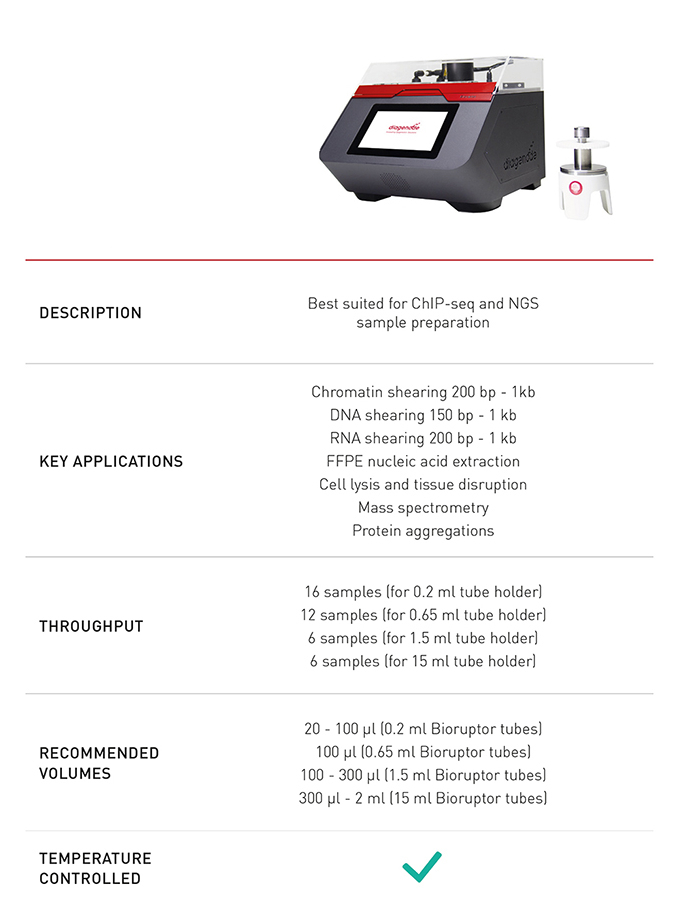
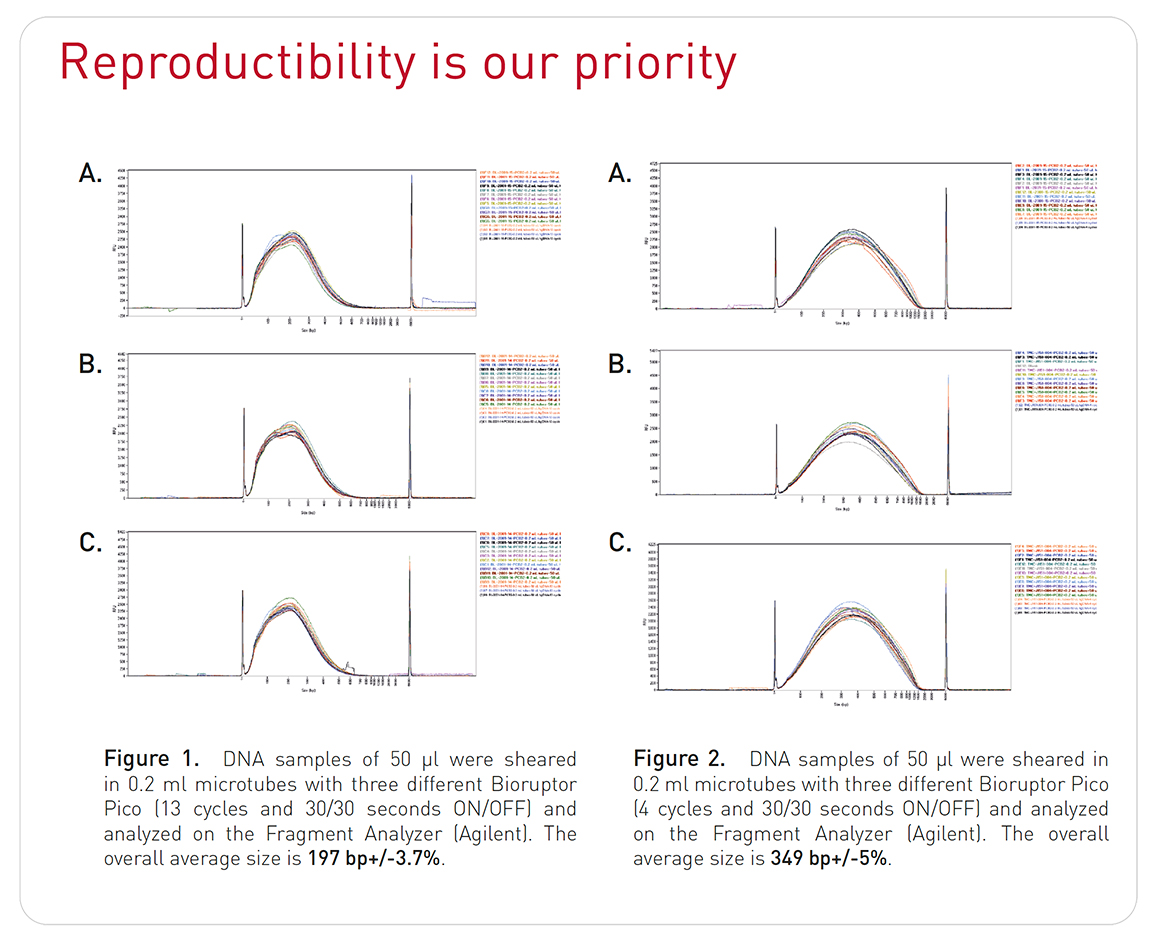
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: Bioruptor® Pico sonication device (Hologic Diagenode Cat# B01080010). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
High‐Throughput Targeted Sequencing Identifies an HPV Methylation Panel for Detecting Cervical Lesion Progression
Liu, Hui et al.
High‐risk human papillomavirus (hrHPV) infection is the primary cause of cervical cancer. However, hrHPV testing lacks specificity in detecting neoplastic changes. This study explored the utility of quantitative methylated HPV DNA markers for precise detection of cervical lesions. Using hybridization capture‐based b... |
Refined ChIP‐Seq Protocol for High‐Quality Chromatin Profiling in Solid Tissues Using the Complete Genomics/MGI Sequencing Platform
Alloway, Hayley et al.
The chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP‐seq) assay is an instrumental and accurate method for understanding chromatin dynamics in eukaryotic cells. It provides critical insights into the regulation of gene expression and enables identification of regulatory elements, patterns of histone modifi... |
Mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas demonstrate in situ production of estrogen
Kim, Jinyong et al.
Introduction
Mucinous cystic neoplasms (MCNs) are rare cystic tumors that may occur in the liver, pancreas, or retroperitoneum, defined histologically by the presence of an “ovarian type stroma.” While this morphology has been well characterized, it remains unknown whether the tumor stroma is function... |
Seed structure and phosphorylation in the fuzzy coat impact tau seeding competency
Kasen, Alysa et al.
Tau misfolding into β-sheet–rich filaments and subsequent recruitment of monomeric tau are central to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathogenesis. While cryo-EM has resolved the conformation of the AD tau core, the structural features conferring biological activity remain unclear. Here, we investigated ho... |
Gut microbiota-metabolome remodeling associated with low bone mass: an integrated multi-omics study in fracture patients
Zhao, Xian et al.
Background: The gut microbiota is increasingly implicated in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis, but its role in the specific context of fracture patients remains poorly defined. High-resolution multi-omics studies are needed to elucidate the complex interplay between microbes, their metabolites, and bone health.... |
A brain-shuttled antibody targeting alpha synuclein aggregates for the treatment of synucleinopathies
An, Sungwon et al.
Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy are members of a class of devastating neurodegenerative diseases called synucleinopathies, which are characterized by the presence of alpha-synuclein (α-Syn) rich aggregates in the brains of patients. Passive immunotherapy targeting these aggregates is an att... |
Cortico-striatal circuit mechanisms drive the effects of D1 dopamine agonists on memory capacity in mice through cAMP/PKA signalling
De Risi M, et al.
Working memory capacity (WMC), the number of items remembered in a short-time interval, is regulated by fronto-striatal dopamine (DA) and is reduced in schizophrenia. We investigated how excessive and insufficient D1 dopamine receptor stimulation impairs and expands WMC, focusing on the cAMP/PKA pathway in the f... |
In vivo prime editing rescues photoreceptor degeneration in nonsense mutant retinitis pigmentosa
Fu, Yidian et al.
The next-generation gene editing tool, prime editing (PE), is adept at correcting point mutations precisely with high editing efficiency and rare off-target events and shows promising therapeutic value in treating hereditary diseases. Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is the most common type of inherited retinal dystrophy a... |
Maternal obesity alters histone modifications mediated by the interaction between EZH2 and AMPK, impairing neural differentiation in the developing embryonic brain cortex
Alawathugoda, Thilina T. et al.
Neurodevelopmental disorders have complex origins that manifest early during embryonic growth and are associated with intricate gene regulation dynamics. A perturbed metabolic environment such as hyperglycemia or dyslipidemia, particularly due to maternal obesity, poses a threat to the optimal development of the emb... |
Epi-microRNA mediated metabolic reprogramming counteracts hypoxia to preserve affinity maturation
Rinako Nakagawa et al.
To increase antibody affinity against pathogens, positively selected GC-B cells initiate cell division in the light zone (LZ) of germinal centers (GCs). Among these, higher-affinity clones migrate to the dark zone (DZ) and vigorously proliferate by utilizing energy provided by oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). How... |
LEO1 Is Required for Efficient Entry into Quiescence, Control of H3K9 Methylation and Gene Expression in Human Fibroblasts
Laurent M. et al.
(1) Background: The LEO1 (Left open reading frame 1) protein is a conserved subunit of the PAF1C complex (RNA polymerase II-associated factor 1 complex). PAF1C has well-established mechanistic functions in elongation of transcription and RNA processing. We previously showed, in fission yeast, that LEO1 controls hist... |
DeSUMOylation of chromatin-bound proteins limits the rapidtranscriptional reprogramming induced by daunorubicin in acute myeloidleukemias.
Boulanger M. et al.
Genotoxicants have been used for decades as front-line therapies against cancer on the basis of their DNA-damaging actions. However, some of their non-DNA-damaging effects are also instrumental for killing dividing cells. We report here that the anthracycline Daunorubicin (DNR), one of the main drugs used to treat A... |
RNA polymerase II CTD is dispensable for transcription and requiredfor termination in human cells.
Yahia Y. et al.
The largest subunit of RNA polymerase (Pol) II harbors an evolutionarily conserved C-terminal domain (CTD), composed of heptapeptide repeats, central to the transcriptional process. Here, we analyze the transcriptional phenotypes of a CTD-Δ5 mutant that carries a large CTD truncation in human cells. Our... |
Targeting lymphoid-derived IL-17 signaling to delay skin aging.
Paloma S. et al.
Skin aging is characterized by structural and functional changes that contribute to age-associated frailty. This probably depends on synergy between alterations in the local niche and stem cell-intrinsic changes, underscored by proinflammatory microenvironments that drive pleotropic changes. The nature of these age-... |
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase sustains a core epigenetic programthat promotes metastatic colonization in breast cancer.
Couto J.P. et al.
Metastatic colonization of distant organs accounts for over 90% of deaths related to solid cancers, yet the molecular determinants of metastasis remain poorly understood. Here, we unveil a mechanism of colonization in the aggressive basal-like subtype of breast cancer that is driven by the NAD+ metabolic enzyme... |
SOX expression in prostate cancer drives resistance to nuclear hormonereceptor signaling inhibition through the WEE1/CDK1 signaling axis.
Williams A. et al.
The development of androgen receptor signaling inhibitor (ARSI) drug resistance in prostate cancer (PC) remains therapeutically challenging. Our group has described the role of sex determining region Y-box 2 (SOX2) overexpression in ARSI-resistant PC. Continuing this work, we report that NR3C1, the gene encoding glu... |
The Effect of Metformin and Carbohydrate-Controlled Diet onDNA Methylation and Gene Expression in the Endometrium of Womenwith Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
Garcia-Gomez E. et al.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine disease associated with infertility and metabolic disorders in reproductive-aged women. In this study, we evaluated the expression of eight genes related to endometrial function and their DNA methylation levels in the endometrium of PCOS patients and women without the... |
Chromatin profiling identifies transcriptional readthrough as a conservedmechanism for piRNA biogenesis in mosquitoes.
Qu J. et al.
The piRNA pathway in mosquitoes differs substantially from other model organisms, with an expanded PIWI gene family and functions in antiviral defense. Here, we define core piRNA clusters as genomic loci that show ubiquitous piRNA expression in both somatic and germline tissues. These core piRNA clusters are enriche... |
Activation of AKT induces EZH2-mediated β-catenin trimethylation incolorectal cancer.
Ghobashi A. H. et al.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) develops in part through the deregulation of different signaling pathways, including activation of the WNT/β-catenin and PI3K/AKT pathways. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is a lysine methyltransferase that is involved in regulating stem cell development and differentiation and is ove... |
Detailed molecular and epigenetic characterization of the Pig IPECJ2and Chicken SL-29 cell lines
de Vos J. et al.
The pig IPECJ2 and chicken SL-29 cell lines are of interest because of their untransformed nature and wide use in functional studies. Molecular characterization of these cell lines is important to gain insight into possible molecular aberrations. The aims of this paper are providing a molecular and epigenetic charac... |
Signal-induced enhancer activation requires Ku70 to readtopoisomerase1-DNA covalent complexes.
Tan Y. et al.
Enhancer activation serves as the main mechanism regulating signal-dependent transcriptional programs, ensuring cellular plasticity, yet central questions persist regarding their mechanism of activation. Here, by successfully mapping topoisomerase I-DNA covalent complexes genome-wide, we find that most, if no... |
Cotranscriptional demethylation induces global loss of H3K4me2 fromactive genes in Arabidopsis
Mori S. et al.
Based on studies of animals and yeasts, methylation of histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1/2/3, for mono-, di-, and tri-methylation, respectively) is regarded as the key epigenetic modification of transcriptionally active genes. In plants, however, H3K4me2 correlates negatively with transcription, and the regulatory mechan... |
Epigenetic regulation of plastin 3 expression by the macrosatelliteDXZ4 and the transcriptional regulator CHD4.
Strathmann E. A. et al.
Dysregulated Plastin 3 (PLS3) levels associate with a wide range of skeletal and neuromuscular disorders and the most common types of solid and hematopoietic cancer. Most importantly, PLS3 overexpression protects against spinal muscular atrophy. Despite its crucial role in F-actin dynamics in healthy cells and its i... |
A dataset of definitive endoderm and hepatocyte differentiations fromhuman induced pluripotent stem cells.
Tanaka Y. et al.
Hepatocytes are a major parenchymal cell type in the liver and play an essential role in liver function. Hepatocyte-like cells can be differentiated in vitro from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) via definitive endoderm (DE)-like cells and hepatoblast-like cells. Here, we explored the in vitro differentiation ... |
The mineralocorticoid receptor modulates timing and location of genomicbinding by glucocorticoid receptor in response to synthetic glucocorticoidsin keratinocytes.
Carceller-Zazo E. et al.
Glucocorticoids (GCs) exert potent antiproliferative and anti-inflammatory properties, explaining their therapeutic efficacy for skin diseases. GCs act by binding to the GC receptor (GR) and the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR), co-expressed in classical and non-classical targets including keratinocytes. Using knocko... |
Gene Regulatory Interactions at Lamina-Associated Domains
Madsen-Østerbye J. et al.
The nuclear lamina provides a repressive chromatin environment at the nuclear periphery. However, whereas most genes in lamina-associated domains (LADs) are inactive, over ten percent reside in local euchromatic contexts and are expressed. How these genes are regulated and whether they are able to interact with regu... |
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor cell intrinsically promotes resident memoryCD8 T cell differentiation and function.
Dean J. W. et al.
The Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr) regulates the differentiation and function of CD4 T cells; however, its cell-intrinsic role in CD8 T cells remains elusive. Herein we show that Ahr acts as a promoter of resident memory CD8 T cell (T) differentiation and function. Genetic ablation of Ahr in mouse CD... |
Impact of Fetal Exposure to Endocrine Disrupting ChemicalMixtures on FOXA3 Gene and Protein Expression in Adult RatTestes.
Walker C. et al.
Perinatal exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) has been shown to affect male reproductive functions. However, the effects on male reproduction of exposure to EDC mixtures at doses relevant to humans have not been fully characterized. In previous studies, we found that in utero exposure to mixtures of th... |
Transfer of blocker-based qPCR reactions for DNA methylation analysisinto a microfluidic LoC system using thermal modeling.
Kärcher J.et al.
Changes in the DNA methylation landscape are associated with many diseases like cancer. Therefore, DNA methylation analysis is of great interest for molecular diagnostics and can be applied, e.g., for minimally invasive diagnostics in liquid biopsy samples like blood plasma. Sensitive detection of local methylation,... |
Intranasal administration of Acinetobacter lwoffii in a murine model ofasthma induces IL-6-mediated protection associated with cecal microbiotachanges.
Alashkar A. B. et al.
BACKGROUND: Early-life exposure to certain environmental bacteria including Acinetobacter lwoffii (AL) has been implicated in protection from chronic inflammatory diseases including asthma later in life. However, the underlying mechanisms at the immune-microbe interface remain largely unknown. METHODS: The effects o... |
Trichoderma root colonization triggers epigenetic changes in jasmonic andsalicylic acid pathway-related genes.
Agostini R. B. et al.
Beneficial interactions between plant-roots and Trichoderma spp. lead to a local and systemic enhancement of the plant immune system through a mechanism known as priming of defenses. In recent reports, we outlined a repertoire of genes and proteins differentially regulated in distant tissues of maize plants previous... |
DNA sequence and chromatin modifiers cooperate to confer epigeneticbistability at imprinting control regions.
Butz S. et al.
Genomic imprinting is regulated by parental-specific DNA methylation of imprinting control regions (ICRs). Despite an identical DNA sequence, ICRs can exist in two distinct epigenetic states that are memorized throughout unlimited cell divisions and reset during germline formation. Here, we systematically study the ... |
Smc5/6 silences episomal transcription by a three-step function.
Abdul F. et al.
In addition to its role in chromosome maintenance, the six-membered Smc5/6 complex functions as a restriction factor that binds to and transcriptionally silences viral and other episomal DNA. However, the underlying mechanism is unknown. Here, we show that transcriptional silencing by the human Smc5/6 complex is a t... |
Exploration of nuclear body-enhanced sumoylation reveals that PMLrepresses 2-cell features of embryonic stem cells.
Tessier S. et al.
Membrane-less organelles are condensates formed by phase separation whose functions often remain enigmatic. Upon oxidative stress, PML scaffolds Nuclear Bodies (NBs) to regulate senescence or metabolic adaptation. PML NBs recruit many partner proteins, but the actual biochemical mechanism underlying their pleiotropi... |
Loss of epigenetic regulation disrupts lineage integrity, inducesaberrant alveogenesis and promotes breast cancer.
Langille E. et al.
Systematically investigating the scores of genes mutated in cancer and discerning disease drivers from inconsequential bystanders is a prerequisite for Precision Medicine but remains challenging. Here, we developed a somatic CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis screen to study 215 recurrent 'long-tail' breast cancer genes, which... |
A brain-shuttled antibody targeting alpha synuclein aggregates for the treatment of synucleinopathies
An, Sungwon et al.
Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy are members of a class of devastating neurodegenerative diseases called synucleinopathies, which are characterized by the presence of alpha-synuclein (α-Syn) rich aggregates in the brains of patients. Passive immunotherapy targeting these aggregates is an att... |
RAD51 protects human cells from transcription-replication conflicts.
Bhowmick R. et al.
Oncogene activation during tumorigenesis promotes DNA replication stress (RS), which subsequently drives the formation of cancer-associated chromosomal rearrangements. Many episodes of physiological RS likely arise due to conflicts between the DNA replication and transcription machineries operating simultaneously at... |
The Arabidopsis APOLO and human UPAT sequence-unrelated longnoncoding RNAs can modulate DNA and histone methylation machineries inplants.
Fonouni-Farde C. et al.
BACKGROUND: RNA-DNA hybrid (R-loop)-associated long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), including the Arabidopsis lncRNA AUXIN-REGULATED PROMOTER LOOP (APOLO), are emerging as important regulators of three-dimensional chromatin conformation and gene transcriptional activity. RESULTS: Here, we show that in addition to the PRC1... |
Prolonged FOS activity disrupts a global myogenic transcriptionalprogram by altering 3D chromatin architecture in primary muscleprogenitor cells.
Barutcu A Rasim et al.
BACKGROUND: The AP-1 transcription factor, FBJ osteosarcoma oncogene (FOS), is induced in adult muscle satellite cells (SCs) within hours following muscle damage and is required for effective stem cell activation and muscle repair. However, why FOS is rapidly downregulated before SCs enter cell cycle as progenitor c... |
Androgen-Induced MIG6 Regulates Phosphorylation ofRetinoblastoma Protein and AKT to Counteract Non-Genomic ARSignaling in Prostate Cancer Cells.
Schomann T. et al.
The bipolar androgen therapy (BAT) includes the treatment of prostate cancer (PCa) patients with supraphysiological androgen level (SAL). Interestingly, SAL induces cell senescence in PCa cell lines as well as ex vivo in tumor samples of patients. The SAL-mediated cell senescence was shown to be androgen receptor (A... |
Variation in PU.1 binding and chromatin looping at neutrophil enhancersinfluences autoimmune disease susceptibility
Watt S. et al.
Neutrophils play fundamental roles in innate inflammatory response, shape adaptive immunity1, and have been identified as a potentially causal cell type underpinning genetic associations with immune system traits and diseases2,3 The majority of these variants are non-coding and the underlying mechanisms are not full... |
CREBBP/EP300 acetyltransferase inhibition disrupts FOXA1-bound enhancers to inhibit the proliferation of ER+ breast cancer cells.
Bommi-Reddy A. et al.
Therapeutic targeting of the estrogen receptor (ER) is a clinically validated approach for estrogen receptor positive breast cancer (ER+ BC), but sustained response is limited by acquired resistance. Targeting the transcriptional coactivators required for estrogen receptor activity represents an alternative approach... |
Transient regulation of focal adhesion via Tensin3 is required fornascent oligodendrocyte differentiation
Merour E. et al.
The differentiation of oligodendroglia from oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs) to complex and extensive myelinating oligodendrocytes (OLs) is a multistep process that involves largescale morphological changes with significant strain on the cytoskeleton. While key chromatin and transcriptional regulators of diffe... |
The long noncoding RNA H19 regulates tumor plasticity inneuroendocrine prostate cancer
Singh N. et al.
Neuroendocrine (NE) prostate cancer (NEPC) is a lethal subtype of castration-resistant prostate cancer (PCa) arising either de novo or from transdifferentiated prostate adenocarcinoma following androgen deprivation therapy (ADT). Extensive computational analysis has identified a high degree of association between th... |
Epromoters function as a hub to recruit key transcription factorsrequired for the inflammatory response
Santiago-Algarra D. et al.
Gene expression is controlled by the involvement of gene-proximal (promoters) and distal (enhancers) regulatory elements. Our previous results demonstrated that a subset of gene promoters, termed Epromoters, work as bona fide enhancers and regulate distal gene expression. Here, we hypothesized that Epromoters play a... |
Differential contribution to gene expression prediction of histonemodifications at enhancers or promoters.
González-Ramírez M. et al.
The ChIP-seq signal of histone modifications at promoters is a good predictor of gene expression in different cellular contexts, but whether this is also true at enhancers is not clear. To address this issue, we develop quantitative models to characterize the relationship of gene expression with histone modification... |
Atg7 deficiency in microglia drives an altered transcriptomic profileassociated with an impaired neuroinflammatory response
Friess L. et al.
Microglia, resident immunocompetent cells of the central nervous system, can display a range of reaction states and thereby exhibit distinct biological functions across development, adulthood and under disease conditions. Distinct gene expression profiles are reported to define each of these microglial reaction stat... |
Lasp1 regulates adherens junction dynamics and fibroblast transformationin destructive arthritis
Beckmann D. et al.
The LIM and SH3 domain protein 1 (Lasp1) was originally cloned from metastatic breast cancer and characterised as an adaptor molecule associated with tumourigenesis and cancer cell invasion. However, the regulation of Lasp1 and its function in the aggressive transformation of cells is unclear. Here we use integrativ... |
The lncRNA and the transcription factor WRKY42 target common cell wallEXTENSIN encoding genes to trigger root hair cell elongation.
Pacheco, J. M. et al.
Plant long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are key chromatin dynamics regulators, directing the transcriptional programs driving a wide variety of developmental outputs. Recently, we uncovered how the lncRNA () directly recognizes the locus encoding the root hair (RH) master regulator () modulating its transcriptional acti... |
Placental uptake and metabolism of 25(OH)Vitamin D determines itsactivity within the fetoplacental unit
Ashley, B. et al.
Pregnancy 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) concentrations are associated with maternal and fetal health outcomes, but the underlying mechanisms have not been elucidated. Using physiological human placental perfusion approaches and intact villous explants we demonstrate a role for the placenta in regulating the relation... |
Waves of sumoylation support transcription dynamics during adipocytedifferentiation
Zhao, X. et al.
Tight control of gene expression networks required for adipose tissue formation and plasticity is essential for adaptation to energy needs and environmental cues. However, little is known about the mechanisms that orchestrate the dramatic transcriptional changes leading to adipocyte differentiation. We investigated ... |
Androgen receptor positively regulates gonadotropin-releasing hormonereceptor in pituitary gonadotropes.
Ryan, Genevieve E. et al.
Within pituitary gonadotropes, the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor (GnRHR) receives hypothalamic input from GnRH neurons that is critical for reproduction. Previous studies have suggested that androgens may regulate GnRHR, although the mechanisms remain unknown. In this study, we demonstrated that androgens ... |
Genetic perturbation of PU.1 binding and chromatin looping at neutrophilenhancers associates with autoimmune disease.
Watt, Stephen et al.
Neutrophils play fundamental roles in innate immune response, shape adaptive immunity, and are a potentially causal cell type underpinning genetic associations with immune system traits and diseases. Here, we profile the binding of myeloid master regulator PU.1 in primary neutrophils across nearly a hundred voluntee... |
Fra-1 regulates its target genes via binding to remote enhancers withoutexerting major control on chromatin architecture in triple negative breastcancers.
Bejjani, Fabienne and Tolza, Claire and Boulanger, Mathias and Downes,Damien and Romero, Raphaël and Maqbool, Muhammad Ahmad and Zine ElAabidine, Amal and Andrau, Jean-Christophe and Lebre, Sophie and Brehelin,Laurent and Parrinello, Hughes and Rohmer,
The ubiquitous family of dimeric transcription factors AP-1 is made up of Fos and Jun family proteins. It has long been thought to operate principally at gene promoters and how it controls transcription is still ill-understood. The Fos family protein Fra-1 is overexpressed in triple negative breast cancers (TNBCs) w... |
Cell-specific alterations inPitx1regulatory landscape activation caused bythe loss of a single enhancer
Rouco, R. et al.
Most developmental genes rely on multiple transcriptional enhancers for their accurate expression during embryogenesis. Because enhancers may have partially redundant activities, the loss of one of them often leads to a partial loss of gene expression and concurrent moderate phenotypic outcome, if any. While such a ... |
Transgenic mice for in vivo epigenome editing with CRISPR-based systems
Gemberling, M. et al.
The discovery, characterization, and adaptation of the RNA-guided clustered regularly interspersed short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)-Cas9 system has greatly increased the ease with which genome and epigenome editing can be performed. Fusion of chromatin-modifying domains to the nuclease-deactivated form of Cas9 (dCa... |
Transcriptional programming drives Ibrutinib-resistance evolution in mantlecell lymphoma.
Zhao, Xiaohong et al.
Ibrutinib, a bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, provokes robust clinical responses in aggressive mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), yet many patients relapse with lethal Ibrutinib-resistant (IR) disease. Here, using genomic, chemical proteomic, and drug screen profiling, we report that enhancer remodeling-mediated t... |
Coordinated changes in gene expression, H1 variant distribution and genome3D conformation in response to H1 depletion
Serna-Pujol, Nuria and Salinas-Pena, Monica and Mugianesi, Francesca and LeDily, François and Marti-Renom, Marc A. and Jordan, Albert
Up to seven members of the histone H1 family may contribute to chromatin compaction and its regulation in human somatic cells. In breast cancer cells, knock-down of multiple H1 variants deregulates many genes, promotes the appearance of genome-wide accessibility sites and triggers an interferon response via activati... |
REPROGRAMMING CBX8-PRC1 FUNCTION WITH A POSITIVE ALLOSTERICMODULATOR
Suh, J. L. et al.
Canonical targeting of Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 (PRC1) to repress developmental genes is mediated by cell type-specific, paralogous chromobox (CBX) proteins (CBX2, 4, 6, 7 and 8). Based on their central role in silencing and their misregulation associated with human disease including cancer, CBX proteins are at... |
Germline activity of the heat shock factor HSF-1 programs theinsulin-receptor daf-2 in C. elegans
Das, S. et al.
The mechanisms by which maternal stress alters offspring phenotypes remain poorly understood. Here we report that the heat shock transcription factor HSF-1, activated in the C. elegans maternal germline upon stress, epigenetically programs the insulin-like receptor daf-2 by increasing repressive H3K9me2 levels throu... |
The epigenetic landscape in purified myonuclei from fast and slow muscles
Bengtsen, M. et al.
Muscle cells have different phenotypes adapted to different usage and can be grossly divided into fast/glycolytic and slow/oxidative types. While most muscles contain a mixture of such fiber types, we aimed at providing a genome-wide analysis of chromatin environment by ChIP-Seq in two muscle extremes, the almost co... |
The glucocorticoid receptor recruits the COMPASS complex to regulateinflammatory transcription at macrophage enhancers.
Greulich, Franziska et al.
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are effective anti-inflammatory drugs; yet, their mechanisms of action are poorly understood. GCs bind to the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), a ligand-gated transcription factor controlling gene expression in numerous cell types. Here, we characterize GR's protein interactome and find the SETD1A ... |
A distinct metabolic response characterizes sensitivity to EZH2inhibition in multiple myeloma.
Nylund P. et al.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a heterogeneous haematological disease that remains clinically challenging. Increased activity of the epigenetic silencer EZH2 is a common feature in patients with poor prognosis. Previous findings have demonstrated that metabolic profiles can be sensitive markers for response to treatment i... |
BAF complexes drive proliferation and block myogenic differentiation in fusion-positive rhabdomyosarcoma
Laubscher et. al.
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a pediatric malignancy of skeletal muscle lineage. The aggressive alveolar subtype is characterized by t(2;13) or t(1;13) translocations encoding for PAX3- or PAX7-FOXO1 chimeric transcription factors, respectively, and are referred to as fusion positive RMS (FP-RMS). The fusion gene alters... |
A Tumor Suppressor Enhancer of PTEN in T-cell development and leukemia
L. Tottone at al.
Long-range oncogenic enhancers play an important role in cancer. Yet, whether similar regulation of tumor suppressor genes is relevant remains unclear. Loss of expression of PTEN is associated with the pathogenesis of various cancers, including T-cell leukemia (T-ALL). Here, we identify a highly conserved distal enh... |
Stronger induction of trained immunity by mucosal BCG or MTBVAC vaccination compared to standard intradermal vaccination.
Vierboom, M.P.M. et al.
BCG vaccination can strengthen protection against pathogens through the induction of epigenetic and metabolic reprogramming of innate immune cells, a process called trained immunity. We and others recently demonstrated that mucosal or intravenous BCG better protects rhesus macaques from infection and TB disease than... |
Postoperative abdominal sepsis induces selective and persistent changes inCTCF binding within the MHC-II region of human monocytes.
Siegler B. et al.
BACKGROUND: Postoperative abdominal infections belong to the most common triggers of sepsis and septic shock in intensive care units worldwide. While monocytes play a central role in mediating the initial host response to infections, sepsis-induced immune dysregulation is characterized by a defective antigen present... |
S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine hydrolase links methionine metabolism to thecircadian clock and chromatin remodeling.
Greco C. M. et al.
Circadian gene expression driven by transcription activators CLOCK and BMAL1 is intimately associated with dynamic chromatin remodeling. However, how cellular metabolism directs circadian chromatin remodeling is virtually unexplored. We report that the S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) hydrolyzing enzyme adenosylhomocyst... |
Genomic profiling of T-cell activation suggests increased sensitivity ofmemory T cells to CD28 costimulation.
Glinos, Dafni A and Soskic, Blagoje and Williams, Cayman and Kennedy, Alanand Jostins, Luke and Sansom, David M and Trynka, Gosia
T-cell activation is a critical driver of immune responses. The CD28 costimulation is an essential regulator of CD4 T-cell responses, however, its relative importance in naive and memory T cells is not fully understood. Using different model systems, we observe that human memory T cells are more sensitive to CD28 co... |
A genetic variant controls interferon-β gene expression in human myeloidcells by preventing C/EBP-β binding on a conserved enhancer.
Assouvie, Anaïs and Rotival, Maxime and Hamroune, Juliette and Busso,Didier and Romeo, Paul-Henri and Quintana-Murci, Lluis and Rousselet,Germain
Interferon β (IFN-β) is a cytokine that induces a global antiviral proteome, and regulates the adaptive immune response to infections and tumors. Its effects strongly depend on its level and timing of expression. Therefore, the transcription of its coding gene IFNB1 is strictly controlled. We have previous... |
BCG Vaccination Induces Long-Term Functional Reprogramming of HumanNeutrophils.
Moorlag, Simone J C F M and Rodriguez-Rosales, Yessica Alina and Gillard,Joshua and Fanucchi, Stephanie and Theunissen, Kate and Novakovic, Borisand de Bont, Cynthia M and Negishi, Yutaka and Fok, Ezio T and Kalafati,Lydia and Verginis, Panayotis and M
The tuberculosis vaccine bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) protects against some heterologous infections, probably via induction of non-specific innate immune memory in monocytes and natural killer (NK) cells, a process known as trained immunity. Recent studies have revealed that the induction of trained immunit... |
Macrophage Immune Memory Controls Endometriosis in Mice and Humans.
Jeljeli, Mohamed and Riccio, Luiza G C and Chouzenoux, Sandrine and Moresi,Fabiana and Toullec, Laurie and Doridot, Ludivine and Nicco, Carole andBourdon, Mathilde and Marcellin, Louis and Santulli, Pietro and Abrão,Mauricio S and Chapron, Charles and
Endometriosis is a frequent, chronic, inflammatory gynecological disease characterized by the presence of ectopic endometrial tissue causing pain and infertility. Macrophages have a central role in lesion establishment and maintenance by driving chronic inflammation and tissue remodeling. Macrophages can be reprogra... |
UTX/KDM6A suppresses AP-1 and a gliogenesis program during neuraldifferentiation of human pluripotent stem cells.
Xu, Beisi and Mulvey, Brett and Salie, Muneeb and Yang, Xiaoyang andMatsui, Yurika and Nityanandam, Anjana and Fan, Yiping and Peng, Jamy C
BACKGROUND: UTX/KDM6A is known to interact and influence multiple different chromatin modifiers to promote an open chromatin environment to facilitate gene activation, but its molecular activities in developmental gene regulation remain unclear. RESULTS: We report that in human neural stem cells, UTX binding correla... |
Epigenetic regulation of the lineage specificity of primary human dermallymphatic and blood vascular endothelial cells.
Tacconi, Carlotta and He, Yuliang and Ducoli, Luca and Detmar, Michael
Lymphatic and blood vascular endothelial cells (ECs) share several molecular and developmental features. However, these two cell types possess distinct phenotypic signatures, reflecting their different biological functions. Despite significant advances in elucidating how the specification of lymphatic and blood vasc... |
Combined treatment with CBP and BET inhibitors reverses inadvertentactivation of detrimental super enhancer programs in DIPG cells.
Wiese, M and Hamdan, FH and Kubiak, K and Diederichs, C and Gielen, GHand Nussbaumer, G and Carcaboso, AM and Hulleman, E and Johnsen, SA andKramm, CM
Diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas (DIPG) are the most aggressive brain tumors in children with 5-year survival rates of only 2%. About 85% of all DIPG are characterized by a lysine-to-methionine substitution in histone 3, which leads to global H3K27 hypomethylation accompanied by H3K27 hyperacetylation. Hyperacetyla... |
Methylation in pericytes after acute injury promotes chronic kidneydisease.
Chou, YH and Pan, SY and Shao, YH and Shih, HM and Wei, SY andLai, CF and Chiang, WC and Schrimpf, C and Yang, KC and Lai, LC andChen, YM and Chu, TS and Lin, SL
The origin and fate of renal myofibroblasts is not clear after acute kidney injury (AKI). Here, we demonstrate that myofibroblasts were activated from quiescent pericytes (qPericytes) and the cell numbers increased after ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced AKI (IRI-AKI). Myofibroblasts underwent apoptosis during ren... |
Exploring the virulence gene interactome with CRISPR/dCas9 in the humanmalaria parasite.
Bryant, JM and Baumgarten, S and Dingli, F and Loew, D and Sinha, A andClaës, A and Preiser, PR and Dedon, PC and Scherf, A
Mutually exclusive expression of the var multigene family is key to immune evasion and pathogenesis in Plasmodium falciparum, but few factors have been shown to play a direct role. We adapted a CRISPR-based proteomics approach to identify novel factors associated with var genes in their natural chromatin context. Ca... |
Targeted bisulfite sequencing for biomarker discovery.
Morselli, M and Farrell, C and Rubbi, L and Fehling, HL and Henkhaus, Rand Pellegrini, M
Cytosine methylation is one of the best studied epigenetic modifications. In mammals, DNA methylation patterns vary among cells and is mainly found in the CpG context. DNA methylation is involved in important processes during development and differentiation and its dysregulation can lead to or is associated with dis... |
Battle of the sex chromosomes: competition between X- and Y-chromosomeencoded proteins for partner interaction and chromatin occupancy drivesmulti-copy gene expression and evolution in muroid rodents.
Moretti, C and Blanco, M and Ialy-Radio, C and Serrentino, ME and Gobé,C and Friedman, R and Battail, C and Leduc, M and Ward, MA and Vaiman, Dand Tores, F and Cocquet, J
Transmission distorters (TDs) are genetic elements that favor their own transmission to the detriments of others. Slx/Slxl1 (Sycp3-like-X-linked and Slx-like1) and Sly (Sycp3-like-Y-linked) are TDs which have been co-amplified on the X and Y chromosomes of Mus species. They are involved in an intragenomic conflict i... |
BET protein inhibition sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomidetreatment by attenuating MGMT expression
Tancredi A. et al.
Bromodomain and extra-terminal tail (BET) proteins have been identified as potential epigenetic targets in cancer, including glioblastoma. These epigenetic modifiers link the histone code to gene transcription that can be disrupted with small molecule BET inhibitors (BETi). With the aim of developing rational combin... |