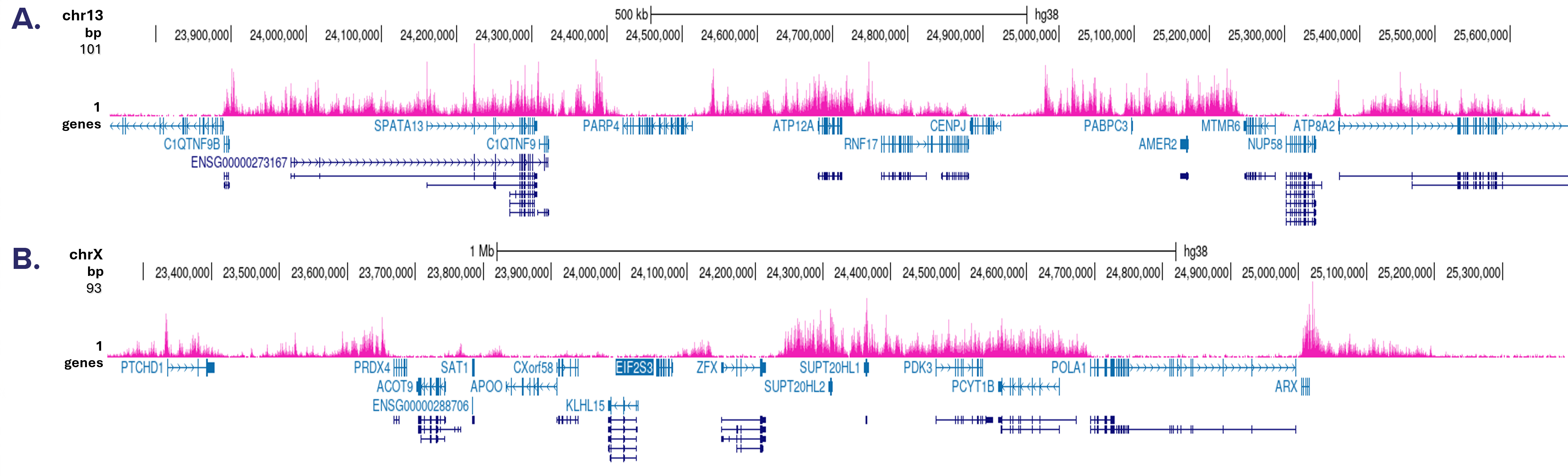
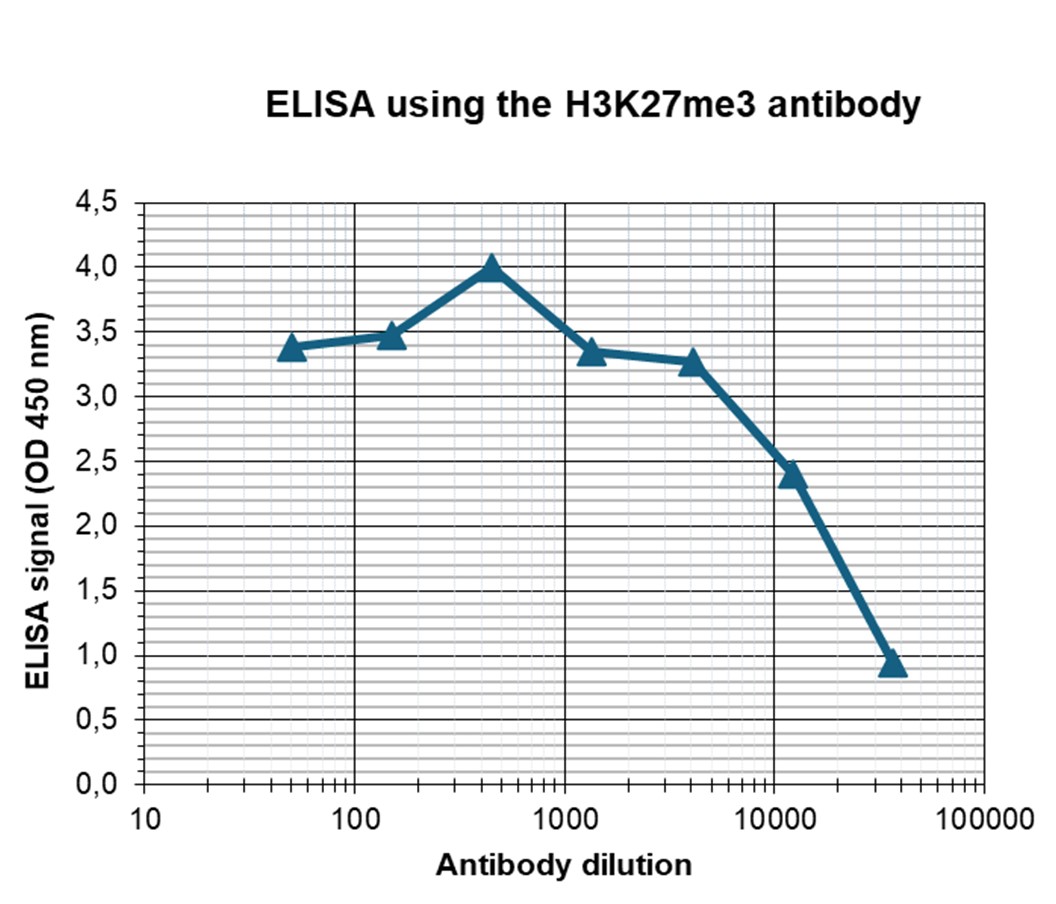
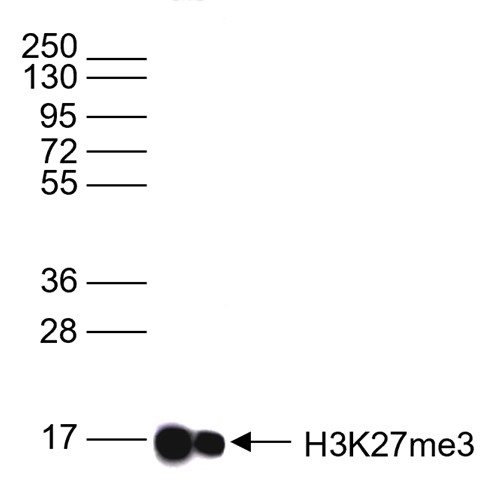
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K27me3 Antibody (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410069 Lot# A3239P). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Multimodal epigenetic and enhancer network remodeling shape the transcriptional landscape of human beige adipocytes
Hazell Pickering, Sarah et al.
Epigenetic regulation is a key determinant of adipocyte fate, driving the differentiation toward white or thermogenic beige phenotypes in response to environmental cues. To dissect the mechanisms orchestrating this plasticity in human adipocytes, we conducted an integrative analysis of transcriptomic, epigenomic... |
Endurance training increases a ubiquitylated form of histone H3 in the skeletal muscle, supporting Notch1 upregulation in an MDM2-dependent manner
Lam, Brian et al.
At the onset of training, each exercise session transiently shifts the distribution of histone post-transcriptional modifications (HPTMs) to activate genes that drive muscle adaptations. The resulting cyclic changes in gene expression promote the acquisition of high oxidative capacities and gains in capillaries. I... |
Epigenetic alterations affecting hematopoietic regulatory networks as drivers of mixed myeloid/lymphoid leukemia
Roger Mulet-Lazaro et al.
Leukemias with ambiguous lineage comprise several loosely defined entities, often without a clear mechanistic basis. Here, we extensively profile the epigenome and transcriptome of a subgroup of such leukemias with CpG Island Methylator Phenotype. These leukemias exhibit comparable hybrid myeloid/lymphoid epigenetic... |
Master corepressor inactivation through multivalent SLiM-induced polymerization mediated by the oncogene suppressor RAI2
Goradia N. et al.
While the elucidation of regulatory mechanisms of folded proteins is facilitated due to their amenability to high-resolution structural characterization, investigation of these mechanisms in disordered proteins is more challenging due to their structural heterogeneity, which can be captured by a variety of biophysic... |
Master corepressor inactivation through multivalent SLiM-induced polymerization mediated by the oncogene suppressor RAI2
Nishit Goradia et al.
While the elucidation of regulatory mechanisms of folded proteins is facilitated due to their amenability to high-resolution structural characterization, investigation of these mechanisms in disordered proteins is more challenging due to their structural heterogeneity, which can be captured by a variety of biophysic... |
Distinct regulation of EZH2 and its repressive H3K27me3 mark inPolyomavirus -positive and -negative Merkel cell carcinoma.
Durand M-A et al.
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is an aggressive skin cancer for which Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV) integration and expression of viral oncogenes small T and Large T have been identified as major oncogenic determinants. Recently, a component of the PRC2 complex, the histone methyltransferase EZH2 that induces H3K27 ... |
Gene Regulatory Interactions at Lamina-Associated Domains
Madsen-Østerbye J. et al.
The nuclear lamina provides a repressive chromatin environment at the nuclear periphery. However, whereas most genes in lamina-associated domains (LADs) are inactive, over ten percent reside in local euchromatic contexts and are expressed. How these genes are regulated and whether they are able to interact with regu... |
Histone lysine demethylase inhibition reprograms prostate cancermetabolism and mechanics.
Chianese Ugo and Papulino Chiara and Passaro Eugenia andEvers Tom Mj and Babaei Mehrad and Toraldo Antonella andDe Marchi Tommaso and Niméus Emma and Carafa Vincenzo andNicoletti Maria Maddalena and Del Gaudio Nunzio andIaccarino Nunzia an
OBJECTIVE: Aberrant activity of androgen receptor (AR) is the primary cause underlying development and progression of prostate cancer (PCa) and castration-resistant PCa (CRPC). Androgen signaling regulates gene transcription and lipid metabolism, facilitating tumor growth and therapy resistance in early and advanced... |
Histone H3K36me2 and H3K36me3 form a chromatin platform essentialfor DNMT3A-dependent DNA methylation in mouse oocytes.
Yano Seiichi at al.
Establishment of the DNA methylation landscape of mammalian oocytes, mediated by the DNMT3A-DNMT3L complex, is crucial for reproduction and development. In mouse oocytes, high levels of DNA methylation occur exclusively in the transcriptionally active regions, with moderate to low levels of methylation in other regi... |
HOTAIR interacts with PRC2 complex regulating the regional preadipocytetranscriptome and human fat distribution.
Kuo Feng-Chih et al.
Mechanisms governing regional human adipose tissue (AT) development remain undefined. Here, we show that the long non-coding RNA HOTAIR (HOX transcript antisense RNA) is exclusively expressed in gluteofemoral AT, where it is essential for adipocyte development. We find that HOTAIR interacts with polycomb repressive ... |
Effects of GSK-J4 on JMJD3 Histone Demethylase in Mouse Prostate Cancer Xenografts
Sanchez A. et al.
Background/aim: Histone methylation status is required to control gene expression. H3K27me3 is an epigenetic tri-methylation modification to histone H3 controlled by the demethylase JMJD3. JMJD3 is dysregulated in a wide range of cancers and has been shown to control the expression of a specific growth-modulato... |
Epigenetic Mechanisms Mediating Cell State Transitions in Chondrocytes
Wuelling M. et al.
Epigenetic modifications play critical roles in regulating cell lineage differentiation, but the epigenetic mechanisms guiding specific differentiation steps within a cell lineage have rarely been investigated. To decipher such mechanisms, we used the defined transition from proliferating (PC) into hypertrophic chon... |
Epigenetic integrity of paternal imprints enhances the developmental
potential of androgenetic haploid embryonic stem cells.
Zhang, Hongling and Li, Yuanyuan and Ma, Yongjian and Lai,
Chongping and Yu, Qian and Shi, Guangyong and Li, Jinsong
The use of two inhibitors of Mek1/2 and Gsk3β (2i) promotes the
generation of mouse diploid and haploid embryonic stem cells (ESCs) from
the inner cell mass of biparental and uniparental blastocysts,
respectively. However, a system enabling long-term maintenance of
imprints in ESCs has proven challenging. Here, we r... |
Cell-type specific transcriptional networks in root xylem adjacent celllayers
Asensi Fabado Maria Amparo et al.
Transport of water, ions and signals from roots to leaves via the xylem vessels is essential for plant life and needs to be tightly regulated. The final composition of the transpiration stream before passage into the shoots is controlled by the xylem-adjacent cell layers, namely xylem parenchyma and pericycle, in th... |
Loss of KMT2C reprograms the epigenomic landscape in hPSCsresulting in NODAL overexpression and a failure of hemogenic endotheliumspecification.
Maurya Shailendra et al.
Germline or somatic variation in the family of KMT2 lysine methyltransferases have been associated with a variety of congenital disorders and cancers. Notably, -fusions are prevalent in 70\% of infant leukaemias but fail to phenocopy short latency leukaemogenesis in mammalian models, suggesting additional factors ar... |
Effects of GSK-J4 on JMJD3 Histone Demethylase in MouseProstate Cancer Xenografts.
Sanchez A. et al.
BACKGROUND/AIM: Histone methylation status is required to control gene expression. H3K27me3 is an epigenetic tri-methylation modification to histone H3 controlled by the demethylase JMJD3. JMJD3 is dysregulated in a wide range of cancers and has been shown to control the expression of a specific growth-modulatory ge... |
Chemokine switch regulated by TGF-β1 in cancer-associated fibroblastsubsets determines the efficacy of chemo-immunotherapy.
Vienot A. et al.
Combining immunogenic cell death-inducing chemotherapies and PD-1 blockade can generate remarkable tumor responses. It is now well established that TGF-β1 signaling is a major component of treatment resistance and contributes to the cancer-related immunosuppressive microenvironment. However, whether TGF-β1... |
Coordination of EZH2 and SOX2 specifies human neural fate decision.
Zhao Yuan et al.
Polycomb repressive complexes (PRCs) are essential in mouse gastrulation and specify neural ectoderm in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), but the underlying molecular basis remains unclear. Here in this study, by employing an array of different approaches, such as gene knock-out, RNA-seq, ChIP-seq, et al., we unco... |
A regulatory variant at 3q21.1 confers an increased pleiotropic risk forhyperglycemia and altered bone mineral density.
Sinnott-Armstrong, Nasa et al.
Skeletal and glycemic traits have shared etiology, but the underlying genetic factors remain largely unknown. To identify genetic loci that may have pleiotropic effects, we studied Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) for bone mineral density and glycemic traits and identified a bivariate risk locus at 3q21. Usin... |
Functional annotations of three domestic animal genomes provide vitalresources for comparative and agricultural research.
Kern C. et al.
Gene regulatory elements are central drivers of phenotypic variation and thus of critical importance towards understanding the genetics of complex traits. The Functional Annotation of Animal Genomes consortium was formed to collaboratively annotate the functional elements in animal genomes, starting with domesticate... |
The histone modification H3K4me3 is altered at the locus in Alzheimer'sdisease brain.
Smith, Adam et al.
Several epigenome-wide association studies of DNA methylation have highlighted altered DNA methylation in the gene in Alzheimer's disease (AD) brain samples. However, no study has specifically examined histone modifications in the disease. We use chromatin immunoprecipitation-qPCR to quantify tri-methylation at hist... |
The Essential Function of SETDB1 in Homologous Chromosome Pairing andSynapsis during Meiosis.
Cheng, Ee-Chun et al.
SETDB1 is a histone-lysine N-methyltransferase critical for germline development. However, its function in early meiotic prophase I remains unknown. Here, we report that Setdb1 null spermatocytes display aberrant centromere clustering during leptotene, bouquet formation during zygotene, and subsequent failure in pai... |
The tropical coral displays an unusual chromatin structure and showshistone H3 clipping plasticity upon bleaching.
Roquis D. et al.
is a hermatypic coral with strong ecological importance. Anthropogenic disturbances and global warming are major threats that can induce coral bleaching, the disruption of the mutualistic symbiosis between the coral host and its endosymbiotic algae. Previous works have shown that somaclonal colonies display differen... |
EZH2 and KDM6B Expressions Are Associated with Specific EpigeneticSignatures during EMT in Non Small Cell Lung Carcinomas.
Lachat C. et al.
The role of Epigenetics in Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) has recently emerged. Two epigenetic enzymes with paradoxical roles have previously been associated to EMT, EZH2 (Enhancer of Zeste 2 Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) Subunit), a lysine methyltranserase able to add the H3K27me3 mark, and the hist... |
A histone H3.3K36M mutation in mice causes an imbalance of histonemodifications and defects in chondrocyte differentiation.
Abe, Shusaku and Nagatomo, Hiroaki and Sasaki, Hiroyuki and Ishiuchi,Takashi
Histone lysine-to-methionine (K-to-M) mutations have been identified as driver mutations in human cancers. Interestingly, these 'oncohistone' mutations inhibit the activity of histone methyltransferases. Therefore, they can potentially be used as versatile tools to investigate the roles of histone modifications. In ... |
Trans- and cis-acting effects of Firre on epigenetic features of theinactive X chromosome.
Fang, He and Bonora, Giancarlo and Lewandowski, Jordan P and Thakur,Jitendra and Filippova, Galina N and Henikoff, Steven and Shendure, Jay andDuan, Zhijun and Rinn, John L and Deng, Xinxian and Noble, William S andDisteche, Christine M
Firre encodes a lncRNA involved in nuclear organization. Here, we show that Firre RNA expressed from the active X chromosome maintains histone H3K27me3 enrichment on the inactive X chromosome (Xi) in somatic cells. This trans-acting effect involves SUZ12, reflecting interactions between Firre RNA and components of t... |
NSD1-deposited H3K36me2 directs de novo methylation in the mouse malegermline and counteracts Polycomb-associated silencing.
Shirane, Kenjiro and Miura, Fumihito and Ito, Takashi and Lorincz, MatthewC
De novo DNA methylation (DNAme) in mammalian germ cells is dependent on DNMT3A and DNMT3L. However, oocytes and spermatozoa show distinct patterns of DNAme. In mouse oocytes, de novo DNAme requires the lysine methyltransferase (KMTase) SETD2, which deposits H3K36me3. We show here that SETD2 is dispensable for de nov... |
Distinct and temporary-restricted epigenetic mechanisms regulate human αβ and γδ T cell development
Roels J, Kuchmiy A, De Decker M, et al.
The development of TCRαβ and TCRγδ T cells comprises a step-wise process in which regulatory events control differentiation and lineage outcome. To clarify these mechanisms, we employed RNA-sequencing, ATAC-sequencing and ChIPmentation on well-defined thymocyte subsets that represent the conti... |
MeCP2 regulates gene expression through recognition of H3K27me3.
Lee, W and Kim, J and Yun, JM and Ohn, T and Gong, Q
MeCP2 plays a multifaceted role in gene expression regulation and chromatin organization. Interaction between MeCP2 and methylated DNA in the regulation of gene expression is well established. However, the widespread distribution of MeCP2 suggests it has additional interactions with chromatin. Here we demonstra... |
TET-Mediated Hypermethylation Primes SDH-Deficient Cells for HIF2α-Driven Mesenchymal Transition.
Morin A, Goncalves J, Moog S, Castro-Vega LJ, Job S, Buffet A, Fontenille MJ, Woszczyk J, Gimenez-Roqueplo AP, Letouzé E, Favier J
Loss-of-function mutations in the SDHB subunit of succinate dehydrogenase predispose patients to aggressive tumors characterized by pseudohypoxic and hypermethylator phenotypes. The mechanisms leading to DNA hypermethylation and its contribution to SDH-deficient cancers remain undemonstrated. We examine th... |
Alu retrotransposons modulate Nanog expression through dynamic changes in regional chromatin conformation via aryl hydrocarbon receptor.
González-Rico FJ, Vicente-García C, Fernández A, Muñoz-Santos D, Montoliu L, Morales-Hernández A, Merino JM, Román AC, Fernández-Salguero PM
Transcriptional repression of Nanog is an important hallmark of stem cell differentiation. Chromatin modifications have been linked to the epigenetic profile of the Nanog gene, but whether chromatin organization actually plays a causal role in Nanog regulation is still unclear. Here, we report that the formation of ... |
Inhibition of methyltransferase activity of enhancer of zeste 2 leads to enhanced lipid accumulation and altered chromatin status in zebrafish.
den Broeder MJ, Ballangby J, Kamminga LM, Aleström P, Legler J, Lindeman LC, Kamstra JH
BACKGROUND: Recent studies indicate that exposure to environmental chemicals may increase susceptibility to developing metabolic diseases. This susceptibility may in part be caused by changes to the epigenetic landscape which consequently affect gene expression and lead to changes in lipid metabolism. The epigenetic... |
Polycomb Group Proteins Regulate Chromatin Architecture in Mouse Oocytes and Early Embryos.
Du Z, Zheng H, Kawamura YK, Zhang K, Gassler J, Powell S, Xu Q, Lin Z, Xu K, Zhou Q, Ozonov EA, Véron N, Huang B, Li L, Yu G, Liu L, Au Yeung WK, Wang P, Chang L, Wang Q, He A, Sun Y, Na J, Sun Q, Sasaki H, Tachibana K, Peters AHFM, Xie W
In mammals, chromatin organization undergoes drastic reorganization during oocyte development. However, the dynamics of three-dimensional chromatin structure in this process is poorly characterized. Using low-input Hi-C (genome-wide chromatin conformation capture), we found that a unique chromatin organization gradu... |
Allelic H3K27me3 to allelic DNA methylation switch maintains noncanonical imprinting in extraembryonic cells
Chen Zhiyuan, Yin Qiangzong, Inoue Azusa, Zhang Chunxia, Zhang Yi
Faithful maintenance of genomic imprinting is essential for mammalian development. While germline DNA methylation–dependent (canonical) imprinting is relatively stable during development, the recently found oocyte-derived H3K27me3-mediated noncanonical imprinting is mostly transient in early embryos, with some... |
Inhibition of Histone Demethylases LSD1 and UTX Regulates ERα Signaling in Breast Cancer.
Benedetti R, Dell'Aversana C, De Marchi T, Rotili D, Liu NQ, Novakovic B, Boccella S, Di Maro S, Cosconati S, Baldi A, Niméus E, Schultz J, Höglund U, Maione S, Papulino C, Chianese U, Iovino F, Federico A, Mai A, Stunnenberg HG, Nebbioso A, Altucci L
In breast cancer, Lysine-specific demethylase-1 (LSD1) and other lysine demethylases (KDMs), such as Lysine-specific demethylase 6A also known as Ubiquitously transcribed tetratricopeptide repeat, X chromosome (UTX), are co-expressed and co-localize with estrogen receptors (ERs), suggesting the potential use of hybr... |
Transit amplifying cells coordinate mouse incisor mesenchymal stem cell activation.
Walker JV, Zhuang H, Singer D, Illsley CS, Kok WL, Sivaraj KK, Gao Y, Bolton C, Liu Y, Zhao M, Grayson PRC, Wang S, Karbanová J, Lee T, Ardu S, Lai Q, Liu J, Kassem M, Chen S, Yang K, Bai Y, Tredwin C, Zambon AC, Corbeil D, Adams R, Abdallah BM, Hu B
Stem cells (SCs) receive inductive cues from the surrounding microenvironment and cells. Limited molecular evidence has connected tissue-specific mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) with mesenchymal transit amplifying cells (MTACs). Using mouse incisor as the model, we discover a population of MSCs neibouring to the MTACs... |
The Toxoplasma effector TEEGR promotes parasite persistence by modulating NF-κB signalling via EZH2.
Braun L, Brenier-Pinchart MP, Hammoudi PM, Cannella D, Kieffer-Jaquinod S, Vollaire J, Josserand V, Touquet B, Couté Y, Tardieux I, Bougdour A, Hakimi MA
The protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii has co-evolved with its homeothermic hosts (humans included) strategies that drive its quasi-asymptomatic persistence in hosts, hence optimizing the chance of transmission to new hosts. Persistence, which starts with a small subset of parasites that escape host immune killing... |
Kdm6b regulates context-dependent hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal and leukemogenesis.
Mallaney C, Ostrander EL, Celik H, Kramer AC, Martens A, Kothari A, Koh WK, Haussler E, Iwamori N, Gontarz P, Zhang B, Challen GA
The histone demethylase KDM6B (JMJD3) is upregulated in blood disorders, suggesting that it may have important pathogenic functions. Here we examined the function of Kdm6b in hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) to evaluate its potential as a therapeutic target. Loss of Kdm6b lead to depletion of phenotypic and functional... |
H3K27me3 is an epigenetic barrier while KDM6A overexpression improves nuclear reprogramming efficiency.
Zhou C, Wang Y, Zhang J, Su J, An Q, Liu X, Zhang M, Wang Y, Liu J, Zhang Y
Aberrant epigenetic reprogramming is a major factor of developmental failure of cloned embryos. Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3), a histone mark for transcriptional repression, plays important roles in mammalian embryonic development and induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) generation. The global loss ... |
Comprehensive Analysis of Chromatin States in Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor Identifies Diverging Roles for SWI/SNF and Polycomb in Gene Regulation.
Erkek S, Johann PD, Finetti MA, Drosos Y, Chou HC, Zapatka M, Sturm D, Jones DTW, Korshunov A, Rhyzova M, Wolf S, Mallm JP, Beck K, Witt O, Kulozik AE, Frühwald MC, Northcott PA, Korbel JO, Lichter P, Eils R, Gajjar A, Roberts CWM, Williamson D, Hasselbla
Biallelic inactivation of SMARCB1, encoding a member of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, is the hallmark genetic aberration of atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors (ATRT). Here, we report how loss of SMARCB1 affects the epigenome in these tumors. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) on pri... |
Gamma radiation induces locus specific changes to histone modification enrichment in zebrafish and Atlantic salmon.
Lindeman LC, Kamstra JH, Ballangby J, Hurem S, Martín LM, Brede DA, Teien HC, Oughton DH, Salbu B, Lyche JL, Aleström P
Ionizing radiation is a recognized genotoxic agent, however, little is known about the role of the functional form of DNA in these processes. Post translational modifications on histone proteins control the organization of chromatin and hence control transcriptional responses that ultimately affect the phenotype. Th... |
Mutant p63 Affects Epidermal Cell Identity through Rewiring the Enhancer Landscape.
Qu J, Tanis SEJ, Smits JPH, Kouwenhoven EN, Oti M, van den Bogaard EH, Logie C, Stunnenberg HG, van Bokhoven H, Mulder KW, Zhou H
Transcription factor p63 is a key regulator of epidermal keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation. Mutations in the p63 DNA-binding domain are associated with ectrodactyly, ectodermal dysplasia, and cleft lip/palate (EEC) syndrome. However, the underlying molecular mechanism of these mutations remains unclear.... |
TIP60: an actor in acetylation of H3K4 and tumor development in breast cancer.
Judes G, Dubois L, Rifaï K, Idrissou M, Mishellany F, Pajon A, Besse S, Daures M, Degoul F, Bignon YJ, Penault-Llorca F, Bernard-Gallon D
AIM: The acetyltransferase TIP60 is reported to be downregulated in several cancers, in particular breast cancer, but the molecular mechanisms resulting from its alteration are still unclear. MATERIALS & METHODS: In breast tumors, H3K4ac enrichment and its link with TIP60 were evaluated by chromatin immunoprecip... |
PWWP2A binds distinct chromatin moieties and interacts with an MTA1-specific core NuRD complex.
Link S, Spitzer RMM, Sana M, Torrado M, Völker-Albert MC, Keilhauer EC, Burgold T, Pünzeler S, Low JKK, Lindström I, Nist A, Regnard C, Stiewe T, Hendrich B, Imhof A, Mann M, Mackay JP, Bartkuhn M, Hake SB
Chromatin structure and function is regulated by reader proteins recognizing histone modifications and/or histone variants. We recently identified that PWWP2A tightly binds to H2A.Z-containing nucleosomes and is involved in mitotic progression and cranial-facial development. Here, using in vitro assays, we show that... |
Accurate annotation of accessible chromatin in mouse and human primordial germ cells.
Li J, Shen S, Chen J, Liu W, Li X, Zhu Q, Wang B, Chen X, Wu L, Wang M, Gu L, Wang H, Yin J, Jiang C, Gao S
Extensive and accurate chromatin remodeling is essential during primordial germ cell (PGC) development for the perpetuation of genetic information across generations. Here, we report that distal cis-regulatory elements (CREs) marked by DNase I-hypersensitive sites (DHSs) show temporally restricted activities during ... |
Loss of H3K27me3 Imprinting in Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer Embryos Disrupts Post-Implantation Development.
Matoba S, Wang H, Jiang L, Lu F, Iwabuchi KA, Wu X, Inoue K, Yang L, Press W, Lee JT, Ogura A, Shen L, Zhang Y
Animal cloning can be achieved through somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), although the live birth rate is relatively low. Recent studies have identified H3K9me3 in donor cells and abnormal Xist activation as epigenetic barriers that impede SCNT. Here we overcome these barriers using a combination of Xist knockout... |
Polycomb repressive complex 1 shapes the nucleosome landscape but not accessibility at target genes.
King HW, Fursova NA, Blackledge NP, Klose RJ
Polycomb group (PcG) proteins are transcriptional repressors that play important roles in regulating gene expression during animal development. In vitro experiments have shown that PcG protein complexes can compact chromatin to limit the activity of chromatin remodeling enzymes and access of the transcriptional mach... |
HIV-2/SIV viral protein X counteracts HUSH repressor complex.
Ghina Chougui, Soundasse Munir-Matloob, Roy Matkovic, Michaël M Martin, Marina Morel, Hichem Lahouassa, Marjorie Leduc, Bertha Cecilia Ramirez, Lucie Etienne and Florence Margottin-Goguet
To evade host immune defences, human immunodeficiency viruses 1 and 2 (HIV-1 and HIV-2) have evolved auxiliary proteins that target cell restriction factors. Viral protein X (Vpx) from the HIV-2/SIVsmm lineage enhances viral infection by antagonizing SAMHD1 (refs ), but this antagonism is not sufficient to explain a... |
The transcriptional factor ZEB1 represses Syndecan 1 expression in prostate cancer.
Farfán N, Ocarez N, Castellón EA, Mejía N, de Herreros AG, Contreras HR
Syndecan 1 (SDC-1) is a cell surface proteoglycan with a significant role in cell adhesion, maintaining epithelial integrity. SDC1 expression is inversely related to aggressiveness in prostate cancer (PCa). During epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), loss of epithelial markers is mediated by transcriptional r... |
TSPYL2 Regulates the Expression of EZH2 Target Genes in Neurons
Hang Liu et al.
Testis-specific protein, Y-encoded-like 2 (TSPYL2) is an X-linked gene in the locus for several neurodevelopmental disorders. We have previously shown that Tspyl2 knockout mice had impaired learning and sensorimotor gating, and TSPYL2 facilitates the expression of Grin2a and Grin2b through interaction with CREB-bind... |
Forskolin Sensitizes Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells to H3K27me2/3 Demethylases GSKJ4 Inhibitor via Protein Kinase A.
Illiano M, Conte M, Sapio L, Nebbioso A, Spina A, Altucci L, Naviglio S
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is an aggressive hematological malignancy occurring very often in older adults, with poor prognosis depending on both rapid disease progression and drug resistance occurrence. Therefore, new therapeutic approaches are demanded. Epigenetic marks play a relevant role in AML. GSKJ4 is a nov... |
HMGB2 Loss upon Senescence Entry Disrupts Genomic Organization and Induces CTCF Clustering across Cell Types.
Zirkel A, Nikolic M, Sofiadis K, Mallm JP, Brackley CA, Gothe H, Drechsel O, Becker C, Altmüller J, Josipovic N, Georgomanolis T, Brant L, Franzen J, Koker M, Gusmao EG, Costa IG, Ullrich RT, Wagner W, Roukos V, Nürnberg P, Marenduzzo D, Rippe K, Papanton
Processes like cellular senescence are characterized by complex events giving rise to heterogeneous cell populations. However, the early molecular events driving this cascade remain elusive. We hypothesized that senescence entry is triggered by an early disruption of the cells' three-dimensional (3D) genome org... |
A new metabolic gene signature in prostate cancer regulated by JMJD3 and EZH2.
Daures M, Idrissou M, Judes G, Rifaï K, Penault-Llorca F, Bignon YJ, Guy L, Bernard-Gallon D
Histone methylation is essential for gene expression control. Trimethylated lysine 27 of histone 3 (H3K27me3) is controlled by the balance between the activities of JMJD3 demethylase and EZH2 methyltransferase. This epigenetic mark has been shown to be deregulated in prostate cancer, and evidence shows H3K27me3 enri... |
GATA2/3-TFAP2A/C transcription factor network couples human pluripotent stem cell differentiation to trophectoderm with repression of pluripotency
Krendl C. et al.
To elucidate the molecular basis of BMP4-induced differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) toward progeny with trophectoderm characteristics, we produced transcriptome, epigenome H3K4me3, H3K27me3, and CpG methylation maps of trophoblast progenitors, purified using the surface marker APA. We combined th... |
Rapid Communication: The correlation between histone modifications and expression of key genes involved in accumulation of adipose tissue in the pig.
Kociucka B. et al.
Histone modification is a well-known epigenetic mechanism involved in regulation of gene expression; however, it has been poorly studied in adipose tissues of the pig. Understanding the molecular background of adipose tissue development and function is essential for improving production efficiency and meat quality. ... |
Genomic imprinting of Xist by maternal H3K27me3
Azusa Inoue, Lan Jiang, Falong Lu, and Yi Zhang
Maternal imprinting at the Xist gene is essential to achieve paternal allele-specific imprinted X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) in female mammals. However, the mechanism underlying Xist imprinting is unclear. Here we show that the Xist locus is coated with a broad H3K27me3 domain that is established during oocyte gr... |
DNA methylation of intragenic CpG islands depends on their transcriptional activity during differentiation and disease
Jeziorska D.M. et al.
The human genome contains ∼30,000 CpG islands (CGIs). While CGIs associated with promoters nearly always remain unmethylated, many of the ∼9,000 CGIs lying within gene bodies become methylated during development and differentiation. Both promoter and intragenic CGIs may also become abnormally methylated as a... |
A lipodystrophy-causing lamin A mutant alters conformation and epigenetic regulation of the anti-adipogenic MIR335 locus
Oldenburg A. et al.
Mutations in the Lamin A/C (LMNA) gene-encoding nuclear LMNA cause laminopathies, which include partial lipodystrophies associated with metabolic syndromes. The lipodystrophy-associated LMNA p.R482W mutation is known to impair adipogenic differentiation, but the mechanisms involved are unclear. We show in this study... |
DNMT and HDAC inhibitors induce cryptic transcription start sites encoded in long terminal repeats
Brocks D. et al.
Several mechanisms of action have been proposed for DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibitors (DNMTi and HDACi), primarily based on candidate-gene approaches. However, less is known about their genome-wide transcriptional and epigenomic consequences. By mapping global transcription start site (TSS) an... |
H2A monoubiquitination in Arabidopsis thaliana is generally independent of LHP1 and PRC2 activity
Zhou Y. et al.
BACKGROUND:
Polycomb group complexes PRC1 and PRC2 repress gene expression at the chromatin level in eukaryotes. The classic recruitment model of Polycomb group complexes in which PRC2-mediated H3K27 trimethylation recruits PRC1 for H2A monoubiquitination was recently challenged by data showing that PRC1 activity... |
Decoupling of DNA methylation and activity of intergenic LINE-1 promoters in colorectal cancer
Vafadar-Isfahani N. et al.
Hypomethylation of LINE-1 repeats in cancer has been proposed as the main mechanism behind their activation; this assumption, however, was based on findings from early studies that were biased toward young and transpositionally active elements. Here, we investigate the relationship between methylation of 2 intergeni... |
HMCan-diff: a method to detect changes in histone modifications in cells with different genetic characteristics
Ashoor H. et al.
Comparing histone modification profiles between cancer and normal states, or across different tumor samples, can provide insights into understanding cancer initiation, progression and response to therapy. ChIP-seq histone modification data of cancer samples are distorted by copy number variation innate to any cancer... |
Jarid2 binds mono-ubiquitylated H2A lysine 119 to mediate crosstalk between Polycomb complexes PRC1 and PRC2
Cooper S. et al.
The Polycomb repressive complexes PRC1 and PRC2 play a central role in developmental gene regulation in multicellular organisms. PRC1 and PRC2 modify chromatin by catalysing histone H2A lysine 119 ubiquitylation (H2AK119u1), and H3 lysine 27 methylation (H3K27me3), respectively. Reciprocal crosstalk between these mo... |
Iterative Fragmentation Improves the Detection of ChIP-seq Peaks for Inactive Histone Marks
Laczik M. et al.
As chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) sequencing is becoming the dominant technique for studying chromatin modifications, new protocols surface to improve the method. Bioinformatics is also essential to analyze and understand the results, and precise analysis helps us to identify the effects of protocol optimizati... |
Overexpression of histone demethylase Fbxl10 leads to enhanced migration in mouse embryonic fibroblasts.
Rohde M. et al.
Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. Tissue formation during embryonic development, wound healing, immune responses and invasive tumors all require the orchestrated movement of cells to specific locations. Histone demethylase proteins alter transcription ... |
Allelic reprogramming of the histone modification H3K4me3 in early mammalian development
Zhang B et al.
Histone modifications are fundamental epigenetic regulators that control many crucial cellular processes1. However, whether these marks can be passed on from mammalian gametes to the next generation is a long-standing question that remains unanswered. Here, by developing a highly sensitive approach, STAR ChIP–... |
Fumarate is an epigenetic modifier that elicits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Sciacovelli M et al.
Mutations of the tricarboxylic acid cycle enzyme fumarate hydratase cause hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer1. Fumarate hydratase-deficient renal cancers are highly aggressive and metastasize even when small, leading to a very poor clinical outcome2. Fumarate, a small molecule metabolite that accumulate... |
H3K4 acetylation, H3K9 acetylation and H3K27 methylation in breast tumor molecular subtypes
Judes G et al.
AIM:
Here, we investigated how the St Gallen breast molecular subtypes displayed distinct histone H3 profiles.
PATIENTS & METHODS:
192 breast tumors divided into five St Gallen molecular subtypes (luminal A, luminal B HER2-, luminal B HER2+, HER2+ and basal-like) were evaluated for their histone H3 modifica... |
Epigenetic Modifications with DZNep, NaBu and SAHA in Luminal and Mesenchymal-like Breast Cancer Subtype Cells
Dagdemir A et al.
BACKGROUND/AIM:
Numerous studies have shown that breast cancer and epigenetic mechanisms have a very powerful interactive relation. The MCF7 cell line, representative of luminal subtype and the MDA-MB 231 cell line representative of mesenchymal-like subtype were treated respectively with a Histone Methyl Transferas... |
Molecular and Epigenetic Biomarkers in Luminal Androgen Receptor: A Triple Negative Breast Cancer Subtype
Judes G et al.
|
Frequency and mitotic heritability of epimutations in Schistosoma mansoni
Roquis D, Rognon A, Chaparro C, Boissier J, Arancibia N, Cosseau C, Parrinello H, Grunau C
Schistosoma mansoni is a parasitic platyhelminth responsible for intestinal bilharzia. It has a complex life cycle, infecting a freshwater snail of the Biomphalaria genus, and then a mammalian host. Schistosoma mansoni adapts rapidly to new (allopatric) strains of its intermediate host. To study the importance of ep... |
BPA-Induced Deregulation Of Epigenetic Patterns: Effects On Female Zebrafish Reproduction
Santangeli S, Maradonna F, Gioacchini G, Cobellis G, Piccinetti CC, Dalla Valle L, Carnevali O
Bisphenol A (BPA) is one of the commonest Endocrine Disruptor Compounds worldwide. It interferes with vertebrate reproduction, possibly by inducing deregulation of epigenetic mechanisms. To determine its effects on female reproductive physiology and investigate whether changes in the expression levels of genes relat... |
The JMJD3 Histone Demethylase and the EZH2 Histone Methyltransferase in Prostate Cancer
Daures M, Ngollo M, Judes G, Rifaï K, Kemeny JL, Penault-Llorca F, Bignon YJ, Guy L, Bernard-Gallon D
Prostate cancer is themost common cancer in men. It has been clearly established that genetic and epigenetic alterations of histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) are common events in prostate cancer. This mark is deregulated in prostate cancer (Ngollo et al., 2014). Furthermore, H3K27me3 levels are determine... |
Epigenetic priming of inflammatory response genes by high glucose in adipose progenitor cells
Rønningen T, Shah A, Reiner AH, Collas P, Moskaug JØ
Cellular metabolism confers wide-spread epigenetic modifications required for regulation of transcriptional networks that determine cellular states. Mesenchymal stromal cells are responsive to metabolic cues including circulating glucose levels and modulate inflammatory responses. We show here that long term exposur... |
Selective targeting of the BRG/PB1 bromodomains impairs embryonic and trophoblast stem cell maintenance
Fedorov O et al.
Mammalian SWI/SNF [also called Brg/Brahma-associated factors (BAFs)] are evolutionarily conserved chromatin-remodeling complexes regulating gene transcription programs during development and stem cell differentiation. BAF complexes contain an ATP (adenosine 5'-triphosphate)-driven remodeling enzyme (either BRG1 or B... |
The Epigenome of Schistosoma mansoni Provides Insight about How Cercariae Poise Transcription until Infection
Roquis D, Lepesant JM, Picard MA, Freitag M, Parrinello H, Groth M4, Emans R, Cosseau C, Grunau C
BACKGROUND:
Chromatin structure can control gene expression and can define specific transcription states. For example, bivalent methylation of histone H3K4 and H3K27 is linked to poised transcription in vertebrate embryonic stem cells (ESC). It allows them to rapidly engage specific developmental pathways. We rea... |
Deciphering the role of Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 (PRC1) variants in regulating the acquisition of flowering competence in Arabidopsis.
Pico S, Ortiz-Marchena MI, Merini W, Calonje M
Polycomb Group (PcG) proteins play important roles in regulating developmental phase transitions in plants; however, little is known about the role the PcG machinery in regulating the transition from juvenile to adult phase. Here, we show that Arabidopsis BMI1 (AtBMI1) PRC1 components participate in the repression o... |
An ultra-low-input native ChIP-seq protocol for genome-wide profiling of rare cell populations.
Brind'Amour J, Liu S, Hudson M, Chen C, Karimi MM, Lorincz MC
Combined chromatin immunoprecipitation and next-generation sequencing (ChIP-seq) has enabled genome-wide epigenetic profiling of numerous cell lines and tissue types. A major limitation of ChIP-seq, however, is the large number of cells required to generate high-quality data sets, precluding the study of rare cell p... |
Exposure to Hycanthone alters chromatin structure around specific gene functions and specific repeats in Schistosoma mansoni
Roquis D, Lepesant JM, Villafan E, Vieira C, Cosseau C, Grunau C
Schistosoma mansoni is a parasitic plathyhelminth responsible for intestinal schistosomiasis (or bilharziasis), a disease affecting 67 million people worldwide and causing an important economic burden. The schistosomicides hycanthone, and its later proxy oxamniquine, were widely used for treatments in endemic areas ... |
Targeting Polycomb to Pericentric Heterochromatin in Embryonic Stem Cells Reveals a Role for H2AK119u1 in PRC2 Recruitment.
Cooper S, Dienstbier M, Hassan R, Schermelleh L, Sharif J, Blackledge NP, De Marco V, Elderkin S, Koseki H, Klose R, Heger A, Brockdorff N
The mechanisms by which the major Polycomb group (PcG) complexes PRC1 and PRC2 are recruited to target sites in vertebrate cells are not well understood. Building on recent studies that determined a reciprocal relationship between DNA methylation and Polycomb activity, we demonstrate that, in methylation-deficient e... |
Variant PRC1 Complex-Dependent H2A Ubiquitylation Drives PRC2 Recruitment and Polycomb Domain Formation.
Blackledge NP, Farcas AM, Kondo T, King HW, McGouran JF, Hanssen LL, Ito S, Cooper S, Kondo K, Koseki Y, Ishikura T, Long HK, Sheahan TW, Brockdorff N, Kessler BM, Koseki H, Klose RJ
Chromatin modifying activities inherent to polycomb repressive complexes PRC1 and PRC2 play an essential role in gene regulation, cellular differentiation, and development. However, the mechanisms by which these complexes recognize their target sites and function together to form repressive chromatin domains remain ... |
Ezh2 regulates transcriptional and posttranslational expression of T-bet and promotes Th1 cell responses mediating aplastic anemia in mice.
Tong Q, He S, Xie F, Mochizuki K, Liu Y, Mochizuki I, Meng L, Sun H, Zhang Y, Guo Y, Hexner E, Zhang Y
Acquired aplastic anemia (AA) is a potentially fatal bone marrow (BM) failure syndrome. IFN-γ-producing Th1 CD4(+) T cells mediate the immune destruction of hematopoietic cells, and they are central to the pathogenesis. However, the molecular events that control the development of BM-destructive Th1 cells remain lar... |
Nitric oxide-induced neuronal to glial lineage fate-change depends on NRSF/REST function in neural progenitor cells.
Bergsland M, Covacu R, Perez Estrada C, Svensson M, Brundin L
Degeneration of CNS tissue commonly occurs during neuroinflammatory conditions, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) and neurotrauma. During such conditions, neural stem/progenitor cell (NPC) populations have been suggested to provide new cells to degenerated areas. In the normal brain, NPCs from the SVZ generate neurons... |
Polycomb binding precedes early-life stress responsive DNA methylation at the Avp enhancer.
Murgatroyd C, Spengler D
Early-life stress (ELS) in mice causes sustained hypomethylation at the downstream Avp enhancer, subsequent overexpression of hypothalamic Avp and increased stress responsivity. The sequence of events leading to Avp enhancer methylation is presently unknown. Here, we used an embryonic stem cell-derived model of hypo... |
Epigenetics of prostate cancer: distribution of histone H3K27me3 biomarkers in peri-tumoral tissue.
Ngollo M, Dagdemir A, Judes G, Kemeny JL, Penault-Llorca F, Boiteux JP, Lebert A, Bignon YJ, Guy L, Bernard-Gallon D
Prostate cancer is the second most common cause of cancer and the sixth leading cause of cancer fatalities in men world- wide (Ferlay et al., 2010). Genetic abnormalities and mutations are primary causative factors, but epigenetic mechanisms are now recognized as playing a key role in prostate cancer de- velopment. ... |
Epigenomic alterations define lethal CIMP-positive ependymomas of infancy.
Mack SC, Witt H, Piro RM, Gu L, Zuyderduyn S, Stütz AM, Wang X, Gallo M, Garzia L, Zayne K, Zhang X, Ramaswamy V, Jäger N, Jones DT, Sill M, Pugh TJ, Ryzhova M, Wani KM, Shih DJ, Head R, Remke M, Bailey SD, Zichner T, Faria CC, Barszczyk M, Stark S, Seker
Ependymomas are common childhood brain tumours that occur throughout the nervous system, but are most common in the paediatric hindbrain. Current standard therapy comprises surgery and radiation, but not cytotoxic chemotherapy as it does not further increase survival. Whole-genome and whole-exome sequencing of 47 hi... |
A novel microscopy-based high-throughput screening method to identify proteins that regulate global histone modification levels.
Baas R, Lelieveld D, van Teeffelen H, Lijnzaad P, Castelijns B, van Schaik FM, Vermeulen M, Egan DA, Timmers HT, de Graaf P
Posttranslational modifications of histones play an important role in the regulation of gene expression and chromatin structure in eukaryotes. The balance between chromatin factors depositing (writers) and removing (erasers) histone marks regulates the steady-state levels of chromatin modifications. Here we describe... |
SUPT6H controls estrogen receptor activity and cellular differentiation by multiple epigenomic mechanisms.
Bedi U, Scheel AH, Hennion M, Begus-Nahrmann Y, Rüschoff J, Johnsen SA
The estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) is the central transcriptional regulator of ductal mammary epithelial lineage specification and is an important prognostic marker in human breast cancer. Although antiestrogen therapies are initially highly effective at treating ERα-positive tumors, a large number of tumors progress... |
A key role for EZH2 in epigenetic silencing of HOX genes in mantle cell lymphoma.
Kanduri M, Sander B, Ntoufa S, Papakonstantinou N, Sutton LA, Stamatopoulos K, Kanduri C, Rosenquist R
The chromatin modifier EZH2 is overexpressed and associated with inferior outcome in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). Recently, we demonstrated preferential DNA methylation of HOX genes in MCL compared with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), despite these genes not being expressed in either entity. Since EZH2 has been s... |
Targeted disruption of hotair leads to homeotic transformation and gene derepression.
Li L, Liu B, Wapinski OL, Tsai MC, Qu K, Zhang J, Carlson JC, Lin M, Fang F, Gupta RA, Helms JA, Chang HY
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are thought to be prevalent regulators of gene expression, but the consequences of lncRNA inactivation in vivo are mostly unknown. Here, we show that targeted deletion of mouse Hotair lncRNA leads to derepression of hundreds of genes, resulting in homeotic transformation of the spine an... |
VAL- and AtBMI1-Mediated H2Aub Initiate the Switch from Embryonic to Postgerminative Growth in Arabidopsis.
Yang C, Bratzel F, Hohmann N, Koch M, Turck F, Calonje M
Plant B3-domain transcription factors have an important role in regulating seed development, in particular seed maturation and germination [1]. Among the B3 factors, the AFL (ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE3 [ABI3], FUSCA3 [FUS3], and LEAFY COTYLEDON2 [LEC2]) proteins activate the seed maturation program in a complex netw... |
Disease-Related Growth Factor and Embryonic Signaling Pathways Modulate an Enhancer of TCF21 Expression at the 6q23.2 Coronary Heart Disease Locus.
Miller CL, Anderson DR, Kundu RK, Raiesdana A, Nürnberg ST, Diaz R, Cheng K, Leeper NJ, Chen CH, Chang IS, Schadt EE, Hsiung CA, Assimes TL, Quertermous T
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is the leading cause of mortality in both developed and developing countries worldwide. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have now identified 46 independent susceptibility loci for CHD, however, the biological and disease-relevant mechanisms for these associations remain elusive. Th... |
Passaging Techniques and ROCK Inhibitor Exert Reversible Effects on Morphology and Pluripotency Marker Gene Expression of Human Embryonic Stem Cell Lines.
Holm F, Nikdin H, Kjartansdóttir KR, Gaudenzi G, Fried K, Aspenström P, Hermanson O, Bergström-Tengzelius R
Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) are known for their potential usage in regenerative medicine, but also for handling sensitivity. Much effort has been put into optimizing the culture methods of hESCs. It has been shown that the use of Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase inhibitor (ROCKi) decreases the cellular stres... |
Expression of a large LINE-1-driven antisense RNA is linked to epigenetic silencing of the metastasis suppressor gene TFPI-2 in cancer.
Cruickshanks HA, Vafadar-Isfahani N, Dunican DS, Lee A, Sproul D, Lund JN, Meehan RR, Tufarelli C
LINE-1 retrotransposons are abundant repetitive elements of viral origin, which in normal cells are kept quiescent through epigenetic mechanisms. Activation of LINE-1 occurs frequently in cancer and can enable LINE-1 mobilization but also has retrotransposition-independent consequences. We previously reported that i... |
Histone lysine trimethylation or acetylation can be modulated by phytoestrogen, estrogen or anti-HDAC in breast cancer cell lines.
Dagdemir A, Durif J, Ngollo M, Bignon YJ, Bernard-Gallon D
AIM: The isoflavones genistein, daidzein and equol (daidzein metabolite) have been reported to interact with epigenetic modifications, specifically hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes. The objective of this study was to analyze and understand the mechanisms by which phytoestrogens act on chromatin in breast c... |
Epigenetic Regulation of Nestin Expression During Neurogenic Differentiation of Adipose Tissue Stem Cells.
Boulland JL, Mastrangelopoulou M, Boquest AC, Jakobsen R, Noer A, Glover JC, Collas P.
Adipose-tissue-derived stem cells (ASCs) have received considerable attention due to their easy access, expansion potential, and differentiation capacity. ASCs are believed to have the potential to differentiate into neurons. However, the mechanisms by which this may occur remain largely unknown. Here, we show that ... |
New partners in regulation of gene expression: the enhancer of trithorax and polycomb corto interacts with methylated ribosomal protein l12 via its chromodomain.
Coléno-Costes A, Jang SM, de Vanssay A, Rougeot J, Bouceba T, Randsholt NB, Gibert JM, Le Crom S, Mouchel-Vielh E, Bloyer S, Peronnet F
Chromodomains are found in many regulators of chromatin structure, and most of them recognize methylated lysines on histones. Here, we investigate the role of the Drosophila melanogaster protein Corto's chromodomain. The Enhancer of Trithorax and Polycomb Corto is involved in both silencing and activation of gene ex... |
Multigenerational epigenetic adaptation of the hepatic wound-healing response.
Zeybel M, Hardy T, Wong YK, Mathers JC, Fox CR, Gackowska A, Oakley F, Burt AD, Wilson CL, Anstee QM, Barter MJ, Masson S, Elsharkawy AM, Mann DA, Mann J
We investigated whether ancestral liver damage leads to heritable reprogramming of hepatic wound healing in male rats. We found that a history of liver damage corresponds with transmission of an epigenetic suppressive adaptation of the fibrogenic component of wound healing to the male F(1) and F(2) generations. Unde... |
The H3K4me3 histone demethylase Fbxl10 is a regulator of chemokine expression, cellular morphology and the metabolome of fibroblasts
Janzer A, Stamm K, Becker A, Zimmer A, Buettner R, Kirfel J
Fbxl10 (Jhdm1b/Kdm2b) is a conserved and ubiquitously expressed member of the JHDM (JmjC-domain-containing histone demethy-lase) family. Fbxl10 was implicated in the demethylation of H3K4me3 or H3K36me2 thereby removing active chromatin marks and inhibiting gene transcription. Apart from the JmjC domain, Fbxl10 cons... |
The histone H2B monoubiquitination regulatory pathway is required for differentiation of multipotent stem cells.
Karpiuk O, Najafova Z, Kramer F, Hennion M, Galonska C, König A, Snaidero N, Vogel T, Shchebet A, Begus-Nahrmann Y, Kassem M, Simons M, Shcherbata H, Beissbarth T, Johnsen SA
Extensive changes in posttranslational histone modifications accompany the rewiring of the transcriptional program during stem cell differentiation. However, the mechanisms controlling the changes in specific chromatin modifications and their function during differentiation remain only poorly understood. We show tha... |
Intronic RNAs mediate EZH2 regulation of epigenetic targets.
Guil S, Soler M, Portela A, Carrère J, Fonalleras E, Gómez A, Villanueva A, Esteller M
Epigenetic deregulation at a number of genomic loci is one of the hallmarks of cancer. A role for some RNA molecules in guiding repressive polycomb complex PRC2 to specific chromatin regions has been proposed. Here we use an in vivo cross-linking method to detect and identify direct PRC2-RNA interactions in human ca... |
Chromatin structural changes around satellite repeats on the female sex chromosome in Schistosoma mansoni and their possible role in sex chromosome emergence.
Lepesant JM, Cosseau C, Boissier J, Freitag M, Portela J, Climent D, Perrin C, Zerlotini A, Grunau C
BACKGROUND: In the leuphotrochozoan parasitic platyhelminth Schistosoma mansoni, male individuals are homogametic (ZZ) whereas females are heterogametic (ZW). To elucidate the mechanisms that led to the emergence of sex chromosomes, we compared the genomic sequence and the chromatin structure of male and female indi... |
Prepatterning of developmental gene expression by modified histones before zygotic genome activation.
Lindeman LC, Andersen IS, Reiner AH, Li N, Aanes H, Østrup O, Winata C, Mathavan S, Müller F, Aleström P, Collas P
A hallmark of anamniote vertebrate development is a window of embryonic transcription-independent cell divisions before onset of zygotic genome activation (ZGA). Chromatin determinants of ZGA are unexplored; however, marking of developmental genes by modified histones in sperm suggests a predictive role of histone m... |
Silencing of Kruppel-like factor 2 by the histone methyltransferase EZH2 in human cancer.
Taniguchi H, Jacinto FV, Villanueva A, Fernandez AF, Yamamoto H, Carmona FJ, Puertas S, Marquez VE, Shinomura Y, Imai K, Esteller M
The Kruppel-like factor (KLF) proteins are multitasked transcriptional regulators with an expanding tumor suppressor function. KLF2 is one of the prominent members of the family because of its diminished expression in malignancies and its growth-inhibitory, pro-apoptotic and anti-angiogenic roles. In this study, we ... |