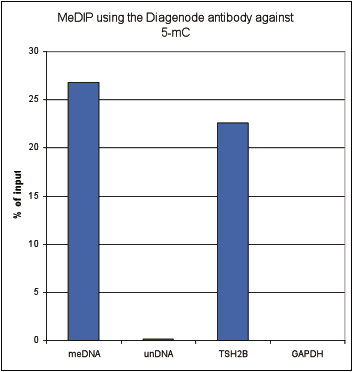
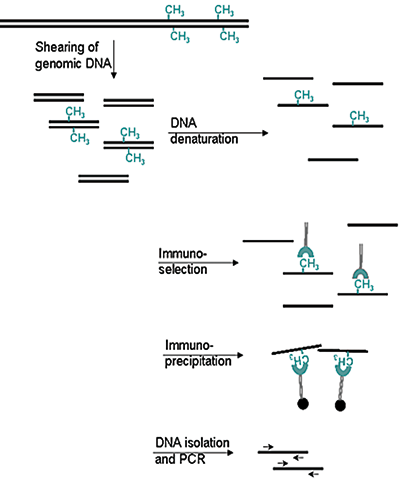
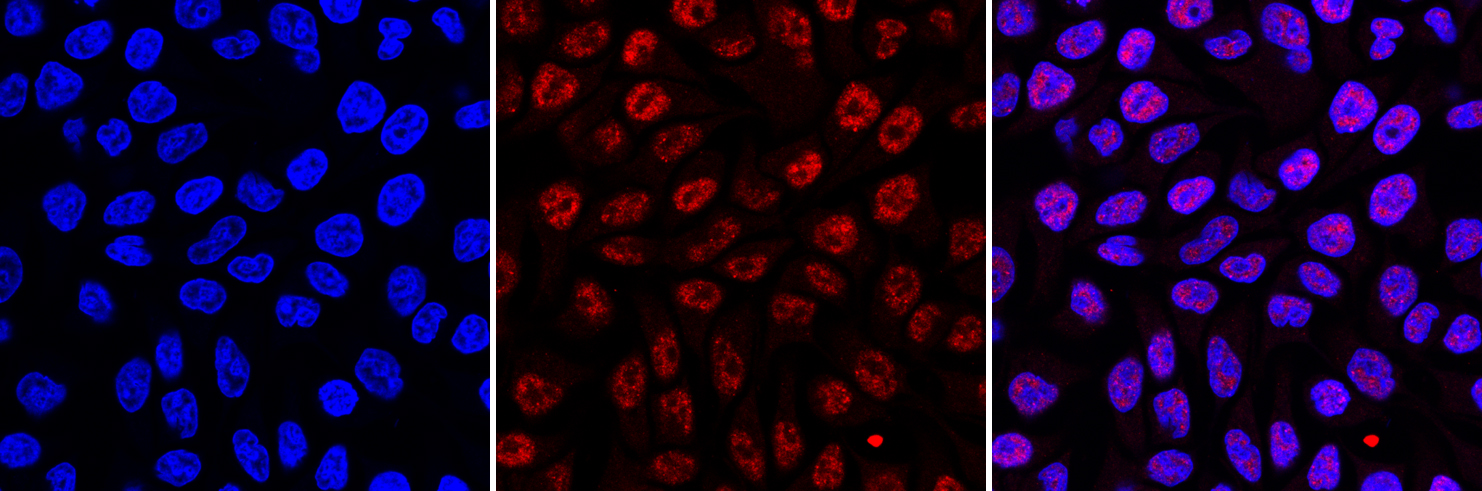
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) monoclonal antibody cl. b (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15200006-100 Lot# 008). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
An enriched maternal environment and stereotypies of sows differentiallyaffect the neuro-epigenome of brain regions related to emotionality intheir piglets.
Tatemoto P. et al.
Epigenetic mechanisms are important modulators of neurodevelopmental outcomes in the offspring of animals challenged during pregnancy. Pregnant sows living in a confined environment are challenged with stress and lack of stimulation which may result in the expression of stereotypies (repetitive behaviours without an... |
Role of epigenetics in the etiology of hypospadias through penileforeskin DNA methylation alterations.
Kaefer M. et al.
Abnormal penile foreskin development in hypospadias is the most frequent genital malformation in male children, which has increased dramatically in recent decades. A number of environmental factors have been shown to be associated with hypospadias development. The current study investigated the role of epigenetics i... |
Examination of Generational Impacts of Adolescent Chemotherapy:Ifosfamide and Potential for Epigenetic TransgenerationalInheritance
Thompson R. P. et al.
The current study was designed to use a rodent model to determine if exposure to the chemotherapy drug ifosfamide during puberty can induce altered phenotypes and disease in the grand-offspring of exposed individuals through epigenetic transgenerational inheritance. Pathologies such as delayed pubertal onset, kidney... |
Epigenome-wide association study of physical activity and physiologicalparameters in discordant monozygotic twins.
Duncan Glen E et al.
An epigenome-wide association study (EWAS) was performed on buccal cells from monozygotic-twins (MZ) reared together as children, but who live apart as adults. Cohorts of twin pairs were used to investigate associations between neighborhood walkability and objectively measured physical activity (PA) levels. Due to d... |
Environmental induced transgenerational inheritance impacts systemsepigenetics in disease etiology.
Beck D. et al.
Environmental toxicants have been shown to promote the epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of disease through exposure specific epigenetic alterations in the germline. The current study examines the actions of hydrocarbon jet fuel, dioxin, pesticides (permethrin and methoxychlor), plastics, and herbicides (glyp... |
GBS-MeDIP: A protocol for parallel identification of genetic andepigenetic variation in the same reduced fraction of genomes acrossindividuals.
Rezaei S. et al.
The GBS-MeDIP protocol combines two previously described techniques, Genotype-by-Sequencing (GBS) and Methylated-DNA-Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP). Our method allows for parallel and cost-efficient interrogation of genetic and methylomic variants in the DNA of many reduced genomes, taking advantage of the barcoding of... |
Preterm birth buccal cell epigenetic biomarkers to facilitatepreventative medicine.
Winchester P. et al.
Preterm birth is the major cause of newborn and infant mortality affecting nearly one in every ten live births. The current study was designed to develop an epigenetic biomarker for susceptibility of preterm birth using buccal cells from the mother, father, and child (triads). An epigenome-wide association study (EW... |
Epigenetic inheritance of DNA methylation changes in fish living inhydrogen sulfide-rich springs.
Kelley J. et al.
Environmental factors can promote phenotypic variation through alterations in the epigenome and facilitate adaptation of an organism to the environment. Although hydrogen sulfide is toxic to most organisms, the fish has adapted to survive in environments with high levels that exceed toxicity thresholds by orders of ... |
Epigenome-wide association study for pesticide (Permethrin and DEET)induced DNA methylation epimutation biomarkers for specifictransgenerational disease.
Thorson, Jennifer L M and Beck, Daniel and Ben Maamar, Millissia andNilsson, Eric E and Skinner, Michael K
BACKGROUND: Permethrin and N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET) are the pesticides and insect repellent most commonly used by humans. These pesticides have been shown to promote the epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of disease in rats. The current study was designed as an epigenome-wide association study (EWAS) ... |
Between-Generation Phenotypic and Epigenetic Stability in a Clonal Snail.
Smithson, Mark and Thorson, Jennifer L M and Sadler-Riggleman, Ingrid andBeck, Daniel and Skinner, Michael K and Dybdahl, Mark
Epigenetic variation might play an important role in generating adaptive phenotypes by underpinning within-generation developmental plasticity, persistent parental effects of the environment (e.g., transgenerational plasticity), or heritable epigenetically based polymorphism. These adaptive mechanisms should be most... |
DNA methylation variation in the brain of laying hens in relation to differential behavioral patterns
Guerrero-Bosagna Carlos, Pértille Fábio, Gomez Yamenah, Rezaei Shiva, Gebhardt Sabine, Vögeli Sabine, Stratmann Ariane, Vöelkl Bernhard, Toscano Michael J.
Domesticated animals are unique to investigate the contribution of genetic and non-genetic factors to specific phenotypes. Among non-genetic factors involved in phenotype formation are epigenetic mechanisms. Here we aimed to identify whether relative DNA methylation differences in the nidopallium between groups of i... |
Sperm DNA Methylation Epimutation Biomarkers for Male Infertility and FSH Therapeutic Responsiveness.
Luján S, Caroppo E, Niederberger C, Arce JC, Sadler-Riggleman I, Beck D, Nilsson E, Skinner MK
Male factor infertility is increasing and recognized as playing a key role in reproductive health and disease. The current primary diagnostic approach is to assess sperm quality associated with reduced sperm number and motility, which has been historically of limited success in separating fertile from infertile male... |
Epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of parent-of-origin allelic transmission of outcross pathology and sperm epimutations
Ben Maamar Millissia, King Stephanie E., Nilsson Eric, Beck Daniel, Skinner Michael K.
Epigenetic transgenerational inheritance potentially impacts disease etiology, phenotypic variation, and evolution. An increasing number of environmental factors from nutrition to toxicants have been shown to promote the epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of disease. Previous observations have demonstrated tha... |
TET3 prevents terminal differentiation of adult NSCs by a non-catalytic action at Snrpn.
Montalbán-Loro R, Lozano-Ureña A, Ito M, Krueger C, Reik W, Ferguson-Smith AC, Ferrón SR
Ten-eleven-translocation (TET) proteins catalyze DNA hydroxylation, playing an important role in demethylation of DNA in mammals. Remarkably, although hydroxymethylation levels are high in the mouse brain, the potential role of TET proteins in adult neurogenesis is unknown. We show here that a non-catalytic action o... |
Environmental Toxicant Induced Epigenetic Transgenerational Inheritance of Prostate Pathology and Stromal-Epithelial Cell Epigenome and Transcriptome Alterations: Ancestral Origins of Prostate Disease.
Klukovich R, Nilsson E, Sadler-Riggleman I, Beck D, Xie Y, Yan W, Skinner MK
Prostate diseases include prostate cancer, which is the second most common male neoplasia, and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), which affects approximately 50% of men. The incidence of prostate disease is increasing, and some of this increase may be attributable to ancestral exposure to environmental toxicants an... |
Genomic integrity of ground-state pluripotency.
Jafari N, Giehr P, Hesaraki M, Baas R, de Graaf P, Timmers HTM, Walter J, Baharvand H, Totonchi M
Pluripotent cells appear to be in a transient state during early development. These cells have the capability to transition into embryonic stem cells (ESCs). It has been reported that mouse pluripotent cells cultivated in chemically defined media sustain the ground state of pluripotency. Because the epigenetic patte... |
Developmental origins of transgenerational sperm DNA methylation epimutations following ancestral DDT exposure.
Ben Maamar M, Nilsson E, Sadler-Riggleman I, Beck D, McCarrey JR, Skinner MK
Epigenetic alterations in the germline can be triggered by a number of different environmental factors from diet to toxicants. These environmentally induced germline changes can promote the epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of disease and phenotypic variation. In previous studies, the pesticide DDT was shown ... |
Molecular Signatures of Regression of the Canine Transmissible Venereal Tumor.
Frampton D, Schwenzer H, Marino G, Butcher LM, Pollara G, Kriston-Vizi J, Venturini C, Austin R, de Castro KF, Ketteler R, Chain B, Goldstein RA, Weiss RA, Beck S, Fassati A
The canine transmissible venereal tumor (CTVT) is a clonally transmissible cancer that regresses spontaneously or after treatment with vincristine, but we know little about the regression mechanisms. We performed global transcriptional, methylation, and functional pathway analyses on serial biopsies of vincristine-t... |
Environmental toxicant induced epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of ovarian pathology and granulosa cell epigenome and transcriptome alterations: ancestral origins of polycystic ovarian syndrome and primary ovarian insufiency.
Nilsson E, Klukovich R, Sadler-Riggleman I, Beck D, Xie Y, Yan W, Skinner MK
Two of the most prevalent ovarian diseases affecting women's fertility and health are Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (POI) and Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS). Previous studies have shown that exposure to a number of environmental toxicants can promote the epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of ovarian diseas... |
Epigenetic variation between urban and rural populations of Darwin's finches
McNew S.M. et al.
Background
The molecular basis of evolutionary change is assumed to be genetic variation. However, growing evidence suggests that epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation, may also be involved in rapid adaptation to new environments. An important first step in evaluating this hypothesis is to test for the... |
Mercury-induced epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of abnormal neurobehavior is correlated with sperm epimutations in zebrafish.
Carvan M.J. et al.
Methylmercury (MeHg) is a ubiquitous environmental neurotoxicant, with human exposures predominantly resulting from fish consumption. Developmental exposure of zebrafish to MeHg is known to alter their neurobehavior. The current study investigated the direct exposure and transgenerational effects of MeHg, at tissue ... |
Genomic characterization and dynamic methylation of promoter facilitates transcriptional regulation of H2A variants, H2A.1 and H2A.2 in various pathophysiological states of hepatocyte
Tyagi M. et al.
Differential expression of homomorphous variants of H2A family of histone H2A.1 and H2A.2 have been associated with hepatocellular carcinoma and maintenance of undifferentiated state of hepatocyte. However, not much is known about the transcriptional regulation of these H2A variants. The current study revealed the p... |
Differential DNA Methylation Regions in Adult Human Sperm following Adolescent Chemotherapy: Potential for Epigenetic Inheritance.
Shnorhavorian M. et al.
BACKGROUND:
The potential that adolescent chemotherapy can impact the epigenetic programming of the germ line to influence later life adult fertility and promote epigenetic inheritance was investigated. Previous studies have demonstrated a number of environmental exposures such as abnormal nutrition and toxicants... |
Combined analysis of DNA methylome and transcriptome reveal novel candidate genes with susceptibility to bovine Staphylococcus aureus subclinical mastitis
Song M et al.
Subclinical mastitis is a widely spread disease of lactating cows. Its major pathogen is Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). In this study, we performed genome-wide integrative analysis of DNA methylation and transcriptional expression to identify candidate genes and pathways relevant to bovine S. aureus subclinical ... |
RESEARCH RESOURCE: Changes in gene expression and Estrogen Receptor cistrome in mouse liver upon acute E2 treatment.
Palierne G et al.
Transcriptional regulation by the Estrogen Receptor α (ER) has been investigated mainly in breast cancer cell lines but estrogens such as 17β-Estradiol (E2) exert numerous extra-reproductive effects, particularly in the liver where E2 exhibits both protective metabolic and deleterious thrombotic actions. ... |
Alteration of Gene Expression, DNA Methylation, and Histone Methylation in Free Radical Scavenging Networks in Adult Mouse Hippocampus following Fetal Alcohol Exposure
Chater-Diehl EJ, Laufer BI, Castellani CA, Alberry BL, Singh SM
The molecular basis of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) is poorly understood; however, epigenetic and gene expression changes have been implicated. We have developed a mouse model of FASD characterized by learning and memory impairment and persistent gene expression changes. Epigenetic marks may maintain expr... |
3/16 Epigenetic Programming Alterations in Alligators from Environmentally Contaminated Lakes.
Guillette LJ Jr et al.
Previous studies examining the reproductive health of alligators in Florida lakes indicate that a variety of developmental and health impacts can be attributed to a combination of environmental quality and exposures to environmental contaminants. The majority of these environmental contaminants have been shown to di... |
Differential Expression of Genes and DNA Methylation associated with Prenatal Protein Undernutrition by Albumen Removal in an avian model
Willems E, Guerrero-Bosagna C, Decuypere E, Janssens S, Buyse J, Buys N, Jensen P, Everaert N
Previously, long-term effects on body weight and reproductive performance have been demonstrated in the chicken model of prenatal protein undernutrition by albumen removal. Introduction of such persistent alterations in phenotype suggests stable changes in gene expression. Therefore, a genome-wide screening of the h... |
TET-catalyzed oxidation of intragenic 5-methylcytosine regulates CTCF-dependent alternative splicing.
Marina RJ et al.
Intragenic 5-methylcytosine and CTCF mediate opposing effects on pre-mRNA splicing: CTCF promotes inclusion of weak upstream exons through RNA polymerase II pausing, whereas 5-methylcytosine evicts CTCF, leading to exon exclusion. However, the mechanisms governing dynamic DNA methylation at CTCF-binding sites were u... |
Optimized method for methylated DNA immuno-precipitation
Guerrero-Bosagna C, Jensen P
Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) is one of the most widely used methods to evaluate DNA methylation on a whole genome scale, and involves the capture of the methylated fraction of the DNA by an antibody specific to methyl-cytosine. MeDIP was initially coupled with microarray hybridization to detect local D... |
Arabidopsis CMT3 activity is positively regulated by AtSIZ1-mediated sumoylation
Kim do Y, Han YJ, Kim SI, Song JT, Seo HS
The activities of mammalian DNA and histone methyltransferases are regulated by post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation and sumoylation; however, it is unclear how the activities of these enzymes are regulated at the post-translational level in plants. Here, we demonstrate that the DNA methylation a... |
Loss of neuronal 3D chromatin organization causes transcriptional and behavioural deficits related to serotonergic dysfunction.
Ito S, Magalska A, Alcaraz-Iborra M, Lopez-Atalaya JP, Rovira V, Contreras-Moreira B, Lipinski M, Olivares R, Martinez-Hernandez J, Ruszczycki B, Lujan R, Geijo-Barrientos E, Wilczynski GM, Barco A
The interior of the neuronal cell nucleus is a highly organized three-dimensional (3D) structure where regions of the genome that are linearly millions of bases apart establish sub-structures with specialized functions. To investigate neuronal chromatin organization and dynamics in vivo, we generated bitransgenic mi... |
Prenatal Exposure to BPA Alters the Epigenome of the Rat Mammary Gland and Increases the Propensity to Neoplastic Development.
Dhimolea E, Wadia PR, Murray TJ, Settles ML, Treitman JD, Sonnenschein C, Shioda T, Soto AM
Exposure to environmental estrogens (xenoestrogens) may play a causal role in the increased breast cancer incidence which has been observed in Europe and the US over the last 50 years. The xenoestrogen bisphenol A (BPA) leaches from plastic food/beverage containers and dental materials. Fetal exposure to BPA induces... |
Analysis of the leaf methylomes of parents and their hybrids provides new insight into hybrid vigor in Populus deltoides
Gao M, Huang Q, Chu Y, Ding C, Zhang B, Su X
Background Plants with heterosis/hybrid vigor perform better than their parents in many traits. However, the biological mechanisms underlying heterosis remain unclear. To investigate the significance of DNA methylation to heterosis, a comprehensive analysis of whole-genome DNA methylome profiles of Populus deltoide... |
Imprinted Chromatin around DIRAS3 Regulates Alternative Splicing of GNG12-AS1, a Long Noncoding RNA.
Niemczyk M, Ito Y, Huddleston J, Git A, Abu-Amero S, Caldas C, Moore GE, Stojic L, Murrell A
Imprinted gene clusters are regulated by long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), CCCTC binding factor (CTCF)-mediated boundaries, and DNA methylation. DIRAS3 (also known as ARH1 or NOEY1) is an imprinted gene encoding a protein belonging to the RAS superfamily of GTPases and is located within an intron of a lncRNA called GNG... |
Dynamics of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and chromatin marks in Mammalian neurogenesis.
Hahn MA, Qiu R, Wu X, Li AX, Zhang H, Wang J, Jui J, Jin SG, Jiang Y, Pfeifer GP, Lu Q
DNA methylation in mammals is highly dynamic during germ cell and preimplantation development but is relatively static during the development of somatic tissues. 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), created by oxidation of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) by Tet proteins and most abundant in the brain, is thought to be an intermed... |
Features of the Arabidopsis recombination landscape resulting from the combined loss of sequence variation and DNA methylation.
Colomé-Tatché M, Cortijo S, Wardenaar R, Morgado L, Lahouze B, Sarazin A, Etcheverry M, Martin A, Feng S, Duvernois-Berthet E, Labadie K, Wincker P, Jacobsen SE, Jansen RC, Colot V, Johannes F
The rate of meiotic crossing over (CO) varies considerably along chromosomes, leading to marked distortions between physical and genetic distances. The causes underlying this variation are being unraveled, and DNA sequence and chromatin states have emerged as key factors. However, the extent to which the suppression... |
Dynamic DNA cytosine methylation in the Populus trichocarpa genome: tissue-level variation and relationship to gene expression.
Vining KJ, Pomraning KR, Wilhelm LJ, Priest HD, Pellegrini M, Mockler TC, Freitag M, Strauss S
ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: DNA cytosine methylation is an epigenetic modification that has been implicated in many biological processes. However, large-scale epigenomic studies have been applied to very few plant species, and variability in methylation among specialized tissues and its relationship to gene expression is... |
Distinct Epigenomic Features in End-Stage Failing Human Hearts
Movassagh M, Choy MK, Knowles DA, Cordeddu L, Haider S, Down T, Siggens L, Vujic A, Simeoni I, Penkett C, Goddard M, Lio P, Bennett MR, Foo RSY,
Background—The epigenome refers to marks on the genome, including DNA methylation and histone modifications, that regulate the expression of underlying genes. A consistent profile of gene expression changes in end-stage cardiomyopathy led us to hypothesize that distinct global patterns of the epigenome may also exis... |
CTCF-promoted RNA polymerase II pausing links DNA methylation to splicing.
Shukla S, Kavak E, Gregory M, Imashimizu M, Shutinoski B, Kashlev M, Oberdoerffer P, Sandberg R, Oberdoerffer S
Alternative splicing of pre-messenger RNA is a key feature of transcriptome expansion in eukaryotic cells, yet its regulation is poorly understood. Spliceosome assembly occurs co-transcriptionally, raising the possibility that DNA structure may directly influence alternative splicing. Supporting such an association,... |
Epigenetic switch involved in activation of pioneer factor FOXA1-dependent enhancers.
Sérandour AA, Avner S, Percevault F, Demay F, Bizot M, Lucchetti-Miganeh C, Barloy-Hubler F, Brown M, Lupien M, Métivier R, Salbert G, Eeckhoute J
Transcription factors (TFs) bind specifically to discrete regions of mammalian genomes called cis-regulatory elements. Among those are enhancers, which play key roles in regulation of gene expression during development and differentiation. Despite the recognized central regulatory role exerted by chromatin in contro... |
Comprehensive analysis of DNA-methylation in mammalian tissues using MeDIP-chip.
Pälmke N, Santacruz D, Walter J
Genome-wide mapping of epigenetic changes is essential for understanding the mechanisms involved in gene regulation during cell differentiation and embryonic development. DNA-methylation is one of these key epigenetic marks that is directly linked to gene expression is. Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) is ... |
Microplate-based platform for combined chromatin and DNA methylation immunoprecipitation assays.
Yu J, Feng Q, Ruan Y, Komers R, Kiviat N, Bomsztyk K
UNLABELLED: ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: The processes that compose expression of a given gene are far more complex than previously thought presenting unprecedented conceptual and mechanistic challenges that require development of new tools. Chromatin structure, which is regulated by DNA methylation and histone modificatio... |
Genome-wide conserved consensus transcription factor binding motifs are hyper-methylated.
Choy MK, Movassagh M, Goh HG, Bennett MR, Down TA, Foo RS
BACKGROUND: DNA methylation can regulate gene expression by modulating the interaction between DNA and proteins or protein complexes. Conserved consensus motifs exist across the human genome ("predicted transcription factor binding sites": "predicted TFBS") but the large majority of these are proven by chromatin imm... |
The epigenetic landscape of latent Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus genomes.
Günther T, Grundhoff A
Herpesvirus latency is generally thought to be governed by epigenetic modifications, but the dynamics of viral chromatin at early timepoints of latent infection are poorly understood. Here, we report a comprehensive spatial and temporal analysis of DNA methylation and histone modifications during latent infection wi... |
Genome-wide analysis of aberrant methylation in human breast cancer cells using methyl-DNA immunoprecipitation combined with high-throughput sequencing.
Ruike Y, Imanaka Y, Sato F, Shimizu K, Tsujimoto G
BACKGROUND: Cancer cells undergo massive alterations to their DNA methylation patterns that result in aberrant gene expression and malignant phenotypes. However, the mechanisms that underlie methylome changes are not well understood nor is the genomic distribution of DNA methylation changes well characterized. RESUL... |
Genome-wide high throughput analysis of DNA methylation in eukaryotes.
Pomraning KR, Smith KM, Freitag M
Cytosine methylation is the quintessential epigenetic mark. Two well-established methods, bisulfite sequencing and methyl-DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) lend themselves to the genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation by high throughput sequencing. Here we provide an overview and brief review of these methods. We sum... |
Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and microarray-based analysis: detection of DNA methylation in breast cancer cell lines.
Weng YI, Huang TH, Yan PS
The methylated DNA immunoprecipitation microarray (MeDIP-chip) is a genome-wide, high-resolution approach to detect DNA methylation in whole genome or CpG (cytosine base followed by a guanine base) islands. The method utilizes anti-methylcytosine antibody to immunoprecipitate DNA that contains highly methylated CpG ... |
Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis in filamentous fungi.
Boedi S, Reyes-Dominguez Y, Strauss J.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) is used to map the interaction between proteins and DNA at a specific genomic locus in the living cell. The protein-DNA complexes are stabilized already in vivo by reversible crosslinking and the DNA is sheared by sonication or enzymatic digestion into fragments suitable for the ... |
Role of transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of methionine adenosyltransferases in liver cancer progression
Frau M, Tomasi ML, Simile MM, Demartis MI, Salis F, Latte G, Calvisi DF, Seddaiu MA, Daino L, Feo CF, Brozzetti S, Solinas G, Yamashita S, Ushijima T, Feo F, Pascale RM
Downregulation of liver-specific MAT1Agene, encoding S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) synthesizing isozymes MATI/III, and upregulation of widely expressedMAT2A, encoding MATII isozyme, known as MAT1A:MAT2A switch, occurs in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here, we found Mat1A:Mat2A switch and low SAM levels, associated wi... |
Promoter DNA Methylation Patterns of Differentiated Cells Are Largely Programmed at the Progenitor Stage
Sørensen AL, Jacobsen BM, Reiner AH, Andersen IS, Collas P
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) isolated from various tissues share common phenotypic and functional properties. However, intrinsic molecular evidence supporting these observations has been lacking. Here, we unravel overlapping genome-wide promoter DNA methylation patterns between MSCs from adipose tissue, bone marrow... |
Chromatin Environment of Histone Variant H3.3 Revealed by Quantitative Imaging and Genome-scale Chromatin and DNA Immunoprecipitation
Delbarre E, Jacobsen BM, Reiner AH, Sørensen AL, Kuntziger T, Collas P
In contrast to canonical histones, histone variant H3.3 is incorporated into chromatin in a replication-independent manner. Posttranslational modifications of H3.3 have been identified; however, the epigenetic environment of incorporated H3.3 is unclear. We have investigated the genomic distribution of epitope-tagge... |