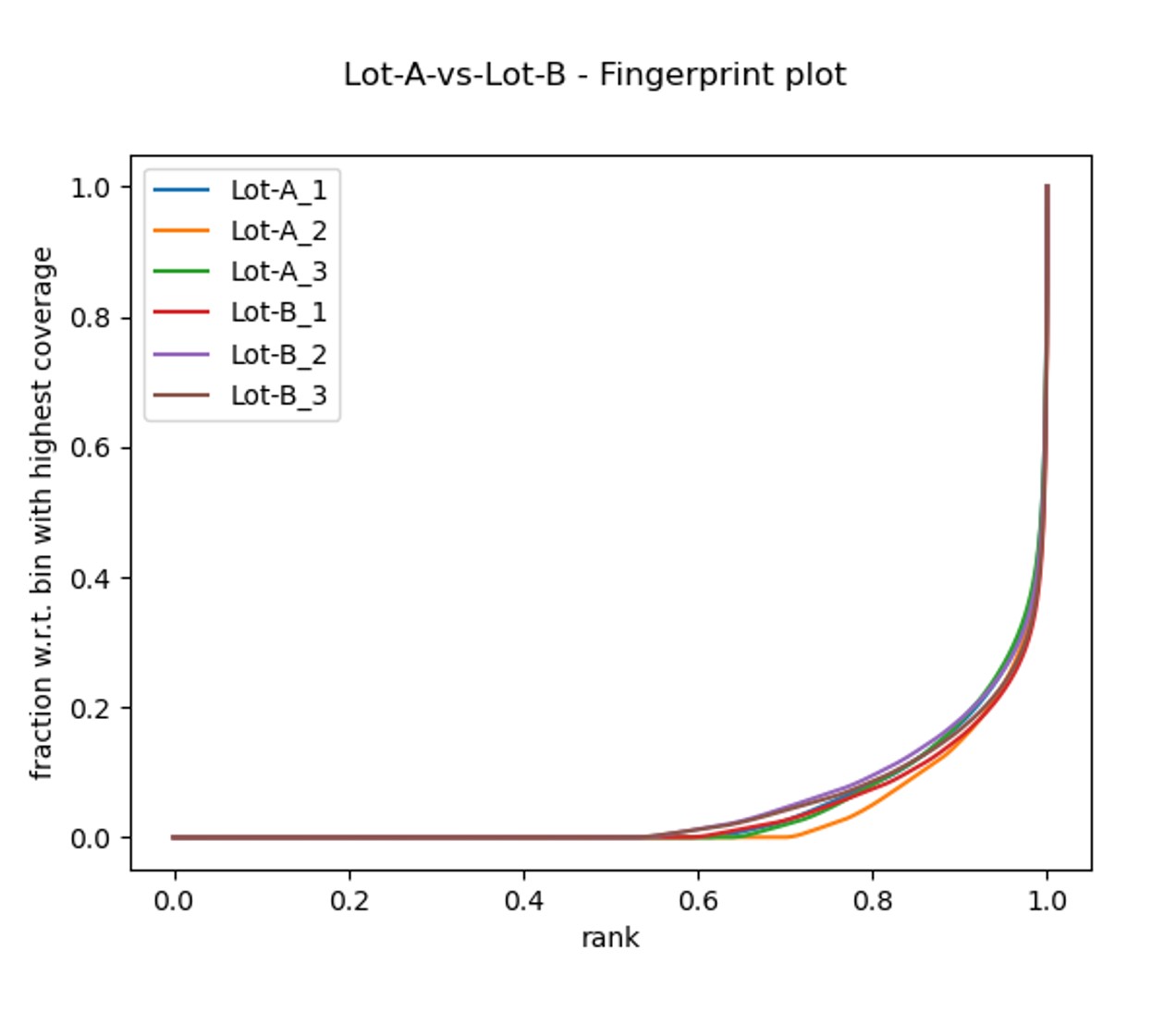
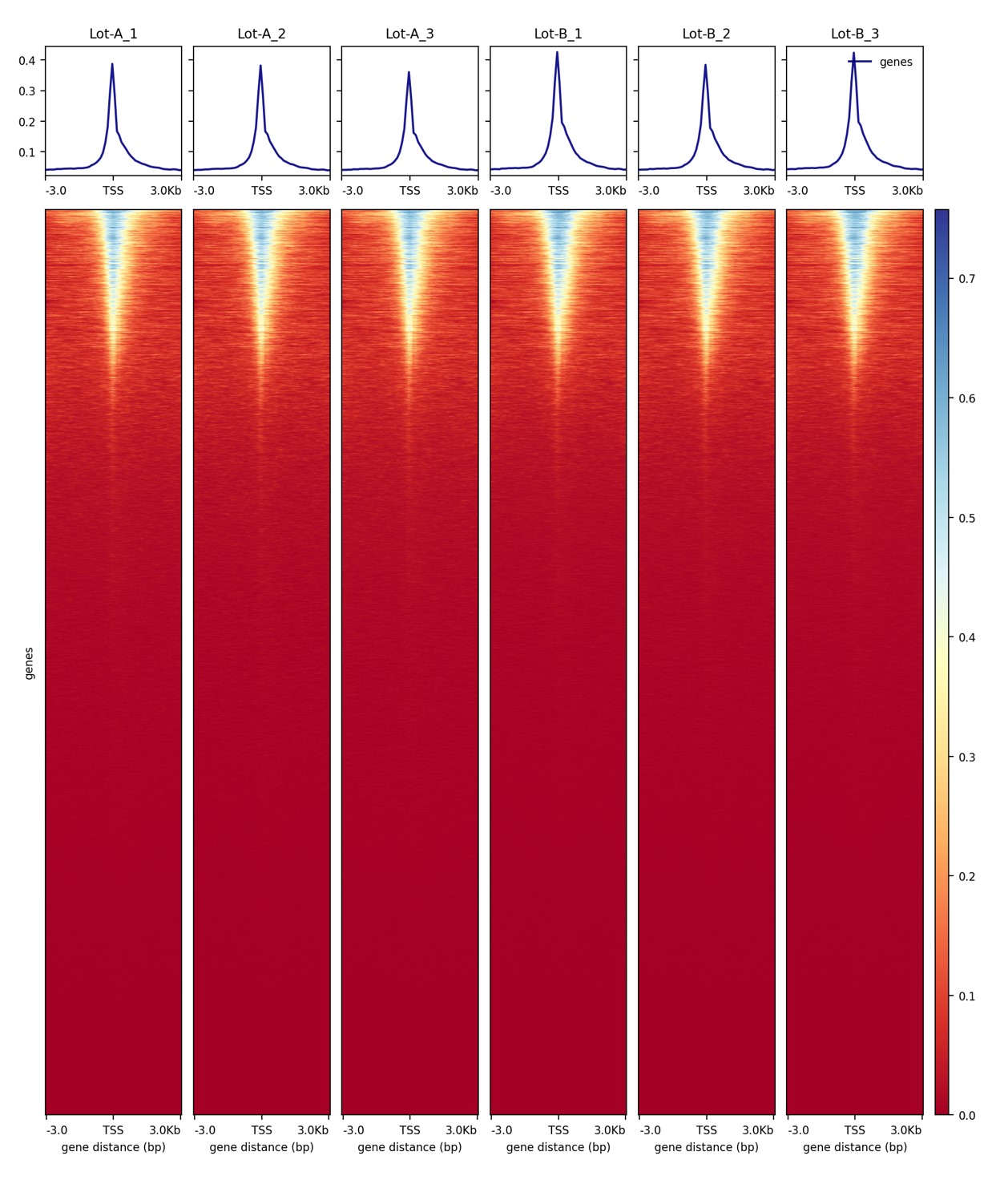
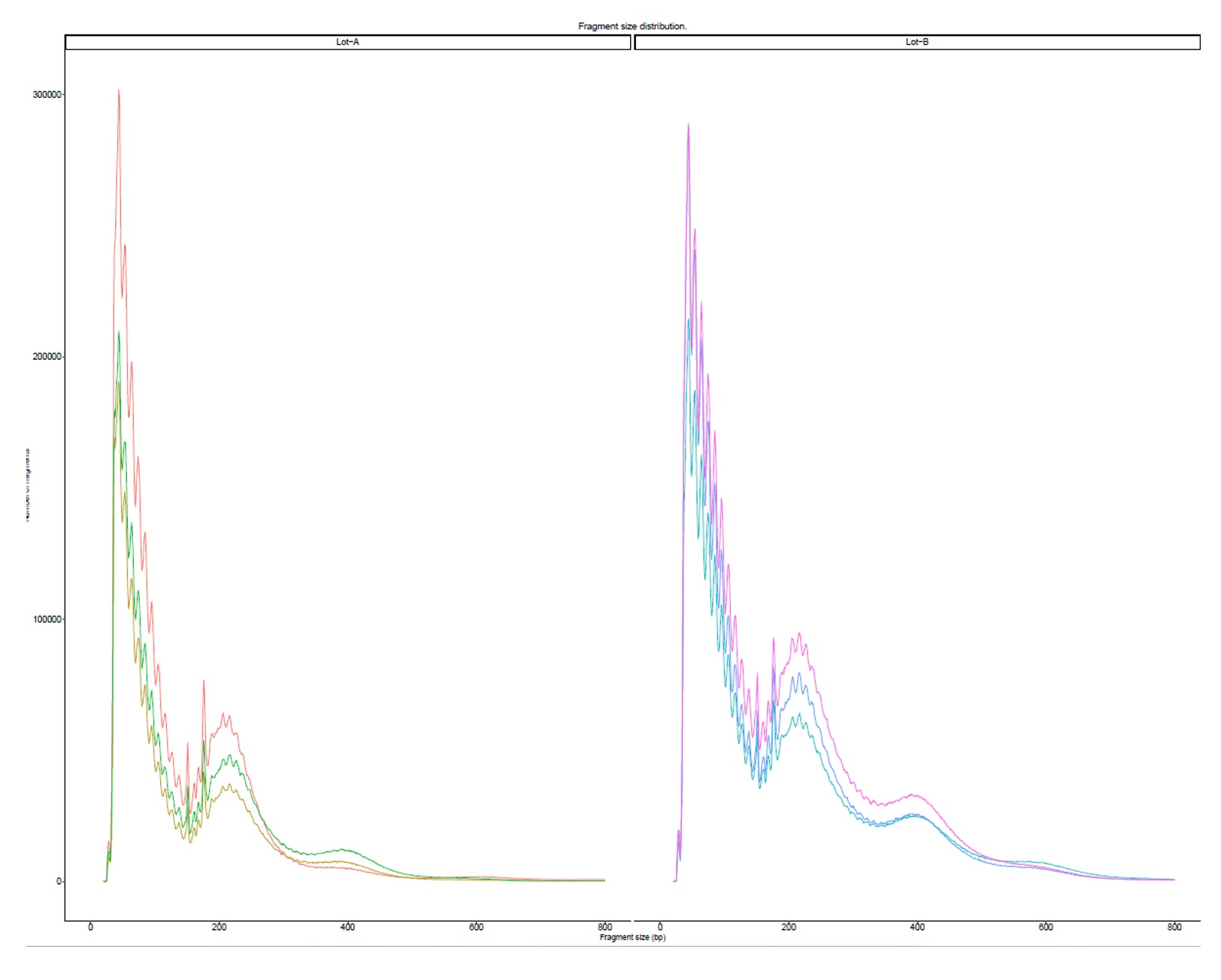
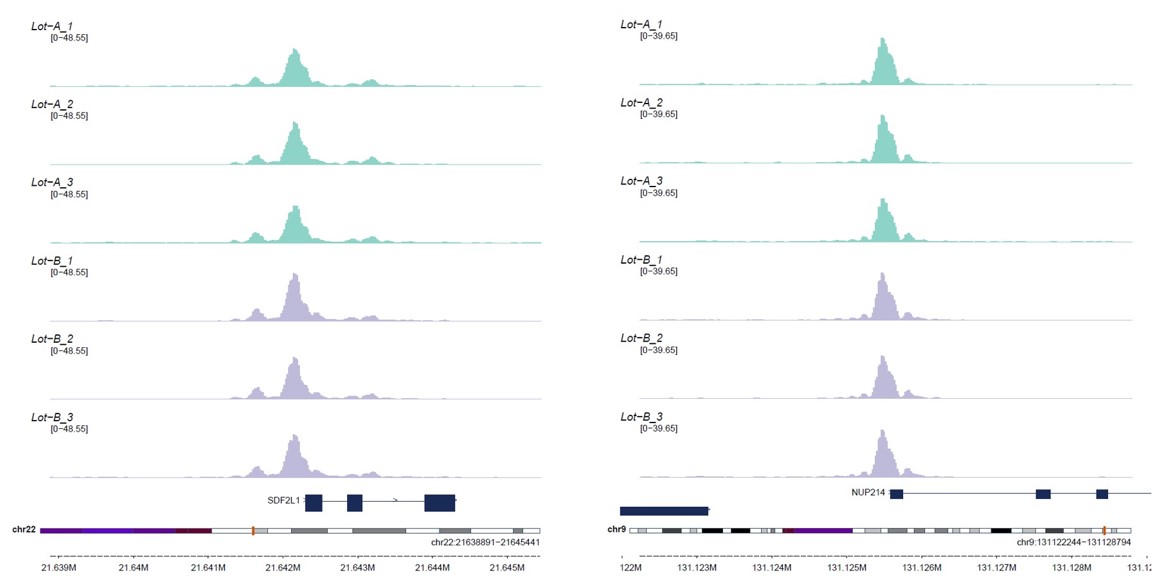
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: Tagmentase (Tn5 transposase) – loaded (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C01070013-400). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
CUT homeobox factors modulate chromatin accessibility in neurons
Jordá-Llorens, José Ignacio et al.
Abstract
Neuronal identity relies on coordinated transcriptional programs that include both neuron type-specific features and broadly shared pan-neuronal properties. While transcription factors that control neuronal gene expression have been defined, how these regulators interface with chromatin accessibility at ne... |
Adrenergic signaling coordinates distant and local responses to amputation in axolotl
Payzin-Dogru, Duygu et al.
Many species regenerate lost body parts following amputation. Most limb regeneration research has focused on the immediate injury site. Meanwhile, body-wide injury responses remain largely unexplored but may be critical for regeneration. Here, we discovered a role for the sympathetic nervous system in stimulating ... |
Menin-MLL1 complex cooperates with NF-Y to promote hepatocellular carcinoma survival
Dzama-Karels, Margarita
Chromatin regulators are frequently mutated or aberrantly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), suggesting that the dysregulation of chromatin is a key feature driving liver cancer. In this study, using an epigenome-focused CRISPR screen in two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) conditions, we find... |
Interphase chromosome conformation is specified by distinct folding programmes inherited through mitotic chromosomes or the cytoplasm
Schooley, Allana et al.
Identity-specific chromosome conformation must be re-established at each cell division. To uncover how interphase folding is inherited, we developed an approach that segregates chromosome-intrinsic mechanisms from those propagated through the cytoplasm during G1 nuclear reassembly. Inducible degradation of prote... |
Human iPSCs-based modeling unveils SETBP1 as a driver of chromatin rewiring in GATA2 deficiency
Pera, Joan et al.
Patients with GATA2 deficiency are predisposed to developing myelodysplastic neoplasms (MDS), which can progress to acute myeloid leukemia. This progression is often associated with cytogenetic and somatic alterations. Mutations in SETBP1 and ASXL1 genes are recurrently observed in GATA2 patients, although their... |
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A mediates mouse line- and fate-dependent cellular responses in Cx3cr1-Cre genetic tools
Yamasaki, Ayato et al.
Microglia, the resident macrophages in the central nervous system (CNS), have been intensively studied using rodent genetic models, including the Cre-loxP system. Among them are tamoxifen (TAM)-inducible CX3C chemokine receptor 1 (Cx3cr1)-Cre mouse lines (Cx3cr1CreERT2), which have enabled in-depth analyses of the... |
Quantitative measurement of phenotype dynamics during cancer drug resistance evolution using genetic barcoding
Whiting, F.J.H., Mossner, M., Gabbutt, C. et al.
Cancer treatment frequently fails due to the evolution of drug-resistant cell phenotypes driven by genetic or non-genetic changes. The origin, timing, and rate of spread of these adaptations are critical for understanding drug resistance mechanisms but remain challenging to observe directly. We present a mathe... |
Neuronal migration induces DNA damage in developing brain
Zhang, Zhejing et al.
Migratory cells tend to have soft nuclei that deform and penetrate narrow spaces1,2. Extensive nuclear deformation during migration can cause nuclear envelope rupture and DNA damage in cancer cells, which may contribute to the malignant transformation during tumor progression3,4,5,6. However, the significance of D... |
Androgen receptor-mediated assisted loading of the glucocorticoid receptor modulates transcriptional responses in prostate cancer cells
Hiltunen, Johannes et al.
Steroid receptors are involved in a wide array of crosstalk mechanisms that regulate diverse biological processes, with significant implications in diseases, particularly in cancers. In prostate cancer, indirect crosstalk between androgen receptor (AR) and glucocorticoid receptor NR3C1 (also known as GR) is well... |
CRISPR screen decodes SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex assembly
Schwaemmle, Hanna et al.
The SWI/SNF (or BAF) complex is an essential chromatin remodeler, which is frequently mutated in cancer and neurodevelopmental disorders. These are often heterozygous loss-of-function mutations, indicating a dosage-sensitive role for SWI/SNF subunits. However, the molecular mechanisms regulating SWI/SNF subunit dosa... |
Menin-MLL1 complex cooperates with NF-Y to promote HCC survival
Dzama-Karels, M., et al.
Abstract
Identification of new therapeutic targets in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains critical. Chromatin regulating complexes are frequently mutated or aberrantly expressed in HCC, suggesting dysregulation of chromatin environments is a key feature driving liver cancer. To investigate whether the altered ch... |
Eosinophil innate immune memory after bacterial skin infection promotes allergic lung inflammation
Radhouani, Mariem et al.
Microbial exposure at barrier interfaces drives development and balance of the immune system, but the consequences of local infections for systemic immunity and secondary inflammation are unclear. Here, we show that skin exposure to the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus persistently shapes the immune sys... |
SIRT6 activator fucoidan extends healthspan and lifespan in aged wild-type mice
Biashad, S., et al.
Abstract
SIRT6 is a protein deacylase, deacetylase, and mono-ADP-ribosylase (mADPr) regulating biological pathways important for longevity including DNA repair and silencing of LINE1 retrotransposons. SIRT6 knockout mice die by 30 days of age, whereas SIRT6 overexpression increases lifespan in male mice. Finding sa... |
Distinct molecular mechanisms of stress habituation in the mouse hippocampus
Rebecca Waag et al.
Chronic stress is a risk factor for neuropsychiatric disorders, making the ability to adapt to repeated stress a crucial determinant of mental health. On a molecular level, it remains unclear whether repeated exposure to stress is characterized by habituation - a decreased responsiveness to the same stimulus - or by... |
A20’s Linear Ubiquitin Binding Motif Restrains Pathogenic Activation of TH17/22 cells and IL-22 Driven Enteritis
Christopher John Bowman et al.
A20, encoded by the TNFAIP3 gene, is a protein linked to Crohn's disease and celiac disease in humans. We now find that mice expressing point mutations in A20's M1 ubiquitin binding motif (ZF7) spontaneously develop proximate enteritis that requires both luminal microbes and T cells. Cellular and transcrip... |
Gene mobility elements mediate cell type specific genome organization and radial gene movement in vivo
Tanguy Lucas et al.
Understanding the level of genome organization that governs gene regulation remains a challenge despite advancements in chromatin profiling techniques. Cell type specific chromatin architectures may be obscured by averaging heterogeneous cell populations. Here we took a reductionist perspective, starting with the re... |
HIRA protects telomeres against R-loop-induced instability in ALT cancer cells
Michelle Lee Lynskey et al.
Highlights
HIRA establishes greater telomeric chromatin accessibility after ATRX-DAXX loss
Deposition of new H3.3 by HIRA-UBN restricts telomeric ssDNA and TERRA R-loops
Unresolved TERRA R-loops block new H3.3 deposition by HIRA-UBN
CHK1 phosphorylation of H3.3 is critical to pr... |
Steroid receptor-assisted loading modulates transcriptional responses in prostate cancer cells
Johannes Hiltunen et al.
Steroid receptors are involved in a wide array of crosstalk mechanisms that regulate diverse biological processes, with significant implications in diseases, particularly in cancers. In prostate cancer, indirect crosstalk between androgen receptor (AR) and glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is well-documented, where GR re... |
ARMC5 selectively degrades SCAP-free SREBF1 and is essential for fatty acid desaturation in adipocytes
Akifumi Uota et al.
SREBF1 plays the central role in lipid metabolism. It has been known that full-length SREBF1 that did not associate with SCAP (SCAP-free SREBF1) is actively degraded, but its molecular mechanism and its biological meaning remain unclear. ARMC5-CUL3 complex was recently identified as E3 ubiquitin ligase of full-lengt... |
On the identification of differentially-active transcription factors from ATAC-seq data
Felix Ezequiel Gerbaldo et al.
ATAC-seq has emerged as a rich epigenome profiling technique, and is commonly used to identify Transcription Factors (TFs) underlying given phenomena. A number of methods can be used to identify differentially-active TFs through the accessibility of their DNA-binding motif, however little is known on the best approa... |
HNF1β bookmarking involves Topoisomerase 1 activation and DNA topology relaxation in mitotic chromatin
Alessia Bagattin et al.
Highlights
HNF1β mitotic site binding is preserved with a specific methanol/formaldehyde ChIP
BTBD2, an HNF1β partner, mediates mitosis-specific interaction with TOP1
HNF1β recruits TOP1 and induces DNA relaxation around bookmarked HNF1β sites
An HNF1β m... |
Nuclear lamin A/C phosphorylation by loss of androgen receptor leads to cancer-associated fibroblast activation
Ghosh S. et al.
Alterations in nuclear structure and function are hallmarks of cancer cells. Little is known about these changes in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs), crucial components of the tumor microenvironment. Loss of the androgen receptor (AR) in human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs), which triggers early steps of CAF act... |
A critical role for HNF4α in polymicrobial sepsis-associated metabolic reprogramming and death
van Dender C. et al.
In sepsis, limited food intake and increased energy expenditure induce a starvation response, which is compromised by a quick decline in the expression of hepatic PPARα, a transcription factor essential in intracellular catabolism of free fatty acids. The mechanism upstream of this PPARα downregulation i... |
Peripheral nervous system mediates body-wide stem cell activation for limb regeneration
Duygu Payzin-Dogru et al.
Many species throughout the animal kingdom naturally regenerate complex body parts following amputation. Most research in appendage regeneration has focused on identifying mechanisms that influence cell behaviors in the remaining stump tissue immediately adjacent to the injury site. Roles for activation steps that o... |
Rhabdomyosarcoma fusion oncoprotein initially pioneers a neural signature in vivo
Jack Kucinski et al.
Fusion-positive rhabdomyosarcoma is an aggressive pediatric cancer molecularly characterized by arrested myogenesis. The defining genetic driver, PAX3::FOXO1, functions as a chimeric gain-of-function transcription factor. An incomplete understanding of PAX3::FOXO1’s in vivo epigenetic mechanisms has hindered t... |
CRISPR screen decodes SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex assembly
Hanna Schwaemmle et al.
The SWI/SNF (or BAF) complex is an essential chromatin remodeler that regulates DNA accessibility at developmental genes and enhancers. SWI/SNF subunits are among the most frequently mutated genes in cancer and neurodevelopmental disorders. These mutations are often heterozygous loss-of-function alleles, indicating ... |
Clock-dependent chromatin accessibility rhythms regulate circadian transcription
Ye Yuan et al.
Chromatin organization plays a crucial role in gene regulation by controlling the accessibility of DNA to transcription machinery. While significant progress has been made in understanding the regulatory role of clock proteins in circadian rhythms, how chromatin organization affects circadian rhythms remains poorly ... |
PBK/TOPK mediates Ikaros, Aiolos and CTCF displacement from mitotic chromosomes and alters chromatin accessibility at selected C2H2-zinc finger protein binding sites
Andrew Dimond et al.
PBK/TOPK is a mitotic kinase implicated in haematological and non-haematological cancers. Here we show that the key haemopoietic regulators Ikaros and Aiolos require PBK-mediated phosphorylation to dissociate from chromosomes in mitosis. Eviction of Ikaros is rapidly reversed by addition of the PBK-inhibitor OTS514,... |
Widespread impact of nucleosome remodelers on transcription at cis-regulatory elements
Benjamin J. Patty et al.
Nucleosome remodeling complexes and other regulatory factors work in concert to build a chromatin environment that directs the expression of a distinct set of genes in each cell using cis-regulatory elements (CREs), such as promoters and enhancers, that drive transcription of both mRNAs and CRE-associated non-coding... |
High-throughput sequencing of insect specimens with sub-optimal DNA preservation using a practical, plate-based Illumina-compatible Tn5 transposase library preparation method
Cobb L. et all.
Entomological sampling and storage conditions often prioritise efficiency, practicality and conservation of morphological characteristics, and may therefore be suboptimal for DNA preservation. This practice can impact downstream molecular applications, such as the generation of high-throughput genomic libraries, whi... |
EP300/CREBBP acetyltransferase inhibition limits steroid receptor and FOXA1 signaling in prostate cancer cells
Jasmin Huttunen et al.
The androgen receptor (AR) is a primary target for treating prostate cancer (PCa), forming the bedrock of its clinical management. Despite their efficacy, resistance often hampers AR-targeted therapies, necessitating new strategies against therapy-resistant PCa. These resistances involve various mechanisms, includin... |
On the identification of differentially-active transcription factors from ATAC-seq data
Gerbaldo F. et al.
ATAC-seq has emerged as a rich epigenome profiling technique, and is commonly used to identify Transcription Factors (TFs) underlying given phenomena. A number of methods can be used to identify differentially-active TFs through the accessibility of their DNA-binding motif, however little is known on the best approa... |
Cellular reprogramming in vivo initiated by SOX4 pioneer factor activity
Katsuda T.
Tissue damage elicits cell fate switching through a process called metaplasia, but how the starting cell fate is silenced and the new cell fate is activated has not been investigated in animals. In cell culture, pioneer transcription factors mediate “reprogramming” by opening new chromatin sites for expr... |
Improved metagenome assemblies through selective enrichment of bacterial genomic DNA from eukaryotic host genomic DNA using ATAC-seq
Lindsey J Cantin et al.
Genomics can be used to study the complex relationships between hosts and their microbiota. Many bacteria cannot be cultured in the laboratory, making it difficult to obtain adequate amounts of bacterial DNA and to limit host DNA contamination for the construction of metagenome-assembled genomes (MAGs). For example,... |
The ncBAF complex regulates transcription in AML through H3K27ac sensing by BRD9
Klein D.C. et al.
The non-canonical BAF complex (ncBAF) subunit BRD9 is essential for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell viability but has an unclear role in leukemogenesis. Because BRD9 is required for ncBAF complex assembly through its DUF3512 domain, precise bromodomain inhibition is necessary to parse the role of BRD9 as a transcr... |
Revisiting chromatin packaging in mouse sperm
Qiangzong Yin et al.
|
A fast and inexpensive plate-based NGS library preparation method for insect genomics
Lauren Cobb et al.
Entomological sampling and storage conditions often prioritise efficiency, practicality and conservation of morphological characteristics, and may therefore be suboptimal for DNA preservation. This practice can impact downstream molecular applications, such as the generation of high-throughput genomic libraries, whi... |
Therapeutic targeting of EP300/CBP by bromodomain inhibition in hematologic malignancies
Luciano Nicosia et al.
CCS1477 (inobrodib) is a potent, selective EP300/CBP bromodomain inhibitor which induces cell-cycle arrest and differentiation in hematologic malignancy model systems. In myeloid leukemia cells, it promotes rapid eviction of EP300/CBP from an enhancer subset marked by strong MYB occupancy and high H3K27 acetylation,... |
ARID1A governs the silencing of sex-linked transcription during male meiosis in the mouse
Menon D.U. et al.
We present evidence implicating the BAF (BRG1/BRM Associated Factor) chromatin remodeler in meiotic sex chromosome inactivation (MSCI). By immunofluorescence (IF), the putative BAF DNA binding subunit, ARID1A (AT-rich Interaction Domain 1a), appeared enriched on the male sex chromosomes during diplonema of meiosis I... |
Zfp296 knockout enhances chromatin accessibility and induces a uniquestate of pluripotency in embryonic stem cells.
Miyazaki S. et al.
The Zfp296 gene encodes a zinc finger-type protein. Its expression is high in mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) but rapidly decreases following differentiation. Zfp296-knockout (KO) ESCs grew as flat colonies, which were reverted to rounded colonies by exogenous expression of Zfp296. KO ESCs could not form teratomas... |
YAP/BRD4-controlled ROR1 promotes tumor-initiating cells andhyperproliferation in pancreatic cancer.
Yamazaki M. et al.
Tumor-initiating cells are major drivers of chemoresistance and attractive targets for cancer therapy, however, their identity in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and the key molecules underlying their traits remain poorly understood. Here, we show that a cellular subpopulation with partial epithelial-m... |
Analyzing genomic and epigenetic profiles in single cells by hybridtransposase (scGET-seq).
Cittaro D. et al.
scGET-seq simultaneously profiles euchromatin and heterochromatin. scGET-seq exploits the concurrent action of transposase Tn5 and its hybrid form TnH, which targets H3K9me3 domains. Here we present a step-by-step protocol to profile single cells by scGET-seq using a 10× Chromium Controller. We describ... |
A neurodevelopmental epigenetic programme mediated bySMARCD3-DAB1-Reelin signalling is hijacked to promote medulloblastomametastasis.
Zou Han et al.
How abnormal neurodevelopment relates to the tumour aggressiveness of medulloblastoma (MB), the most common type of embryonal tumour, remains elusive. Here we uncover a neurodevelopmental epigenomic programme that is hijacked to induce MB metastatic dissemination. Unsupervised analyses of integrated publicly availab... |
Physiological reprogramming in vivo mediated by Sox4 pioneer factoractivity
Katsuda T. et al.
Tissue damage elicits cell fate switching through a process called metaplasia, but how the starting cell fate is silenced and the new cell fate is activated has not been investigated in animals. In cell culture, pioneer transcription factors mediate “reprogramming” by opening new chromatin sites for expr... |
EBF1 is continuously required for stabilizing local chromatinaccessibility in pro-B cells.
Zolotarev Nikolay et al.
The establishment of de novo chromatin accessibility in lymphoid progenitors requires the "pioneering" function of transcription factor (TF) early B cell factor 1 (EBF1), which binds to naïve chromatin and induces accessibility by recruiting the BRG1 chromatin remodeler subunit. However, it remains unclear whet... |