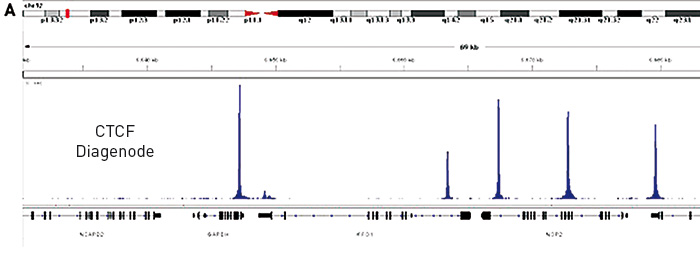
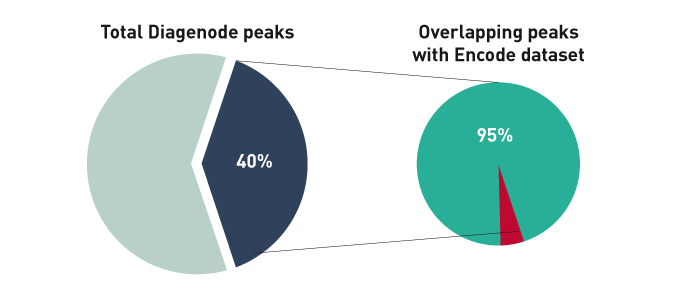
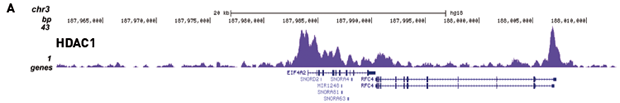
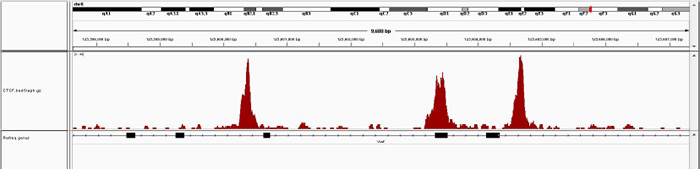
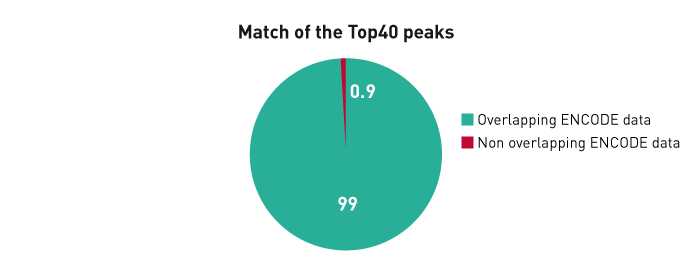
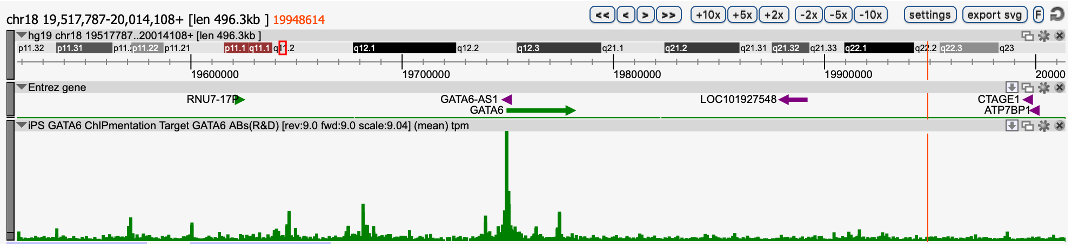
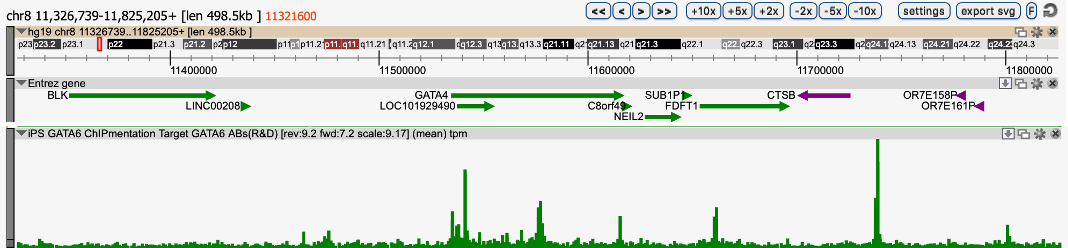
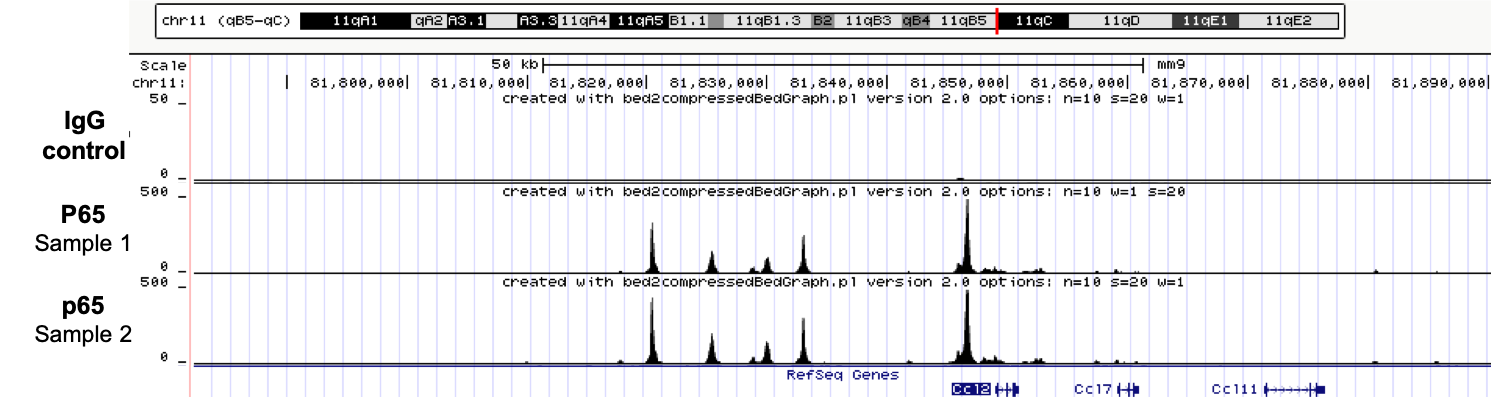
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: iDeal ChIP-seq kit for Transcription Factors (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C01010054). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
ZFTA-RELA ependymomas make itaconate to epigenetically drive fusion expression
Natarajan, Siva Kumar et al.
Abstract
ZFTA-RELA+ ependymomas are malignant brain tumours defined by fusions formed between the putative chromatin remodeller ZFTA and the NF-κB mediator RELA1. Here we show that ZFTA-RELA+ cells produce itaconate, a key macrophage-associated immunomodulatory metabolite2. Itaconate is generated ... |
Targeting histone H2B acetylated enhanceosomes via p300/CBP degradation in prostate cancer
Luo, Jie et al.
Prostate cancer is driven by oncogenic transcription factor enhanceosomes comprising chromatin and epigenetic regulators. The lysine acetyltransferases p300 and CREB-binding protein (CBP) are key cofactors that activate enhancers through histone acetylation. Here we identify p300/CBP-mediated multisite histone H... |
KANSL3 directs transcriptional programs essential for hepatic metabolism and differentiation
Wiese, Meike et al.
Liver disease is a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Emerging evidence highlights the significant role of epigenetic regulation in sustaining liver homeostasis, providing new therapeutic strategies for liver disease. Hepatocyte-specific deletion of the epigenetic regulator KANSL3, a key component of the NSL ... |
PTTG1IP Orchestrates Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and DNA Damage Response in Thyroid Cancer Progression
Zhang, Henglu et al.
Background:
Thyroid cancer progression involves cell-state plasticity in the form of epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), and defects in DNA damage response (DDR), both of which are linked to metastasis and treatment failure. The role of pituitary tumor transforming 1 interacting protein (PTTG1IP/PBF)... |
Charting the regulatory landscape of TP53 on transposable elements in cancer
Qu, Xuan et al.
The relationship between TP53 and transposable elements (TEs) has been obscure. Given the important role of TEs in oncogenesis, a comprehensive profiling of TE expression dynamics under the regulation of TP53 provides valuable resources for more clarity in TP53's roles in cancer. In this study, we characterized the ... |
Charting the regulatory landscape of TP53 on transposable elements in cancer
Xuan Qu et al.
The relationship between TP53 and transposable elements (TEs) has been obscure. Given the important role of TEs in oncogenesis, a comprehensive profiling of TE expression dynamics under the regulation of TP53 provides valuable resources for more clarity in TP53's roles in cancer. In this study, we characterized the ... |
An ISWI-related chromatin remodeller regulates stage-specific gene expression in Toxoplasma gondii
Pachano, Belen et al.
ATP-dependent chromatin remodellers are specialized multiprotein machines that organize the genome in eukaryotic cells and regulate its accessibility by repositioning, ejecting or modifying nucleosomes. However, their role in Toxoplasma gondii is poorly understood. Here we show that T. gondii&n... |
Overlapping and distinct functions of SPT6, PNUTS, and PCF11 in regulating transcription termination
Fabienne Bejjani et al.
The histone chaperone and transcription elongation factor SPT6 is integral to RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) activity. SPT6 also plays a crucial role in regulating transcription termination, although the mechanisms involved are largely unknown. In an attempt to identify the pathways employed by SPT6 in this regulation, ... |
ZEB1 transcription factor induces tumor cell PD-L1 expression in melanoma
Chloé Wirbel et al.
Tumor cells can evade antitumor immune response by expressing the PD-L1 ligand, leading to the inhibition of PD-1-expressing T lymphocytes. The mechanisms that regulate PD-L1 expression in cancer cells are imperfectly characterized. The transcription factor ZEB1, a major regulator of phenotype switching in melanoma ... |
H2AJ Is a Direct Androgen Receptor Target Gene That Regulates Androgen-Induced Cellular Senescence and Inhibits Mesenchymal Markers in Prostate Cancer Cells
Mehdi Heidari Horestani et al.
Background: Prostate cancer (PCa) is a significant public health issue, particularly in developed countries. The androgen receptor (AR) plays a key role in regulating both the normal development and the proliferation of PCa. Bipolar androgen therapy, which involves treatment with supraphysiological androgen lev... |
Chromatin environment-dependent effects of DOT1L on gene expression in male germ cells
Manon Coulée et al.
The H3K79 methyltransferase DOT1L is essential for multiple aspects of mammalian development where it has been shown to regulate gene expression. Here, by producing and integrating epigenomic and spike-in RNA-seq data, we decipher the molecular role of DOT1L during mouse spermatogenesis and show that it has opposite... |
Dysregulation of Myelination in Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type II of the Human Frontal Lobe
Catharina Donkels et al.
Focal cortical dysplasias (FCDs) are local malformations of the human neocortex and a leading cause of intractable epilepsy. FCDs are classified into different subtypes including FCD IIa and IIb, characterized by a blurred gray-white matter boundary or a transmantle sign indicating abnormal white matter myelination.... |
The oncogenic lncRNA MIR503HG suppresses cellular senescence counteracting supraphysiological androgen treatment in prostate cancer
Julia Kallenbach et al.
Background
The androgen receptor (AR), a ligand-dependent transcription factor, plays a key role in regulating prostate cancer (PCa) growth. The novel bipolar androgen therapy (BAT) uses supraphysiological androgen levels (SAL) that suppresses growth of PCa cells and induces cellular senescence functioning as a tum... |
EOMES establishes mesoderm and endoderm differentiation potential through SWI/SNF-mediated global enhancer remodeling
Chiara M. Schröder et al.
Highlights
Enhancer chromatin is dynamically remodeled during mesoderm/endoderm (ME) differentiation
Global ME enhancer accessibility during pluripotency exit relies on the Tbx factor EOMES
EOMES and SWI/SNF cooperate to instruct chromatin accessibility at ME gene enhancers
ME e... |
The Novel Direct AR Target Gene Annexin A2 Mediates Androgen-Induced Cellular Senescence in Prostate Cancer Cells
Kimia Mirzakhani et al.
Clinical trials for prostate cancer (PCa) patients have implemented the bipolar androgen therapy (BAT) that includes the treatment with supraphysiological androgen level (SAL). SAL treatment induces cellular senescence in tumor samples of PCa patients and in various PCa cell lines, including castration-resistant PCa... |
TEAD-targeting small molecules induce a cofactor switch to regulate the Hippo pathway
Alissa D. Guarnaccia et al.
TEAD proteins are the main transcriptional effectors of the Hippo signaling pathway and a pharmacological target in oncology. Most TEAD-targeting small molecules act by disrupting interaction with the oncogenic transcriptional activators YAP and TAZ. Here, we describe an alternative mechanism for TEAD lipid pocket b... |
Reciprocal inhibition of NOTCH and SOX2 shapes tumor cell plasticity and therapeutic escape in triple-negative breast cancer
Morgane Fournier et al.
Cancer cell plasticity contributes significantly to the failure of chemo- and targeted therapies in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Molecular mechanisms of therapy-induced tumor cell plasticity and associated resistance are largely unknown. Using a genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screen, we investigated escape mechani... |
Biochemical characterization of the feedforward loop between CDK1 and FOXM1 in epidermal stem cells
Maria Pia Polito et al.
The complex network governing self-renewal in epidermal stem cells (EPSCs) is only partially defined. FOXM1 is one of the main players in this network, but the upstream signals regulating its activity remain to be elucidated. In this study, we identify cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) as the principal kinase control... |
An ERRα-ZEB1 transcriptional signature predicts survival in triple-negative breast cancers
Shi J-R et al.
Background.
Transcription factors (TFs) act together with co-regulators to modulate the expression of their target genes, which eventually dictates their pathophysiological effects. Depending on the co-regulator, TFs can exert different activities. The Estrogen Related Receptor α (ERRα) acts as a transc... |
Nuclear lamin A/C phosphorylation by loss of androgen receptor leads to cancer-associated fibroblast activation
Ghosh S. et al.
Alterations in nuclear structure and function are hallmarks of cancer cells. Little is known about these changes in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs), crucial components of the tumor microenvironment. Loss of the androgen receptor (AR) in human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs), which triggers early steps of CAF act... |
Biochemical role of FOXM1-dependent histone linker H1B in human epidermal stem cells
Piolito M. P. et al.
Epidermal stem cells orchestrate epidermal renewal and timely wound repair through a tight regulation of self-renewal, proliferation, and differentiation. In culture, human epidermal stem cells generate a clonal type referred to as holoclone, which give rise to transient amplifying progenitors (meroclone and paraclo... |
The landscape of RNA-chromatin interaction reveals small non-coding RNAs as essential mediators of leukemia maintenance
Haiyang Yun et al.
RNA constitutes a large fraction of chromatin. Spatial distribution and functional relevance of most of RNA-chromatin interactions remain unknown. We established a landscape analysis of RNA-chromatin interactions in human acute myeloid leukemia (AML). In total more than 50 million interactions were captured in an AM... |
Focal cortical dysplasia type II-dependent maladaptive myelination in the human frontal lobe
Donkels C. et al.
Focal cortical dysplasias (FCDs) are local malformations of the human neocortex and a leading cause of intractable epilepsy. FCDs are classified into different subtypes including FCD IIa and IIb, characterized by a blurred gray-white matter boundary or a transmantle sign indicating abnormal white matter myelination.... |
Cancer Cell Biomechanical Properties Accompany Tspan8-Dependent Cutaneous Melanoma Invasion
Runel G. et al.
The intrinsic biomechanical properties of cancer cells remain poorly understood. To decipher whether cell stiffness modulation could increase melanoma cells’ invasive capacity, we performed both in vitro and in vivo experiments exploring cell stiffness by atomic force microscopy (AFM). We correlated stiffn... |
ANKRD1 is a mesenchymal-specific driver of cancer-associated fibroblast activation bridging androgen receptor loss to AP-1 activation
Mazzeo L. et al.
There are significant commonalities among several pathologies involving fibroblasts, ranging from auto-immune diseases to fibrosis and cancer. Early steps in cancer development and progression are closely linked to fibroblast senescence and transformation into tumor-promoting cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), su... |
Targeting the mSWI/SNF Complex in POU2F-POU2AF Transcription Factor-Driven Malignancies
Tongchen He et al.
The POU2F3-POU2AF2/3 (OCA-T1/2) transcription factor complex is the master regulator of the tuft cell lineage and tuft cell-like small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Here, we found that the POU2F3 molecular subtype of SCLC (SCLC-P) exhibits an exquisite dependence on the activity of the mammalian switch/sucrose non-fermen... |
In vitro production of cat-restricted Toxoplasma pre-sexual stages
Antunes, A.V. et al.
Sexual reproduction of Toxoplasma gondii, confined to the felid gut, remains largely uncharted owing to ethical concerns regarding the use of cats as model organisms. Chromatin modifiers dictate the developmental fate of the parasite during its multistage life cycle, but their targeting to stage-specific cistro... |
ThPOK is a critical multifaceted regulator of myeloid lineagedevelopment.
Basu J. et al.
The transcription factor ThPOK (encoded by Zbtb7b) is well known for its role as a master regulator of CD4 lineage commitment in the thymus. Here, we report an unexpected and critical role of ThPOK as a multifaceted regulator of myeloid lineage commitment, differentiation and maturation. Using reporter and knockout ... |
Mediator 1 ablation induces enamel-to-hair lineage conversion in micethrough enhancer dynamics.
Thaler R. et al.
Postnatal cell fate is postulated to be primarily determined by the local tissue microenvironment. Here, we find that Mediator 1 (Med1) dependent epigenetic mechanisms dictate tissue-specific lineage commitment and progression of dental epithelia. Deletion of Med1, a key component of the Mediator complex linking enh... |
Supraphysiological Androgens Promote the Tumor Suppressive Activity of the Androgen Receptor Through cMYC Repression and Recruitment of the DREAM Complex
Nyquist M. et al.
The androgen receptor (AR) pathway regulates key cell survival programs in prostate epithelium. The AR represents a near-universal driver and therapeutic vulnerability in metastatic prostate cancer, and targeting AR has a remarkable therapeutic index. Though most approaches directed toward AR focus on inhibiting AR ... |
In skeletal muscle and neural crest cells, SMCHD1 regulates biologicalpathways relevant for Bosma syndrome and facioscapulohumeral dystrophyphenotype.
Laberthonnière C. et al.
Many genetic syndromes are linked to mutations in genes encoding factors that guide chromatin organization. Among them, several distinct rare genetic diseases are linked to mutations in SMCHD1 that encodes the structural maintenance of chromosomes flexible hinge domain containing 1 chromatin-associated factor. In hu... |
Vitamin D Receptor Cross-talk with p63 Signaling PromotesEpidermal Cell Fate.
Oda Y. et al.
The vitamin D receptor with its ligand 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D (1,25D) regulates epidermal stem cell fate, such that VDR removal from Krt14 expressing keratinocytes delays re-epithelialization of epidermis after wound injury in mice. In this study we deleted Vdr from Lrig1 expressing stem cells in the isthmus of th... |
SOX expression in prostate cancer drives resistance to nuclear hormonereceptor signaling inhibition through the WEE1/CDK1 signaling axis.
Williams A. et al.
The development of androgen receptor signaling inhibitor (ARSI) drug resistance in prostate cancer (PC) remains therapeutically challenging. Our group has described the role of sex determining region Y-box 2 (SOX2) overexpression in ARSI-resistant PC. Continuing this work, we report that NR3C1, the gene encoding glu... |
Epigenetic silencing of selected hypothalamic neuropeptides in narcolepsywith cataplexy.
Seifinejad A. et al.
Narcolepsy with cataplexy is a sleep disorder caused by deficiency in the hypothalamic neuropeptide hypocretin/orexin (HCRT), unanimously believed to result from autoimmune destruction of hypocretin-producing neurons. HCRT deficiency can also occur in secondary forms of narcolepsy and be only temporary, suggest... |
Activation of AKT induces EZH2-mediated β-catenin trimethylation incolorectal cancer.
Ghobashi A. H. et al.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) develops in part through the deregulation of different signaling pathways, including activation of the WNT/β-catenin and PI3K/AKT pathways. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is a lysine methyltransferase that is involved in regulating stem cell development and differentiation and is ove... |
Low affinity CTCF binding drives transcriptional regulation whereashigh affinity binding encompasses architectural functions
Marina-Zárate E. et al.
CTCF is a DNA-binding protein which plays critical roles in chromatin structure organization and transcriptional regulation; however, little is known about the functional determinants of different CTCF-binding sites (CBS). Using a conditional mouse model, we have identified one set of CBSs that are lost upon CTCF de... |
ZEB1 controls a lineage-specific transcriptional program essential formelanoma cell state transitions
Tang Y. et al.
Cell plasticity sustains intra-tumor heterogeneity and treatment resistance in melanoma. Deciphering the transcriptional mechanisms governing reversible phenotypic transitions between proliferative/differentiated and invasive/stem-like states is required in order to design novel therapeutic strategies. EMT-inducing ... |
A dataset of definitive endoderm and hepatocyte differentiations fromhuman induced pluripotent stem cells.
Tanaka Y. et al.
Hepatocytes are a major parenchymal cell type in the liver and play an essential role in liver function. Hepatocyte-like cells can be differentiated in vitro from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) via definitive endoderm (DE)-like cells and hepatoblast-like cells. Here, we explored the in vitro differentiation ... |
The mineralocorticoid receptor modulates timing and location of genomicbinding by glucocorticoid receptor in response to synthetic glucocorticoidsin keratinocytes.
Carceller-Zazo E. et al.
Glucocorticoids (GCs) exert potent antiproliferative and anti-inflammatory properties, explaining their therapeutic efficacy for skin diseases. GCs act by binding to the GC receptor (GR) and the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR), co-expressed in classical and non-classical targets including keratinocytes. Using knocko... |
A Systemic and Integrated Analysis of p63-Driven RegulatoryNetworks in Mouse Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Glathar A. R. et al.
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is the most common malignancy of the oral cavity and is linked to tobacco exposure, alcohol consumption, and human papillomavirus infection. Despite therapeutic advances, a lack of molecular understanding of disease etiology, and delayed diagnoses continue to negatively affect sur... |
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor cell intrinsically promotes resident memoryCD8 T cell differentiation and function.
Dean J. W. et al.
The Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr) regulates the differentiation and function of CD4 T cells; however, its cell-intrinsic role in CD8 T cells remains elusive. Herein we show that Ahr acts as a promoter of resident memory CD8 T cell (T) differentiation and function. Genetic ablation of Ahr in mouse CD... |
Impact of Fetal Exposure to Endocrine Disrupting ChemicalMixtures on FOXA3 Gene and Protein Expression in Adult RatTestes.
Walker C. et al.
Perinatal exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) has been shown to affect male reproductive functions. However, the effects on male reproduction of exposure to EDC mixtures at doses relevant to humans have not been fully characterized. In previous studies, we found that in utero exposure to mixtures of th... |
Expression of RNA polymerase I catalytic core is influenced byRPA12.
Ford B. L. et al.
RNA Polymerase I (Pol I) has recently been recognized as a cancer therapeutic target. The activity of this enzyme is essential for ribosome biogenesis and is universally activated in cancers. The enzymatic activity of this multi-subunit complex resides in its catalytic core composed of RPA194, RPA135, and RPA12, a s... |
ΔNp63α facilitates proliferation and migration, and modulates the chromatin landscape in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells
Anghui Peng et al.
p63 plays a crucial role in epithelia-originating tumours; however, its role in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) has not been completely explored. Our study revealed the oncogenic properties of p63 in iCCA and identified the major expressed isoform as ΔNp63α. We collected iCCA clinical data from Th... |
Identification of an E3 ligase that targets the catalytic subunit ofRNA polymerase I upon transcription stress.
Pitts Stephanie et al.
RNA polymerase I (Pol I) synthesizes ribosomal RNA (rRNA), which is the first and rate-limiting step in ribosome biogenesis. Factors governing the stability of the polymerase complex are not known. Previous studies characterizing the Pol I inhibitor BMH-21 revealed a transcriptional stress-dependent pathway for degr... |
Histone Deacetylases 1 and 2 target gene regulatory networks of nephronprogenitors to control nephrogenesis.
Liu Hongbing et al.
Our studies demonstrated the critical role of Histone deacetylases (HDACs) in the regulation of nephrogenesis. To better understand the key pathways regulated by HDAC1/2 in early nephrogenesis, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-Seq) of Hdac1/2 on isolated nephron progenitor cells (NPCs) fro... |
Identification of genomic binding sites and direct target genes for thetranscription factor DDIT3/CHOP.
Osman A. et al.
DDIT3 is a tightly regulated basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor and key regulator in cellular stress responses. It is involved in a variety of pathological conditions and may cause cell cycle block and apoptosis. It is also implicated in differentiation of some specialized cell types and as an oncogene... |
Androgen-Induced MIG6 Regulates Phosphorylation ofRetinoblastoma Protein and AKT to Counteract Non-Genomic ARSignaling in Prostate Cancer Cells.
Schomann T. et al.
The bipolar androgen therapy (BAT) includes the treatment of prostate cancer (PCa) patients with supraphysiological androgen level (SAL). Interestingly, SAL induces cell senescence in PCa cell lines as well as ex vivo in tumor samples of patients. The SAL-mediated cell senescence was shown to be androgen receptor (A... |
Co-inhibition of ATM and ROCK synergistically improves cellproliferation in replicative senescence by activating FOXM1 and E2F1.
Yang Eun Jae et al.
The multifaceted nature of senescent cell cycle arrest necessitates the targeting of multiple factors arresting or promoting the cell cycle. We report that co-inhibition of ATM and ROCK by KU-60019 and Y-27632, respectively, synergistically increases the proliferation of human diploid fibroblasts undergoing replicat... |
Derailed peripheral circadian genes in polycystic ovary syndrome patientsalters peripheral conversion of androgens synthesis.
Johnson B.S. et al.
STUDY QUESTION: Do circadian genes exhibit an altered profile in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) patients and do they have a potential role in androgen excess? SUMMARY ANSWER: Our findings revealed that an impaired circadian clock could hamper the regulation of peripher... |
GATA6 is predicted to regulate DNA methylation in an in vitro model ofhuman hepatocyte differentiation.
Suzuki T. et al.
Hepatocytes are the dominant cell type in the human liver, with functions in metabolism, detoxification, and producing secreted proteins. Although gene regulation and master transcription factors involved in the hepatocyte differentiation have been extensively investigated, little is known about how the epigenome is... |
A systematic comparison of FOSL1, FOSL2 and BATF-mediatedtranscriptional regulation during early human Th17 differentiation.
Shetty A. et al.
Th17 cells are essential for protection against extracellular pathogens, but their aberrant activity can cause autoimmunity. Molecular mechanisms that dictate Th17 cell-differentiation have been extensively studied using mouse models. However, species-specific differences underscore the need to validate these findin... |
An obesogenic feedforward loop involving PPARγ, acyl-CoA bindingprotein and GABA receptor.
Anagnostopoulos Gerasimos et al.
Acyl-coenzyme-A-binding protein (ACBP), also known as a diazepam-binding inhibitor (DBI), is a potent stimulator of appetite and lipogenesis. Bioinformatic analyses combined with systematic screens revealed that peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) is the transcription factor that best expl... |
Transient regulation of focal adhesion via Tensin3 is required fornascent oligodendrocyte differentiation
Merour E. et al.
The differentiation of oligodendroglia from oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs) to complex and extensive myelinating oligodendrocytes (OLs) is a multistep process that involves largescale morphological changes with significant strain on the cytoskeleton. While key chromatin and transcriptional regulators of diffe... |
Characteristics of Immediate-Early 2 (IE2) and UL84 Proteins in UL84-Independent Strains of Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV)
Salome Manska and Cyprian C Rossetto
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) immediate-early 2 (IE2) protein is the major transactivator for viral gene expression and is required for lytic replication. In addition to transcriptional activation, IE2 is known to mediate transcriptional repression of promoters, including the major immediate-early (MIE) promoter and ... |
Essential role of a ThPOK autoregulatory loop in the maintenance ofmature CD4 T cell identity and function.
Basu Jayati et al.
The transcription factor ThPOK (encoded by the Zbtb7b gene) controls homeostasis and differentiation of mature helper T cells, while opposing their differentiation to CD4 intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) in the intestinal mucosa. Thus CD4 IEL differentiation requires ThPOK transcriptional repression via reactivati... |
Environmental enrichment preserves a young DNA methylation landscape inthe aged mouse hippocampus
Zocher S. et al.
The decline of brain function during aging is associated with epigenetic changes, including DNA methylation. Lifestyle interventions can improve brain function during aging, but their influence on age-related epigenetic changes is unknown. Using genome-wide DNA methylation sequencing, we here show that experiencing ... |
Sarcomere function activates a p53-dependent DNA damage response that promotes polyploidization and limits in vivo cell engraftment.
Pettinato, Anthony M. et al.
Human cardiac regeneration is limited by low cardiomyocyte replicative rates and progressive polyploidization by unclear mechanisms. To study this process, we engineer a human cardiomyocyte model to track replication and polyploidization using fluorescently tagged cyclin B1 and cardiac troponin T. Using time-lapse i... |
VPRBP functions downstream of the androgen receptor and OGT to restrict p53 activation in prostate cancer
Poulose N. et al.
Androgen receptor (AR) is a major driver of prostate cancer (PCa) initiation and progression. O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT), the enzyme that catalyses the covalent addition of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) to serine and threonine residues of proteins, is often up-regulated in PCa with its expression correlated w... |
BAF complexes drive proliferation and block myogenic differentiation in fusion-positive rhabdomyosarcoma
Laubscher et. al.
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a pediatric malignancy of skeletal muscle lineage. The aggressive alveolar subtype is characterized by t(2;13) or t(1;13) translocations encoding for PAX3- or PAX7-FOXO1 chimeric transcription factors, respectively, and are referred to as fusion positive RMS (FP-RMS). The fusion gene alters... |
The epigenetic regulator RINF (CXXC5) maintains SMAD7 expression in human immature erythroid cells and sustains red blood cellsexpansion.
Astori A. et al.
The gene CXXC5, encoding a Retinoid-Inducible Nuclear Factor (RINF), is located within a region at 5q31.2 commonly deleted in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML). RINF may act as an epigenetic regulator and has been proposed as a tumor suppressor in hematopoietic malignancies. Howev... |
ΔNp63 is a pioneer factor that binds inaccessible chromatin and elicitchromatin remodeling
Yu X. et al.
Background: ΔNp63 is a master transcriptional regulator playing critical roles in epidermal development and other cellular processes. Recent studies suggest that ΔNp63 functions as a pioneer factor that can target its binding sites within inaccessible chromatin and induce chromatin remodeling. Methods: I... |
Battle of the sex chromosomes: competition between X- and Y-chromosomeencoded proteins for partner interaction and chromatin occupancy drivesmulti-copy gene expression and evolution in muroid rodents.
Moretti, C and Blanco, M and Ialy-Radio, C and Serrentino, ME and Gobé,C and Friedman, R and Battail, C and Leduc, M and Ward, MA and Vaiman, Dand Tores, F and Cocquet, J
Transmission distorters (TDs) are genetic elements that favor their own transmission to the detriments of others. Slx/Slxl1 (Sycp3-like-X-linked and Slx-like1) and Sly (Sycp3-like-Y-linked) are TDs which have been co-amplified on the X and Y chromosomes of Mus species. They are involved in an intragenomic conflict i... |
Dysregulation of BRD4 Function Underlies the Functional Abnormalities of MeCP2 Mutant Neurons.
Xiang Y, Tanaka Y, Patterson B, Hwang SM, Hysolli E, Cakir B, Kim KY, Wang W, Kang YJ, Clement EM, Zhong M, Lee SH, Cho YS, Patra P, Sullivan GJ, Weissman SM, Park IH
Rett syndrome (RTT), mainly caused by mutations in methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2), is one of the most prevalent intellectual disorders without effective therapies. Here, we used 2D and 3D human brain cultures to investigate MeCP2 function. We found that MeCP2 mutations cause severe abnormalities in human inter... |
MYC transcription activation mediated by OCT4 as a mechanism of resistance to 13-cisRA-mediated differentiation in neuroblastoma.
Wei SJ, Nguyen TH, Yang IH, Mook DG, Makena MR, Verlekar D, Hindle A, Martinez GM, Yang S, Shimada H, Reynolds CP, Kang MH
Despite the improvement in clinical outcome with 13-cis-retinoic acid (13-cisRA) + anti-GD2 antibody + cytokine immunotherapy given in first response ~40% of high-risk neuroblastoma patients die of recurrent disease. MYCN genomic amplification is a biomarker of aggressive tumors in the childhood cancer neuroblastoma... |
CRISPR off-target detection with DISCOVER-seq.
Wienert B, Wyman SK, Yeh CD, Conklin BR, Corn JE
DISCOVER-seq (discovery of in situ Cas off-targets and verification by sequencing) is a broadly applicable approach for unbiased CRISPR-Cas off-target identification in cells and tissues. It leverages the recruitment of DNA repair factors to double-strand breaks (DSBs) after genome editing with CRISPR nucleases. Her... |
LncRNA np_5318 promotes renal ischemia‑reperfusion injury through the TGF‑β/Smad signaling pathway
Lu Jing , Miao Jiangang , Sun Jianhua
Long noncoding (Lnc)RNA np_5318 has been proved to be involved in renal injury, while its functionality in renal ischemia‑reperfusion (I/R) injury is unknown. Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate the role of lncRNA np_5318 in the development of renal I/R injury. Renal I/R injury model and I/R cell model... |
Pro-death signaling of cytoprotective heat shock factor 1: upregulation of NOXA leading to apoptosis in heat-sensitive cells.
Janus P, Toma-Jonik A, Vydra N, Mrowiec K, Korfanty J, Chadalski M, Widłak P, Dudek K, Paszek A, Rusin M, Polańska J, Widłak W
Heat shock can induce either cytoprotective mechanisms or cell death. We found that in certain human and mouse cells, including spermatocytes, activated heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) binds to sequences located in the intron(s) of the PMAIP1 (NOXA) gene and upregulates its expression which induces apoptosis. Such a mode... |
17-Estradiol Activates HSF1 via MAPK Signaling in ER-Positive Breast Cancer Cells.
Vydra N, Janus P, Toma-Jonik A, Stokowy T, Mrowiec K, Korfanty J, Długajczyk A, Wojtaś B, Gielniewski B, Widłak W
Heat Shock Factor 1 (HSF1) is a key regulator of gene expression during acute environmental stress that enables the cell survival, which is also involved in different cancer-related processes. A high level of HSF1 in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer patients correlated with a worse prognosis. Here we de... |
Cooperation of cancer drivers with regulatory germline variants shapes clinical outcomes.
Musa J, Cidre-Aranaz F, Aynaud MM, Orth MF, Knott MML, Mirabeau O, Mazor G, Varon M, Hölting TLB, Grossetête S, Gartlgruber M, Surdez D, Gerke JS, Ohmura S, Marchetto A, Dallmayer M, Baldauf MC, Stein S, Sannino G, Li J, Romero-Pérez L, Westermann F, Hart
Pediatric malignancies including Ewing sarcoma (EwS) feature a paucity of somatic alterations except for pathognomonic driver-mutations that cannot explain overt variations in clinical outcome. Here, we demonstrate in EwS how cooperation of dominant oncogenes and regulatory germline variants determine tumor growth, ... |
The Toxoplasma effector TEEGR promotes parasite persistence by modulating NF-κB signalling via EZH2.
Braun L, Brenier-Pinchart MP, Hammoudi PM, Cannella D, Kieffer-Jaquinod S, Vollaire J, Josserand V, Touquet B, Couté Y, Tardieux I, Bougdour A, Hakimi MA
The protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii has co-evolved with its homeothermic hosts (humans included) strategies that drive its quasi-asymptomatic persistence in hosts, hence optimizing the chance of transmission to new hosts. Persistence, which starts with a small subset of parasites that escape host immune killing... |
Preformed chromatin topology assists transcriptional robustness of during limb development.
Paliou C, Guckelberger P, Schöpflin R, Heinrich V, Esposito A, Chiariello AM, Bianco S, Annunziatella C, Helmuth J, Haas S, Jerković I, Brieske N, Wittler L, Timmermann B, Nicodemi M, Vingron M, Mundlos S, Andrey G
Long-range gene regulation involves physical proximity between enhancers and promoters to generate precise patterns of gene expression in space and time. However, in some cases, proximity coincides with gene activation, whereas, in others, preformed topologies already exist before activation. In this study, we inves... |
NRG1 is a critical regulator of differentiation in TP63-driven squamous cell carcinoma.
Hegde GV, de la Cruz C, Giltnane JM, Crocker L, Venkatanarayan A, Schaefer G, Dunlap D, Hoeck JD, Piskol R, Gnad F, Modrusan Z, de Sauvage FJ, Siebel CW, Jackson EL
Squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) account for the majority of cancer mortalities. Although TP63 is an established lineage-survival oncogene in SCCs, therapeutic strategies have not been developed to target TP63 or it's downstream effectors. In this study we demonstrate that TP63 directly regulates NRG1 expression in h... |
Guidelines for optimized gene knockout using CRISPR/Cas9
Campenhout CV et al.
CRISPR/Cas9 technology has evolved as the most powerful approach to generate genetic models both for fundamental and preclinical research. Despite its apparent simplicity, the outcome of a genome-editing experiment can be substantially impacted by technical parameters and biological considerations. Here, we present ... |
Maintenance of MYC expression promotes de novo resistance to BET bromodomain inhibition in castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Coleman DJ, Gao L, Schwartzman J, Korkola JE, Sampson D, Derrick DS, Urrutia J, Balter A, Burchard J, King CJ, Chiotti KE, Heiser LM, Alumkal JJ
The BET bromodomain protein BRD4 is a chromatin reader that regulates transcription, including in cancer. In prostate cancer, specifically, the anti-tumor activity of BET bromodomain inhibition has been principally linked to suppression of androgen receptor (AR) function. MYC is a well-described BRD4 target gene in ... |
Crosstalk Between Glucocorticoid Receptor and Early-growth Response Protein 1 Accounts for Repression of Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Transcript 4 Expression.
Chen H, Amazit L, Lombès M, Le Menuet D
The brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a key player in brain functions such as synaptic plasticity, stress, and behavior. Its gene structure in rodents contains 8 untranslated exons (I to VIII) whose expression is finely regulated and which spliced onto a common and unique translated exon IX. Altered Bdnf e... |
Glucocorticoids stimulate hypothalamic dynorphin expression accounting for stress-induced impairment of GnRH secretion during preovulatory period.
Ayrout M, Le Billan F, Grange-Messent V, Mhaouty-Kodja S, Lombès M, Chauvin S
Stress-induced reproductive dysfunction is frequently associated with increased glucocorticoid (GC) levels responsible for suppressed GnRH/LH secretion and impaired ovulation. Besides the major role of the hypothalamic kisspeptin system, other key regulators may be involved in such regulatory mechanisms. Herein, we ... |
Epigenetic Co-Deregulation of EZH2/TET1 is a Senescence-Countering, Actionable Vulnerability in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.
Yu Y, Qi J, Xiong J, Jiang L, Cui D, He J, Chen P, Li L, Wu C, Ma T, Shao S, Wang J, Yu D, Zhou B, Huang D, Schmitt CA, Tao R
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells lack the expression of ER, PR and HER2. Thus, TNBC patients cannot benefit from hormone receptor-targeted therapy as non-TNBC patients, but can only receive chemotherapy as the systemic treatment and have a worse overall outcome. More effective therapeutic targets and combi... |
The long noncoding RNA and nuclear paraspeckles are up-regulated by the transcription factor HSF1 in the heat shock response.
Lellahi SM, Rosenlund IA, Hedberg A, Kiær LT, Mikkola I, Knutsen E, Perander M
The long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) (nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1) is the architectural component of nuclear paraspeckles, and it has recently gained considerable attention as it is abnormally expressed in pathological conditions such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. and paraspeckle formation are incr... |
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling Cell Intrinsically Inhibits Intestinal Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Function.
Li S, Bostick JW, Ye J, Qiu J, Zhang B, Urban JF, Avram D, Zhou L
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are important for mucosal immunity. The intestine harbors all ILC subsets, but how these cells are balanced to achieve immune homeostasis and mount appropriate responses during infection remains elusive. Here, we show that aryl hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr) expression in the gut regulates I... |
RRAD, IL4I1, CDKN1A, and SERPINE1 genes are potentially co-regulated by NF-κB and p53 transcription factors in cells exposed to high doses of ionizing radiation.
Szołtysek K, Janus P, Zając G, Stokowy T, Walaszczyk A, Widłak W, Wojtaś B, Gielniewski B, Cockell S, Perkins ND, Kimmel M, Widlak P
BACKGROUND: The cellular response to ionizing radiation involves activation of p53-dependent pathways and activation of the atypical NF-κB pathway. The crosstalk between these two transcriptional networks include (co)regulation of common gene targets. Here we looked for novel genes potentially (co)regulated by... |
H3K4me2 and WDR5 enriched chromatin interacting long non-coding RNAs maintain transcriptionally competent chromatin at divergent transcriptional units.
Subhash S, Mishra K, Akhade VS, Kanduri M, Mondal T, Kanduri C
Recently lncRNAs have been implicated in the sub-compartmentalization of eukaryotic genome via genomic targeting of chromatin remodelers. To explore the function of lncRNAs in the maintenance of active chromatin, we characterized lncRNAs from the chromatin enriched with H3K4me2 and WDR5 using chromatin RNA immunopre... |
The long non-coding RNA NEAT1 and nuclear paraspeckles are upregulated by the transcription factor HSF1 in the heat shock response.
Lellahi SM, Rosenlund IA, Hedberg A, Kiær LT, Mikkola I, Knutsen E, Perander M
The long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) NEAT1 is the architectural component of nuclear paraspeckles, and has recently gained considerable attention as it is abnormally expressed in pathological conditions such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. NEAT1 and paraspeckle formation are increased in cells upon expos... |
ΔNp63-driven recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells promotes metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer.
Kumar S, Wilkes DW, Samuel N, Blanco MA, Nayak A, Alicea-Torres K, Gluck C, Sinha S, Gabrilovich D, Chakrabarti R
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is particularly aggressive, with enhanced incidence of tumor relapse, resistance to chemotherapy, and metastases. As the mechanistic basis for this aggressive phenotype is unclear, treatment options are limited. Here, we showed an increased population of myeloid-derived immunosup... |
FACT Sets a Barrier for Cell Fate Reprogramming in Caenorhabditis elegans and Human Cells.
Kolundzic E, Ofenbauer A, Bulut SI, Uyar B, Baytek G, Sommermeier A, Seelk S, He M, Hirsekorn A, Vucicevic D, Akalin A, Diecke S, Lacadie SA, Tursun B
The chromatin regulator FACT (facilitates chromatin transcription) is essential for ensuring stable gene expression by promoting transcription. In a genetic screen using Caenorhabditis elegans, we identified that FACT maintains cell identities and acts as a barrier for transcription factor-mediated cell fate reprogr... |
The Alzheimer's disease-associated TREM2 gene is regulated by p53 tumor suppressor protein.
Zajkowicz A, Gdowicz-Kłosok A, Krześniak M, Janus P, Łasut B, Rusin M
TREM2 mutations evoke neurodegenerative disorders, and recently genetic variants of this gene were correlated to increased risk of Alzheimer's disease. The signaling cascade originating from the TREM2 membrane receptor includes its binding partner TYROBP, BLNK adapter protein, and SYK kinase, which can be activated ... |
Genome-wide association study identifies multiple new loci associated with Ewing sarcoma susceptibility.
Machiela MJ, Grünewald TGP, Surdez D, Reynaud S, Mirabeau O, Karlins E, Rubio RA, Zaidi S, Grossetete-Lalami S, Ballet S, Lapouble E, Laurence V, Michon J, Pierron G, Kovar H, Gaspar N, Kontny U, González-Neira A, Picci P, Alonso J, Patino-Garcia A, Corra
Ewing sarcoma (EWS) is a pediatric cancer characterized by the EWSR1-FLI1 fusion. We performed a genome-wide association study of 733 EWS cases and 1346 unaffected individuals of European ancestry. Our study replicates previously reported susceptibility loci at 1p36.22, 10q21.3 and 15q15.1, and identifies new loci a... |
Methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 mediates antifibrotic effects in scleroderma fibroblasts.
He Y, Tsou PS, Khanna D, Sawalha AH
OBJECTIVE: Emerging evidence supports a role for epigenetic regulation in the pathogenesis of scleroderma (SSc). We aimed to assess the role of methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2), a key epigenetic regulator, in fibroblast activation and fibrosis in SSc. METHODS: Dermal fibroblasts were isolated from patients with ... |
The BRG1/SOX9 axis is critical for acinar cell-derived pancreatic tumorigenesis.
Tsuda M, Fukuda A, Roy N, Hiramatsu Y, Leonhardt L, Kakiuchi N, Hoyer K, Ogawa S, Goto N, Ikuta K, Kimura Y, Matsumoto Y, Takada Y, Yoshioka T, Maruno T, Yamaga Y, Kim GE, Akiyama H, Ogawa S, Wright CV, Saur D, Takaori K, Uemoto S, Hebrok M, Chiba T, Seno
Chromatin remodeler Brahma related gene 1 (BRG1) is silenced in approximately 10% of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDAs). We previously showed that BRG1 inhibits the formation of intraductal pancreatic mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) and that IPMN-derived PDA originated from ductal cells. However, the role of BR... |
Wnt receptor Frizzled 8 is a target of ERG in prostate cancer
Balabhadrapatruni V. S. K. Chakravarthi et al.
Prostate cancer (PCa) is one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers among men. Many molecular changes have been detailed during PCa progression. The gene encoding the transcription factor ERG shows recurrent rearrangement, resulting in the overexpression of ERG in the majority of prostate cancers. Overexpression o... |
Pro-inflammatory cytokine and high doses of ionizing radiation have similar effects on the expression of NF-kappaB-dependent genes.
Janus P, Szołtysek K, Zając G, Stokowy T, Walaszczyk A, Widłak W, Wojtaś B, Gielniewski B, Iwanaszko M, Braun R, Cockell S, Perkins ND, Kimmel M, Widlak P
The NF-κB transcription factors are activated via diverse molecular mechanisms in response to various types of stimuli. A plethora of functions associated with specific sets of target genes could be regulated differentially by this factor, affecting cellular response to stress including an anticancer treatment... |
UTX-mediated enhancer and chromatin remodeling suppresses myeloid leukemogenesis through noncatalytic inverse regulation of ETS and GATA programs.
Gozdecka M, Meduri E, Mazan M, Tzelepis K, Dudek M, Knights AJ, Pardo M, Yu L, Choudhary JS, Metzakopian E, Iyer V, Yun H, Park N, Varela I, Bautista R, Collord G, Dovey O, Garyfallos DA, De Braekeleer E, Kondo S, Cooper J, Göttgens B, Bullinger L, Northc
The histone H3 Lys27-specific demethylase UTX (or KDM6A) is targeted by loss-of-function mutations in multiple cancers. Here, we demonstrate that UTX suppresses myeloid leukemogenesis through noncatalytic functions, a property shared with its catalytically inactive Y-chromosome paralog, UTY (or KDM6C). In keeping wi... |
Corticosteroid receptors adopt distinct cyclical transcriptional signatures
Florian Le Billan, Larbi Amazit, Kevin Bleakley, Qiong-Yao Xue, Eric Pussard, Christophe Lhadj, Peter Kolkhof, Say Viengchareun, Jérôme Fagart, and Marc Lombès
Mineralocorticoid receptors (MRs) and glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) are two closely related hormone-activated transcription factors that regulate major pathophysiologic functions. High homology between these receptors accounts for the crossbinding of their corresponding ligands, MR being activated by both aldostero... |
Corticosteroid receptors adopt distinct cyclical transcriptional signatures.
Le Billan F, Amazit L, Bleakley K, Xue QY, Pussard E, Lhadj C, Kolkhof P, Viengchareun S, Fagart J, Lombès M
Mineralocorticoid receptors (MRs) and glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) are two closely related hormone-activated transcription factors that regulate major pathophysiologic functions. High homology between these receptors accounts for the crossbinding of their corresponding ligands, MR being activated by both aldostero... |
Bcl11b, a novel GATA3-interacting protein, suppresses Th1 while limiting Th2 cell differentiation.
Fang D, Cui K, Hu G, Gurram RK, Zhong C, Oler AJ, Yagi R, Zhao M, Sharma S, Liu P, Sun B, Zhao K, Zhu J
GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA3) acts as the master transcription factor for type 2 T helper (Th2) cell differentiation and function. However, it is still elusive how GATA3 function is precisely regulated in Th2 cells. Here, we show that the transcription factor B cell lymphoma 11b (Bcl11b), a previously unknown compo... |
Corticosteroid receptors adopt distinct cyclical transcriptional signatures
Florian Le Billan, Larbi Amazit, Kevin Bleakley, Qiong-Yao Xue, Eric Pussard, Christophe Lhadj, Peter Kolkhof, Say Viengchareun, Jérôme Fagart, and Marc Lombès
Mineralocorticoid receptors (MRs) and glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) are two closely related hormone-activated transcription factors that regulate major pathophysiologic functions. High homology between these receptors accounts for the crossbinding of their corresponding ligands, MR being activated by both aldostero... |
Corticosteroid receptors adopt distinct cyclical transcriptional signatures
Florian Le Billan, Larbi Amazit, Kevin Bleakley, Qiong-Yao Xue, Eric Pussard, Christophe Lhadj, Peter Kolkhof, Say Viengchareun, Jérôme Fagart, and Marc Lombès
Mineralocorticoid receptors (MRs) and glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) are two closely related hormone-activated transcription factors that regulate major pathophysiologic functions. High homology between these receptors accounts for the crossbinding of their corresponding ligands, MR being activated by both aldostero... |
DNA methylation signatures follow preformed chromatin compartments in cardiac myocytes
Nothjunge S. et al.
Storage of chromatin in restricted nuclear space requires dense packing while ensuring DNA accessibility. Thus, different layers of chromatin organization and epigenetic control mechanisms exist. Genome-wide chromatin interaction maps revealed large interaction domains (TADs) and higher order A and B compartments, r... |
MYC drives overexpression of telomerase RNA (hTR/TERC) in prostate cancer
Baena-Del Valle JA et al.
Telomerase consists of at least two essential elements, an RNA component hTR or TERC that contains the template for telomere DNA addition and a catalytic reverse transcriptase (TERT). While expression of TERT has been considered the key rate-limiting component for telomerase activity, increasing evidence suggests an... |
The complex genetics of hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Liu X. et al.
Congenital heart disease (CHD) affects up to 1% of live births. Although a genetic etiology is indicated by an increased recurrence risk, sporadic occurrence suggests that CHD genetics is complex. Here, we show that hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS), a severe CHD, is multigenic and genetically heterogeneous. Us... |
Evolutionary re-wiring of p63 and the epigenomic regulatory landscape in keratinocytes and its potential implications on species-specific gene expression and phenotypes
Sethi I. et al.
Although epidermal keratinocyte development and differentiation proceeds in similar fashion between humans and mice, evolutionary pressures have also wrought significant species-specific physiological differences. These differences between species could arise in part, by the rewiring of regulatory network due to cha... |
Glucocorticoid receptor represses brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in neuron-like cells
Chen H. et al.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is involved in many functions such as neuronal growth, survival, synaptic plasticity and memorization. Altered expression levels are associated with many pathological situations such as depression, epilepsy, Alzheimer's, Huntington's and Parkinson's diseases. Glucocorticoid r... |
First landscape of binding to chromosomes for a domesticated mariner transposase in the human genome: diversity of genomic targets of SETMAR isoforms in two colorectal cell lines
Antoine-Lorquin A. et al.
Setmar is a 3-exons gene coding a SET domain fused to a Hsmar1 transposase. Its different transcripts theoretically encode 8 isoforms with SET moieties differently spliced. In vitro, the largest isoform binds specifically to Hsmar1 DNA ends and with no specificity to DNA when it is associated with hPso4. In colon ce... |
Suppression of RUNX1/ETO oncogenic activity by a small molecule inhibitor of tetramerization
Schanda J. et al.
RUNX1/ETO, the product of the t(8;21) chromosomal translocation, is required for the onset and maintenance of one of the most common forms of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). RUNX1/ETO has a modular structure and, besides the DN A-binding domain (Runt), contains four evolutionary conserved functional domains named nerv... |
Foxo3 Transcription Factor Drives Pathogenic T Helper 1 Differentiation by Inducing the Expression of Eomes
Stienne C. et al.
The transcription factor Foxo3 plays a crucial role in myeloid cell function but its role in lymphoid cells remains poorly defined. Here, we have shown that Foxo3 expression was increased after T cell receptor engagement and played a specific role in the polarization of CD4+ T cells toward pathogenic T hel... |
Loss of cohesin complex components STAG2 or STAG3 confers resistance to BRAF inhibition in melanoma
Shen CH et al.
The protein kinase B-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase (BRAF) is an oncogenic driver and therapeutic target in melanoma. Inhibitors of BRAF (BRAFi) have shown high response rates and extended survival in patients with melanoma who bear tumors that express mutations encoding BRAF proteins mutant at Val600, ... |
BET protein inhibition sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomidetreatment by attenuating MGMT expression
Tancredi A. et al.
Bromodomain and extra-terminal tail (BET) proteins have been identified as potential epigenetic targets in cancer, including glioblastoma. These epigenetic modifiers link the histone code to gene transcription that can be disrupted with small molecule BET inhibitors (BETi). With the aim of developing rational combin... |