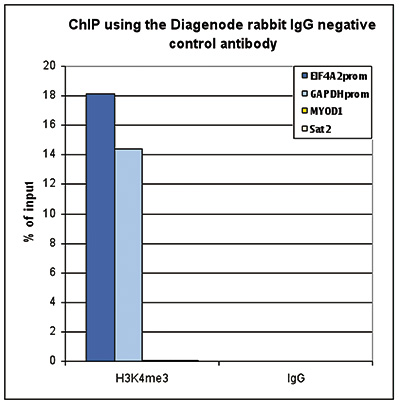
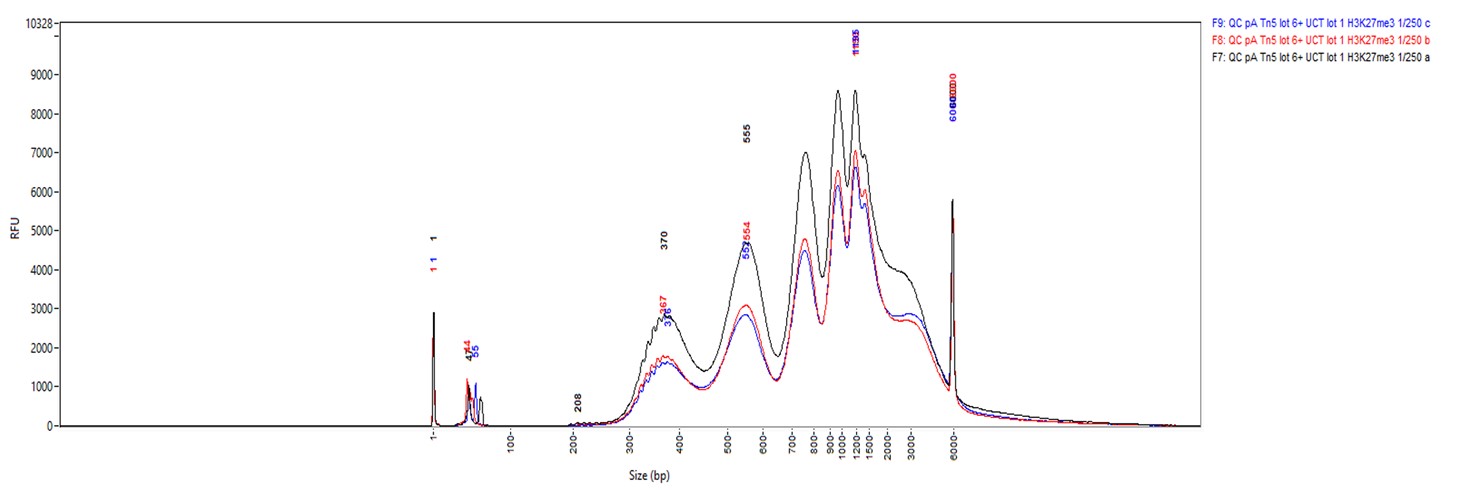
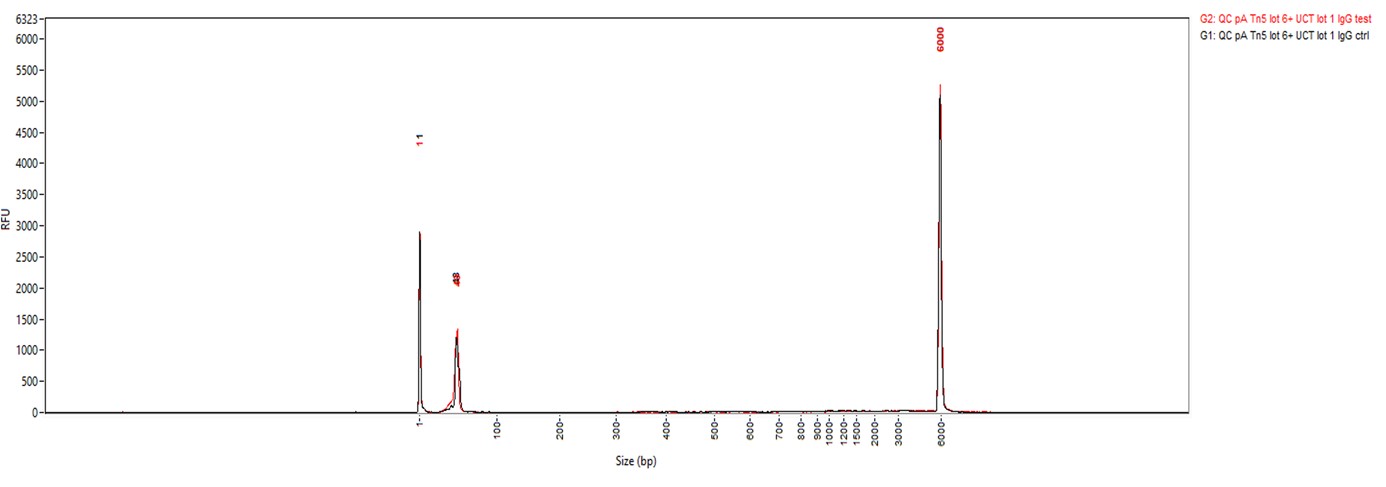
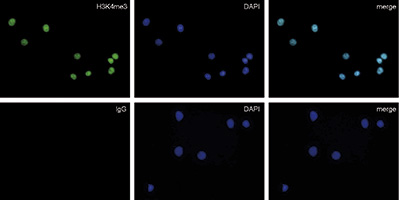
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: Rabbit IgG (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410206 Lot# RIG004A). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Role of MNX1-mediated Histone Modifications and PBX Gene Family in MNX1-induced Leukemogenesis
Malmhäll-Bah, Eric et al.
The t(7;12)(q36;p13) AML subtype in pediatric patients is associated with the upregulation of homeodomain protein MNX1 as the initiating event for leukemogenesis. In this study, we investigated the downstream targets of MNX1 and their relationship to MNX1-induced histone modifications. Using a comprehensive appr... |
Endurance training increases a ubiquitylated form of histone H3 in the skeletal muscle, supporting Notch1 upregulation in an MDM2-dependent manner
Lam, Brian et al.
At the onset of training, each exercise session transiently shifts the distribution of histone post-transcriptional modifications (HPTMs) to activate genes that drive muscle adaptations. The resulting cyclic changes in gene expression promote the acquisition of high oxidative capacities and gains in capillaries. I... |
Overlapping and distinct functions of SPT6, PNUTS, and PCF11 in regulating transcription termination
Fabienne Bejjani et al.
The histone chaperone and transcription elongation factor SPT6 is integral to RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) activity. SPT6 also plays a crucial role in regulating transcription termination, although the mechanisms involved are largely unknown. In an attempt to identify the pathways employed by SPT6 in this regulation, ... |
Accelerated epigenetic aging in Huntington’s disease involves polycomb repressive complex 1
Baptiste Brulé et al.
Loss of epigenetic information during physiological aging compromises cellular identity, leading to de-repression of developmental genes. Here, we assessed the epigenomic landscape of vulnerable neurons in two reference mouse models of Huntington neurodegenerative disease (HD), using cell-type-specific multi-omics, ... |
Dysregulation of Myelination in Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type II of the Human Frontal Lobe
Catharina Donkels et al.
Focal cortical dysplasias (FCDs) are local malformations of the human neocortex and a leading cause of intractable epilepsy. FCDs are classified into different subtypes including FCD IIa and IIb, characterized by a blurred gray-white matter boundary or a transmantle sign indicating abnormal white matter myelination.... |
ETV2/ER71 regulates hematovascular lineage generation and vascularization through an H3K9 demethylase, KDM4A
Min Seong Kim et al.
Highlights
Interaction of ETV2 and KDM4A decreases H3K9 trimethylation on hematovascular genes.
ETV2 and KDM4A cooperatively regulates the expression of hematovascular genes.
Mice lacking endothelial Etv2 and Kdm4a display a severe angiogenic impairment.
... |
Legionella pneumophila modulates macrophage functions through epigenetic reprogramming via the C-type lectin receptor Mincle
Stegmann F. et al.
Legionella pneumophila is a pathogen which can lead to a severe form of pneumonia in humans known as Legionnaires disease after replication in alveolar macrophages. Viable L. pneumophila actively secrete effector molecules to modulate the host’s immune response. Here, we report that L.... |
RNA sequestration in P-bodies sustains myeloid leukaemia
Srikanth Kodali et al.
Post-transcriptional mechanisms are fundamental safeguards of progenitor cell identity and are often dysregulated in cancer. Here, we identified regulators of P-bodies as crucial vulnerabilities in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) through genome-wide CRISPR screens in normal and malignant haematopoietic progenitors. We... |
Innate immune training restores pro-reparative myeloid functions to promote remyelination in the aged central nervous system
Tiwari V. et al.
The reduced ability of the central nervous system to regenerate with increasing age limits functional recovery following demyelinating injury. Previous work has shown that myelin debris can overwhelm the metabolic capacity of microglia, thereby impeding tissue regeneration in aging, but the underlying mechanisms are... |
Master corepressor inactivation through multivalent SLiM-induced polymerization mediated by the oncogene suppressor RAI2
Goradia N. et al.
While the elucidation of regulatory mechanisms of folded proteins is facilitated due to their amenability to high-resolution structural characterization, investigation of these mechanisms in disordered proteins is more challenging due to their structural heterogeneity, which can be captured by a variety of biophysic... |
Master corepressor inactivation through multivalent SLiM-induced polymerization mediated by the oncogene suppressor RAI2
Nishit Goradia et al.
While the elucidation of regulatory mechanisms of folded proteins is facilitated due to their amenability to high-resolution structural characterization, investigation of these mechanisms in disordered proteins is more challenging due to their structural heterogeneity, which can be captured by a variety of biophysic... |
Focal cortical dysplasia type II-dependent maladaptive myelination in the human frontal lobe
Donkels C. et al.
Focal cortical dysplasias (FCDs) are local malformations of the human neocortex and a leading cause of intractable epilepsy. FCDs are classified into different subtypes including FCD IIa and IIb, characterized by a blurred gray-white matter boundary or a transmantle sign indicating abnormal white matter myelination.... |
Identification of a deltaNp63-Dependent Basal-Like ASubtype-Specific Transcribed Enhancer Program (B-STEP) in Aggressive Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.
Wang X. et al.
A major hurdle to the application of precision oncology in pancreatic cancer is the lack of molecular stratification approaches and targeted therapy for defined molecular subtypes. In this work, we sought to gain further insight and identify molecular and epigenetic signatures of the basal-like A pancreatic ductal a... |
Myelodysplastic Syndrome associated TET2 mutations affect NK cellfunction and genome methylation.
Boy M. et al.
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are clonal hematopoietic disorders, representing high risk of progression to acute myeloid leukaemia, and frequently associated to somatic mutations, notably in the epigenetic regulator TET2. Natural Killer (NK) cells play a role in the anti-leukemic immune response via their cytolyti... |
Temporal modification of H3K9/14ac and H3K4me3 histone marksmediates mechano-responsive gene expression during the accommodationprocess in poplar
Ghosh R. et al.
Plants can attenuate their molecular response to repetitive mechanical stimulation as a function of their mechanical history. For instance, a single bending of stem is sufficient to attenuate the gene expression in poplar plants to the subsequent mechanical stimulation, and the state of desensitization can last for ... |
Epigenetic regulation of plastin 3 expression by the macrosatelliteDXZ4 and the transcriptional regulator CHD4.
Strathmann E. A. et al.
Dysregulated Plastin 3 (PLS3) levels associate with a wide range of skeletal and neuromuscular disorders and the most common types of solid and hematopoietic cancer. Most importantly, PLS3 overexpression protects against spinal muscular atrophy. Despite its crucial role in F-actin dynamics in healthy cells and its i... |
Histone Deacetylases 1 and 2 target gene regulatory networks of nephronprogenitors to control nephrogenesis.
Liu Hongbing et al.
Our studies demonstrated the critical role of Histone deacetylases (HDACs) in the regulation of nephrogenesis. To better understand the key pathways regulated by HDAC1/2 in early nephrogenesis, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-Seq) of Hdac1/2 on isolated nephron progenitor cells (NPCs) fro... |
Systems-biology analysis of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-likesynoviocytes implicates cell line-specific transcription factor function.
Ainsworth R. I. et al.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an immune-mediated disease affecting diarthrodial joints that remains an unmet medical need despite improved therapy. This limitation likely reflects the diversity of pathogenic pathways in RA, with individual patients demonstrating variable responses to targeted therapies. Better unders... |
Vitamin C enhances NF-κB-driven epigenomic reprogramming andboosts the immunogenic properties of dendritic cells.
Morante-Palacios O. et al.
Dendritic cells (DCs), the most potent antigen-presenting cells, are necessary for effective activation of naïve T cells. DCs' immunological properties are modulated in response to various stimuli. Active DNA demethylation is crucial for DC differentiation and function. Vitamin C, a known cofactor of ten-eleven... |
Exploration of nuclear body-enhanced sumoylation reveals that PMLrepresses 2-cell features of embryonic stem cells.
Tessier S. et al.
Membrane-less organelles are condensates formed by phase separation whose functions often remain enigmatic. Upon oxidative stress, PML scaffolds Nuclear Bodies (NBs) to regulate senescence or metabolic adaptation. PML NBs recruit many partner proteins, but the actual biochemical mechanism underlying their pleiotropi... |
bESCs from cloned embryos do not retain transcriptomic or epigenetic memory from somatic donor cells.
Navarro M. et al.
Embryonic stem cells (ESC) indefinitely maintain the pluripotent state of the blastocyst epiblast. Stem cells are invaluable for studying development and lineage commitment, and in livestock they constitute a useful tool for genomic improvement and in vitro breeding programs. Although these cells have been recently ... |
Prolonged FOS activity disrupts a global myogenic transcriptionalprogram by altering 3D chromatin architecture in primary muscleprogenitor cells.
Barutcu A Rasim et al.
BACKGROUND: The AP-1 transcription factor, FBJ osteosarcoma oncogene (FOS), is induced in adult muscle satellite cells (SCs) within hours following muscle damage and is required for effective stem cell activation and muscle repair. However, why FOS is rapidly downregulated before SCs enter cell cycle as progenitor c... |
Caffeine intake exerts dual genome-wide effects on hippocampal metabolismand learning-dependent transcription.
Paiva I. et al.
Caffeine is the most widely consumed psychoactive substance in the world. Strikingly, the molecular pathways engaged by its regular consumption remain unclear. We herein addressed the mechanisms associated with habitual (chronic) caffeine consumption in the mouse hippocampus using untargeted orthogonal omics techniq... |
Effects of GSK-J4 on JMJD3 Histone Demethylase in Mouse Prostate Cancer Xenografts
Sanchez A. et al.
Background/aim: Histone methylation status is required to control gene expression. H3K27me3 is an epigenetic tri-methylation modification to histone H3 controlled by the demethylase JMJD3. JMJD3 is dysregulated in a wide range of cancers and has been shown to control the expression of a specific growth-modulato... |
AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR 16 (StARF16) regulates defense gene StNPR1 upon infection with necrotrophic pathogen in potato.
Kalsi HS et al.
We demonstrate a new regulatory mechanism in the jasmonic acid (JA) and salicylic acid (SA) mediated crosstalk in potato defense response, wherein, miR160 target StARF16 (a gene involved in growth and development) binds to the promoter of StNPR1 (a defense gene) and negatively regulates its expression to suppress th... |
The CpG Island-Binding Protein SAMD1 Contributes to anUnfavorable Gene Signature in HepG2 Hepatocellular CarcinomaCells.
Simon C. et al.
The unmethylated CpG island-binding protein SAMD1 is upregulated in many human cancer types, but its cancer-related role has not yet been investigated. Here, we used the hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2 as a cancer model and investigated the cellular and transcriptional roles of SAMD1 using ChIP-Seq and RNA-... |
Loss of KMT2C reprograms the epigenomic landscape in hPSCsresulting in NODAL overexpression and a failure of hemogenic endotheliumspecification.
Maurya Shailendra et al.
Germline or somatic variation in the family of KMT2 lysine methyltransferases have been associated with a variety of congenital disorders and cancers. Notably, -fusions are prevalent in 70\% of infant leukaemias but fail to phenocopy short latency leukaemogenesis in mammalian models, suggesting additional factors ar... |
Effects of GSK-J4 on JMJD3 Histone Demethylase in MouseProstate Cancer Xenografts.
Sanchez A. et al.
BACKGROUND/AIM: Histone methylation status is required to control gene expression. H3K27me3 is an epigenetic tri-methylation modification to histone H3 controlled by the demethylase JMJD3. JMJD3 is dysregulated in a wide range of cancers and has been shown to control the expression of a specific growth-modulatory ge... |
Regulatory interplay between Vav1, Syk and β-catenin occurs in lungcancer cells.
Boudria Rofia et al.
Vav1 exhibits two signal transducing properties as an adaptor protein and a regulator of cytoskeleton organization through its Guanine nucleotide Exchange Factor module. Although the expression of Vav1 is restricted to the hematopoietic lineage, its ectopic expression has been unraveled in a number of solid tumors. ... |
DOT1L O-GlcNAcylation promotes its protein stability andMLL-fusion leukemia cell proliferation.
Song Tanjing et al.
Histone lysine methylation functions at the interface of the extracellular environment and intracellular gene expression. DOT1L is a versatile histone H3K79 methyltransferase with a prominent role in MLL-fusion leukemia, yet little is known about how DOT1L responds to extracellular stimuli. Here, we report that DOT1... |
WT1 regulates HOXB9 gene expression in a bidirectional way.
Schmidt Valentin et al.
The homeoboxB9 (HOXB9) gene is necessary for specification of the anterior-posterior body axis during embryonic development and expressed in various types of cancer. Here we show that the Wilms tumor transcription factor WT1 regulates the HOXB9 gene in a bidirectional manner. Silencing of WT1 activates HOXB9 in Wt1 ... |
Environmental enrichment preserves a young DNA methylation landscape inthe aged mouse hippocampus
Zocher S. et al.
The decline of brain function during aging is associated with epigenetic changes, including DNA methylation. Lifestyle interventions can improve brain function during aging, but their influence on age-related epigenetic changes is unknown. Using genome-wide DNA methylation sequencing, we here show that experiencing ... |
The SAM domain-containing protein 1 (SAMD1) acts as a repressivechromatin regulator at unmethylated CpG islands
Stielow B. et al.
CpG islands (CGIs) are key regulatory DNA elements at most promoters, but how they influence the chromatin status and transcription remains elusive. Here, we identify and characterize SAMD1 (SAM domain-containing protein 1) as an unmethylated CGI-binding protein. SAMD1 has an atypical winged-helix domain that direct... |
USP22 Suppresses Expression in Acute Colitis and Inflammation-AssociatedColorectal Cancer.
Kosinsky, R. L. et al.
As a member of the 11-gene "death-from-cancer" gene expression signature, ubiquitin-specific protease 22 (USP22) has been considered an oncogene in various human malignancies, including colorectal cancer (CRC). We recently identified an unexpected tumor-suppressive function of USP22 in CRC and detected intestinal in... |
The epigenetic landscape in purified myonuclei from fast and slow muscles
Bengtsen, M. et al.
Muscle cells have different phenotypes adapted to different usage and can be grossly divided into fast/glycolytic and slow/oxidative types. While most muscles contain a mixture of such fiber types, we aimed at providing a genome-wide analysis of chromatin environment by ChIP-Seq in two muscle extremes, the almost co... |
Inhibition of HIV-1 gene transcription by KAP1 in myeloid lineage.
Ait-Ammar A. et al.
HIV-1 latency generates reservoirs that prevent viral eradication by the current therapies. To find strategies toward an HIV cure, detailed understandings of the molecular mechanisms underlying establishment and persistence of the reservoirs are needed. The cellular transcription factor KAP1 is known as a potent rep... |
Multi-omic comparison of Alzheimer's variants in human ESC-derivedmicroglia reveals convergence at APOE.
Liu, Tongfei and Zhu, Bing and Liu, Yan and Zhang, Xiaoming and Yin, Junand Li, Xiaoguang and Jiang, LuLin and Hodges, Andrew P and Rosenthal, SaraBrin and Zhou, Lisa and Yancey, Joel and McQuade, Amanda and Blurton-Jones,Mathew and Tanzi, Rudolph E an
Variations in many genes linked to sporadic Alzheimer's disease (AD) show abundant expression in microglia, but relationships among these genes remain largely elusive. Here, we establish isogenic human ESC-derived microglia-like cell lines (hMGLs) harboring AD variants in CD33, INPP5D, SORL1, and TREM2 loci and cura... |
EZH2 and KDM6B Expressions Are Associated with Specific EpigeneticSignatures during EMT in Non Small Cell Lung Carcinomas.
Lachat C. et al.
The role of Epigenetics in Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) has recently emerged. Two epigenetic enzymes with paradoxical roles have previously been associated to EMT, EZH2 (Enhancer of Zeste 2 Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) Subunit), a lysine methyltranserase able to add the H3K27me3 mark, and the hist... |
StE(z)2, a Polycomb group methyltransferase and deposition of H3K27me3 andH3K4me3 regulate the expression of tuberization genes in potato.
Kumar, Amit and Kondhare, Kirtikumar R and Malankar, Nilam N and Banerjee,Anjan K
Polycomb Repressive Complex (PRC) group proteins regulate various developmental processes in plants by repressing the target genes via H3K27 trimethylation, whereas their function is antagonized by Trithorax group proteins-mediated H3K4 trimethylation. Tuberization in potato is widely studied, but the role of histon... |
Digging Deeper into Breast Cancer Epigenetics: Insights from ChemicalInhibition of Histone Acetyltransferase TIP60 .
Idrissou, Mouhamed and Lebert, Andre and Boisnier, Tiphanie and Sanchez,Anna and Houfaf Khoufaf, Fatma Zohra and Penault-Llorca, Frédérique andBignon, Yves-Jean and Bernard-Gallon, Dominique
Breast cancer is often sporadic due to several factors. Among them, the deregulation of epigenetic proteins may be involved. TIP60 or KAT5 is an acetyltransferase that regulates gene transcription through the chromatin structure. This pleiotropic protein acts in several cellular pathways by acetylating proteins. RNA... |
Combined treatment with CBP and BET inhibitors reverses inadvertentactivation of detrimental super enhancer programs in DIPG cells.
Wiese, M and Hamdan, FH and Kubiak, K and Diederichs, C and Gielen, GHand Nussbaumer, G and Carcaboso, AM and Hulleman, E and Johnsen, SA andKramm, CM
Diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas (DIPG) are the most aggressive brain tumors in children with 5-year survival rates of only 2%. About 85% of all DIPG are characterized by a lysine-to-methionine substitution in histone 3, which leads to global H3K27 hypomethylation accompanied by H3K27 hyperacetylation. Hyperacetyla... |
The transcription factor scleraxis differentially regulates gene expressionin tenocytes isolated at different developmental stages.
Paterson, YZ and Evans, N and Kan, S and Cribbs, A and Henson, FMD andGuest, DJ
The transcription factor scleraxis (SCX) is expressed throughout tendon development and plays a key role in directing tendon wound healing. However, little is known regarding its role in fetal or young postnatal tendons, stages in development that are known for their enhanced regenerative capabilities. Here we used ... |
Exploring the virulence gene interactome with CRISPR/dCas9 in the humanmalaria parasite.
Bryant, JM and Baumgarten, S and Dingli, F and Loew, D and Sinha, A andClaës, A and Preiser, PR and Dedon, PC and Scherf, A
Mutually exclusive expression of the var multigene family is key to immune evasion and pathogenesis in Plasmodium falciparum, but few factors have been shown to play a direct role. We adapted a CRISPR-based proteomics approach to identify novel factors associated with var genes in their natural chromatin context. Ca... |
Role of JMJD3 Demethylase and Its Inhibitor GSK-J4 in Regulation of MGMT, TRA2A, RPS6KA2 and U2AF1 Genes in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines.
Sanchez A. et al.
Abstract not availabale |
OxLDL-mediated immunologic memory in endothelial cells.
Sohrabi Y, Lagache SMM, Voges VC, Semo D, Sonntag G, Hanemann I, Kahles F, Waltenberger J, Findeisen HM
Trained innate immunity describes the metabolic reprogramming and long-term proinflammatory activation of innate immune cells in response to different pathogen or damage associated molecular patterns, such as oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL). Here, we have investigated whether the regulatory networks of trai... |
MeCP2 regulates gene expression through recognition of H3K27me3.
Lee, W and Kim, J and Yun, JM and Ohn, T and Gong, Q
MeCP2 plays a multifaceted role in gene expression regulation and chromatin organization. Interaction between MeCP2 and methylated DNA in the regulation of gene expression is well established. However, the widespread distribution of MeCP2 suggests it has additional interactions with chromatin. Here we demonstra... |
AP-1 controls the p11-dependent antidepressant response.
Chottekalapanda RU, Kalik S, Gresack J, Ayala A, Gao M, Wang W, Meller S, Aly A, Schaefer A, Greengard P
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are the most widely prescribed drugs for mood disorders. While the mechanism of SSRI action is still unknown, SSRIs are thought to exert therapeutic effects by elevating extracellular serotonin levels in the brain, and remodel the structural and functional alterations ... |
Attenuated Epigenetic Suppression of Muscle Stem Cell Necroptosis Is Required for Efficient Regeneration of Dystrophic Muscles.
Sreenivasan K, Ianni A, Künne C, Strilic B, Günther S, Perdiguero E, Krüger M, Spuler S, Offermanns S, Gómez-Del Arco P, Redondo JM, Munoz-Canoves P, Kim J, Braun T
Somatic stem cells expand massively during tissue regeneration, which might require control of cell fitness, allowing elimination of non-competitive, potentially harmful cells. How or if such cells are removed to restore organ function is not fully understood. Here, we show that a substantial fraction of muscle stem... |
2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase regulates lipid homeostasis in treatment-resistant prostate cancer.
Blomme A, Ford CA, Mui E, Patel R, Ntala C, Jamieson LE, Planque M, McGregor GH, Peixoto P, Hervouet E, Nixon C, Salji M, Gaughan L, Markert E, Repiscak P, Sumpton D, Blanco GR, Lilla S, Kamphorst JJ, Graham D, Faulds K, MacKay GM, Fendt SM, Zanivan S, Le
Despite the clinical success of Androgen Receptor (AR)-targeted therapies, reactivation of AR signalling remains the main driver of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) progression. In this study, we perform a comprehensive unbiased characterisation of LNCaP cells chronically exposed to multiple AR inhibitors... |
The domesticated transposase ALP2 mediates formation of a novel Polycomb protein complex by direct interaction with MSI1, a core subunit of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2).
Velanis CN, Perera P, Thomson B, de Leau E, Liang SC, Hartwig B, Förderer A, Thornton H, Arede P, Chen J, Webb KM, Gümüs S, De Jaeger G, Page CA, Hancock CN, Spanos C, Rappsilber J, Voigt P, Turck F, Wellmer F, Goodrich J
A large fraction of plant genomes is composed of transposable elements (TE), which provide a potential source of novel genes through "domestication"-the process whereby the proteins encoded by TE diverge in sequence, lose their ability to catalyse transposition and instead acquire novel functions for their hosts. In... |
Aging-regulated anti-apoptotic long non-coding RNA Sarrah augments recovery from acute myocardial infarction.
Trembinski DJ, Bink DI, Theodorou K, Sommer J, Fischer A, van Bergen A, Kuo CC, Costa IG, Schürmann C, Leisegang MS, Brandes RP, Alekseeva T, Brill B, Wietelmann A, Johnson CN, Spring-Connell A, Kaulich M, Werfel S, Engelhardt S, Hirt MN, Yorgan K, Eschen
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) contribute to cardiac (patho)physiology. Aging is the major risk factor for cardiovascular disease with cardiomyocyte apoptosis as one underlying cause. Here, we report the identification of the aging-regulated lncRNA Sarrah (ENSMUST00000140003) that is anti-apoptotic in cardiomyocytes... |
Differential modulation of the androgen receptor for prostate cancer therapy depends on the DNA response element.
Kregel S, Bagamasbad P, He S, LaPensee E, Raji Y, Brogley M, Chinnaiyan A, Cieslik M, Robins DM
Androgen receptor (AR) action is a hallmark of prostate cancer (PCa) with androgen deprivation being standard therapy. Yet, resistance arises and aberrant AR signaling promotes disease. We sought compounds that inhibited genes driving cancer but not normal growth and hypothesized that genes with consensus androgen r... |
LXR Activation Induces a Proinflammatory Trained Innate Immunity-Phenotype in Human Monocytes
Sohrabi Yahya, Sonntag Glenn V. H., Braun Laura C., Lagache Sina M. M., Liebmann Marie, Klotz Luisa, Godfrey Rinesh, Kahles Florian, Waltenberger Johannes, Findeisen Hannes M.
The concept of trained innate immunity describes a long-term proinflammatory memory in innate immune cells. Trained innate immunity is regulated through reprogramming of cellular metabolic pathways including cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis. Here, we have analyzed the role of Liver X Receptor (LXR), a key regula... |
HDAC3 functions as a positive regulator in Notch signal transduction.
Ferrante F, Giaimo BD, Bartkuhn M, Zimmermann T, Close V, Mertens D, Nist A, Stiewe T, Meier-Soelch J, Kracht M, Just S, Klöble P, Oswald F, Borggrefe T
Aberrant Notch signaling plays a pivotal role in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Amplitude and duration of the Notch response is controlled by ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation of the Notch1 intracellular domain (NICD1), a hallmark of the leukemogenic pro... |
Transferrin Receptor 1 Regulates Thermogenic Capacity and Cell Fate in Brown/Beige Adipocytes
Jin Li, Xiaohan Pan, Guihua Pan, Zijun Song, Yao He, Susu Zhang, Xueru Ye, Xiang Yang, Enjun Xie, Xinhui Wang, Xudong Mai, Xiangju Yin, Biyao Tang, Xuan Shu, Pengyu Chen, Xiaoshuang Dai, Ye Tian, Liheng Yao, Mulan Han, Guohuan Xu, Huijie Zhang, Jia Sun, H
Iron homeostasis is essential for maintaining cellular function in a wide range of cell types. However, whether iron affects the thermogenic properties of adipocytes is currently unknown. Using integrative analyses of multi-omics data, transferrin receptor 1 (Tfr1) is identified as a candidate for regulating thermog... |
Recombination may occur in the absence of transcription in the immunoglobulin heavy chain recombination centre.
Oudinet C, Braikia FZ, Dauba A, Khamlichi AA
Developing B cells undergo V(D)J recombination to generate a vast repertoire of Ig molecules. V(D)J recombination is initiated by the RAG1/RAG2 complex in recombination centres (RCs), where gene segments become accessible to the complex. Whether transcription is the causal factor of accessibility or whether it is a ... |
Targeting Macrophage Histone H3 Modification as a Leishmania Strategy to Dampen the NF-κB/NLRP3-Mediated Inflammatory Response.
Lecoeur H, Prina E, Rosazza T, Kokou K, N'Diaye P, Aulner N, Varet H, Bussotti G, Xing Y, Milon G, Weil R, Meng G, Späth GF
Aberrant macrophage activation during intracellular infection generates immunopathologies that can cause severe human morbidity. A better understanding of immune subversion strategies and macrophage phenotypic and functional responses is necessary to design host-directed intervention strategies. Here, we uncover a f... |
Inhibition of histone deacetylation rescues phenotype in a mouse model of Birk-Barel intellectual disability syndrome.
Cooper A, Butto T, Hammer N, Jagannath S, Fend-Guella DL, Akhtar J, Radyushkin K, Lesage F, Winter J, Strand S, Roeper J, Zechner U, Schweiger S
Mutations in the actively expressed, maternal allele of the imprinted KCNK9 gene cause Birk-Barel intellectual disability syndrome (BBIDS). Using a BBIDS mouse model, we identify here a partial rescue of the BBIDS-like behavioral and neuronal phenotypes mediated via residual expression from the paternal Kcnk9 (Kcnk9... |
TIP60/P400/H4K12ac Plays a Role as a Heterochromatin Back-up Skeleton inBreast Cancer.
Idrissou, Mouhamed and Boisnier, Tiphanie and Sanchez, Anna and Khoufaf,Fatma Zohra Houfaf and Penault-Llorca, Frederique and Bignon, Yves-Jean andBernard-Gallon, Dominique
BACKGROUND/AIM: In breast cancer, initiation of carcinogenesis leads to epigenetic dysregulation, which can lead for example to the loss of the heterochromatin skeleton SUV39H1/H3K9me3/HP1 or the supposed secondary skeleton TIP60/P400/H4K12ac/BRD (2/4), which allows the maintenance of chromatin integrity and plastic... |
The Inhibition of the Histone Methyltransferase EZH2 by DZNEP or SiRNA Demonstrates Its Involvement in MGMT, TRA2A, RPS6KA2, and U2AF1 Gene Regulation in Prostate Cancer.
El Ouardi D, Idrissou M, Sanchez A, Penault-Llorca F, Bignon YJ, Guy L, Bernard-Gallon D
In France, prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men (Bray et al., 2018). Previously, our team has reported the involvement of epigenetic factors in prostate cancer (Ngollo et al., 2014, 2017). The histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) is a repressive mark that induces chromatin compaction and thus ge... |
Unraveling the role of H3K4 trimethylation and lncRNA HOTAIR in SATB1 and DUSP4-dependent survival of virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis in macrophages
Subuddhi Arijita, Kumar Manish, Majumder Debayan, Sarkar Arijita, Ghosh Zhumur, Vasudevan Madavan, Kundu Manikuntala, Basu Joyoti
The modification of chromatin influences host transcriptional programs during bacterial infection, at times skewing the balance in favor of pathogen survival. To test the role of chromatin modifications during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, we analysed genome-wide deposition of H3K4me3 marks in macrophages in... |
Functionally Annotating Regulatory Elements in the Equine Genome Using Histone Mark ChIP-Seq.
Kingsley NB, Kern C, Creppe C, Hales EN, Zhou H, Kalbfleisch TS, MacLeod JN, Petersen JL, Finno CJ, Bellone RR
One of the primary aims of the Functional Annotation of ANimal Genomes (FAANG) initiative is to characterize tissue-specific regulation within animal genomes. To this end, we used chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-Seq) to map four histone modifications (H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27ac, and H3K27me... |
Trained immunity modulates inflammation-induced fibrosis.
Jeljeli M, Riccio LGC, Doridot L, Chêne C, Nicco C, Chouzenoux S, Deletang Q, Allanore Y, Kavian N, Batteux F
Chronic inflammation and fibrosis can result from inappropriately activated immune responses that are mediated by macrophages. Macrophages can acquire memory-like characteristics in response to antigen exposure. Here, we show the effect of BCG or low-dose LPS stimulation on macrophage phenotype, cytokine production,... |
SIRT1/2 orchestrate acquisition of DNA methylation and loss of histone H3 activating marks to prevent premature activation of inflammatory genes in macrophages.
Li T, Garcia-Gomez A, Morante-Palacios O, Ciudad L, Özkaramehmet S, Van Dijck E, Rodríguez-Ubreva J, Vaquero A, Ballestar E
Sirtuins 1 and 2 (SIRT1/2) are two NAD-dependent deacetylases with major roles in inflammation. In addition to deacetylating histones and other proteins, SIRT1/2-mediated regulation is coupled with other epigenetic enzymes. Here, we investigate the links between SIRT1/2 activity and DNA methylation in macrophage dif... |
USP22-dependent HSP90AB1 expression promotes resistance to HSP90 inhibition in mammary and colorectal cancer.
Kosinsky RL, Helms M, Zerche M, Wohn L, Dyas A, Prokakis E, Kazerouni ZB, Bedi U, Wegwitz F, Johnsen SA
As a member of the 11-gene "death-from-cancer" gene expression signature, overexpression of the Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 22 (USP22) was associated with poor prognosis in various human malignancies. To investigate the function of USP22 in cancer development and progression, we sought to detect common USP22-depende... |
Autoregulation of RCO by Low-Affinity Binding Modulates Cytokinin Action and Shapes Leaf Diversity.
Hajheidari M, Wang Y, Bhatia N, Vuolo F, Franco-Zorrilla JM, Karady M, Mentink RA, Wu A, Oluwatobi BR, Müller B, Dello Ioio R, Laurent S, Ljung K, Huijser P, Gan X, Tsiantis M
Mechanisms through which the evolution of gene regulation causes morphological diversity are largely unclear. The tremendous shape variation among plant leaves offers attractive opportunities to address this question. In cruciferous plants, the REDUCED COMPLEXITY (RCO) homeodomain protein evolved via gene duplicatio... |
MicroRNAs Establish the Right-Handed Dominance of the Heart Laterality Pathway in Vertebrates
Rago Luciano, Castroviejo Noemi, Fazilaty Hassan, Garcia-Asencio Francisco, Ocaña Oscar H., Galcerán Joan, Nieto M. Angela
Despite their external bilateral symmetry, vertebrates have internal left/right (L/R) asymmetries required for optimal organ function. BMP-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in the lateral plate mesoderm (LPM) triggers L/R asymmetric cell movements toward the midline, higher from the right, which are... |
Methionine metabolism in health and cancer: a nexus of diet and precisionmedicine.
Sanderson, Sydney M and Gao, Xia and Dai, Ziwei and Locasale, Jason W
Methionine uptake and metabolism is involved in a host of cellular functions including methylation reactions, redox maintenance, polyamine synthesis and coupling to folate metabolism, thus coordinating nucleotide and redox status. Each of these functions has been shown in many contexts to be relevant for cancer path... |
Free heme regulates placenta growth factor through NRF2-antioxidant response signaling.
Kapetanaki MG, Gbotosho OT, Sharma D, Weidert F, Ofori-Acquah SF, Kato GJ
Free heme activates erythroblasts to express and secrete Placenta Growth Factor (PlGF), an angiogenic peptide of the VEGF family. High circulating levels of PlGF have been associated in experimental animals and in patients with sickle cell disease with echocardiographic markers of pulmonary hypertension, a life-limi... |
Elevated cyclic-AMP represses expression of exchange protein activated by cAMP (EPAC1) by inhibiting YAP-TEAD activity and HDAC-mediated histone deacetylation.
Ebrahimighaei R, McNeill MC, Smith SA, Wray JP, Ford KL, Newby AC, Bond M
Ligand-induced activation of Exchange Protein Activated by cAMP-1 (EPAC1) is implicated in numerous physiological and pathological processes, including cardiac fibrosis where changes in EPAC1 expression have been detected. However, little is known about how EPAC1 expression is regulated. Therefore, we investigated r... |
Guidelines for optimized gene knockout using CRISPR/Cas9
Campenhout CV et al.
CRISPR/Cas9 technology has evolved as the most powerful approach to generate genetic models both for fundamental and preclinical research. Despite its apparent simplicity, the outcome of a genome-editing experiment can be substantially impacted by technical parameters and biological considerations. Here, we present ... |
Modulation of Gene Silencing by Cdc7p via H4 K16 Acetylation and Phosphorylation of Chromatin Assembly Factor CAF-1 in .
Young TJ, Cui Y, Irudayaraj J, Kirchmaier AL
CAF-1 is an evolutionarily conserved H3/H4 histone chaperone that plays a key role in replication-coupled chromatin assembly and is targeted to the replication fork via interactions with PCNA, which, if disrupted, leads to epigenetic defects. In , when the silent mating-type locus contains point mutations within the... |
Hyper-Editing of Cell-Cycle Regulatory and Tumor Suppressor RNA Promotes Malignant Progenitor Propagation.
Jiang Q, Isquith J, Zipeto MA, Diep RH, Pham J, Delos Santos N, Reynoso E, Chau J, Leu H, Lazzari E, Melese E, Ma W, Fang R, Minden M, Morris S, Ren B, Pineda G, Holm F, Jamieson C
Adenosine deaminase associated with RNA1 (ADAR1) deregulation contributes to therapeutic resistance in many malignancies. Here we show that ADAR1-induced hyper-editing in normal human hematopoietic progenitors impairs miR-26a maturation, which represses CDKN1A expression indirectly via EZH2, thereby accelerating cel... |
DeltaNp63-dependent super enhancers define molecular identity in pancreatic cancer by an interconnected transcription factor network.
Hamdan FH, Johnsen SA
Molecular subtyping of cancer offers tremendous promise for the optimization of a precision oncology approach to anticancer therapy. Recent advances in pancreatic cancer research uncovered various molecular subtypes with tumors expressing a squamous/basal-like gene expression signature displaying a worse prognosis. ... |
Deletion of an intronic HIF-2α binding site suppresses hypoxia-induced WT1 expression.
Krueger K, Catanese L, Sciesielski LK, Kirschner KM, Scholz H
Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) play a key role in the adaptation to low oxygen by interacting with hypoxia response elements (HREs) in the genome. Cellular levels of the HIF-2α transcription factor subunit influence the histopathology and clinical outcome of neuroblastoma, a malignant childhood tumor of the ... |
TIP60: an actor in acetylation of H3K4 and tumor development in breast cancer.
Judes G, Dubois L, Rifaï K, Idrissou M, Mishellany F, Pajon A, Besse S, Daures M, Degoul F, Bignon YJ, Penault-Llorca F, Bernard-Gallon D
AIM: The acetyltransferase TIP60 is reported to be downregulated in several cancers, in particular breast cancer, but the molecular mechanisms resulting from its alteration are still unclear. MATERIALS & METHODS: In breast tumors, H3K4ac enrichment and its link with TIP60 were evaluated by chromatin immunoprecip... |
Differential Methylation of H3K79 Reveals DOT1L Target Genes and Function in the Cerebellum In Vivo.
Bovio PP, Franz H, Heidrich S, Rauleac T, Kilpert F, Manke T, Vogel T
The disruptor of telomeric silencing 1-like (DOT1L) mediates methylation of histone H3 at position lysine 79 (H3K79). Conditional knockout of Dot1l in mouse cerebellar granule cells (Dot1l-cKO) led to a smaller external granular layer with fewer precursors of granule neurons. Dot1l-cKO mice had impaired proliferatio... |
Differential Methylation of H3K79 Reveals DOT1L Target Genes and Function in the Cerebellum In Vivo.
Bovio PP, Franz H, Heidrich S, Rauleac T, Kilpert F, Manke T, Vogel T
The disruptor of telomeric silencing 1-like (DOT1L) mediates methylation of histone H3 at position lysine 79 (H3K79). Conditional knockout of Dot1l in mouse cerebellar granule cells (Dot1l-cKO) led to a smaller external granular layer with fewer precursors of granule neurons. Dot1l-cKO mice had impaired proliferatio... |
Cellular localization of the cell cycle inhibitor Cdkn1c controls growth arrest of adult skeletal muscle stem cells
Despoina Mademtzoglou, Yoko Asakura, Matthew J Borok, Sonia Alonso-Martin, Philippos Mourikis, Yusaku Kodaka, Amrudha Mohan, Atsushi Asakura, Frederic Relaix
Adult skeletal muscle maintenance and regeneration depend on efficient muscle stem cell (MuSC) functions. The mechanisms coordinating cell cycle with activation, renewal, and differentiation of MuSCs remain poorly understood. Here, we investigated how adult MuSCs are regulated by CDKN1c (p57kip2), a cyclin-dependent... |
Cellular localization of the cell cycle inhibitor Cdkn1c controls growth arrest of adult skeletal muscle stem cells
Despoina Mademtzoglou, Yoko Asakura, Matthew J Borok, Sonia Alonso-Martin, Philippos Mourikis, Yusaku Kodaka, Amrudha Mohan, Atsushi Asakura Is a corresponding author , Frederic Relaix
Adult skeletal muscle maintenance and regeneration depend on efficient muscle stem cell (MuSC) functions. The mechanisms coordinating cell cycle with activation, renewal, and differentiation of MuSCs remain poorly understood. Here, we investigated how adult MuSCs are regulated by CDKN1c (p57kip2), a cyclin-dependent... |
Loss of SETDB1 decompacts the inactive X chromosome in part through reactivation of an enhancer in the IL1RAPL1 gene.
Sun Z, Chadwick BP
BACKGROUND: The product of dosage compensation in female mammals is the inactive X chromosome (Xi). Xi facultative heterochromatin is organized into two different types, one of which is defined by histone H3 trimethylated at lysine 9 (H3K9me3). The rationale for this study was to assess SET domain bifurcated 1 (SETD... |
The Alzheimer's disease-associated TREM2 gene is regulated by p53 tumor suppressor protein.
Zajkowicz A, Gdowicz-Kłosok A, Krześniak M, Janus P, Łasut B, Rusin M
TREM2 mutations evoke neurodegenerative disorders, and recently genetic variants of this gene were correlated to increased risk of Alzheimer's disease. The signaling cascade originating from the TREM2 membrane receptor includes its binding partner TYROBP, BLNK adapter protein, and SYK kinase, which can be activated ... |
HIV-2/SIV viral protein X counteracts HUSH repressor complex.
Ghina Chougui, Soundasse Munir-Matloob, Roy Matkovic, Michaël M Martin, Marina Morel, Hichem Lahouassa, Marjorie Leduc, Bertha Cecilia Ramirez, Lucie Etienne and Florence Margottin-Goguet
To evade host immune defences, human immunodeficiency viruses 1 and 2 (HIV-1 and HIV-2) have evolved auxiliary proteins that target cell restriction factors. Viral protein X (Vpx) from the HIV-2/SIVsmm lineage enhances viral infection by antagonizing SAMHD1 (refs ), but this antagonism is not sufficient to explain a... |
Atopic asthma after rhinovirus-induced wheezing is associated with DNA methylation change in the SMAD3 gene promoter.
Lund RJ, Osmala M, Malonzo M, Lukkarinen M, Leino A, Salmi J, Vuorikoski S, Turunen R, Vuorinen T, Akdis C, Lähdesmäki H, Lahesmaa R, Jartti T
Children with rhinovirus-induced severe early wheezing have an increased risk of developing asthma later in life. The exact molecular mechanisms for this association are still mostly unknown. To identify potential changes in the transcriptional and epigenetic regulation in rhinovirus-associated atopic or nonatopic a... |
SIRT1-dependent epigenetic regulation of H3 and H4 histone acetylation in human breast cancer
Khaldoun Rifaï et al.
Breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed malignancy in women worldwide. It is well established that the complexity of carcinogenesis involves profound epigenetic deregulations that contribute to the tumorigenesis process. Deregulated H3 and H4 acetylated histone marks are amongst those alterations. Sirtuin-1 (... |
Cyclin G and the Polycomb Repressive complexes PRC1 and PR-DUB cooperate for developmental stability
Delphine Dardalhon-Cume´nal1, Jerome Deraze, Camille A. Dupont, Valerie Ribeiro, Anne Coleno-Costes, Juliette Pouch, Stephane Le Crom, Helène Thomassin,Vincent Debat, Neel B. Randsholt1, Frederique Peronnet
In Drosophila, ubiquitous expression of a short Cyclin G isoform generates extreme developmental noise estimated by fluctuating asymmetry (FA), providing a model to tackle developmental stability. This transcriptional cyclin interacts with chromatin regulators of the Enhancer of Trithorax and Polycomb (ETP) and Poly... |
Epigenetic regulation of vascular NADPH oxidase expression and reactive oxygen species production by histone deacetylase-dependent mechanisms in experimental diabetes.
Manea SA, Antonescu ML, Fenyo IM, Raicu M, Simionescu M, Manea A
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by up-regulated NADPH oxidase (Nox) contribute to structural-functional alterations of the vascular wall in diabetes. Epigenetic mechanisms, such as histone acetylation, emerged as important regulators of gene expression in cardiovascular disorders. Since their role in diabete... |
Estrogen receptor α dependent regulation of estrogen related receptor β and its role in cell cycle in breast cancer.
Madhu Krishna B, Chaudhary S, Mishra DR, Naik SK, Suklabaidya S, Adhya AK, Mishra SK
BACKGROUND: Breast cancer (BC) is highly heterogeneous with ~ 60-70% of estrogen receptor positive BC patient's response to anti-hormone therapy. Estrogen receptors (ERs) play an important role in breast cancer progression and treatment. Estrogen related receptors (ERRs) are a group of nuclear receptors which... |
Reciprocal signalling by Notch-Collagen V-CALCR retains muscle stem cells in their niche.
Baghdadi MB, Castel D, Machado L, Fukada SI, Birk DE, Relaix F, Tajbakhsh S, Mourikis P
The cell microenvironment, which is critical for stem cell maintenance, contains both cellular and non-cellular components, including secreted growth factors and the extracellular matrix. Although Notch and other signalling pathways have previously been reported to regulate quiescence of stem cells, the co... |
A new metabolic gene signature in prostate cancer regulated by JMJD3 and EZH2.
Daures M, Idrissou M, Judes G, Rifaï K, Penault-Llorca F, Bignon YJ, Guy L, Bernard-Gallon D
Histone methylation is essential for gene expression control. Trimethylated lysine 27 of histone 3 (H3K27me3) is controlled by the balance between the activities of JMJD3 demethylase and EZH2 methyltransferase. This epigenetic mark has been shown to be deregulated in prostate cancer, and evidence shows H3K27me3 enri... |
A Specific PfEMP1 Is Expressed in P. falciparum Sporozoites and Plays a Role in Hepatocyte Infection.
Zanghì G, Vembar SS, Baumgarten S, Ding S, Guizetti J, Bryant JM, Mattei D, Jensen ATR, Rénia L, Goh YS, Sauerwein R, Hermsen CC, Franetich JF, Bordessoulles M, Silvie O, Soulard V, Scatton O, Chen P, Mecheri S, Mazier D, Scherf A
Heterochromatin plays a central role in the process of immune evasion, pathogenesis, and transmission of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum during blood stage infection. Here, we use ChIP sequencing to demonstrate that sporozoites from mosquito salivary glands expand heterochromatin at subtelomeric regions t... |
Epigenetic modifiers promote mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative metabolism leading to enhanced differentiation of neuroprogenitor cells.
Martine Uittenbogaard, Christine A. Brantner, Anne Chiaramello1
During neural development, epigenetic modulation of chromatin acetylation is part of a dynamic, sequential and critical process to steer the fate of multipotent neural progenitors toward a specific lineage. Pan-HDAC inhibitors (HDCis) trigger neuronal differentiation by generating an "acetylation" signature and prom... |
The CUE1 domain of the SNF2-like chromatin remodeler SMARCAD1 mediates its association with KRAB-associated protein 1 (KAP1) and KAP1 target genes.
Ding D, Bergmaier P, Sachs P, Klangwart M, Rückert T, Bartels N, Demmers J, Dekker M, Poot RA, Mermoud JE
Chromatin in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) differs markedly from that in somatic cells, with ESCs exhibiting a more open chromatin configuration. Accordingly, ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes are important regulators of ESC homeostasis. Depletion of the remodeler SMARCAD1, an ATPase of the SNF2 family, has... |
MLL2 conveys transcription-independent H3K4 trimethylation in oocytes
Hanna C.W. et al.
Histone 3 K4 trimethylation (depositing H3K4me3 marks) is typically associated with active promoters yet paradoxically occurs at untranscribed domains. Research to delineate the mechanisms of targeting H3K4 methyltransferases is ongoing. The oocyte provides an attractive system to investigate these mechanisms, becau... |
EZH2 Histone Methyltransferase and JMJD3 Histone Demethylase Implications in Prostate Cancer
Idrissou M. et al.
|
Distinguishing States of Arrest: Genome-Wide Descriptions of Cellular Quiescence Using ChIP-Seq and RNA-Seq Analysis.
Srivastava S. et al.
Regenerative potential in adult stem cells is closely associated with the establishment of-and exit from-a temporary state of quiescence. Emerging evidence not only provides a rationale for the link between lineage determination programs and cell cycle regulation but also highlights the understanding of quiescence a... |
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) in Mouse T-cell Lines
Giaimo B.D. et al.
Signaling pathways regulate gene expression programs via the modulation of the chromatin structure at different levels, such as by post-translational modifications (PTMs) of histone tails, the exchange of canonical histones with histone variants, and nucleosome eviction. Such regulation requires the binding of signa... |
Neuropeptide Y expression marks partially differentiated β cells in mice and humans
Rodnoi P. et al.
β Cells are formed in embryonic life by differentiation of endocrine progenitors and expand by replication during neonatal life, followed by transition into functional maturity. In this study, we addressed the potential contribution of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in pancreatic β cell development and maturation. W... |
Histone deacetylase inhibitors potentiate photodynamic therapy in colon cancer cells marked by chromatin-mediated epigenetic regulation of CDKN1A
Halaburková A. et al.
Background
Hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy (HY-PDT) has recently captured increased attention as an alternative minimally invasive anticancer treatment, although cancer cells may acquire resistance. Therefore, combination treatments may be necessary to enhance HY-PDT efficacy. Histone deacetylase inhibi... |
Characterization of the Polycomb-Group Mark H3K27me3 in Unicellular Algae
Mikulski P. et al.
Polycomb Group (PcG) proteins mediate chromatin repression in plants and animals by catalyzing H3K27 methylation and H2AK118/119 mono-ubiquitination through the activity of the Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) and PRC1, respectively. PcG proteins were extensively studied in higher plants, but their function and ... |
DNA breaks and chromatin structural changes enhance the transcription of Autoimmune Regulator target genes
Guha M. et al.
The autoimmune regulator (AIRE) protein is the key factor in thymic negative selection of autoreactive T cells by promoting the ectopic expression of tissue-specific genes in the thymic medullary epithelium. Mutations in AIRE cause a monogenic autoimmune disease called autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectod... |
Global analysis of H3K27me3 as an epigenetic marker in prostate cancer progression
Ngollo M. et al.
BACKGROUND:
H3K27me3 histone marks shape the inhibition of gene transcription. In prostate cancer, the deregulation of H3K27me3 marks might play a role in prostate tumor progression.
METHODS:
We investigated genome-wide H3K27me3 histone methylation profile using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and 2X400K p... |
Trimethylation and Acetylation of β-Catenin at Lysine 49 Represent Key Elements in ESC Pluripotency
Hoffmeyer K. et al.
Wnt/β-catenin signaling is required for embryonic stem cell (ESC) pluripotency by inducing mesodermal differentiation and inhibiting neuronal differentiation; however, how β-catenin counter-regulates these differentiation pathways is unknown. Here, we show that lysine 49 (K49) of β-catenin is trimethy... |
Suppression of RUNX1/ETO oncogenic activity by a small molecule inhibitor of tetramerization
Schanda J. et al.
RUNX1/ETO, the product of the t(8;21) chromosomal translocation, is required for the onset and maintenance of one of the most common forms of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). RUNX1/ETO has a modular structure and, besides the DN A-binding domain (Runt), contains four evolutionary conserved functional domains named nerv... |
Snail2 and Zeb2 repress P-Cadherin to define embryonic territories in the chick embryo
Acloque H. et al.
Snail and Zeb transcription factors induce epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in embryonic and adult tissues by direct repression of E-Cadherin transcription. The repression of E-Cadherin transcription by the EMT inducers Snail1 and Zeb2 plays a fundamental role in defining embryonic territories in the mouse... |
Phenotypic Plasticity through Transcriptional Regulation of the Evolutionary Hotspot Gene tan in Drosophila melanogaster
Gibert JM et al.
Phenotypic plasticity is the ability of a given genotype to produce different phenotypes in response to distinct environmental conditions. Phenotypic plasticity can be adaptive. Furthermore, it is thought to facilitate evolution. Although phenotypic plasticity is a widespread phenomenon, its molecular mechanisms are... |
MEF2C protects bone marrow B-lymphoid progenitors during stress haematopoiesis
Wang W et al.
DNA double strand break (DSB) repair is critical for generation of B-cell receptors, which are pre-requisite for B-cell progenitor survival. However, the transcription factors that promote DSB repair in B cells are not known. Here we show that MEF2C enhances the expression of DNA repair and recombination factors in ... |
Role of CREB on heme oxygenase-1 induction in adrenal cells: involvement of the PI3K pathway
Astort F et al.
In addition to the well-known function of ACTH as the main regulator of adrenal steroidogenesis, we have previously demonstrated its effect on the transcriptional stimulation of HO-1 expression, a component of the cellular antioxidant defense system. In agreement, we hereby demonstrate that, in adrenocortical Y1 cel... |
H3K4 acetylation, H3K9 acetylation and H3K27 methylation in breast tumor molecular subtypes
Judes G et al.
AIM:
Here, we investigated how the St Gallen breast molecular subtypes displayed distinct histone H3 profiles.
PATIENTS & METHODS:
192 breast tumors divided into five St Gallen molecular subtypes (luminal A, luminal B HER2-, luminal B HER2+, HER2+ and basal-like) were evaluated for their histone H3 modifica... |
Epigenetic Modifications with DZNep, NaBu and SAHA in Luminal and Mesenchymal-like Breast Cancer Subtype Cells
Dagdemir A et al.
BACKGROUND/AIM:
Numerous studies have shown that breast cancer and epigenetic mechanisms have a very powerful interactive relation. The MCF7 cell line, representative of luminal subtype and the MDA-MB 231 cell line representative of mesenchymal-like subtype were treated respectively with a Histone Methyl Transferas... |
Expression of the Parkinson's Disease-Associated Gene Alpha-Synuclein is Regulated by the Neuronal Cell Fate Determinant TRIM32
Pavlou MA et al.
Alpha-synuclein is an abundant neuronal protein which has been associated with physiological processes like synaptic function, neurogenesis, and neuronal differentiation but also with pathological neurodegeneration. Indeed, alpha-synuclein (snca) is one of the major genes implicated in Parkinson's disease (PD). Howe... |
PHF13 is a molecular reader and transcriptional co-regulator of H3K4me2/3
Chung HR et al.
PHF13 is a chromatin affiliated protein with a functional role in differentiation, cell division, DNA damage response and higher chromatin order. To gain insight into PHF13's ability to modulate these processes, we elucidate the mechanisms targeting PHF13 to chromatin, its genome wide localization and its molecular ... |
mTOR transcriptionally and post-transcriptionally regulates Npm1 gene expression to contribute to enhanced proliferation in cells with Pten inactivation
Boudra R et al.
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) plays essential roles in the regulation of growth-related processes such as protein synthesis, cell sizing and metabolism in both normal and pathological growing conditions. These functions of mTOR are thought to be largely a consequence of its cytoplasmic activity in regulat... |
EZH2 is overexpressed in adrenocortical carcinoma and is associated with disease progression.
Drelon C et al.
Adrenal Cortex Carcinoma (ACC) is an aggressive tumour with poor prognosis. Common alterations in patients include constitutive WNT/β-catenin signalling and overexpression of the growth factor IGF2. However, the combination of both alterations in transgenic mice is not sufficient to trigger malignant tumour pro... |
Kaiso mediates human ICR1 methylation maintenance and H19 transcriptional fine regulation
Bohne F et al.
Background
Genomic imprinting evolved in a common ancestor to marsupials and eutherian mammals and ensured the transcription of developmentally important genes from defined parental alleles. The regulation of imprinted genes is often mediated by differentially methylated imprinting control regions (ICRs) that are... |
EZH2 regulates neuroepithelium structure and neuroblast proliferation by repressing p21
Akizu N, García MA, Estarás C, Fueyo R, Badosa C, de la Cruz X, Martínez-Balbás MA
The function of EZH2 as a transcription repressor is well characterized. However, its role during vertebrate development is still poorly understood, particularly in neurogenesis. Here, we uncover the role of EZH2 in controlling the integrity of the neural tube and allowing proper progenitor proliferation. We demonst... |
Active and Repressive Chromatin-Associated Proteome after MPA Treatment and the Role of Midkine in Epithelial Monolayer Permeability
Khan N, Lenz C, Binder L, Pantakani DVK, Asif AR
Mycophenolic acid (MPA) is prescribed to maintain allografts in organ-transplanted patients. However, gastrointestinal (GI) complications, particularly diarrhea, are frequently observed as a side effect following MPA therapy. We recently reported that MPA altered the tight junction (TJ)-mediated barrier function in ... |
Overexpression of caspase 7 is ERα dependent to affect proliferation and cell growth in breast cancer cells by targeting p21(Cip)
Chaudhary S, Madhukrishna B, Adhya AK, Keshari S, Mishra SK
Caspase 7 (CASP7) expression has important function during cell cycle progression and cell growth in certain cancer cells and is also involved in the development and differentiation of dental tissues. However, the function of CASP7 in breast cancer cells is unclear. The aim of this study was to analyze the expressio... |
Comprehensive genome and epigenome characterization of CHO cells in response to evolutionary pressures and over time
Feichtinger J, Hernández I, Fischer C, Hanscho M, Auer N, Hackl M, Jadhav V, Baumann M, Krempl PM, Schmidl C, Farlik M, Schuster M, Merkel A, Sommer A, Heath S, Rico D, Bock C, Thallinger GG, Borth N
The most striking characteristic of CHO cells is their adaptability, which enables efficient production of proteins as well as growth under a variety of culture conditions, but also results in genomic and phenotypic instability. To investigate the relative contribution of genomic and epigenetic modifications towards... |
PIAS1 binds p300 and behaves as a coactivator or corepressor of the transcription factor c-Myb dependent on SUMO-status
Ledsaak M, Bengtsen M, Molværsmyr AK, Fuglerud BM, Matre V, Eskeland R, Gabrielsen OS
The PIAS proteins (Protein Inhibitor of Activated STATs) constitute a family of multifunctional nuclear proteins operating as SUMO E3 ligases and being involved in a multitude of interactions. They participate in a range of biological processes, also beyond their well-established role in the immune system and cytoki... |
The JMJD3 Histone Demethylase and the EZH2 Histone Methyltransferase in Prostate Cancer
Daures M, Ngollo M, Judes G, Rifaï K, Kemeny JL, Penault-Llorca F, Bignon YJ, Guy L, Bernard-Gallon D
Prostate cancer is themost common cancer in men. It has been clearly established that genetic and epigenetic alterations of histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) are common events in prostate cancer. This mark is deregulated in prostate cancer (Ngollo et al., 2014). Furthermore, H3K27me3 levels are determine... |
Expression of the MOZ-TIF2 oncoprotein in mice represses senescence.
Largeot A, Perez-Campo FM, Marinopoulou E, Lie-A-Ling M, Kouskoff V, Lacaud G.
The MOZ-TIF2 translocation, that fuses MOZ (Monocytic Leukemia Zinc finger protein) histone acetyltransferase (HAT) with the nuclear co-activator TIF2, is associated the development of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. We recently showed that in the absence of MOZ HAT activity, p16INK4atranscriptional levels are sig... |
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay for the Identification of Arabidopsis Protein-DNA Interactions In Vivo
Komar DN, Mouriz A, Jarillo JA, Piñeiro M
Intricate gene regulatory networks orchestrate biological processes and developmental transitions in plants. Selective transcriptional activation and silencing of genes mediate the response of plants to environmental signals and developmental cues. Therefore, insights into the mechanisms that control plant gene expr... |
DOT1L Activity Promotes Proliferation and Protects Cortical Neural Stem Cells from Activation of ATF4-DDIT3-Mediated ER Stress In Vitro
Roidl D, Hellbach N, Bovio PP, Villarreal A, Heidrich S, Nestel S, Grüning BA, Boenisch U, Vogel T
Growing evidence suggests that the lysine methyltransferase DOT1L/KMT4 has important roles in proliferation, survival, and differentiation of stem cells in development and in disease. We investigated the function of DOT1L in neural stem cells (NSCs) of the cerebral cortex. The pharmacological inhibition and shRNA-me... |
A highly conserved NF-κB-responsive enhancer is critical for thymic expression of Aire in mice
Haljasorg U et al.
Autoimmune regulator (Aire) has a unique expression pattern in thymic medullary epithelial cells (mTECs), in which it plays a critical role in the activation of tissue-specific antigens. The expression of Aire in mTECs is activated by receptor activator of nuclear factor κB (RANK) signaling; however, the molec... |
Identification of Critical Elements for Regulation of Inorganic Pyrophosphatase (PPA1) in MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells.
Mishra DR, Chaudhary S, Krishna BM, Mishra SK
Cytosolic inorganic pyrophosphatase plays an important role in the cellular metabolism by hydrolyzing inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi) formed as a by-product of various metabolic reactions. Inorganic pyrophosphatases are known to be associated with important functions related to the growth and development of various or... |
The histone demethylase enzyme KDM3A is a key estrogen receptor regulator in breast cancer.
Wade MA, Jones D, Wilson L, Stockley J, Coffey K, Robson CN, Gaughan L
Endocrine therapy has successfully been used to treat estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer, but this invariably fails with cancers becoming refractory to treatment. Emerging evidence has suggested that fluctuations in ER co-regulatory protein expression may facilitate resistance to therapy and be involved i... |
Identification of SCAN Domain Zinc-Finger Gene ZNF449 as a Novel Factor of Chondrogenesis.
Okada K, Fukai A, Mori D, Hosaka Y, Yano F, Chung UI, Kawaguchi H, Tanaka S, Ikeda T, Saito T
Transcription factors SOX9, SOX5 and SOX6 are indispensable for generation and differentiation of chondrocytes. However, molecular mechanisms to induce the SOX genes are poorly understood. To address this issue, we previously determined the human embryonic enhancer of SOX6 by 5'RACE analysis, and identified the 46-b... |
A Distal Locus Element Mediates IFN-γ Priming of Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated TNF Gene Expression.
Chow NA, Jasenosky LD, Goldfeld AE
Interferon γ (IFN-γ) priming sensitizes monocytes and macrophages to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation, resulting in augmented expression of a set of genes including TNF. Here, we demonstrate that IFN-γ priming of LPS-stimulated TNF transcription requires a distal TNF/LT locus element 8 kb upstream of the TNF tra... |
The cytokine TGF-β co-opts signaling via STAT3-STAT4 to promote the differentiation of human TFH cells.
Schmitt N, Liu Y, Bentebibel SE, Munagala I, Bourdery L, Venuprasad K, Banchereau J, Ueno H
Understanding the developmental mechanisms of follicular helper T cells (TFH cells) in humans is relevant to the clinic. However, the factors that drive the differentiation of human CD4(+) helper T cells into TFH cells remain largely undefined. Here we found that transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) provided critica... |
The interaction of MYC with the trithorax protein ASH2L promotes gene transcription by regulating H3K27 modification.
Ullius A, Lüscher-Firzlaff J, Costa IG, Walsemann G, Forst AH, Gusmao EG, Kapelle K, Kleine H, Kremmer E, Vervoorts J, Lüscher B
The appropriate expression of the roughly 30,000 human genes requires multiple layers of control. The oncoprotein MYC, a transcriptional regulator, contributes to many of the identified control mechanisms, including the regulation of chromatin, RNA polymerases, and RNA processing. Moreover, MYC recruits core histone... |
Therapeutic targeting of BET bromodomain proteins in castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Asangani IA, Dommeti VL, Wang X, Malik R, Cieslik M, Yang R, Escara-Wilke J, Wilder-Romans K, Dhanireddy S, Engelke C, Iyer MK, Jing X, Wu YM, Cao X, Qin ZS, Wang S, Feng FY, Chinnaiyan AM
Men who develop metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) invariably succumb to the disease. Progression to CRPC after androgen ablation therapy is predominantly driven by deregulated androgen receptor (AR) signalling. Despite the success of recently approved therapies targeting AR signalling, such as a... |
Epigenetics of prostate cancer: distribution of histone H3K27me3 biomarkers in peri-tumoral tissue.
Ngollo M, Dagdemir A, Judes G, Kemeny JL, Penault-Llorca F, Boiteux JP, Lebert A, Bignon YJ, Guy L, Bernard-Gallon D
Prostate cancer is the second most common cause of cancer and the sixth leading cause of cancer fatalities in men world- wide (Ferlay et al., 2010). Genetic abnormalities and mutations are primary causative factors, but epigenetic mechanisms are now recognized as playing a key role in prostate cancer de- velopment. ... |
Extensive amplification of the E2F transcription factor binding sites by transposons during evolution of Brassica species.
Hénaff E, Vives C, Desvoyes B, Chaurasia A, Payet J, Gutierrez C, Casacuberta JM
Transposable elements (TEs) are major players in genome evolution. The effects of their movement vary from gene knockouts to more subtle effects such as changes in gene expression. It has recently been shown that TEs may contain transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs), and it has been proposed that they may rewir... |
Lysine-specific demethylase 1 regulates differentiation onset and migration of trophoblast stem cells.
Zhu D, Hölz S, Metzger E, Pavlovic M, Jandausch A, Jilg C, Galgoczy P, Herz C, Moser M, Metzger D, Günther T, Arnold SJ, Schüle R
Propagation and differentiation of stem cell populations are tightly regulated to provide sufficient cell numbers for tissue formation while maintaining the stem cell pool. Embryonic parts of the mammalian placenta are generated from differentiating trophoblast stem cells (TSCs) invading the maternal decidua. Here w... |
H19 lncRNA controls gene expression of the Imprinted Gene Network by recruiting MBD1.
Monnier P, Martinet C, Pontis J, Stancheva I, Ait-Si-Ali S, Dandolo L
The H19 gene controls the expression of several genes within the Imprinted Gene Network (IGN), involved in growth control of the embryo. However, the underlying mechanisms of this control remain elusive. Here, we identified the methyl-CpG-binding domain protein 1 MBD1 as a physical and functional partner of the H19 ... |
Alu Elements in ANRIL Non-Coding RNA at Chromosome 9p21 Modulate Atherogenic Cell Functions through Trans-Regulation of Gene Networks.
Holdt LM, Hoffmann S, Sass K, Langenberger D, Scholz M, Krohn K, Finstermeier K, Stahringer A, Wilfert W, Beutner F, Gielen S, Schuler G, Gäbel G, Bergert H, Bechmann I, Stadler PF, Thiery J, Teupser D
The chromosome 9p21 (Chr9p21) locus of coronary artery disease has been identified in the first surge of genome-wide association and is the strongest genetic factor of atherosclerosis known today. Chr9p21 encodes the long non-coding RNA (ncRNA) antisense non-coding RNA in the INK4 locus (ANRIL). ANRIL expression is ... |
Progesterone receptor induces bcl-x expression through intragenic binding sites favoring RNA polymerase II elongation.
Bertucci PY, Nacht AS, Alló M, Rocha-Viegas L, Ballaré C, Soronellas D, Castellano G, Zaurin R, Kornblihtt AR, Beato M, Vicent GP, Pecci A
Steroid receptors were classically described for regulating transcription by binding to target gene promoters. However, genome-wide studies reveal that steroid receptors-binding sites are mainly located at intragenic regions. To determine the role of these sites, we examined the effect of progestins on the transcrip... |
Liver x receptors protect from development of prostatic intra-epithelial neoplasia in mice.
Pommier AJ, Dufour J, Alves G, Viennois E, De Boussac H, Trousson A, Volle DH, Caira F, Val P, Arnaud P, Lobaccaro JM, Baron S
LXR (Liver X Receptors) act as "sensor" proteins that regulate cholesterol uptake, storage, and efflux. LXR signaling is known to influence proliferation of different cell types including human prostatic carcinoma (PCa) cell lines. This study shows that deletion of LXR in mouse fed a high-cholesterol diet recapitula... |
Histone lysine trimethylation or acetylation can be modulated by phytoestrogen, estrogen or anti-HDAC in breast cancer cell lines.
Dagdemir A, Durif J, Ngollo M, Bignon YJ, Bernard-Gallon D
AIM: The isoflavones genistein, daidzein and equol (daidzein metabolite) have been reported to interact with epigenetic modifications, specifically hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes. The objective of this study was to analyze and understand the mechanisms by which phytoestrogens act on chromatin in breast c... |
Interplay between KLF4 and ZEB2/SIP1 in the regulation of E-cadherin expression
Koopmansch B, Berx G, Foidart J-M, Gilles C, Winkler R
E-cadherin expression is repressed by ZEB2/SIP1 while it is induced by KLF4. Independent data from the literature indicate that these two transcription factors could bind close to each other in the proximal region of the E-cadherin gene promoter. We have here explored a potential competition between ZEB2 and KLF4 fo... |
Inhibition of Tumor Promotion by Parthenolide: Epigenetic Modulation of p21.
Ghantous A, Saikali M, Rau T, Gali-Muhtasib H, Schneider-Stock R, Darwiche N
The promotion stage in the multistep process of epidermal tumorigenesis is NF-кB-dependent, epigenetically regulated, and reversible, thus, a suitable target for chemoprevention. We investigated whether the NF-кB inhibitor, parthenolide, currently in cancer clinical trials, attenuates tumor promotion by modulating t... |
Genome-wide localization and expression profiling establish Sp2 as a sequence-specific transcription factor regulating vitally important genes.
Terrados G, Finkernagel F, Stielow B, Sadic D, Neubert J, Herdt O, Krause M, Scharfe M, Jarek M, Suske G
The transcription factor Sp2 is essential for early mouse development and for proliferation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts in culture. Yet its mechanisms of action and its target genes are largely unknown. In this study, we have combined RNA interference, in vitro DNA binding, chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencin... |
Lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) and histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) synergistically repress proinflammatory cytokines and classical complement pathway components
Janzer A, Lim S, Fronhoffs F, Niazy N, Buettner R, Kirfel J
|
DNA methylation in an intron of the IBM1 histone demethylase gene stabilizes chromatin modification patterns.
Rigal M, Kevei Z, Pélissier T, Mathieu O
The stability of epigenetic patterns is critical for genome integrity and gene expression. This highly coordinated process involves interrelated positive and negative regulators that impact distinct epigenetic marks, including DNA methylation and dimethylation at histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2). In Arabidopsis, mutati... |
Dendritic Cells Activated by IFN-γ/STAT1 Express IL-31 Receptor and Release Proinflammatory Mediators upon IL-31 Treatment.
Horejs-Hoeck J, Schwarz H, Lamprecht S, Maier E, Hainzl S, Schmittner M, Posselt G, Stoecklinger A, Hawranek T, Duschl A
IL-31 is a T cell-derived cytokine that signals via a heterodimeric receptor composed of IL-31Rα and oncostatin M receptor β. Although several studies have aimed to investigate IL-31-mediated effects, the biological functions of this cytokine are currently not well understood. IL-31 expression correlates with the ex... |
C/EBPβ and RUNX2 cooperate to degrade cartilage with MMP-13 as the target and HIF-2α as the inducer in chondrocytes.
Hirata M, Kugimiya F, Fukai A, Saito T, Yano F, Ikeda T, Mabuchi A, Sapkota BR, Akune T, Nishida N, Yoshimura N, Nakagawa T, Tokunaga K, Nakamura K, Chung UI, Kawaguchi H
To elucidate the molecular mechanism underlying the endochondral ossification process during the skeletal growth and osteoarthritis (OA) development, we examined the signal network around CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-β (C/EBPβ, encoded by CEBPB), a potent regulator of this process. Computational predictions and a ... |
Bivalent histone modifications in stem cells poise miRNA loci for CpG island hypermethylation in human cancer.
Iliou MS, Lujambio A, Portela A, Brüstle O, Koch P, Andersson-Vincent PH, Sundström E, Hovatta O, Esteller M
It has been proposed that the existence of stem cell epigenetic patterns confer a greater likelihood of CpG island hypermethylation on tumor suppressor-coding genes in cancer. The suggested mechanism is based on the Polycomb-mediated methylation of K27 of histone H3 and the recruitment of DNA methyltransferases on t... |
Reciprocal repression between Sox3 and snail transcription factors defines embryonic territories at gastrulation.
Acloque H, Ocaña OH, Matheu A, Rizzoti K, Wise C, Lovell-Badge R, Nieto MA
In developing amniote embryos, the first epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) occurs at gastrulation, when a subset of epiblast cells moves to the primitive streak and undergoes EMT to internalize and generate the mesoderm and the endoderm. We show that in the chick embryo this decision to internalize is media... |
Disruption of the histone acetyltransferase MYST4 leads to a Noonan syndrome-like phenotype and hyperactivated MAPK signaling in humans and mice.
Kraft M, Cirstea IC, Voss AK, Thomas T, Goehring I, Sheikh BN, Gordon L, Scott H, Smyth GK, Ahmadian MR, Trautmann U, Zenker M, Tartaglia M, Ekici A, Reis A, Dörr HG, Rauch A, Thiel CT
Epigenetic regulation of gene expression, through covalent modification of histones, is a key process controlling growth and development. Accordingly, the transcription factors regulating these processes are important targets of genetic diseases. However, surprisingly little is known about the relationship between a... |
Epigenetic profile of the euchromatic region of human Y chromosome.
Singh NP, Madabhushi SR, Srivastava S, Senthilkumar R, Neeraja C, Khosla S, Mishra RK
The genome of a multi-cellular organism acquires various functional capabilities in different cell types by means of distinct chromatin modifications and packaging states. Acquired during early development, the cell type-specific epigenotype is maintained by cellular memory mechanisms that involve epigenetic modific... |
Inhibition of suppressive T cell factor 1 (TCF-1) isoforms in naive CD4+ T cells is mediated by IL-4/STAT6 signaling.
Maier E, Hebenstreit D, Posselt G, Hammerl P, Duschl A, Horejs-Hoeck J
The Wnt pathway transcription factor T cell factor 1 (TCF-1) plays essential roles in the control of several developmental processes, including T cell development in the thymus. Although previously regarded as being required only during early T cell development, recent studies demonstrate an important role for TCF-1... |
Epigenetic regulation on the 5'-proximal CpG island of human porcine endogenous retrovirus subgroup A receptor 2/GPR172B.
Nakaya Y, Shojima T, Yasuda J, Imakawa K, Miyazawa T
Porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERVs) have been considered one of the major risks of xenotransplantation from pigs to humans. PERV-A efficiently utilizes human PERV-A receptor 2 (HuPAR-2)/GPR172B to infect human cells; however, there has been no study on the regulation mechanisms of HuPAR-2/GPR172B expression. In ... |
Epigenetic activation of SOX11 in lymphoid neoplasms by histone modifications.
Vegliante MC, Royo C, Palomero J, Salaverria I, Balint B, Martín-Guerrero I, Agirre X, Lujambio A, Richter J, Xargay-Torrent S, Bea S, Hernandez L, Enjuanes A, Calasanz MJ, Rosenwald A, Ott G, Roman-Gomez J, Prosper F, Esteller M, Jares P, Siebert R, Camp
Recent studies have shown aberrant expression of SOX11 in various types of aggressive B-cell neoplasms. To elucidate the molecular mechanisms leading to such deregulation, we performed a comprehensive SOX11 gene expression and epigenetic study in stem cells, normal hematopoietic cells and different lymphoid neoplasm... |
Survival motor neuron gene 2 silencing by DNA methylation correlates with spinal muscular atrophy disease severity and can be bypassed by histone deacetylase inhibition.
Hauke J, Riessland M, Lunke S, Eyüpoglu IY, Blümcke I, El-Osta A, Wirth B, Hahnen E
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a common neuromuscular disorder, is caused by homozygous absence of the survival motor neuron gene 1 (SMN1), while the disease severity is mainly influenced by the number of SMN2 gene copies. This correlation is not absolute, suggesting the existence of yet unknown factors modulating d... |
Role of Transcriptional Corepressor CtBP1 in Prostate Cancer Progression
Wang R, Asangani IA, Chakravarthi BV, Ateeq B, Lonigro RJ, Cao Q, Mani RS, Camacho DF, McGregor N, Schumann TE, Jing X, Menawat R, Tomlins SA, Zheng H, Otte AP, Mehra R, Siddiqui J, Dhanasekaran SM, Nyati MK, Pienta KJ, Palanisamy N, Kunju LP, Rubin MA, C
Transcriptional repressors and corepressors play a critical role in cellular homeostasis and are frequently altered in cancer. C-terminal binding protein 1 (CtBP1), a transcriptional corepressor that regulates the expression of tumor suppressors and genes involved in cell death, is known to play a role in multiple c... |
A ChIP-on-chip tiling array approach detects functional histone-free regions associated with boundaries at vertebrate HOX genes
Srivastava S, Sowpati DT, Garapati HS, Puri D, Dhawan J, Mishra RK.
|
BET protein inhibition sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomidetreatment by attenuating MGMT expression
Tancredi A. et al.
Bromodomain and extra-terminal tail (BET) proteins have been identified as potential epigenetic targets in cancer, including glioblastoma. These epigenetic modifiers link the histone code to gene transcription that can be disrupted with small molecule BET inhibitors (BETi). With the aim of developing rational combin... |