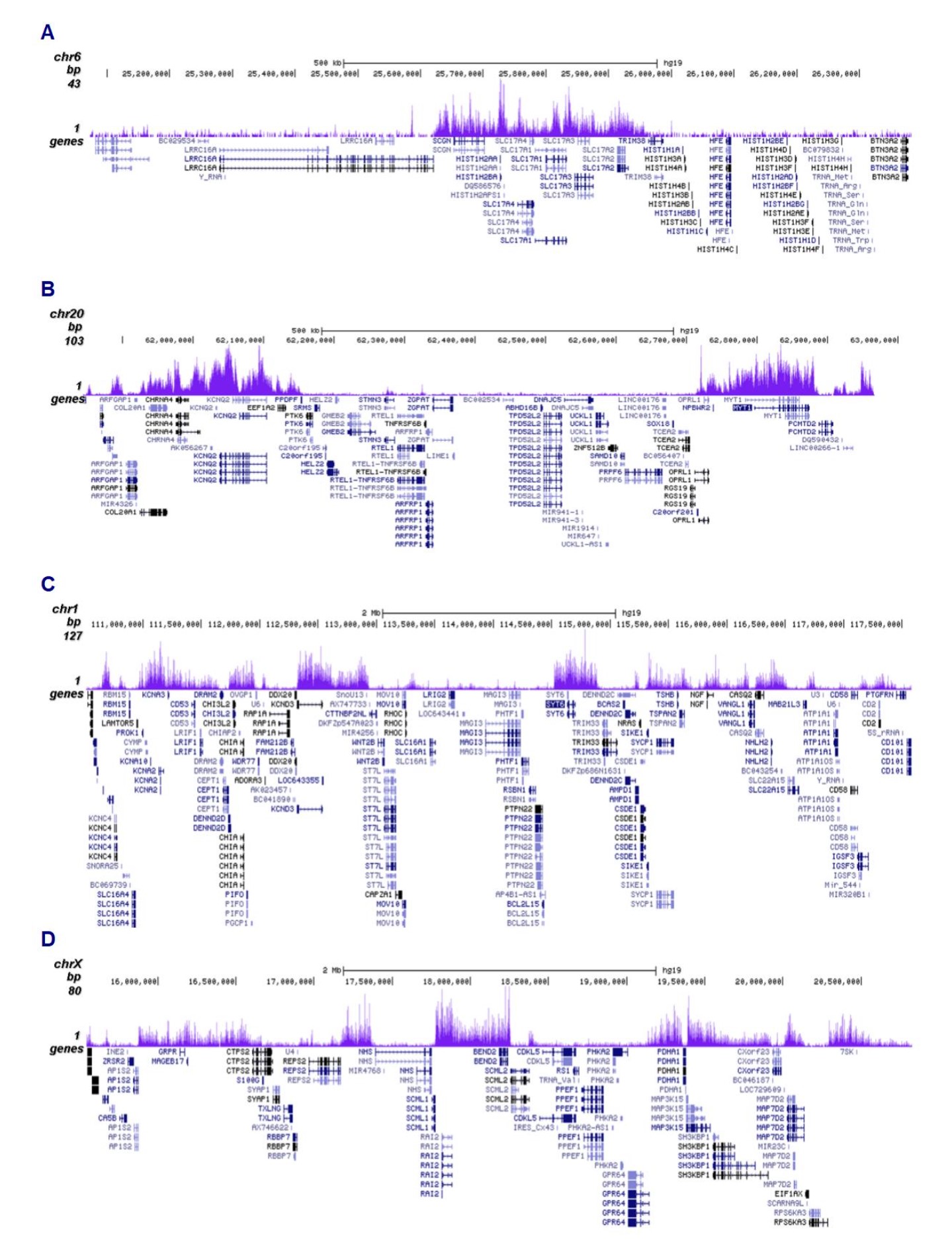
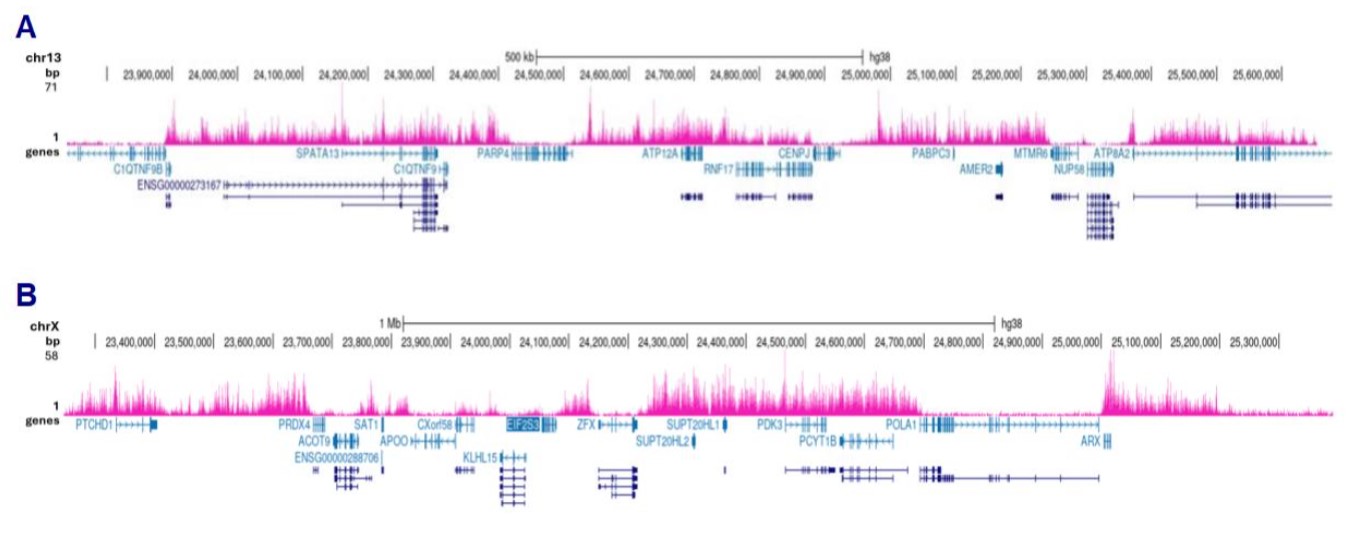
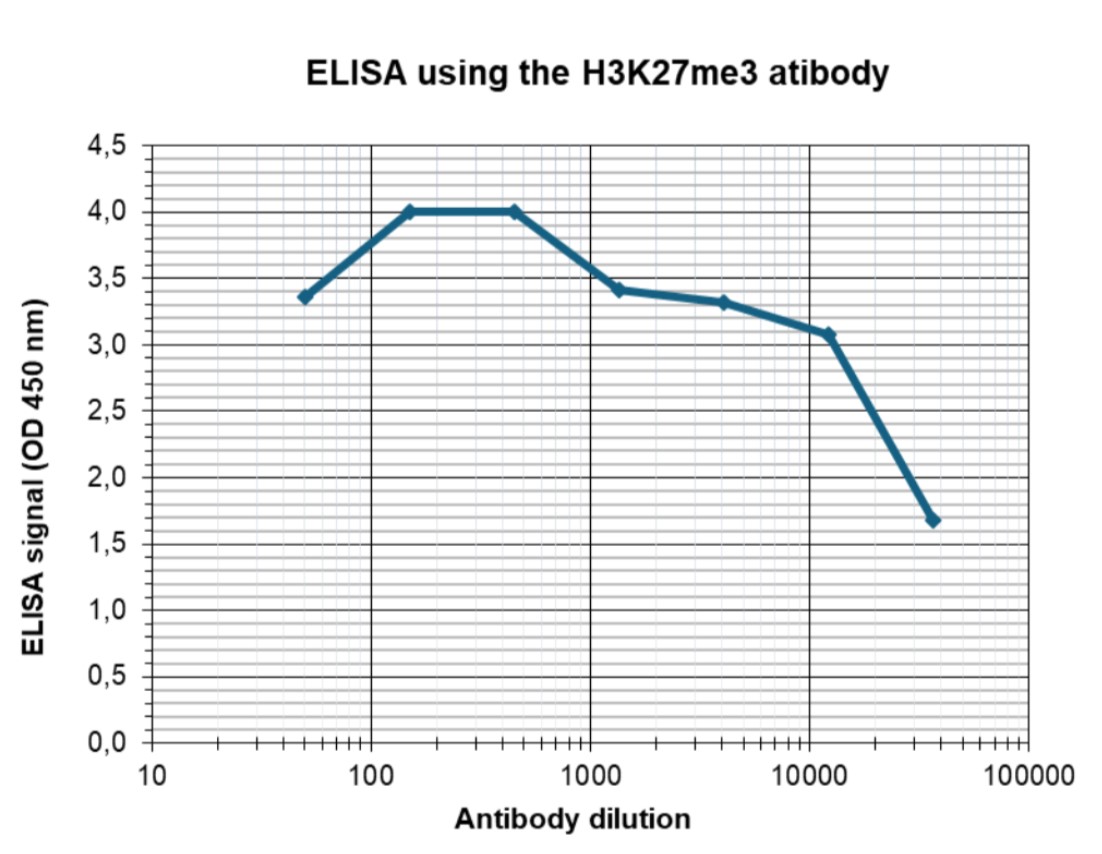
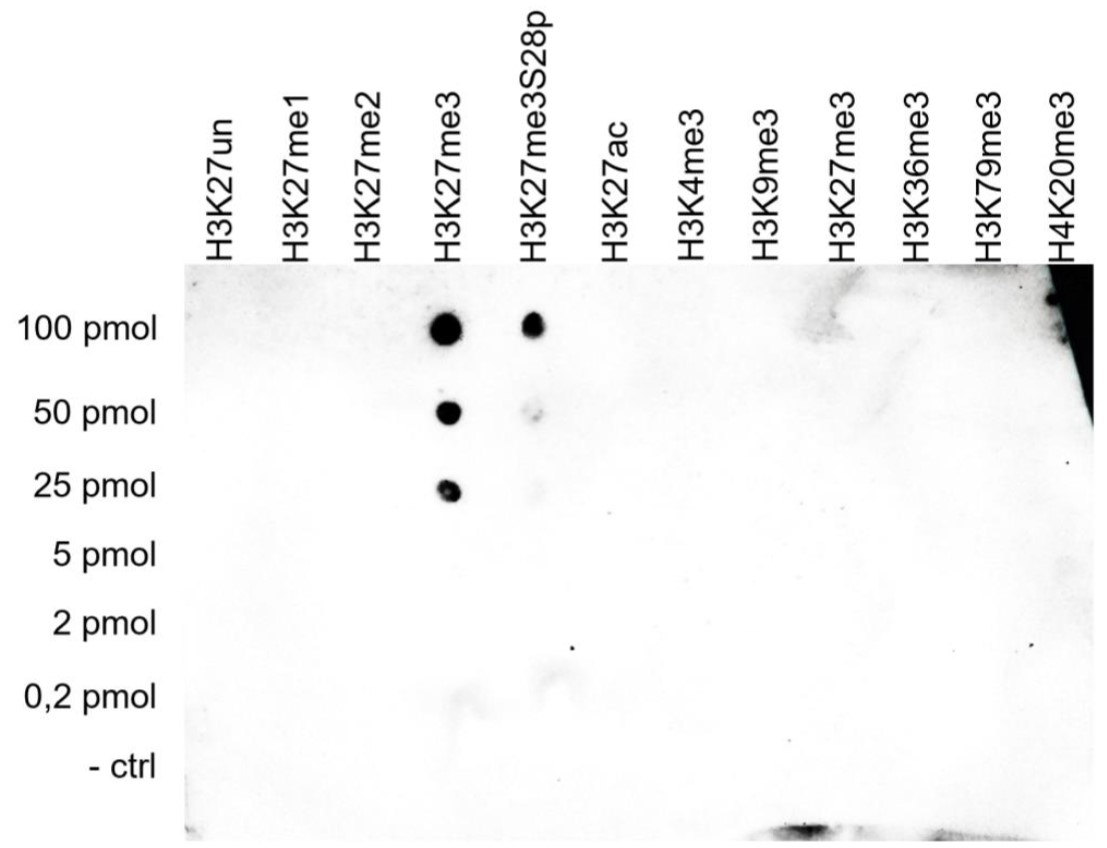
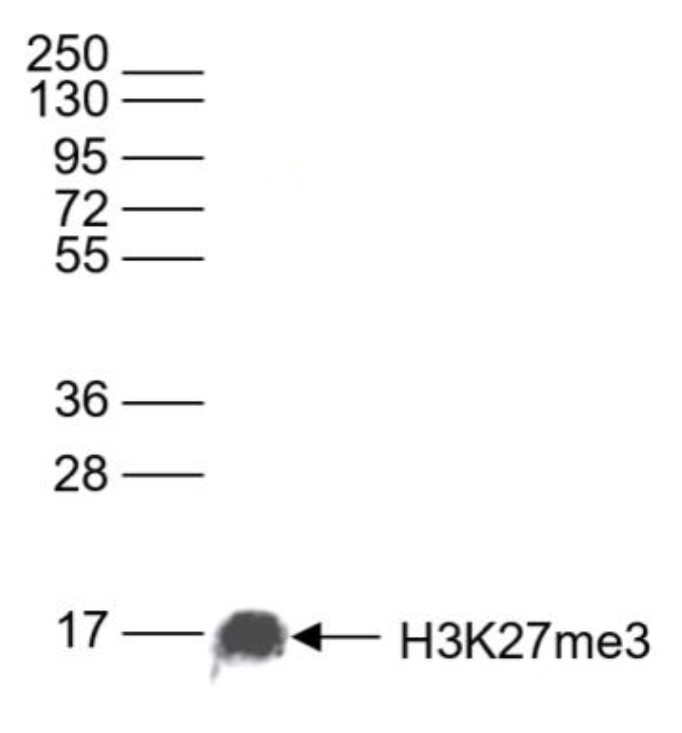
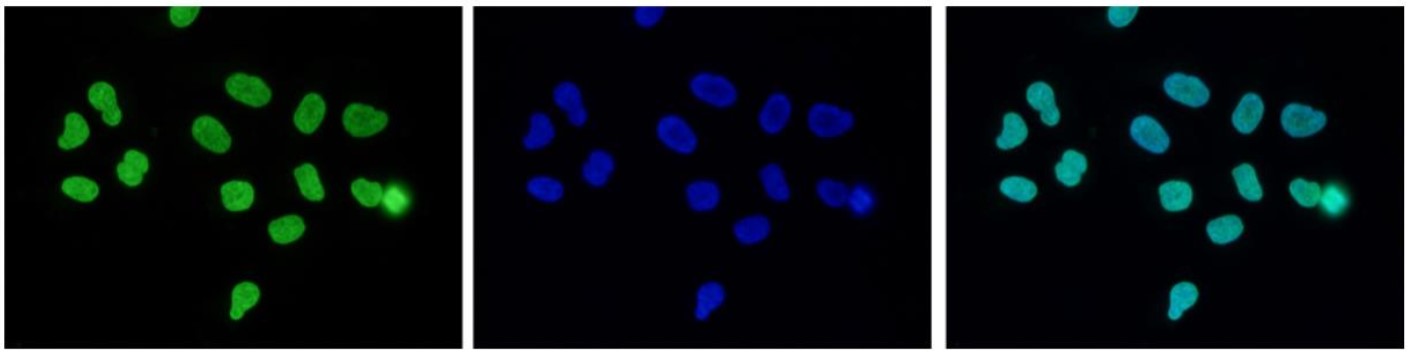
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K27me3 antibody (sample size) (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410195-10 Lot# A3236P). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
CRISPR-based precise methylation of specific FUT8 promoter regions allows isolation of CHO cells with a fine-tuned glycoprofile
Jiménez Lancho, Víctor et al.
A major advantage of producing therapeutic proteins in mammalian cells is their ability to tailor proteins with human-like posttranslational modifications such as glycosylation, which ultimately defines aspects like stability, protein folding or immunogenicity. However, producing therapeutic proteins with a consis... |
Neurons undergo IFNγ-driven persistent epigenetic shifts and synaptopathy in encephalitis
Shammas, Ghazal et al.
In infectious and autoimmune disorders of the central nervous system, neurons can become cognate immunological targets of cytotoxic T cells, leading to persistent functional and synaptic impairments. However, the molecular underpinnings of such irreversible alterations remain unclear. Using a cytotoxic T cell-driv... |
Epigenomics of embryogenesis in turbot
Aramburu, Oscar et al.
Embryogenesis is the foundational step of ontogeny, where a complex organism emerges from a single totipotent cell. This process is orchestrated by changes in transcriptional regulation, influenced by chromatin accessibility and epigenetic modifications, enabling transcription factor accessibility. Epigenomic re... |
Role of MNX1-mediated Histone Modifications and PBX Gene Family in MNX1-induced Leukemogenesis
Malmhäll-Bah, Eric et al.
The t(7;12)(q36;p13) AML subtype in pediatric patients is associated with the upregulation of homeodomain protein MNX1 as the initiating event for leukemogenesis. In this study, we investigated the downstream targets of MNX1 and their relationship to MNX1-induced histone modifications. Using a comprehensive appr... |
Coordinated control of genome-nuclear lamina interactions by topoisomerase 2B and lamin B receptor
van Schaik, Tom et al.
Lamina-associated domains (LADs) are megabase-sized genomic regions anchored to the nuclear lamina (NL). Factors controlling the interactions of the genome with the NL have largely remained elusive. Here, we identified DNA topoisomerase 2 beta (TOP2B) as a regulator of these interactions. TOP2B binds predominant... |
Endurance training increases a ubiquitylated form of histone H3 in the skeletal muscle, supporting Notch1 upregulation in an MDM2-dependent manner
Lam, Brian et al.
At the onset of training, each exercise session transiently shifts the distribution of histone post-transcriptional modifications (HPTMs) to activate genes that drive muscle adaptations. The resulting cyclic changes in gene expression promote the acquisition of high oxidative capacities and gains in capillaries. I... |
H3K27me3-mediated epigenetic regulation of TET1 in the eutopic endometrium of women with endometriosis and infertility
Adamczyk, Magdalena et al.
Endometriosis is a common gynecological condition associated with chronic inflammation, epigenetic dysregulation, and infertility. The TET1 gene, involved in DNA demethylation, may be regulated by repressive histone modifications such as H3K27me3, but its role in endometriosis remains poorly understood. This study... |
Plasma cell-free DNA chromatin immunoprecipitation profiling depicts phenotypic and clinical heterogeneity in advanced prostate cancer
Sipola, Joonatan et al.
Cell phenotype underlies prostate cancer presentation and treatment resistance and can be regulated by epigenomic features. However, the osteotropic tendency of prostate cancer limits access to metastatic tissue, meaning most prior insights into prostate cancer chromatin biology are from preclinical models that do n... |
Accelerated epigenetic aging in Huntington’s disease involves polycomb repressive complex 1
Baptiste Brulé et al.
Loss of epigenetic information during physiological aging compromises cellular identity, leading to de-repression of developmental genes. Here, we assessed the epigenomic landscape of vulnerable neurons in two reference mouse models of Huntington neurodegenerative disease (HD), using cell-type-specific multi-omics, ... |
Ectopic expression of DNMT3L in human trophoblast stem cells restores features of the placental methylome
Lea, Georgia et al.
The placental DNA methylation landscape is unique, with widespread partially methylated domains (PMDs). The placental "methylome" is conserved across mammals, a shared feature of many cancers, and extensively studied for links with pregnancy complications. Human trophoblast stem cells (hTSCs) offer exciting potent... |
Motif distribution and DNA methylation underlie distinct Cdx2 binding during development and homeostasis
Alireza Lorzadeh et al.
Transcription factors guide tissue development by binding to developmental stage-specific targets and establishing an appropriate enhancer landscape. In turn, DNA and chromatin modifications direct the genomic binding of transcription factors. However, how transcription factors navigate chromatin features to selecti... |
The senolytic cocktail, dasatinib and quercetin, impacts the chromatin structure of both young and senescent vascular smooth muscle cells
Agnieszka Gadecka et al.
One promising strategy to alleviate aging symptoms is the treatment with senolytics that is compounds which selectively eliminate senescent cells. Some therapies aim to reduce symptoms of cellular senescence without senescent cell eradication (senomorphic activity). However, senotherapies raise many questions concer... |
Nuclear localization of MTHFD2 is required for correct mitosis progression
Natalia Pardo-Lorente et al.
Subcellular compartmentalization of metabolic enzymes establishes a unique metabolic environment that elicits specific cellular functions. Indeed, the nuclear translocation of certain metabolic enzymes is required for epigenetic regulation and gene expression control. Here, we show that the nuclear localization of t... |
GTSF1 is required for transposon silencing in the unicellular eukaryote Paramecium tetraurelia
Chundi Wang et al.
The PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) pathway is crucial for transposon repression and the maintenance of genomic integrity. Gametocyte-specific factor 1 (GTSF1), a PIWI-associated protein indispensable for transposon repression, has been recently shown to potentiate the catalytic activity of PIWI in many metazoans. Whet... |
Systematic prioritization of functional variants and effector genes underlying colorectal cancer risk
Law P.J. et al.
Genome-wide association studies of colorectal cancer (CRC) have identified 170 autosomal risk loci. However, for most of these, the functional variants and their target genes are unknown. Here, we perform statistical fine-mapping incorporating tissue-specific epigenetic annotations and massively parallel reporter as... |
Bivalent chromatin accommodates survivin and BRG1/SWI complex to activate DNA damage response in CD4+ cells
Chandrasekaran V. et al.
Background
Bivalent regions of chromatin (BvCR) are characterized by trimethylated lysine 4 (H3K4me3) and lysine 27 on histone H3 (H3K27me3) deposition which aid gene expression control during cell differentiation. The role of BvCR in post-transcriptional DNA damage response remains unidentified. Oncoprotein ... |
RNA sequestration in P-bodies sustains myeloid leukaemia
Srikanth Kodali et al.
Post-transcriptional mechanisms are fundamental safeguards of progenitor cell identity and are often dysregulated in cancer. Here, we identified regulators of P-bodies as crucial vulnerabilities in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) through genome-wide CRISPR screens in normal and malignant haematopoietic progenitors. We... |
LL37/self-DNA complexes mediate monocyte reprogramming
Aman Damara et al.
LL37 alone and in complex with self-DNA triggers inflammatory responses in myeloid cells and plays a crucial role in the development of systemic autoimmune diseases, like psoriasis and systemic lupus erythematosus. We demonstrated that LL37/self-DNA complexes induce long-term metabolic and epigenetic changes in mono... |
A multiomic atlas of the aging hippocampus reveals molecular changes in response to environmental enrichment
Perez R. F. at al.
Aging involves the deterioration of organismal function, leading to the emergence of multiple pathologies. Environmental stimuli, including lifestyle, can influence the trajectory of this process and may be used as tools in the pursuit of healthy aging. To evaluate the role of epigenetic mechanisms in this context, ... |
Single-cell epigenomic reconstruction of developmental trajectories from pluripotency in human neural organoid systems
Fides Zenk et al.
Cell fate progression of pluripotent progenitors is strictly regulated, resulting in high human cell diversity. Epigenetic modifications also orchestrate cell fate restriction. Unveiling the epigenetic mechanisms underlying human cell diversity has been difficult. In this study, we use human brain and retina organoi... |
Brassica rapa CURLY LEAF is a major H3K27 methyltransferase regulating flowering time
Poza-Viejo L. et al.
Main conclusion
In Brassica rapa, the epigenetic modifier BraA.CLF orchestrates flowering by modulating H3K27me3 levels at the floral integrator genes FT, SOC1, and SEP3, thereby influencing their expression.
Abstract
CURLY LEAF (CLF) is the catalytic subunit of the plant Polycomb Repressive C... |
SURVIVIN IN SYNERGY WITH BAF/SWI COMPLEX BINDS BIVALENT CHROMATIN REGIONS AND ACTIVATES DNA DAMAGE RESPONSE IN CD4+ T CELLS
Chandrasekaran V. et al.
This study explores a regulatory role of oncoprotein survivin on the bivalent regions of chromatin (BvCR) characterized by concomitant deposition of trimethylated lysine of histone H3 at position 4 (H3K4me3) and 27 (H3K27me3).
Intersect between BvCR and chromatin sequences bound to survivin demonstrated their co-lo... |
Multiomics uncovers the epigenomic and transcriptomic response to viral and bacterial stimulation in turbot
Aramburu O. et al.
Uncovering the epigenomic regulation of immune responses is essential for a comprehensive understanding of host defence mechanisms but remains poorly described in farmed fish. Here, we report the first annotation of the innate immune regulatory response in the genome of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus), a farmed flatfi... |
Revisiting chromatin packaging in mouse sperm
Qiangzong Yin et al.
|
SUMO protease FUG1, histone reader AL3 and the PRC1 Complex areintegral to repeat-expansion induced epigenetic silencing in Arabidopsisthaliana
Sureshkumar S. et al.
Epigenetic gene silencing induced by expanded repeats can cause diverse phenotypes ranging from severe growth defects in plants to genetic diseases such as Friedreich’s ataxia in humans1. The molecular mechanisms underlying repeat expansion-induced epigenetic silencing remain largely unknown2,3. Using a plant ... |
Alterations in the hepatocyte epigenetic landscape in steatosis.
Maji Ranjan K. et al.
Fatty liver disease or the accumulation of fat in the liver, has been reported to affect the global population. This comes with an increased risk for the development of fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Yet, little is known about the effects of a diet containing high fat and alcohol towards epigenet... |
Polycomb protein SCML2 mediates paternal epigenetic inheritance throughsperm chromatin.
Sakashita A. et al.
Sperm chromatin retains small amounts of histones, and chromatin states of sperm mirror gene expression programs of the next generation. However, it remains largely unknown how paternal epigenetic information is transmitted through sperm chromatin. Here, we present a novel mouse model of paternal epigenetic inherita... |
Mutant FUS induces chromatin reorganization in the hippocampus andalters memory processes.
Tzeplaeff L. et al.
Cytoplasmic mislocalization of the nuclear Fused in Sarcoma (FUS) protein is associated to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). Cytoplasmic FUS accumulation is recapitulated in the frontal cortex and spinal cord of heterozygous Fus mice. Yet, the mechanisms linking FUS mislocalizati... |
RUNX1 colludes with NOTCH1 to reprogram chromatin in T-cell acutelymphoblastic leukemia
Islam R. et al.
Runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) is oncogenic in diverse types of leukemia and epithelial cancers where its expression is associated with poor prognosis. Current models suggest that RUNX1 cooperates with other oncogenic factors (e.g., NOTCH1, TAL1) to drive the expression of proto-oncogenes in T cell... |
Farrerol directly activates the deubiqutinase UCHL3 to promote DNArepair and reprogramming when mediated by somatic cell nuclear transfer.
Zhang W. et al.
Farrerol, a natural flavanone, promotes homologous recombination (HR) repair to improve genome-editing efficiency, but the specific protein that farrerol directly targets to regulate HR repair and the underlying molecular mechanisms have not been determined. Here, we find that the deubiquitinase UCHL3 is the direct ... |
Epigenetic dosage identifies two major and functionally distinct beta cells ubtypes.
Dror E.et al.
The mechanisms that specify and stabilize cell subtypes remain poorly understood. Here, we identify two major subtypes of pancreatic β cells based on histone mark heterogeneity (beta HI and beta LO). Beta HI cells exhibit 4-fold higher levels of H3K27me3, distinct chromatin organization and compaction, a... |
Detailed molecular and epigenetic characterization of the Pig IPECJ2and Chicken SL-29 cell lines
de Vos J. et al.
The pig IPECJ2 and chicken SL-29 cell lines are of interest because of their untransformed nature and wide use in functional studies. Molecular characterization of these cell lines is important to gain insight into possible molecular aberrations. The aims of this paper are providing a molecular and epigenetic charac... |
Temporal modification of H3K9/14ac and H3K4me3 histone marksmediates mechano-responsive gene expression during the accommodationprocess in poplar
Ghosh R. et al.
Plants can attenuate their molecular response to repetitive mechanical stimulation as a function of their mechanical history. For instance, a single bending of stem is sufficient to attenuate the gene expression in poplar plants to the subsequent mechanical stimulation, and the state of desensitization can last for ... |
Histone remodeling reflects conserved mechanisms of bovine and humanpreimplantation development.
Zhou C. et al.
How histone modifications regulate changes in gene expression during preimplantation development in any species remains poorly understood. Using CUT\&Tag to overcome limiting amounts of biological material, we profiled two activating (H3K4me3 and H3K27ac) and two repressive (H3K9me3 and H3K27me3) marks in bovine... |
Analyzing the Genome-Wide Distribution of Histone Marks byCUT\&Tag in Drosophila Embryos.
Zenk F. et al.
CUT&Tag is a method to map the genome-wide distribution of histone modifications and some chromatin-associated proteins. CUT&Tag relies on antibody-targeted chromatin tagmentation and can easily be scaled up or automatized. This protocol provides clear experimental guidelines and helpful considerations when ... |
Trichoderma root colonization triggers epigenetic changes in jasmonic andsalicylic acid pathway-related genes.
Agostini R. B. et al.
Beneficial interactions between plant-roots and Trichoderma spp. lead to a local and systemic enhancement of the plant immune system through a mechanism known as priming of defenses. In recent reports, we outlined a repertoire of genes and proteins differentially regulated in distant tissues of maize plants previous... |
Identification of genomic binding sites and direct target genes for thetranscription factor DDIT3/CHOP.
Osman A. et al.
DDIT3 is a tightly regulated basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor and key regulator in cellular stress responses. It is involved in a variety of pathological conditions and may cause cell cycle block and apoptosis. It is also implicated in differentiation of some specialized cell types and as an oncogene... |
Dietary methionine starvation impairs acute myeloid leukemia progression.
Cunningham A. et al.
Targeting altered tumor cell metabolism might provide an attractive opportunity for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). An amino acid dropout screen on primary leukemic stem cells and progenitor populations revealed a number of amino acid dependencies, of which methionine was one of the strongest. By using v... |
bESCs from cloned embryos do not retain transcriptomic or epigenetic memory from somatic donor cells.
Navarro M. et al.
Embryonic stem cells (ESC) indefinitely maintain the pluripotent state of the blastocyst epiblast. Stem cells are invaluable for studying development and lineage commitment, and in livestock they constitute a useful tool for genomic improvement and in vitro breeding programs. Although these cells have been recently ... |
The Arabidopsis APOLO and human UPAT sequence-unrelated longnoncoding RNAs can modulate DNA and histone methylation machineries inplants.
Fonouni-Farde C. et al.
BACKGROUND: RNA-DNA hybrid (R-loop)-associated long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), including the Arabidopsis lncRNA AUXIN-REGULATED PROMOTER LOOP (APOLO), are emerging as important regulators of three-dimensional chromatin conformation and gene transcriptional activity. RESULTS: Here, we show that in addition to the PRC1... |
Prolonged FOS activity disrupts a global myogenic transcriptionalprogram by altering 3D chromatin architecture in primary muscleprogenitor cells.
Barutcu A Rasim et al.
BACKGROUND: The AP-1 transcription factor, FBJ osteosarcoma oncogene (FOS), is induced in adult muscle satellite cells (SCs) within hours following muscle damage and is required for effective stem cell activation and muscle repair. However, why FOS is rapidly downregulated before SCs enter cell cycle as progenitor c... |
Caffeine intake exerts dual genome-wide effects on hippocampal metabolismand learning-dependent transcription.
Paiva I. et al.
Caffeine is the most widely consumed psychoactive substance in the world. Strikingly, the molecular pathways engaged by its regular consumption remain unclear. We herein addressed the mechanisms associated with habitual (chronic) caffeine consumption in the mouse hippocampus using untargeted orthogonal omics techniq... |
PHF13 epigenetically activates TGFβ driven epithelial to mesenchymaltransition
Sun Yating et al.
Epigenetic alteration is a pivotal factor in tumor metastasis. PHD finger protein 13 (PHF13) is a recently identified epigenetic reader of H3K4me2/3 that functions as a transcriptional co-regulator. In this study, we demonstrate that PHF13 is required for pancreatic-cancer-cell growth and metastasis. Integrative ana... |
Variation in PU.1 binding and chromatin looping at neutrophil enhancersinfluences autoimmune disease susceptibility
Watt S. et al.
Neutrophils play fundamental roles in innate inflammatory response, shape adaptive immunity1, and have been identified as a potentially causal cell type underpinning genetic associations with immune system traits and diseases2,3 The majority of these variants are non-coding and the underlying mechanisms are not full... |
ACTL6a coordinates axonal caliber recognition and myelination in theperipheral nerve.
Park H-J et al.
Cells elaborate transcriptional programs in response to external signals. In the peripheral nerves, Schwann cells (SC) sort axons of given caliber and start the process of wrapping their membrane around them. We identify Actin-like protein 6a (ACTL6a), part of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, as critical for th... |
Determinants of heritable gene silencing for KRAB-dCas9 + DNMT3and Ezh2-dCas9 + DNMT3 hit-and-run epigenome editing.
O'Geen H.et al.
Precision epigenome editing has gained significant attention as a method to modulate gene expression without altering genetic information. However, a major limiting factor has been that the gene expression changes are often transient, unlike the life-long epigenetic changes that occur frequently in nature. Here, we ... |
Assessment of TET1 gene expression, DNA methylation and H3K27me3level of its promoter region in eutopic endometrium of women withendometriosis and infertility.
Adamczyk Magdalena et al.
Endometriosis is the cause of infertility. The eutopic endometrium of women with endometriosis showed an aberrant expression pattern of multitude genes. The role of TET1 protein in the pathogenesis of endometriosis and related infertility is not sufficiently known. Further, knowledge on TET1 transcriptional control ... |
Broad domains of histone marks in the highly compact macronucleargenome.
Drews F. et al.
The unicellular ciliate contains a large vegetative macronucleus with several unusual characteristics, including an extremely high coding density and high polyploidy. As macronculear chromatin is devoid of heterochromatin, our study characterizes the functional epigenomic organization necessary for gene regulation a... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple Myeloma
Elina Alaterre et al.
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have been widely used to understand themolecular processes that drive MM biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape of MM wouldadvance our un... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple
Myeloma
Alaterre, Elina and Ovejero, Sara and Herviou, Laurie and de
Boussac, Hugues and Papadopoulos, Giorgio and Kulis, Marta and
Boireau, Stéphanie and Robert, Nicolas and Requirand, Guilhem
and Bruyer, Angélique and Cartron, Guillaume and Vincent,
Laure and M
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have
been widely used to understand the molecular processes that drive MM
biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,
progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the
epigenetic landscape of MM would advance our... |
NR4A1 regulates expression of immediate early genes, suppressingreplication stress in cancer.
Guo Hongshan et al.
Deregulation of oncogenic signals in cancer triggers replication stress. Immediate early genes (IEGs) are rapidly and transiently expressed following stressful signals, contributing to an integrated response. Here, we find that the orphan nuclear receptor NR4A1 localizes across the gene body and 3' UTR of IEGs, wher... |
The prolyl-isomerase PIN1 is essential for nuclear Lamin-Bstructure and function and protects heterochromatin under mechanicalstress.
Napoletano Francesco et al.
Chromatin organization plays a crucial role in tissue homeostasis. Heterochromatin relaxation and consequent unscheduled mobilization of transposable elements (TEs) are emerging as key contributors of aging and aging-related pathologies, including Alzheimer's disease (AD) and cancer. However, the mechanisms governin... |
WT1 regulates HOXB9 gene expression in a bidirectional way.
Schmidt Valentin et al.
The homeoboxB9 (HOXB9) gene is necessary for specification of the anterior-posterior body axis during embryonic development and expressed in various types of cancer. Here we show that the Wilms tumor transcription factor WT1 regulates the HOXB9 gene in a bidirectional manner. Silencing of WT1 activates HOXB9 in Wt1 ... |
Histone deacetylase 4 deletion broadly affects cardiac epigeneticrepression and regulates transcriptional susceptibility via H3K9methylation.
Finke Daniel et al.
Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) is a member of class IIa histone deacetylases (class IIa HDACs) and is believed to possess a low intrinsic deacetylase activity. However, HDAC4 sufficiently represses distinct transcription factors (TFs) such as the myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2). Transcriptional repression by HDAC4 h... |
Enhanced targeted DNA methylation of the CMV and endogenous promoterswith dCas9-DNMT3A3L entails distinct subsequent histonemodification changes in CHO cells.
Marx Nicolas et al.
With the emergence of new CRISPR/dCas9 tools that enable site specific modulation of DNA methylation and histone modifications, more detailed investigations of the contribution of epigenetic regulation to the precise phenotype of cells in culture, including recombinant production subclones, is now possible. These al... |
Lasp1 regulates adherens junction dynamics and fibroblast transformationin destructive arthritis
Beckmann D. et al.
The LIM and SH3 domain protein 1 (Lasp1) was originally cloned from metastatic breast cancer and characterised as an adaptor molecule associated with tumourigenesis and cancer cell invasion. However, the regulation of Lasp1 and its function in the aggressive transformation of cells is unclear. Here we use integrativ... |
The lncRNA and the transcription factor WRKY42 target common cell wallEXTENSIN encoding genes to trigger root hair cell elongation.
Pacheco, J. M. et al.
Plant long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are key chromatin dynamics regulators, directing the transcriptional programs driving a wide variety of developmental outputs. Recently, we uncovered how the lncRNA () directly recognizes the locus encoding the root hair (RH) master regulator () modulating its transcriptional acti... |
Sarcomere function activates a p53-dependent DNA damage response that promotes polyploidization and limits in vivo cell engraftment.
Pettinato, Anthony M. et al.
Human cardiac regeneration is limited by low cardiomyocyte replicative rates and progressive polyploidization by unclear mechanisms. To study this process, we engineer a human cardiomyocyte model to track replication and polyploidization using fluorescently tagged cyclin B1 and cardiac troponin T. Using time-lapse i... |
The SAM domain-containing protein 1 (SAMD1) acts as a repressivechromatin regulator at unmethylated CpG islands
Stielow B. et al.
CpG islands (CGIs) are key regulatory DNA elements at most promoters, but how they influence the chromatin status and transcription remains elusive. Here, we identify and characterize SAMD1 (SAM domain-containing protein 1) as an unmethylated CGI-binding protein. SAMD1 has an atypical winged-helix domain that direct... |
Simplification of culture conditions and feeder-free expansion of bovineembryonic stem cells
Soto D. A. et al.
Bovine embryonic stem cells (bESCs) extend the lifespan of the transient pluripotent bovine inner cell mass in vitro. After years of research, derivation of stable bESCs was only recently reported. Although successful, bESC culture relies on complex culture conditions that require a custom-made base medium and mouse... |
Androgen and glucocorticoid receptor direct distinct transcriptionalprograms by receptor-specific and shared DNA binding sites.
Kulik, Marina et al.
The glucocorticoid (GR) and androgen (AR) receptors execute unique functions in vivo, yet have nearly identical DNA binding specificities. To identify mechanisms that facilitate functional diversification among these transcription factor paralogs, we studied them in an equivalent cellular context. Analysis of chroma... |
Genetic perturbation of PU.1 binding and chromatin looping at neutrophilenhancers associates with autoimmune disease.
Watt, Stephen et al.
Neutrophils play fundamental roles in innate immune response, shape adaptive immunity, and are a potentially causal cell type underpinning genetic associations with immune system traits and diseases. Here, we profile the binding of myeloid master regulator PU.1 in primary neutrophils across nearly a hundred voluntee... |
Unique Patterns of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 in 2-Cell-like Embryonic StemCells.
Zhang, Yanping and Huang, Yixin and Dong, Yu and Liu, Xiaoyu and Kou,Xiaochen and Zhao, Yanhong and Zhao, Anqi and Sun, Jiatong and Su, Zhongquand Li, Zongyu and Zhang, Huan and Li, Yunwei and Cao, Shuyuan and Wei,Junhao and Yin, Jiqing and Kang, Lan a
A small subgroup of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) exhibit molecular features similar to those of two-cell embryos (2C). However, it remains elusive whether 2C-like cells and 2C embryos share similar epigenetic features. Here, we map the genome-wide profiles of histone H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 in 2C-like cells. We found th... |
REPROGRAMMING CBX8-PRC1 FUNCTION WITH A POSITIVE ALLOSTERICMODULATOR
Suh, J. L. et al.
Canonical targeting of Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 (PRC1) to repress developmental genes is mediated by cell type-specific, paralogous chromobox (CBX) proteins (CBX2, 4, 6, 7 and 8). Based on their central role in silencing and their misregulation associated with human disease including cancer, CBX proteins are at... |
The G2-phase enriched lncRNA SNHG26 is necessary for proper cell cycleprogression and proliferation
Samdal, H. et al.
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in the regulation of cell cycle, although only a few have been functionally characterized. By combining RNA sequencing and ChIP sequencing of cell cycle synchronized HaCaT cells we have previously identified lncRNAs highly enriched for cell cycle functions. Based on a cycli... |
Environmental enrichment induces epigenomic and genome organization changesrelevant for cognitive function
Espeso-Gil, S. et al.
In early development, the environment triggers mnemonic epigenomic programs resulting in memory and learning experiences to confer cognitive phenotypes into adulthood. To uncover how environmental stimulation impacts the epigenome and genome organization, we used the paradigm of environmental enrichment (EE) in youn... |
Derivation of Intermediate Pluripotent Stem Cells Amenable to PrimordialGerm Cell Specification.
Yu L. et al.
Dynamic pluripotent stem cell (PSC) states are in vitro adaptations of pluripotency continuum in vivo. Previous studies have generated a number of PSCs with distinct properties. To date, however, no known PSCs have demonstrated dual competency for chimera formation and direct responsiveness to primordial g... |
Epigenetic regulation of the lineage specificity of primary human dermallymphatic and blood vascular endothelial cells.
Tacconi, Carlotta and He, Yuliang and Ducoli, Luca and Detmar, Michael
Lymphatic and blood vascular endothelial cells (ECs) share several molecular and developmental features. However, these two cell types possess distinct phenotypic signatures, reflecting their different biological functions. Despite significant advances in elucidating how the specification of lymphatic and blood vasc... |
Combined treatment with CBP and BET inhibitors reverses inadvertentactivation of detrimental super enhancer programs in DIPG cells.
Wiese, M and Hamdan, FH and Kubiak, K and Diederichs, C and Gielen, GHand Nussbaumer, G and Carcaboso, AM and Hulleman, E and Johnsen, SA andKramm, CM
Diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas (DIPG) are the most aggressive brain tumors in children with 5-year survival rates of only 2%. About 85% of all DIPG are characterized by a lysine-to-methionine substitution in histone 3, which leads to global H3K27 hypomethylation accompanied by H3K27 hyperacetylation. Hyperacetyla... |
Role of JMJD3 Demethylase and Its Inhibitor GSK-J4 in Regulation of MGMT, TRA2A, RPS6KA2 and U2AF1 Genes in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines.
Sanchez A. et al.
Abstract not availabale |
Egr2-guided histone H2B monoubiquitination is required for peripheral nervous system myelination.
Wüst HM, Wegener A, Fröb F, Hartwig AC, Wegwitz F, Kari V, Schimmel M, Tamm ER, Johnsen SA, Wegner M, Sock E
Schwann cells are the nerve ensheathing cells of the peripheral nervous system. Absence, loss and malfunction of Schwann cells or their myelin sheaths lead to peripheral neuropathies such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in humans. During Schwann cell development and myelination chromatin is dramatically modified. How... |
Genomic deregulation of PRMT5 supports growth and stress tolerance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Schnormeier AK, Pommerenke C, Kaufmann M, Drexler HG, Koeppel M
Patients suffering from chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) display highly diverse clinical courses ranging from indolent cases to aggressive disease, with genetic and epigenetic features resembling this diversity. Here, we developed a comprehensive approach combining a variety of molecular and clinical data to pinpo... |
Histone post-translational modifications in Silene latifolia X and Y chromosomes suggest a mammal-like dosage compensation system
Luis Rodríguez Lorenzo José, Hubinský Marcel, Vyskot Boris, Hobza Roman
Silene latifolia is a model organism to study evolutionary young heteromorphic sex chromosome evolution in plants. Previous research indicates a Y-allele gene degeneration and a dosage compensation system already operating. Here, we propose an epigenetic approach based on analysis of several histone post-translation... |
In vitro capture and characterization of embryonic rosette-stage pluripotency between naive and primed states.
Neagu A, van Genderen E, Escudero I, Verwegen L, Kurek D, Lehmann J, Stel J, Dirks RAM, van Mierlo G, Maas A, Eleveld C, Ge Y, den Dekker AT, Brouwer RWW, van IJcken WFJ, Modic M, Drukker M, Jansen JH, Rivron NC, Baart EB, Marks H, Ten Berge D
Following implantation, the naive pluripotent epiblast of the mouse blastocyst generates a rosette, undergoes lumenogenesis and forms the primed pluripotent egg cylinder, which is able to generate the embryonic tissues. How pluripotency progression and morphogenesis are linked and whether intermediate pluripotent st... |
The TGF-β profibrotic cascade targets ecto-5'-nucleotidase gene in proximal tubule epithelial cells and is a traceable marker of progressive diabetic kidney disease.
Cappelli C, Tellez A, Jara C, Alarcón S, Torres A, Mendoza P, Podestá L, Flores C, Quezada C, Oyarzún C, Martín RS
Progressive diabetic nephropathy (DN) and loss of renal function correlate with kidney fibrosis. Crosstalk between TGF-β and adenosinergic signaling contributes to the phenotypic transition of cells and to renal fibrosis in DN models. We evaluated the role of TGF-β on NT5E gene expression coding for the ec... |
ChromID identifies the protein interactome at chromatin marks.
Villaseñor R, Pfaendler R, Ambrosi C, Butz S, Giuliani S, Bryan E, Sheahan TW, Gable AL, Schmolka N, Manzo M, Wirz J, Feller C, von Mering C, Aebersold R, Voigt P, Baubec T
Chromatin modifications regulate genome function by recruiting proteins to the genome. However, the protein composition at distinct chromatin modifications has yet to be fully characterized. In this study, we used natural protein domains as modular building blocks to develop engineered chromatin readers (eCRs) selec... |
A comprehensive epigenomic analysis of phenotypically distinguishable, genetically identical female and male Daphnia pulex.
Kvist J, Athanàsio CG, Pfrender ME, Brown JB, Colbourne JK, Mirbahai L
BACKGROUND: Daphnia species reproduce by cyclic parthenogenesis involving both sexual and asexual reproduction. The sex of the offspring is environmentally determined and mediated via endocrine signalling by the mother. Interestingly, male and female Daphnia can be genetically identical, yet display large difference... |
Analysis of Histone Modifications in Rodent Pancreatic Islets by Native Chromatin Immunoprecipitation.
Sandovici I, Nicholas LM, O'Neill LP
The islets of Langerhans are clusters of cells dispersed throughout the pancreas that produce several hormones essential for controlling a variety of metabolic processes, including glucose homeostasis and lipid metabolism. Studying the transcriptional control of pancreatic islet cells has important implications for ... |
Changes in H3K27ac at Gene Regulatory Regions in Porcine AlveolarMacrophages Following LPS or PolyIC Exposure.
Herrera-Uribe, Juber and Liu, Haibo and Byrne, Kristen A and Bond, Zahra Fand Loving, Crystal L and Tuggle, Christopher K
Changes in chromatin structure, especially in histone modifications (HMs), linked with chromatin accessibility for transcription machinery, are considered to play significant roles in transcriptional regulation. Alveolar macrophages (AM) are important immune cells for protection against pulmonary pathogens, and must... |
The Inhibition of the Histone Methyltransferase EZH2 by DZNEP or SiRNA Demonstrates Its Involvement in MGMT, TRA2A, RPS6KA2, and U2AF1 Gene Regulation in Prostate Cancer.
El Ouardi D, Idrissou M, Sanchez A, Penault-Llorca F, Bignon YJ, Guy L, Bernard-Gallon D
In France, prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men (Bray et al., 2018). Previously, our team has reported the involvement of epigenetic factors in prostate cancer (Ngollo et al., 2014, 2017). The histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) is a repressive mark that induces chromatin compaction and thus ge... |
Functionally Annotating Regulatory Elements in the Equine Genome Using Histone Mark ChIP-Seq.
Kingsley NB, Kern C, Creppe C, Hales EN, Zhou H, Kalbfleisch TS, MacLeod JN, Petersen JL, Finno CJ, Bellone RR
One of the primary aims of the Functional Annotation of ANimal Genomes (FAANG) initiative is to characterize tissue-specific regulation within animal genomes. To this end, we used chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-Seq) to map four histone modifications (H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27ac, and H3K27me... |
CURLY LEAF regulates micro RNA activity by controlling ARGONAUTE 1 degradation in plants.
Ré DA, Cambiagno DA, Arce AL, Tomassi AH, Giustozzi M, Casati P, Ariel FD, Manavella PA
CURLY LEAF (CLF) encodes the methyl-transferase sub-unit of the Polycomb Repressor Complex 2 (PRC2), which regulates the expression of target genes through H3K27 tri-methylation. We isolated a new CLF mutant allele (clf-78) using a genetic screening designed to identify micro RNAs (miRNA) deficient mutants. CLF muta... |
Epigenomic signatures underpin the axonal regenerative ability of dorsal root ganglia sensory neurons.
Palmisano I, Danzi MC, Hutson TH, Zhou L, McLachlan E, Serger E, Shkura K, Srivastava PK, Hervera A, Neill NO, Liu T, Dhrif H, Wang Z, Kubat M, Wuchty S, Merkenschlager M, Levi L, Elliott E, Bixby JL, Lemmon VP, Di Giovanni S
Axonal injury results in regenerative success or failure, depending on whether the axon lies in the peripheral or the CNS, respectively. The present study addresses whether epigenetic signatures in dorsal root ganglia discriminate between regenerative and non-regenerative axonal injury. Chromatin immunoprecipitation... |
Reactivation of super-enhancers by KLF4 in human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Tsompana M, Gluck C, Sethi I, Joshi I, Bard J, Nowak NJ, Sinha S, Buck MJ
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a disease of significant morbidity and mortality and rarely diagnosed in early stages. Despite extensive genetic and genomic characterization, targeted therapeutics and diagnostic markers of HNSCC are lacking due to the inherent heterogeneity and complexity of the dis... |
Development and epigenetic plasticity of murine Müller glia.
Dvoriantchikova G, Seemungal RJ, Ivanov D
The ability to regenerate the entire retina and restore lost sight after injury is found in some species and relies mostly on the epigenetic plasticity of Müller glia. To understand the role of mammalian Müller glia as a source of progenitors for retinal regeneration, we investigated changes in gene expres... |
The alarmin S100A9 hampers osteoclast differentiation from human circulating precursors by reducing the expression of RANK.
Di Ceglie I, Blom AB, Davar R, Logie C, Martens JHA, Habibi E, Böttcher LM, Roth J, Vogl T, Goodyear CS, van der Kraan PM, van Lent PL, van den Bosch MH
The alarmin S100A8/A9 is implicated in sterile inflammation-induced bone resorption and has been shown to increase the bone-resorptive capacity of mature osteoclasts. Here, we investigated the effects of S100A9 on osteoclast differentiation from human CD14 circulating precursors. Hereto, human CD14 monocytes were is... |
Twist2 amplification in rhabdomyosarcoma represses myogenesis and promotes oncogenesis by redirecting MyoD DNA binding.
Li S, Chen K, Zhang Y, Barnes SD, Jaichander P, Zheng Y, Hassan M, Malladi VS, Skapek SX, Xu L, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN, Liu N
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is an aggressive pediatric cancer composed of myoblast-like cells. Recently, we discovered a unique muscle progenitor marked by the expression of the Twist2 transcription factor. Genomic analyses of 258 RMS patient tumors uncovered prevalent copy number amplification events and increased expre... |
Canonical PRC1 controls sequence-independent propagation of Polycomb-mediated gene silencing.
Moussa HF, Bsteh D, Yelagandula R, Pribitzer C, Stecher K, Bartalska K, Michetti L, Wang J, Zepeda-Martinez JA, Elling U, Stuckey JI, James LI, Frye SV, Bell O
Polycomb group (PcG) proteins play critical roles in the epigenetic inheritance of cell fate. The Polycomb Repressive Complexes PRC1 and PRC2 catalyse distinct chromatin modifications to enforce gene silencing, but how transcriptional repression is propagated through mitotic cell divisions remains a key unresolved q... |
The epigenetic basis for the impaired ability of adult murine retinal pigment epithelium cells to regenerate retinal tissue.
Dvoriantchikova G, Seemungal RJ, Ivanov D
The epigenetic plasticity of amphibian retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) allows them to regenerate the entire retina, a trait known to be absent in mammals. In this study, we investigated the epigenetic plasticity of adult murine RPE to identify possible mechanisms that prevent mammalian RPE from regenerating retinal... |
EZH2 is overexpressed in transitional preplasmablasts and is involved in human plasma cell differentiation.
Herviou L, Jourdan M, Martinez AM, Cavalli G, Moreaux J
Plasma cells (PCs) play a major role in the defense of the host organism against pathogens. We have shown that PC generation can be modeled using multi-step culture systems that reproduce the sequential cell differentiation occurring in vivo. Using this unique model, we investigated the role of EZH2 during PC differ... |
Chromatin-Based Classification of Genetically Heterogeneous AMLs into Two Distinct Subtypes with Diverse Stemness Phenotypes.
Yi G, Wierenga ATJ, Petraglia F, Narang P, Janssen-Megens EM, Mandoli A, Merkel A, Berentsen K, Kim B, Matarese F, Singh AA, Habibi E, Prange KHM, Mulder AB, Jansen JH, Clarke L, Heath S, van der Reijden BA, Flicek P, Yaspo ML, Gut I, Bock C, Schuringa JJ
Global investigation of histone marks in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains limited. Analyses of 38 AML samples through integrated transcriptional and chromatin mark analysis exposes 2 major subtypes. One subtype is dominated by patients with NPM1 mutations or MLL-fusion genes, shows activation of the regulat... |
Comprehensive Analysis of Chromatin States in Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor Identifies Diverging Roles for SWI/SNF and Polycomb in Gene Regulation.
Erkek S, Johann PD, Finetti MA, Drosos Y, Chou HC, Zapatka M, Sturm D, Jones DTW, Korshunov A, Rhyzova M, Wolf S, Mallm JP, Beck K, Witt O, Kulozik AE, Frühwald MC, Northcott PA, Korbel JO, Lichter P, Eils R, Gajjar A, Roberts CWM, Williamson D, Hasselbla
Biallelic inactivation of SMARCB1, encoding a member of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, is the hallmark genetic aberration of atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors (ATRT). Here, we report how loss of SMARCB1 affects the epigenome in these tumors. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) on pri... |
Epigenetic suppression of E-cadherin expression by Snail2 during the metastasis of colorectal cancer.
Hu Y, Dai M, Zheng Y, Wu J, Yu B, Zhang H, Kong W, Wu H, Yu X
BACKGROUND: The transcription factor Snail2 is a repressor of E-cadherin expression during carcinogenesis; however, the specific mechanisms involved in this process in human colorectal cancer (CRC) remain largely unknown. METHOD: We checked the expression of Snail2 in several clinical CRC specimens. Then, we establi... |
PRC2 targeting is a therapeutic strategy for EZ score defined high-risk multiple myeloma patients and overcome resistance to IMiDs.
Herviou L, Kassambara A, Boireau S, Robert N, Requirand G, Müller-Tidow C, Vincent L, Seckinger A, Goldschmidt H, Cartron G, Hose D, Cavalli G, Moreaux J
BACKGROUND: Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant plasma cell disease with a poor survival, characterized by the accumulation of myeloma cells (MMCs) within the bone marrow. Epigenetic modifications in MM are associated not only with cancer development and progression, but also with drug resistance. METHODS: We ident... |
The Itaconate Pathway Is a Central Regulatory Node Linking Innate Immune Tolerance and Trained Immunity
Domínguez-Andrés Jorge, Novakovic Boris, Li Yang, Scicluna Brendon P., Gresnigt Mark S., Arts Rob J.W., Oosting Marije, Moorlag Simone J.C.F.M., Groh Laszlo A., Zwaag Jelle, Koch Rebecca M., ter Horst Rob, Joosten Leo A.B., Wijmenga Cisca, Michelucci Ales
Sepsis involves simultaneous hyperactivation of the immune system and immune paralysis, leading to both organ dysfunction and increased susceptibility to secondary infections. Acute activation of myeloid cells induced itaconate synthesis, which subsequently mediated innate immune tolerance in human monocytes. In con... |
Mapping molecular landmarks of human skeletal ontogeny and pluripotent stem cell-derived articular chondrocytes.
Ferguson GB, Van Handel B, Bay M, Fiziev P, Org T, Lee S, Shkhyan R, Banks NW, Scheinberg M, Wu L, Saitta B, Elphingstone J, Larson AN, Riester SM, Pyle AD, Bernthal NM, Mikkola HK, Ernst J, van Wijnen AJ, Bonaguidi M, Evseenko D
Tissue-specific gene expression defines cellular identity and function, but knowledge of early human development is limited, hampering application of cell-based therapies. Here we profiled 5 distinct cell types at a single fetal stage, as well as chondrocytes at 4 stages in vivo and 2 stages during in vitro differen... |
Integrative multi-omics analysis of intestinal organoid differentiation
Rik GH Lindeboom, Lisa van Voorthuijsen1, Koen C Oost, Maria J Rodríguez-Colman, Maria V Luna-Velez, Cristina Furlan, Floriane Baraille, Pascal WTC Jansen, Agnès Ribeiro, Boudewijn MT Burgering, Hugo J Snippert, & Michiel Vermeulen
Intestinal organoids accurately recapitulate epithelial homeostasis in vivo, thereby representing a powerful in vitro system to investigate lineage specification and cellular differentiation. Here, we applied a multi-omics framework on stem cell-enriched and stem cell-depleted mouse intestinal organoids to obtain a ... |
The Polycomb-Dependent Epigenome Controls β Cell Dysfunction, Dedifferentiation, and Diabetes.
Lu TT, Heyne S, Dror E, Casas E, Leonhardt L, Boenke T, Yang CH, Sagar , Arrigoni L, Dalgaard K, Teperino R, Enders L, Selvaraj M, Ruf M, Raja SJ, Xie H, Boenisch U, Orkin SH, Lynn FC, Hoffman BG, Grün D, Vavouri T, Lempradl AM, Pospisilik JA
To date, it remains largely unclear to what extent chromatin machinery contributes to the susceptibility and progression of complex diseases. Here, we combine deep epigenome mapping with single-cell transcriptomics to mine for evidence of chromatin dysregulation in type 2 diabetes. We find two chromatin-state signat... |
The reference epigenome and regulatory chromatin landscape of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Beekman R. et al.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a frequent hematological neoplasm in which underlying epigenetic alterations are only partially understood. Here, we analyze the reference epigenome of seven primary CLLs and the regulatory chromatin landscape of 107 primary cases in the context of normal B cell differentiation.... |
Increased H3K9 methylation and impaired expression of Protocadherins are associated with the cognitive dysfunctions of the Kleefstra syndrome.
Iacono G, Dubos A, Méziane H, Benevento M, Habibi E, Mandoli A, Riet F, Selloum M, Feil R, Zhou H, Kleefstra T, Kasri NN, van Bokhoven H, Herault Y, Stunnenberg HG
Kleefstra syndrome, a disease with intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders and other developmental defects is caused in humans by haploinsufficiency of EHMT1. Although EHMT1 and its paralog EHMT2 were shown to be histone methyltransferases responsible for deposition of the di-methylated H3K9 (H3K9me2), th... |
Pro-inflammatory cytokines activate hypoxia-inducible factor 3α via epigenetic changes in mesenchymal stromal/stem cells.
Cuomo F, Coppola A, Botti C, Maione C, Forte A, Scisciola L, Liguori G, Caiafa I, Ursini MV, Galderisi U, Cipollaro M, Altucci L, Cobellis G
Human mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (hMSCs) emerged as a promising therapeutic tool for ischemic disorders, due to their ability to regenerate damaged tissues, promote angiogenesis and reduce inflammation, leading to encouraging, but still limited results. The outcomes in clinical trials exploring hMSC therapy are ... |
BRACHYURY directs histone acetylation to target loci during mesoderm development.
Beisaw A. et al.
T-box transcription factors play essential roles in multiple aspects of vertebrate development. Here, we show that cooperative function of BRACHYURY (T) with histone-modifying enzymes is essential for mouse embryogenesis. A single point mutation (TY88A) results in decreased histone 3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) ... |
Single-cell absolute contact probability detection reveals chromosomes are organized by multiple low-frequency yet specific interactions
Cattoni DI et al.
At the kilo- to megabase pair scales, eukaryotic genomes are partitioned into self-interacting modules or topologically associated domains (TADs) that associate to form nuclear compartments. Here, we combine high-content super-resolution microscopies with state-of-the-art DNA-labeling methods to reveal the variabili... |
In Situ Fixation Redefines Quiescence and Early Activation of Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells
Machado L. et al.
Summary
State of the art techniques have been developed to isolate and analyze cells from various tissues, aiming to capture their in vivo state. However, the majority of cell isolation protocols involve lengthy mechanical and enzymatic dissociation steps followed by flow cytometry, exposing cells to stres... |
Chromosome contacts in activated T cells identify autoimmune disease candidate genes
Burren OS et al.
BACKGROUND:
Autoimmune disease-associated variants are preferentially found in regulatory regions in immune cells, particularly CD4+ T cells. Linking such regulatory regions to gene promoters in disease-relevant cell contexts facilitates identification of candidate disease genes.
RESULTS:
Within 4 h, act... |
Platelet function is modified by common sequence variation in megakaryocyte super enhancers
Petersen R. et al.
Linking non-coding genetic variants associated with the risk of diseases or disease-relevant traits to target genes is a crucial step to realize GWAS potential in the introduction of precision medicine. Here we set out to determine the mechanisms underpinning variant association with platelet quantitative traits usi... |
Characterization of the Polycomb-Group Mark H3K27me3 in Unicellular Algae
Mikulski P. et al.
Polycomb Group (PcG) proteins mediate chromatin repression in plants and animals by catalyzing H3K27 methylation and H2AK118/119 mono-ubiquitination through the activity of the Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) and PRC1, respectively. PcG proteins were extensively studied in higher plants, but their function and ... |
Global analysis of H3K27me3 as an epigenetic marker in prostate cancer progression
Ngollo M. et al.
BACKGROUND:
H3K27me3 histone marks shape the inhibition of gene transcription. In prostate cancer, the deregulation of H3K27me3 marks might play a role in prostate tumor progression.
METHODS:
We investigated genome-wide H3K27me3 histone methylation profile using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and 2X400K p... |
Epigenetically-driven anatomical diversity of synovial fibroblasts guides joint-specific fibroblast functions
Frank-Bertoncelj M, Trenkmann M, Klein K, Karouzakis E, Rehrauer H, Bratus A, Kolling C, Armaka M, Filer A, Michel BA, Gay RE, Buckley CD, Kollias G, Gay S, Ospelt C
A number of human diseases, such as arthritis and atherosclerosis, include characteristic pathology in specific anatomical locations. Here we show transcriptomic differences in synovial fibroblasts from different joint locations and that HOX gene signatures reflect the joint-specific origins of mouse and human synov... |
RNF40 regulates gene expression in an epigenetic context-dependent manner
Xie W. et al.
BACKGROUND:
Monoubiquitination of H2B (H2Bub1) is a largely enigmatic histone modification that has been linked to transcriptional elongation. Because of this association, it has been commonly assumed that H2Bub1 is an exclusively positively acting histone modification and that increased H2Bub1 occupancy correlat... |
Menin regulates Inhbb expression through an Akt/Ezh2-mediated H3K27 histone modification
Gherardi S. et al.
Although Men1 is a well-known tumour suppressor gene, little is known about the functions of Menin, the protein it encodes for. Since few years, numerous publications support a major role of Menin in the control of epigenetics gene regulation. While Menin interaction with MLL complex favours transcriptional activati... |
DNA methylation heterogeneity defines a disease spectrum in Ewing sarcoma
Sheffield N.C. et al.
Developmental tumors in children and young adults carry few genetic alterations, yet they have diverse clinical presentation. Focusing on Ewing sarcoma, we sought to establish the prevalence and characteristics of epigenetic heterogeneity in genetically homogeneous cancers. We performed genome-scale DNA methylation ... |
Arabidopsis SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex binds both promoters and terminators to regulate gene expression
Archacki R. et al.
ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes are important regulators of gene expression in Eukaryotes. In plants, SWI/SNF-type complexes have been shown critical for transcriptional control of key developmental processes, growth and stress responses. To gain insight into mechanisms underlying these roles, we perfor... |
Co-occurrence of Histone H3 K27M and BRAF V600E mutations in paediatric midline grade I ganglioglioma
Pagès M. et al.
Ganglioglioma (GG) is a grade I tumour characterized by alterations in the MAPK pathway, including BRAF V600E mutation. Recently, diffuse midline glioma with an H3 K27M mutation was added to the WHO 2016 classification as a new grade IV entity. As co-occurrence of H3 K27M and BRAF V600E mutations has been reported i... |
FOXA1 Directs H3K4 Monomethylation at Enhancers via Recruitment of the Methyltransferase MLL3
Jozwik K.M. et al.
FOXA1 is a pioneer factor that binds to enhancer regions that are enriched in H3K4 mono- and dimethylation (H3K4me1 and H3K4me2). We performed a FOXA1 rapid immunoprecipitation mass spectrometry of endogenous proteins (RIME) screen in ERα-positive MCF-7 breast cancer cells and found histone-lysine N-methyltran... |
β-Glucan Reverses the Epigenetic State of LPS-Induced Immunological Tolerance
Novakovic B. et al.
Innate immune memory is the phenomenon whereby innate immune cells such as monocytes or macrophages undergo functional reprogramming after exposure to microbial components such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS). We apply an integrated epigenomic approach to characterize the molecular events involved in LPS-induced to... |
The Hematopoietic Transcription Factors RUNX1 and ERG Prevent AML1-ETO Oncogene Overexpression and Onset of the Apoptosis Program in t(8;21) AMLs
Mandoli A. et al.
The t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia (AML)-associated oncoprotein AML1-ETO disrupts normal hematopoietic differentiation. Here, we have investigated its effects on the transcriptome and epigenome in t(8,21) patient cells. AML1-ETO binding was found at promoter regions of active genes with high levels of histone acetyl... |
Chromatin Preparation and Chromatin Immuno-precipitation from Drosophila Embryos
Löser E. et al.
This protocol provides specific details on how to perform Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) from Drosophila embryos. ChIP allows the matching of proteins or histone modifications to specific genomic regions. Formaldehyde-cross-linked chromatin is isolated and antibodies against the target of interest are used to ... |
Neonatal monocytes exhibit a unique histone modification landscape
Bermick JR et al.
Background
Neonates have dampened expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and difficulty clearing pathogens. This makes them uniquely susceptible to infections, but the factors regulating neonatal-specific immune responses are poorly understood. Epigenetics, including histone modifications, can activate or silen... |
BRD4 localization to lineage-specific enhancers is associated with a distinct transcription factor repertoire
Najafova Z. et al.
Proper temporal epigenetic regulation of gene expression is essential for cell fate determination and tissue development. The Bromodomain-containing Protein-4 (BRD4) was previously shown to control the transcription of defined subsets of genes in various cell systems. In this study we examined the role of BRD4 in pr... |
Coordinate redeployment of PRC1 proteins suppresses tumor formation during Drosophila development
Loubiere V. et al.
Polycomb group proteins form two main complexes, PRC2 and PRC1, which generally coregulate their target genes. Here we show that PRC1 components act as neoplastic tumor suppressors independently of PRC2 function. By mapping the distribution of PRC1 components and trimethylation of histone H3 at Lys27 (H3K27me3) acro... |
Clinical, Imaging, Histopathological and Molecular Characterization of Anaplastic Ganglioglioma
Zanello M et al.
Anaplastic ganglioglioma (AGG) is a rare and malignant variant of ganglioglioma. According to the World Health Organization classification version 2016, their histopathological grading criteria are still ill-defined. The aim of the present study was to assess the clinical, imaging, histopathological, and molecular c... |
reChIP-seq reveals widespread bivalency of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 in CD4(+) memory T cells
Kinkley S et al.
The combinatorial action of co-localizing chromatin modifications and regulators determines chromatin structure and function. However, identifying co-localizing chromatin features in a high-throughput manner remains a technical challenge. Here we describe a novel reChIP-seq approach and tailored bioinformatic analys... |
Epigenetic dynamics of monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation
Wallner S et al.
BACKGROUND:
Monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation involves major biochemical and structural changes. In order to elucidate the role of gene regulatory changes during this process, we used high-throughput sequencing to analyze the complete transcriptome and epigenome of human monocytes that were differentiated in... |
The dynamic interactome and genomic targets of Polycomb complexes during stem-cell differentiation
Kloet S.L. et al.
Although the core subunits of Polycomb group (PcG) complexes are well characterized, little is known about the dynamics of these protein complexes during cellular differentiation. We used quantitative interaction proteomics and genome-wide profiling to study PcG proteins in mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and neur... |
PHF13 is a molecular reader and transcriptional co-regulator of H3K4me2/3
Chung HR et al.
PHF13 is a chromatin affiliated protein with a functional role in differentiation, cell division, DNA damage response and higher chromatin order. To gain insight into PHF13's ability to modulate these processes, we elucidate the mechanisms targeting PHF13 to chromatin, its genome wide localization and its molecular ... |
Comprehensive genome and epigenome characterization of CHO cells in response to evolutionary pressures and over time
Feichtinger J, Hernández I, Fischer C, Hanscho M, Auer N, Hackl M, Jadhav V, Baumann M, Krempl PM, Schmidl C, Farlik M, Schuster M, Merkel A, Sommer A, Heath S, Rico D, Bock C, Thallinger GG, Borth N
The most striking characteristic of CHO cells is their adaptability, which enables efficient production of proteins as well as growth under a variety of culture conditions, but also results in genomic and phenotypic instability. To investigate the relative contribution of genomic and epigenetic modifications towards... |
Epigenetic regulation of diacylglycerol kinase alpha promotes radiation-induced fibrosis
Weigel C. et al.
Radiotherapy is a fundamental part of cancer treatment but its use is limited by the onset of late adverse effects in the normal tissue, especially radiation-induced fibrosis. Since the molecular causes for fibrosis are largely unknown, we analyse if epigenetic regulation might explain inter-individual differences i... |
Standardizing chromatin research: a simple and universal method for ChIP-seq
Laura Arrigoni, Andreas S. Richter, Emily Betancourt, Kerstin Bruder, Sarah Diehl, Thomas Manke and Ulrike Bönisch
Here we demonstrate that harmonization of ChIP-seq workflows across cell types and conditions is possible when obtaining chromatin from properly isolated nuclei. We established an ultrasound-based nuclei extraction method (Nuclei Extraction by Sonication) that is highly effective across various organisms, cell ... |
The homeoprotein DLX3 and tumor suppressor p53 co-regulate cell cycle progression and squamous tumor growth
Palazzo E et al.
Epidermal homeostasis depends on the coordinated control of keratinocyte cell cycle. Differentiation and the alteration of this balance can result in neoplastic development. Here we report on a novel DLX3-dependent network that constrains epidermal hyperplasia and squamous tumorigenesis. By integrating genetic and t... |
Reinforcement of STAT3 activity reprogrammes human embryonic stem cells to naive-like pluripotency.
Chen H, Aksoy I, Gonnot F, Osteil P, Aubry M, Hamela C, Rognard C, Hochard A, Voisin S, Fontaine E, Mure M, Afanassieff M, Cleroux E, Guibert S, Chen J, Vallot C, Acloque H, Genthon C, Donnadieu C, De Vos J, Sanlaville D, Guérin JF, Weber M, Stanton LW, R
Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF)/STAT3 signalling is a hallmark of naive pluripotency in rodent pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), whereas fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-2 and activin/nodal signalling is required to sustain self-renewal of human PSCs in a condition referred to as the primed state. It is unknown why LIF/... |
A lncRNA regulates alternative splicing via establishment of a splicing-specific chromatin signature.
Gonzalez I, Munita R, Agirre E, Dittmer TA, Gysling K, Misteli T, Luco RF
Alternative pre-mRNA splicing is a highly cell type-specific process essential to generating protein diversity. However, the mechanisms responsible for the establishment and maintenance of heritable cell-specific alternative-splicing programs are poorly understood. Recent observations point to a role of histone modi... |
A cohesin-OCT4 complex mediates Sox enhancers to prime an early embryonic lineage.
Abboud N, Moore-Morris T, Hiriart E, Yang H, Bezerra H, Gualazzi MG, Stefanovic S, Guénantin AC, Evans SM, Pucéat M
Short- and long-scales intra- and inter-chromosomal interactions are linked to gene transcription, but the molecular events underlying these structures and how they affect cell fate decision during embryonic development are poorly understood. One of the first embryonic cell fate decisions (that is, mesendoderm deter... |
Epigenome mapping reveals distinct modes of gene regulation and widespread enhancer reprogramming by the oncogenic fusion protein EWS-FLI1.
Tomazou EM, Sheffield NC, Schmidl C, Schuster M, Schönegger A, Datlinger P, Kubicek S, Bock C, Kovar H
Transcription factor fusion proteins can transform cells by inducing global changes of the transcriptome, often creating a state of oncogene addiction. Here, we investigate the role of epigenetic mechanisms in this process, focusing on Ewing sarcoma cells that are dependent on the EWS-FLI1 fusion protein. We establi... |
Global effects of the CSR-1 RNA interference pathway on the transcriptional landscape.
Cecere G, Hoersch S, O'Keeffe S, Sachidanandam R, Grishok A
Argonaute proteins and their small RNA cofactors short interfering RNAs are known to inhibit gene expression at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. In Caenorhabditis elegans, the Argonaute CSR-1 binds thousands of endogenous siRNAs (endo-siRNAs) that are antisense to germline transcripts. However, i... |
Nucleophosmin 1 cooperates with the methyltransferase DOT1L toregulate H3K79me2 levels and DNA satellites expression atperi-nucleolar heterochromatin
Izzo A. et al.
The histone methyltransferase DOT1L catalyzes methylation of H3K79 and it is highly conserved in mammals. DOT1L plays a functional role in several biological processes including cell cycle regulation, DNA repair, RNA splicing and gene expression, suggesting a complex role in chromatin organization and regulation. Su... |