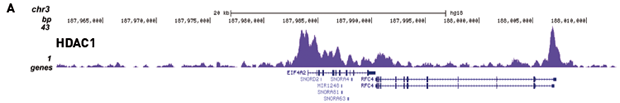
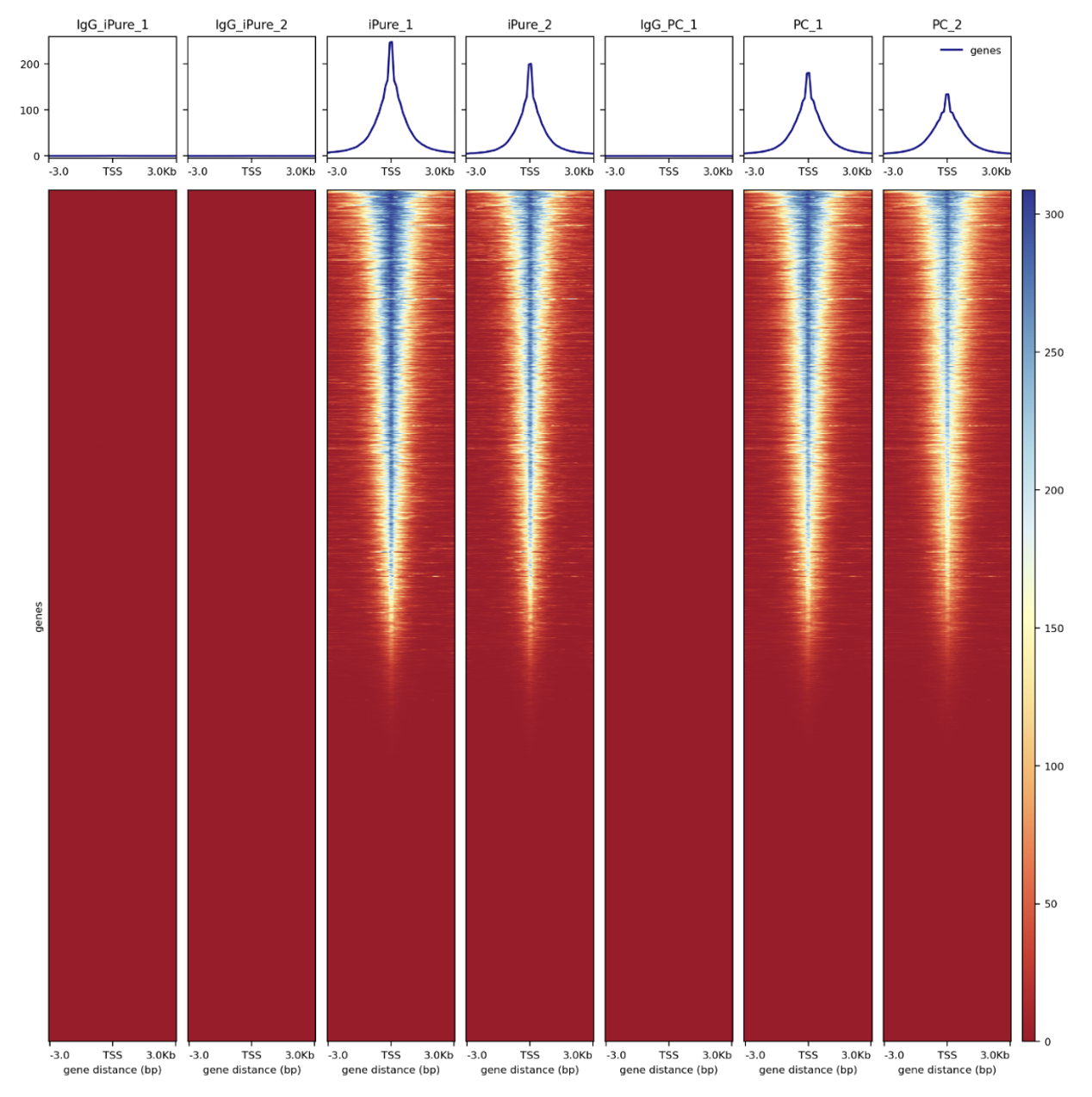
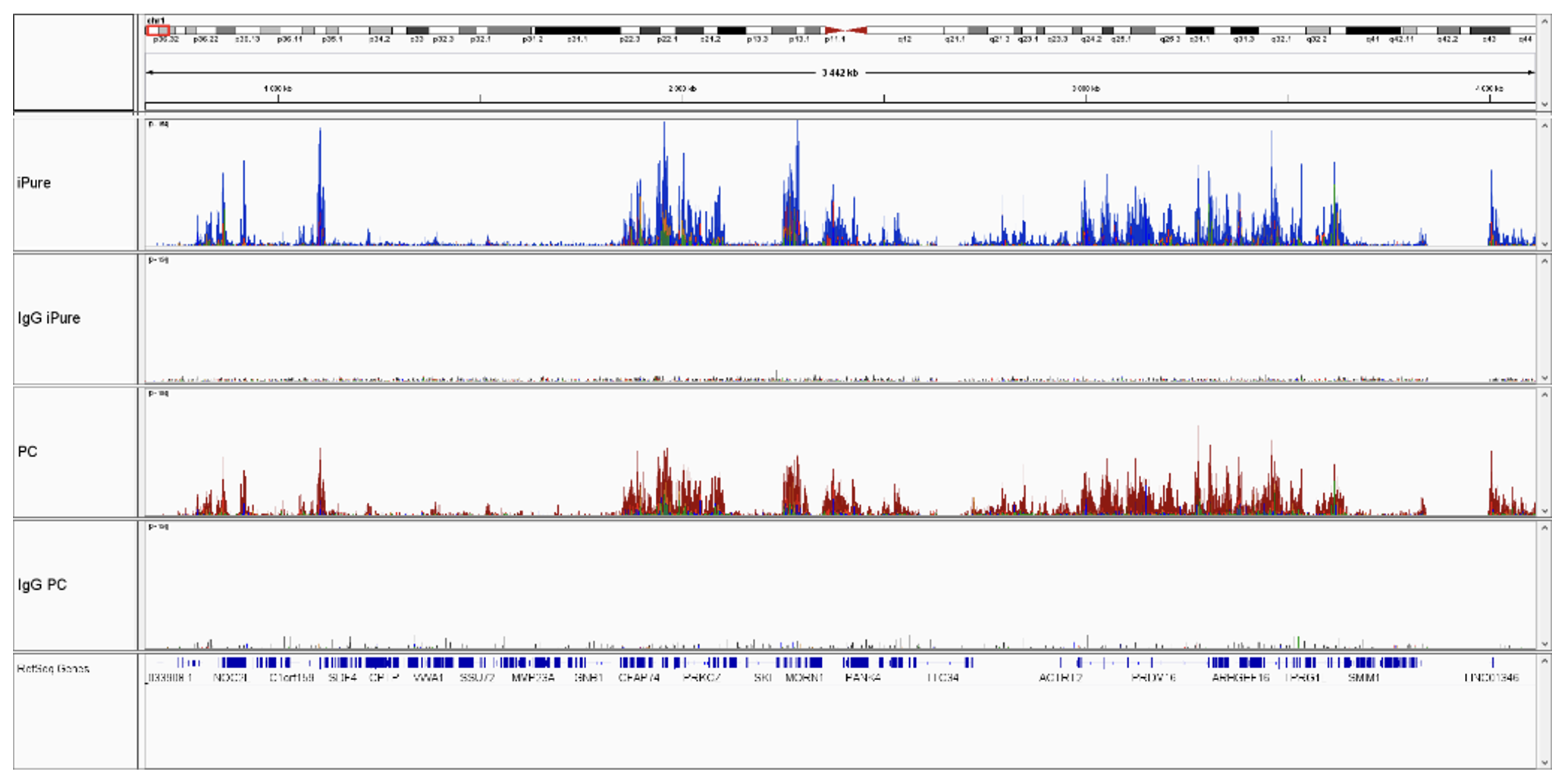
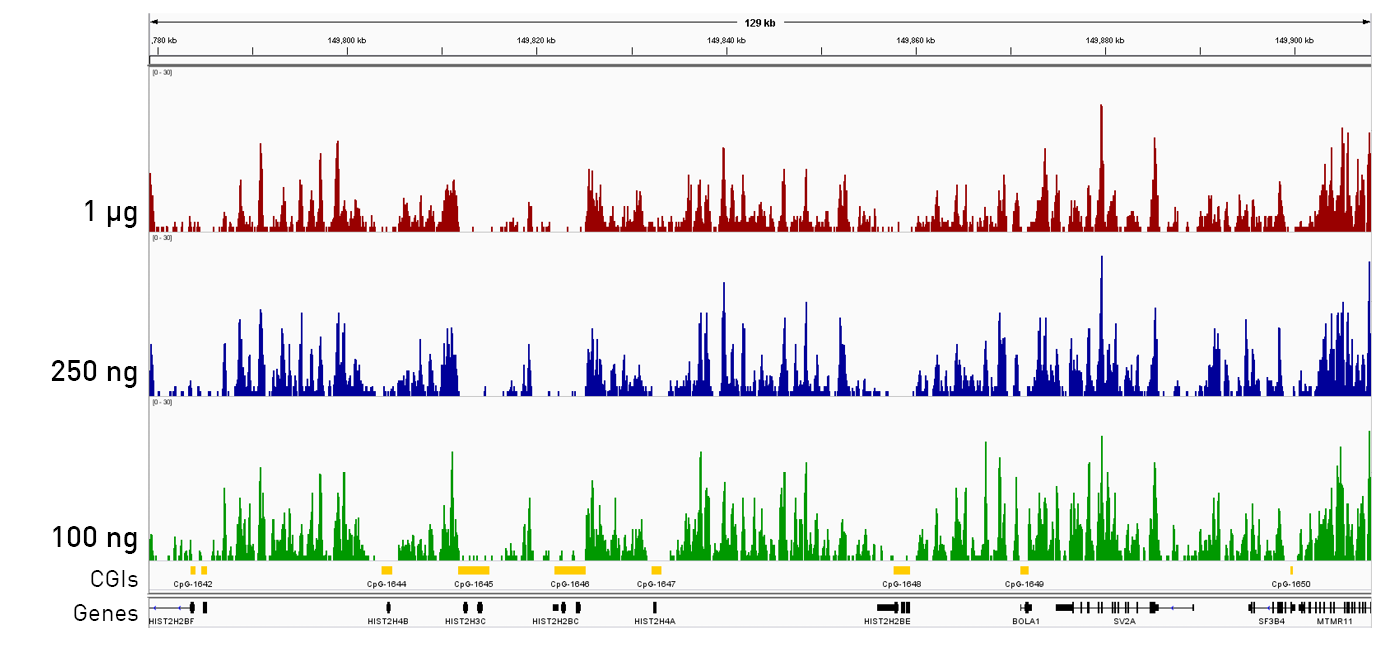
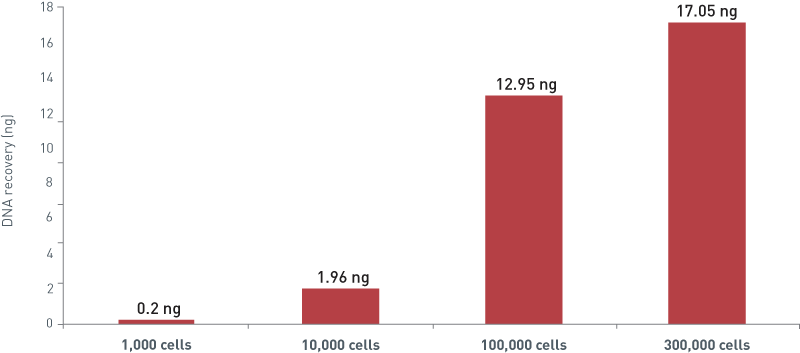
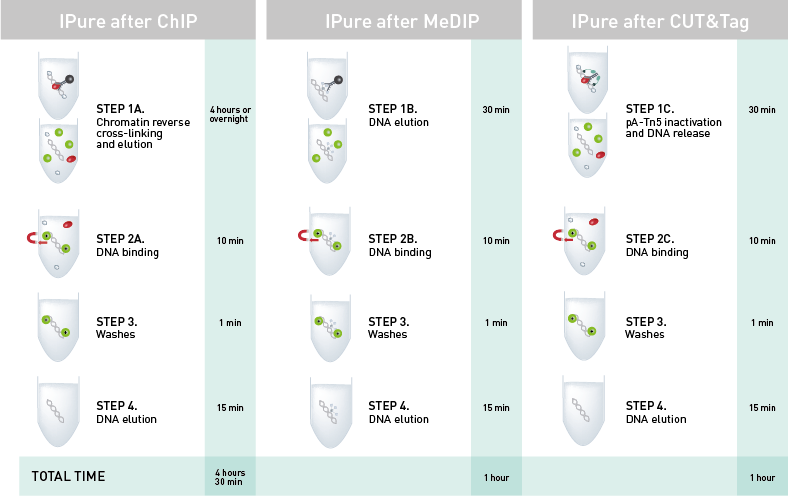
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: IPure kit v2 (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C03010015). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
ZFTA-RELA ependymomas make itaconate to epigenetically drive fusion expression
Natarajan, Siva Kumar et al.
Abstract
ZFTA-RELA+ ependymomas are malignant brain tumours defined by fusions formed between the putative chromatin remodeller ZFTA and the NF-κB mediator RELA1. Here we show that ZFTA-RELA+ cells produce itaconate, a key macrophage-associated immunomodulatory metabolite2. Itaconate is generated ... |
Tel1 is recruited at chromosomal loop/axis contact sites to modulate meiotic DNA double-strand breaks interference
Dorme, Marie et al.
During meiosis, the programmed formation of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) by Spo11, a conserved topoisomerase VI family protein, initiates homologous recombination that leads to crossovers between homologous chromosomes, essential for accurate chromosome segregation and genome evolution. The DSB number, distri... |
H1.3 depletion in AML cells prompts H1.2 redistribution, chromatin remodeling and cell cycle defects
Tellez-Quijorna, Clara et al.
Linker histone H1 variants play critical, yet distinct, roles in chromatin organization and gene regulation. However, very little is known about their specificity in cancer cells. In this study, we investigated the specificity of the H1.3 variant in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. Through chromatin mapping and... |
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 facilitates the transition from heterotrophy to photoautotrophy during seedling emergence
Samo, Naseem et al.
The seed-to-seedling transition represents a key developmental and metabolic switch in plants. Catabolism of seed storage reserves fuels germination and early seedling emergence until photosynthesis is established. The seed-to-seedling developmental transition is controlled by Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2).... |
Coupling Immunoprecipitation with Multiplexed Digital PCR for Cell-Free DNA Methylation Detection in Small Plasma Volumes of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer
Truong, Truong T et al.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a major global health challenge, with an increasing incidence of early-onset cases among young adults. Targeted analysis of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylation in blood has emerged as a promising minimally invasive diagnostic approach. While digital PCR (dPCR) offers high sensitivit... |
An ISWI-related chromatin remodeller regulates stage-specific gene expression in Toxoplasma gondii
Pachano, Belen et al.
ATP-dependent chromatin remodellers are specialized multiprotein machines that organize the genome in eukaryotic cells and regulate its accessibility by repositioning, ejecting or modifying nucleosomes. However, their role in Toxoplasma gondii is poorly understood. Here we show that T. gondii&n... |
Chromatin environment-dependent effects of DOT1L on gene expression in male germ cells
Manon Coulée et al.
The H3K79 methyltransferase DOT1L is essential for multiple aspects of mammalian development where it has been shown to regulate gene expression. Here, by producing and integrating epigenomic and spike-in RNA-seq data, we decipher the molecular role of DOT1L during mouse spermatogenesis and show that it has opposite... |
Dysregulation of Myelination in Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type II of the Human Frontal Lobe
Catharina Donkels et al.
Focal cortical dysplasias (FCDs) are local malformations of the human neocortex and a leading cause of intractable epilepsy. FCDs are classified into different subtypes including FCD IIa and IIb, characterized by a blurred gray-white matter boundary or a transmantle sign indicating abnormal white matter myelination.... |
Interferon-gamma rescues FK506 dampened dendritic cell calcineurin-dependent responses to Aspergillus fumigatus via Stat3 to Stat1 switching
Amit Adlakha et al.
IScience Highlights
Calcineurin inhibitors block DC maturation in response to A. fumigatus
Lack of DC maturation impairs Th1 polarization in response to A. fumigatus
Interferon-γ restores maturation, promotes Th1 polarization and fungal killing
ChIPseq reveals in... |
Prediction of brain metastasis development with DNA methylation signatures
Jeffrey A. Zuccato et al.
Brain metastases (BMs) are the most common and among the deadliest brain tumors. Currently, there are no reliable predictors of BM development from primary cancer, which limits early intervention. Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most common BM source and here we obtained 402 tumor and plasma samples from a large c... |
HNF1β bookmarking involves Topoisomerase 1 activation and DNA topology relaxation in mitotic chromatin
Alessia Bagattin et al.
Highlights
HNF1β mitotic site binding is preserved with a specific methanol/formaldehyde ChIP
BTBD2, an HNF1β partner, mediates mitosis-specific interaction with TOP1
HNF1β recruits TOP1 and induces DNA relaxation around bookmarked HNF1β sites
An HNF1β m... |
Epigenomic signatures of sarcomatoid differentiation to guide the treatment of renal cell carcinoma
Talal El Zarif et al.
Renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation (sRCC) is associated with poor survival and a heightened response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Two major barriers to improving outcomes for sRCC are the limited understanding of its gene regulatory programs and the low diagnostic yield of tumor biopsie... |
Detecting small cell transformation in patients with advanced EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma through epigenomic cfDNA profiling
Talal El Zarif et al.
Purpose: Histologic transformation to small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a mechanism of treatment resistance in patients with advanced oncogene-driven lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) that currently requires histologic review for diagnosis. Herein, we sought to develop an epigenomic cell-free (cf)DNA-based approach to non-i... |
Prostate cancer detection through unbiased capture of methylated cell-free DNA
Ermira Lleshi et al.
Prostate cancer screening using prostate-specific antigen (PSA) has been shown to reduce mortality but with substantial overdiagnosis, leading to unnecessary biopsies. The identification of a highly specific biomarker using liquid biopsies, represents an unmet need in the diagnostic pathway for prostate cancer. In t... |
The ETO2 transcriptional cofactor maintains acute leukemia by driving a MYB/EP300-dependent stemness program
Fagnan A. et al.
Transcriptional cofactors of the ETO family are recurrent fusion partners in acute leukemia. We characterized the ETO2 regulome by integrating transcriptomic and chromatin binding analyses in human erythroleukemia xenografts and controlled ETO2 depletion models. We demonstrate that beyond its well-established repres... |
Focal cortical dysplasia type II-dependent maladaptive myelination in the human frontal lobe
Donkels C. et al.
Focal cortical dysplasias (FCDs) are local malformations of the human neocortex and a leading cause of intractable epilepsy. FCDs are classified into different subtypes including FCD IIa and IIb, characterized by a blurred gray-white matter boundary or a transmantle sign indicating abnormal white matter myelination.... |
In vitro production of cat-restricted Toxoplasma pre-sexual stages
Antunes, A.V. et al.
Sexual reproduction of Toxoplasma gondii, confined to the felid gut, remains largely uncharted owing to ethical concerns regarding the use of cats as model organisms. Chromatin modifiers dictate the developmental fate of the parasite during its multistage life cycle, but their targeting to stage-specific cistro... |
Cerebrospinal fluid methylome-based liquid biopsies for accuratemalignant brain neoplasm classification.
Zuccato Jeffrey A et al.
BACKGROUND: Resolving the differential diagnosis between brain metastases (BM), glioblastomas (GBM), and central nervous system lymphomas (CNSL) is an important dilemma for the clinical management of the main three intra-axial brain tumor types. Currently, treatment decisions require invasive diagnostic surgical bio... |
Differentiation block in acute myeloid leukemia regulated by intronicsequences of FTO
Camera F. et al.
Iroquois transcription factor gene IRX3 is highly expressed in 20–30\% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and contributes to the pathognomonic differentiation block. Intron 8 FTO sequences ∼220kB downstream of IRX3 exhibit histone acetylation, DNA methylation, and contacts with th... |
Mediator 1 ablation induces enamel-to-hair lineage conversion in micethrough enhancer dynamics.
Thaler R. et al.
Postnatal cell fate is postulated to be primarily determined by the local tissue microenvironment. Here, we find that Mediator 1 (Med1) dependent epigenetic mechanisms dictate tissue-specific lineage commitment and progression of dental epithelia. Deletion of Med1, a key component of the Mediator complex linking enh... |
Vitamin D Receptor Cross-talk with p63 Signaling PromotesEpidermal Cell Fate.
Oda Y. et al.
The vitamin D receptor with its ligand 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D (1,25D) regulates epidermal stem cell fate, such that VDR removal from Krt14 expressing keratinocytes delays re-epithelialization of epidermis after wound injury in mice. In this study we deleted Vdr from Lrig1 expressing stem cells in the isthmus of th... |
Pre-diagnosis plasma cell-free DNA methylome profiling up to sevenyears prior to clinical detection reveals early signatures of breast cancer
Cheng N. et al.
Profiling of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has been well demonstrated to be a potential non-invasive screening tool for early cancer detection. However, limited studies have investigated the detectability of cfDNA methylation markers that are predictive of cancers in asymptomatic individuals. We performed cfDNA methylation ... |
Longitudinal monitoring of cell-free DNA methylation in ALK-positivenon-small cell lung cancer patients.
Janke Florian et al.
BACKGROUND: DNA methylation (5-mC) signals in cell-free DNA (cfDNA) of cancer patients represent promising biomarkers for minimally invasive tumor detection. The high abundance of cancer-associated 5-mC alterations permits parallel and highly sensitive assessment of multiple 5-mC biomarkers. Here, we performed ... |
Cell-free DNA methylation-defined prognostic subgroups in small celllung cancer identified by leukocyte methylation subtraction
Ul Haq Sami et al.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) methylome is understudied. Here, we comprehensively profile SCLC using cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq). Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from plasma of 74 SCLC patients pre-treatment and from 20 non-cancer participants, genomic DNA (gDNA) from peri... |
Identification of genomic binding sites and direct target genes for thetranscription factor DDIT3/CHOP.
Osman A. et al.
DDIT3 is a tightly regulated basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor and key regulator in cellular stress responses. It is involved in a variety of pathological conditions and may cause cell cycle block and apoptosis. It is also implicated in differentiation of some specialized cell types and as an oncogene... |
DosR Regulates the Transcription of the Arginine BiosynthesisGene Cluster by Binding to the Regulatory Sequences inMycobacterium bovis Bacille Calmette-Guerin.
Cui Yingying et al.
l-Arginine serves as a carbon and nitrogen source and is critical for (Mtb) survival in the host. Generally, ArgR acts as a repressor regulating arginine biosynthesis by binding to the promoter of the gene cluster. In this study, we report that the dormancy regulator DosR is a novel arginine regulator binding to the... |
Vitamin C enhances NF-κB-driven epigenomic reprogramming andboosts the immunogenic properties of dendritic cells.
Morante-Palacios O. et al.
Dendritic cells (DCs), the most potent antigen-presenting cells, are necessary for effective activation of naïve T cells. DCs' immunological properties are modulated in response to various stimuli. Active DNA demethylation is crucial for DC differentiation and function. Vitamin C, a known cofactor of ten-eleven... |
The cell-free DNA methylome captures distinctions between localized andmetastatic prostate tumors.
Chen Sujun et al.
Metastatic prostate cancer remains a major clinical challenge and metastatic lesions are highly heterogeneous and difficult to biopsy. Liquid biopsy provides opportunities to gain insights into the underlying biology. Here, using the highly sensitive enrichment-based sequencing technology, we provide analysis of 60 ... |
Cell-wall damage activates DOF transcription factors to promote woundhealing and tissue regeneration in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Zhang Ai et al.
Wound healing is a fundamental property of plants and animals that requires recognition of cellular damage to initiate regeneration. In plants, wounding activates a defense response via the production of jasmonic acid and a regeneration response via the hormone auxin and several ethylene response factor (ERF) and NA... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple
Myeloma
Alaterre, Elina and Ovejero, Sara and Herviou, Laurie and de
Boussac, Hugues and Papadopoulos, Giorgio and Kulis, Marta and
Boireau, Stéphanie and Robert, Nicolas and Requirand, Guilhem
and Bruyer, Angélique and Cartron, Guillaume and Vincent,
Laure and M
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have
been widely used to understand the molecular processes that drive MM
biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,
progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the
epigenetic landscape of MM would advance our... |
Coordinated glucocorticoid receptor and MAFB action inducestolerogenesis and epigenome remodeling in dendritic cells
Morante-Palacios Octavio et al.
Abstract Glucocorticoids (GCs) exert potent anti-inflammatory effects in immune cells through the glucocorticoid receptor (GR). Dendritic cells (DCs), central actors for coordinating immune responses, acquire tolerogenic properties in response to GCs. Tolerogenic DCs (tolDCs) have emerged as a potential treatment fo... |
Integrating SNPs-based genetic risk factor with blood epigenomicresponse of differentially arsenic-exposed rural subjects revealsdisease-associated signaling pathways.
Rehman Muhammad Yasir Abdur et al.
Arsenic (As) contamination in groundwater is responsible for numerous adverse health outcomes among millions of people. Epigenetic alterations are among the most widely studied mechanisms of As toxicity. To understand how As exposure alters gene expression through epigenetic modifications, a systematic genome-wide s... |
Expression of in the Stem Cell Domain Is Required for ItsFunction in the Control of Floral Meristem Activity in Arabidopsis
Kwaśniewska K. et al.
In the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, the zinc-finger transcription factor KNUCKLES (KNU) plays an important role in the termination of floral meristem activity, a process that is crucial for preventing the overgrowth of flowers. The KNU gene is activated in floral meristems by the floral organ identity factor AG... |
Contrasting epigenetic control of transgenes and endogenous genespromotes post-transcriptional transgene silencing in
Butel N. et al.
Transgenes that are stably expressed in plant genomes over many generations could be assumed to behave epigenetically the same as endogenous genes. Here, we report that whereas the histone H3K9me2 demethylase IBM1, but not the histone H3K4me3 demethylase JMJ14, counteracts DNA methylation of Arabidopsis endogenous g... |
Coordinated changes in gene expression, H1 variant distribution and genome3D conformation in response to H1 depletion
Serna-Pujol, Nuria and Salinas-Pena, Monica and Mugianesi, Francesca and LeDily, François and Marti-Renom, Marc A. and Jordan, Albert
Up to seven members of the histone H1 family may contribute to chromatin compaction and its regulation in human somatic cells. In breast cancer cells, knock-down of multiple H1 variants deregulates many genes, promotes the appearance of genome-wide accessibility sites and triggers an interferon response via activati... |
Histone modification dynamics at H3K27 are associated with alteredtranscription of in planta induced genes in Magnaporthe oryzae.
Zhang, Wei and Huang, Jun and Cook, David E
Transcriptional dynamic in response to environmental and developmental cues are fundamental to biology, yet many mechanistic aspects are poorly understood. One such example is fungal plant pathogens, which use secreted proteins and small molecules, termed effectors, to suppress host immunity and promote colonization... |
A brain cyst load-associated antigen is a Toxoplasma gondii biomarker forserodetection of persistent parasites and chronic infection.
Dard C. et al.
BACKGROUND: Biomarker discovery remains a major challenge for predictive medicine, in particular, in the context of chronic diseases. This is true for the widespread protozoan Toxoplasma gondii which establishes long-lasting parasitism in metazoans, humans included. This microbe successively unfolds distinct genetic... |
Integrated epigenetic biomarkers in circulating cell-free DNA as a robust classifier for pancreatic cancer.
Cao F, Wei A, Hu X, He Y, Zhang J, Xia L, Tu K, Yuan J, Guo Z, Liu H, Xie D, Li A
BACKGROUND: The high lethal rate of pancreatic cancer is partly due to a lack of efficient biomarkers for screening and early diagnosis. We attempted to develop effective and noninvasive methods using 5-methylcytosine (5mC) and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) markers from circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) for the det... |
Detection of renal cell carcinoma using plasma and urine cell-free DNA methylomes.
Nuzzo PV, Berchuck JE, Korthauer K, Spisak S, Nassar AH, Abou Alaiwi S, Chakravarthy A, Shen SY, Bakouny Z, Boccardo F, Steinharter J, Bouchard G, Curran CR, Pan W, Baca SC, Seo JH, Lee GM, Michaelson MD, Chang SL, Waikar SS, Sonpavde G, Irizarry RA, Pome
Improving early cancer detection has the potential to substantially reduce cancer-related mortality. Cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq) is a highly sensitive assay capable of detecting early-stage tumors. We report accurate classification of patients across all ... |
Removal of H2Aub1 by ubiquitin-specific proteases 12 and 13 is required for stable Polycomb-mediated gene repression in Arabidopsis.
Kralemann LEM, Liu S, Trejo-Arellano MS, Muñoz-Viana R, Köhler C, Hennig L
BACKGROUND: Stable gene repression is essential for normal growth and development. Polycomb repressive complexes 1 and 2 (PRC1&2) are involved in this process by establishing monoubiquitination of histone 2A (H2Aub1) and subsequent trimethylation of lysine 27 of histone 3 (H3K27me3). Previous work proposed that ... |
A Germline Mutation in the Gene Is a Candidate for Familial Non-Medullary Thyroid Cancer.
Srivastava A, Miao B, Skopelitou D, Kumar V, Kumar A, Paramasivam N, Bonora E, Hemminki K, Försti A, Bandapalli OR
Non-medullary thyroid cancer (NMTC) is a common endocrine malignancy with a genetic basis that has yet to be unequivocally established. In a recent whole-genome sequencing study of five families with occurrence of NMTCs, we shortlisted promising variants with the help of bioinformatics tools. Here, we report in sili... |
AP-1 controls the p11-dependent antidepressant response.
Chottekalapanda RU, Kalik S, Gresack J, Ayala A, Gao M, Wang W, Meller S, Aly A, Schaefer A, Greengard P
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are the most widely prescribed drugs for mood disorders. While the mechanism of SSRI action is still unknown, SSRIs are thought to exert therapeutic effects by elevating extracellular serotonin levels in the brain, and remodel the structural and functional alterations ... |
UNBRANCHED3 Expression and Inflorescence Development is Mediated by UNBRANCHED2 and the Distal Enhancer, KRN4, in Maize.
Yanfang Du, Lei Liu, Yong Peng, Manfei Li, Yunfu Li, Dan Liu, Xingwang Li, Zuxin Zhang
Enhancers are cis-acting DNA segments with the ability to increase target gene expression. They show high sensitivity to DNase and contain specific DNA elements in an open chromatin state that allows the binding of transcription factors (TFs). While numerous enhancers are annotated in the maize genome, few have been... |
Differential modulation of the androgen receptor for prostate cancer therapy depends on the DNA response element.
Kregel S, Bagamasbad P, He S, LaPensee E, Raji Y, Brogley M, Chinnaiyan A, Cieslik M, Robins DM
Androgen receptor (AR) action is a hallmark of prostate cancer (PCa) with androgen deprivation being standard therapy. Yet, resistance arises and aberrant AR signaling promotes disease. We sought compounds that inhibited genes driving cancer but not normal growth and hypothesized that genes with consensus androgen r... |
A MORC-driven transcriptional switch controls Toxoplasma developmental trajectories and sexual commitment.
Farhat DC, Swale C, Dard C, Cannella D, Ortet P, Barakat M, Sindikubwabo F, Belmudes L, De Bock PJ, Couté Y, Bougdour A, Hakimi MA
Toxoplasma gondii has a complex life cycle that is typified by asexual development that takes place in vertebrates, and sexual reproduction, which occurs exclusively in felids and is therefore less studied. The developmental transitions rely on changes in the patterns of gene expression, and recent studies have assi... |
Seviteronel, a Novel CYP17 Lyase Inhibitor and Androgen Receptor Antagonist, Radiosensitizes AR-Positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells
Anna R. Michmerhuizen, Benjamin Chandler, Eric Olsen, Kari Wilder-Romans, Leah Moubadder, Meilan Liu, Andrea M. Pesch, Amanda Zhang, Cassandra Ritter, S. Tanner Ward, Alyssa Santola, Shyam Nyati, James M. Rae, Daniel Hayes, Felix Y. Feng, Daniel Spratt, D
Increased rates of locoregional recurrence (LR) have been observed in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) despite multimodality therapy, including radiation (RT). Recent data suggest inhibiting the androgen receptor (AR) may be an effective radiosensitizing strategy, and AR is expressed in 15–35% of TNBC tumo... |
Ikaros antagonizes DNA binding by STAT5 in pre-B cells.
Heizmann, Beate and Le Gras, Stéphanie and Simand, Célestine and Marchal,Patricia and Chan, Susan and Kastner, Philippe
The IKZF1 gene, which encodes the Ikaros transcription factor, is frequently deleted or mutated in patients with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemias that express oncogenes, like BCR-ABL, which activate the JAK-STAT5 pathway. Ikaros functionally antagonizes the transcriptional programs downstream of IL-7/S... |
Identification and Massively Parallel Characterization of Regulatory Elements Driving Neural Induction
Inoue Fumitaka, Kreimer Anat, Ashuach Tal, Ahituv Nadav, Yosef Nir
Epigenomic regulation and lineage-specific gene expression act in concert to drive cellular differentiation, but the temporal interplay between these processes is largely unknown. Using neural induction from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) as a paradigm, we interrogated these dynamics by performing RNA sequenci... |
Epigenetic remodelling licences adult cholangiocytes for organoid formation and liver regeneration.
Aloia L, McKie MA, Vernaz G, Cordero-Espinoza L, Aleksieva N, van den Ameele J, Antonica F, Font-Cunill B, Raven A, Aiese Cigliano R, Belenguer G, Mort RL, Brand AH, Zernicka-Goetz M, Forbes SJ, Miska EA, Huch M
Following severe or chronic liver injury, adult ductal cells (cholangiocytes) contribute to regeneration by restoring both hepatocytes and cholangiocytes. We recently showed that ductal cells clonally expand as self-renewing liver organoids that retain their differentiation capacity into both hepatocytes and ductal ... |
Epigenetic down-regulation of the HIST1 locus predicts better prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia with NPM1 mutation.
Garciaz S, N'guyen Dasi L, Finetti P, Chevalier C, Vernerey J, Poplineau M, Platet N, Audebert S, Pophillat M, Camoin L, Bertucci F, Calmels B, Récher C, Birnbaum D, Chabannon C, Vey N, Duprez E
BACKGROUND: The epigenetic machinery is frequently altered in acute myeloid leukemia. Focusing on cytogenetically normal (CN) AML, we previously described an abnormal H3K27me3 enrichment covering 70 kb on the HIST1 cluster (6.p22) in CN-AML patient blasts. Here, we further investigate the molecular, functional,... |
Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA.
Shen SY, Burgener JM, Bratman SV, De Carvalho DD
Circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) comprises small DNA fragments derived from normal and tumor tissue that are released into the bloodstream. Recently, methylation profiling of cfDNA as a liquid biopsy tool has been gaining prominence due to the presence of tissue-specific markers in cfDNA. We have previously reporte... |
EZH2 as a novel therapeutic target for atrial fibrosis and atrial fibrillation.
Song S, Zhang R, Mo B, Chen L, Liu L, Yu Y, Cao W, Fang G, Wan Y, Gu Y, Wang Y, Li Y, Yu Y, Wang Q
Angiotensin II (Ang-II)-induced fibroblast differentiation plays an important role in the development of atrial fibrosis and atrial fibrillation (AF). Here, we show that the expression of the histone methyltransferase enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is increased in atrial muscle and atrial fibroblasts in patients... |
Clinicopathological evaluation of PD-L1 expression and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte infiltrates across intracranial molecular subgroups of ependymomas: are these tumors potential candidates for immune check-point blockade?
Nambirajan A, Malgulwar PB, Sharma A, Boorgula MT, Doddamani R, Singh M, Suri V, Sarkar C, Sharma MC
Immune check-point blockade (ICB) targeting programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1)/programmed death-1 (PD-1) axis has created paradigm shift in cancer treatment. 'ST-RELA' and 'PF-A' molecular subgroups of ependymomas (EPN) show poor outcomes. We aimed to understand the potential candidature of EPNs for ICB. Suprate... |
The Toxoplasma effector TEEGR promotes parasite persistence by modulating NF-κB signalling via EZH2.
Braun L, Brenier-Pinchart MP, Hammoudi PM, Cannella D, Kieffer-Jaquinod S, Vollaire J, Josserand V, Touquet B, Couté Y, Tardieux I, Bougdour A, Hakimi MA
The protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii has co-evolved with its homeothermic hosts (humans included) strategies that drive its quasi-asymptomatic persistence in hosts, hence optimizing the chance of transmission to new hosts. Persistence, which starts with a small subset of parasites that escape host immune killing... |
A TetR-family transcription factor regulates fatty acid metabolism in the archaeal model organism Sulfolobus acidocaldarius.
Wang K, Sybers D, Maklad HR, Lemmens L, Lewyllie C, Zhou X, Schult F, Bräsen C, Siebers B, Valegård K, Lindås AC, Peeters E
Fatty acid metabolism and its regulation are known to play important roles in bacteria and eukaryotes. By contrast, although certain archaea appear to metabolize fatty acids, the regulation of the underlying pathways in these organisms remains unclear. Here, we show that a TetR-family transcriptional regulator (FadR... |
Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.
Shen SY, Singhania R, Fehringer G, Chakravarthy A, Roehrl MHA, Chadwick D, Zuzarte PC, Borgida A, Wang TT, Li T, Kis O, Zhao Z, Spreafico A, Medina TDS, Wang Y, Roulois D, Ettayebi I, Chen Z, Chow S, Murphy T, Arruda A, O'Kane GM, Liu J, Mansour M, McPher
The use of liquid biopsies for cancer detection and management is rapidly gaining prominence. Current methods for the detection of circulating tumour DNA involve sequencing somatic mutations using cell-free DNA, but the sensitivity of these methods may be low among patients with early-stage cancer given the limited ... |
RbAp48 Protein Is a Critical Component of GPR158/OCN Signaling and Ameliorates Age-Related Memory Loss.
Kosmidis S, Polyzos A, Harvey L, Youssef M, Denny CA, Dranovsky A, Kandel ER
Precisely deciphering the molecular mechanisms of age-related memory loss is crucial to create appropriate therapeutic interventions. We have previously shown that the histone-binding protein RbAp48/Rbbp4 is a molecular determinant of Age-Related Memory Loss. By exploring how this protein regulates the genomic lands... |
Convergent evolution of complex genomic rearrangements in two fungal meiotic drive elements.
Svedberg J, Hosseini S, Chen J, Vogan AA, Mozgova I, Hennig L, Manitchotpisit P, Abusharekh A, Hammond TM, Lascoux M, Johannesson H
Meiotic drive is widespread in nature. The conflict it generates is expected to be an important motor for evolutionary change and innovation. In this study, we investigated the genomic consequences of two large multi-gene meiotic drive elements, Sk-2 and Sk-3, found in the filamentous ascomycete Neurospora intermedi... |
IFN-γ immune priming of macrophages in vivo induces prolonged STAT1 binding and protection against Cryptococcus neoformans.
Leopold Wager CM, Hole CR, Campuzano A, Castro-Lopez N, Cai H, Caballero Van Dyke MC, Wozniak KL, Wang Y, Wormley FL
Development of vaccines against opportunistic infections is difficult as patients most at risk of developing disease are deficient in aspects of the adaptive immune system. Here, we utilized an experimental immunization strategy to induce innate memory in macrophages in vivo. Unlike current trained immunity models, ... |
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) 1 and 2 complexes regulate both histone acetylation and crotonylation in vivo.
Kelly RDW, Chandru A, Watson PJ, Song Y, Blades M, Robertson NS, Jamieson AG, Schwabe JWR, Cowley SM
Proteomic analysis of histones has shown that they are subject to a superabundance of acylations, which extend far beyond acetylation, to include: crotonylation, propionylation, butyrylation, malonylation, succinylation, β-hydroxybutyrylation and 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation. To date, much of the functional data ha... |
Identification of miR-379/miR-656 (C14MC) cluster downregulation and associated epigenetic and transcription regulatory mechanism in oligodendrogliomas.
Kumar A, Nayak S, Pathak P, Purkait S, Malgulawar PB, Sharma MC, Suri V, Mukhopadhyay A, Suri A, Sarkar C
INTRODUCTION: Although role of individual microRNAs (miRNAs) in the pathogenesis of gliomas has been well studied, their role as a clustered remains unexplored in gliomas. METHODS: In this study, we performed the expression analysis of miR-379/miR-656 miRNA-cluster (C14MC) in oligodendrogliomas (ODGs) and also inves... |
Epigenetic regulation of brain region-specific microglia clearance activity.
Ayata P, Badimon A, Strasburger HJ, Duff MK, Montgomery SE, Loh YE, Ebert A, Pimenova AA, Ramirez BR, Chan AT, Sullivan JM, Purushothaman I, Scarpa JR, Goate AM, Busslinger M, Shen L, Losic B, Schaefer A
The rapid elimination of dying neurons and nonfunctional synapses in the brain is carried out by microglia, the resident myeloid cells of the brain. Here we show that microglia clearance activity in the adult brain is regionally regulated and depends on the rate of neuronal attrition. Cerebellar, but not striatal or... |
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 attenuates the very high expression of the Arabidopsis gene NRT2.1.
Bellegarde F, Herbert L, Séré D, Caillieux E, Boucherez J, Fizames C, Roudier F, Gojon A, Martin A
PRC2 is a major regulator of gene expression in eukaryotes. It catalyzes the repressive chromatin mark H3K27me3, which leads to very low expression of target genes. NRT2.1, which encodes a key root nitrate transporter in Arabidopsis, is targeted by H3K27me3, but the function of PRC2 on NRT2.1 remains unclear. Here, ... |
p27 regulates alpha-synuclein expression.
Gallastegui E, Domuro C, Serratosa J, Larrieux A, Sin L, Martinez J, Besson A, Morante-Redolat JM, Orlando S, Aligue R, Fariñas I, Pujol MJ, Bachs O
Alpha-synuclein (α-SYN) is the main component of anomalous protein aggregates (Lewy bodies) that play a crucial role in several neurodegenerative diseases (synucleinopathies) like Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy. However, the mechanisms involved in its transcriptional regulation are poorly unde... |
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay in the Hyperthermoacidophilic Crenarchaeon, Sulfolobus acidocaldarius.
Wang K. et al.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) is a powerful method used for identifying genome-wide DNA-protein interactions in vivo. A large number of essential intracellular processes such as DNA replication, transcription regulation, chromatin stability, and others are all dependent on protein interactions with DNA. The D... |
ChIP-Seq analysis identifies p27(Kip1)-target genes involved in cell adhesion and cell signalling in mouse embryonic fibroblasts
Biçer A. et al.
The protein p27Kip1 (p27), a member of the Cip-Kip family of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, is involved in tumorigenesis and a correlation between reduced levels of this protein in human tumours and a worse prognosis has been established. Recent reports revealed that p27 also behaves as a transcriptional regula... |
PDGFR-modulated miR-23b cluster and miR-125a-5p suppress lung tumorigenesis by targeting multiple components of KRAS and NF-kB pathways
Naidu S. et al.
In NSCLC alterations in PDGF receptors are markers of worst prognosis and efficient targeting of these receptors is yet to be achieved. In this study, we explored PDGFR-regulated microRNAs demonstrating that miR-23b cluster and miR-125a-5p are downregulated by increased expression of PDGFR-α or PDGFR-β in... |
Data on novel DNA methylation changes induced by valproic acid in human hepatocytes
Wolters J. et al.
Valproic acid (VPA) is a widely prescribed antiepileptic drug in the world. Despite its pharmacological importance, it may cause liver toxicity and steatosis. However the exact mechanism of the steatosis formation is unknown. The data presented in this DIB publication is used to further investigate the VPA-induced m... |
Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA Methylation Patterns Induced by Valproic Acid in Human Hepatocytes
Wolters J.E.J. et al.
Valproic acid (VPA) is one of the most widely prescribed antiepileptic drugs in the world. Despite its pharmacological importance, it may cause liver toxicity and steatosis through mitochondrial dysfunction. The aim of this study is to further investigate VPA-induced mechanisms of steatosis by analyzing changes in p... |
Distinguishing States of Arrest: Genome-Wide Descriptions of Cellular Quiescence Using ChIP-Seq and RNA-Seq Analysis.
Srivastava S. et al.
Regenerative potential in adult stem cells is closely associated with the establishment of-and exit from-a temporary state of quiescence. Emerging evidence not only provides a rationale for the link between lineage determination programs and cell cycle regulation but also highlights the understanding of quiescence a... |
High-Resolution Chromatin Immunoprecipitation: ChIP-Sequencing
Diaz R.E. et al.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) coupled with next-generation sequencing (NGS) is widely used for studying the nucleoprotein components that are involved in the various cellular processes required for shaping the bacterial nucleoid. This methodology, termed ChIP-sequencing (ChIP-seq), enables the identification ... |
Epigenome profiling and editing of neocortical progenitor cells during development
Albert M. et al.
The generation of neocortical neurons from neural progenitor cells (NPCs) is primarily controlled by transcription factors binding to DNA in the context of chromatin. To understand the complex layer of regulation that orchestrates different NPC types from the same DNA sequence, epigenome maps with cell type resoluti... |
Plant-Specific Histone Deacetylases HDT1/2 Regulate GIBBERELLIN 2-OXIDASE2 Expression to Control Arabidopsis Root Meristem Cell Number
Li H. et al.
Root growth is modulated by environmental factors and depends on cell production in the root meristem (RM). New cells in the meristem are generated by stem cells and transit-amplifying cells, which together determine RM cell number. Transcription factors and chromatin-remodeling factors have been implicated in regul... |
MAPK-triggered chromatin reprogramming by histone deacetylase in plant innate immunity
Latrasse D. et al.
Background
Microbial-associated molecular patterns activate several MAP kinases, which are major regulators of the innate immune response in Arabidopsis thaliana that induce large-scale changes in gene expression. Here, we determine whether microbial-associated molecular pattern-triggered gene expression involv... |
The Arabidopsis SWI/SNF protein BAF60 mediates seedling growth control by modulating DNA accessibility
Jégu T. et al.
Background
Plant adaptive responses to changing environments involve complex molecular interplays between intrinsic and external signals. Whilst much is known on the signaling components mediating diurnal, light, and temperature controls on plant development, their influence on chromatin-based transcriptional c... |
LRP8-Reelin-Regulated Neuronal Enhancer Signature Underlying Learning and Memory Formation
Telese F. et al.
One of the exceptional properties of the brain is its ability to acquire new knowledge through learning and to store that information through memory. The epigenetic mechanisms linking changes in neuronal transcriptional programs to behavioral plasticity remain largely unknown. Here, we identify the epigenetic signat... |
PPARγ Links BMP2 and TGFβ1 Pathways in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells, Regulating Cell Proliferation and Glucose Metabolism
Laurent Calvier, Philippe Chouvarine, Ekaterina Legchenko, Nadine Hoffmann, Jonas Geldner, Paul Borchert, Danny Jonigk, Miklos M. Mozes, Georg Hansmann
BMP2 and TGFβ1 are functional antagonists of pathological remodeling in the arteries, heart, and lung; however, the mechanisms in VSMCs, and their disturbance in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), are unclear. We found a pro-proliferative TGFβ1-Stat3-FoxO1 axis in VSMCs, and PPARγ as in... |
sgs1: a neomorphic nac52 allele impairing PTGS through SGS3 down-regulation
Butel N. et al.
Post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS) is a defense mechanism that targets invading nucleic acids from endogenous (transposons) or exogenous (pathogens, transgenes) sources. Genetic screens based on the reactivation of silenced transgenes have long been used to identify cellular components and regulators of PTGS... |
Liver receptor homolog-1 (NR5a2) regulates CD95/Fas ligand transcription and associated T-cell effector functions.
Schwaderer J. et al.
CD95/Fas ligand (FasL) is a cell death-promoting member of the tumor necrosis factor family with important functions in the regulation of T-cell homeostasis and cytotoxicity. In T cells, FasL expression is tightly regulated on a transcriptional level involving a complex set of different transcription factors. The or... |
Development of Peptidomimetic Inhibitors of the ERG Gene Fusion Product in Prostate Cancer
Wang W. et al.
Transcription factors play a key role in the development of diverse cancers, and therapeutically targeting them has remained a challenge. In prostate cancer, the gene encoding the transcription factor ERG is recurrently rearranged and plays a critical role in prostate oncogenesis. Here, we identified a series of pep... |
Hoxa9 and Meis1 Cooperatively Induce Addiction to Syk Signaling by Suppressing miR-146a in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Mohr S. et al.
The transcription factor Meis1 drives myeloid leukemogenesis in the context of Hox gene overexpression but is currently considered undruggable. We therefore investigated whether myeloid progenitor cells transformed by Hoxa9 and Meis1 become addicted to targetable signaling pathways. A comprehensive (phospho)pro... |
Type I interferon-enhanced IL-10 expression in human CD4 T cells is regulated by STAT3, STAT2, and BATF transcription factors
Govender U. et al.
Type I IFN can exert pro- and anti-inflammatory activities in the immune system. Here, we have investigated the mechanism by which IFN-α enhances early expression of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in human CD45RA+CD4+ T cells. With the use of transcriptomic and biochemical approaches, we found distinct a... |
H3K23me1 is an evolutionarily conserved histone modification associated with CG DNA methylation in Arabidopsis
Trejo-Arellano M.S. et al.
Amino-terminal tails of histones are targets for diverse post-translational modifications whose combinatorial action may constitute a code that will be read and interpreted by cellular proteins to define particular transcriptional states. Here, we describe monomethylation of histone H3 lysine 23 (H3K23me1) as a hist... |
Applying the INTACT method to purify endosperm nuclei and to generate parental-specific epigenome profiles.
Moreno-Romero J. et al.
The early endosperm tissue of dicot species is very difficult to isolate by manual dissection. This protocol details how to apply the INTACT (isolation of nuclei tagged in specific cell types) system for isolating early endosperm nuclei of Arabidopsis at high purity and how to generate parental-specific epigenome pr... |
Transcriptional Activation of Pericentromeric Satellite Repeats and Disruption of Centromeric Clustering upon Proteasome Inhibition
Natisvili T. et al.
Heterochromatinisation of pericentromeres, which in mice consist of arrays of major satellite repeats, are important for centromere formation and maintenance of genome stability. The dysregulation of this process has been linked to genomic stress and various cancers. Here we show in mice that the proteasome binds to... |
The lncRNA landscape of breast cancer reveals a role for DSCAM-AS1 in breast cancer progression
Niknafs YS et al.
Molecular classification of cancers into subtypes has resulted in an advance in our understanding of tumour biology and treatment response across multiple tumour types. However, to date, cancer profiling has largely focused on protein-coding genes, which comprise <1% of the genome. Here we leverage a compendium o... |
Dynamic Interplay between the Transcriptome and Methylome in Response to Oxidative and Alkylating Stress
Deferme L et al.
In recent years, it has been shown that free radicals not only react directly with DNA but also regulate epigenetic processes such as DNA methylation, which may be relevant within the context of, for example, tumorigenesis. However, how these free radicals impact the epigenome remains unclear. We therefore investiga... |
Parental epigenetic asymmetry of PRC2-mediated histone modifications in the Arabidopsis endosperm
Moreno-Romero J et al.
Parental genomes in the endosperm are marked by differential DNA methylation and are therefore epigenetically distinct. This epigenetic asymmetry is established in the gametes and maintained after fertilization by unknown mechanisms. In this manuscript, we have addressed the key question whether parentally inherited... |