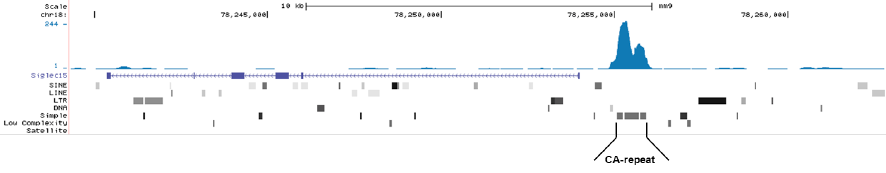
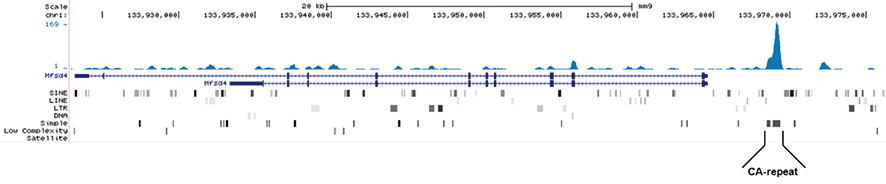
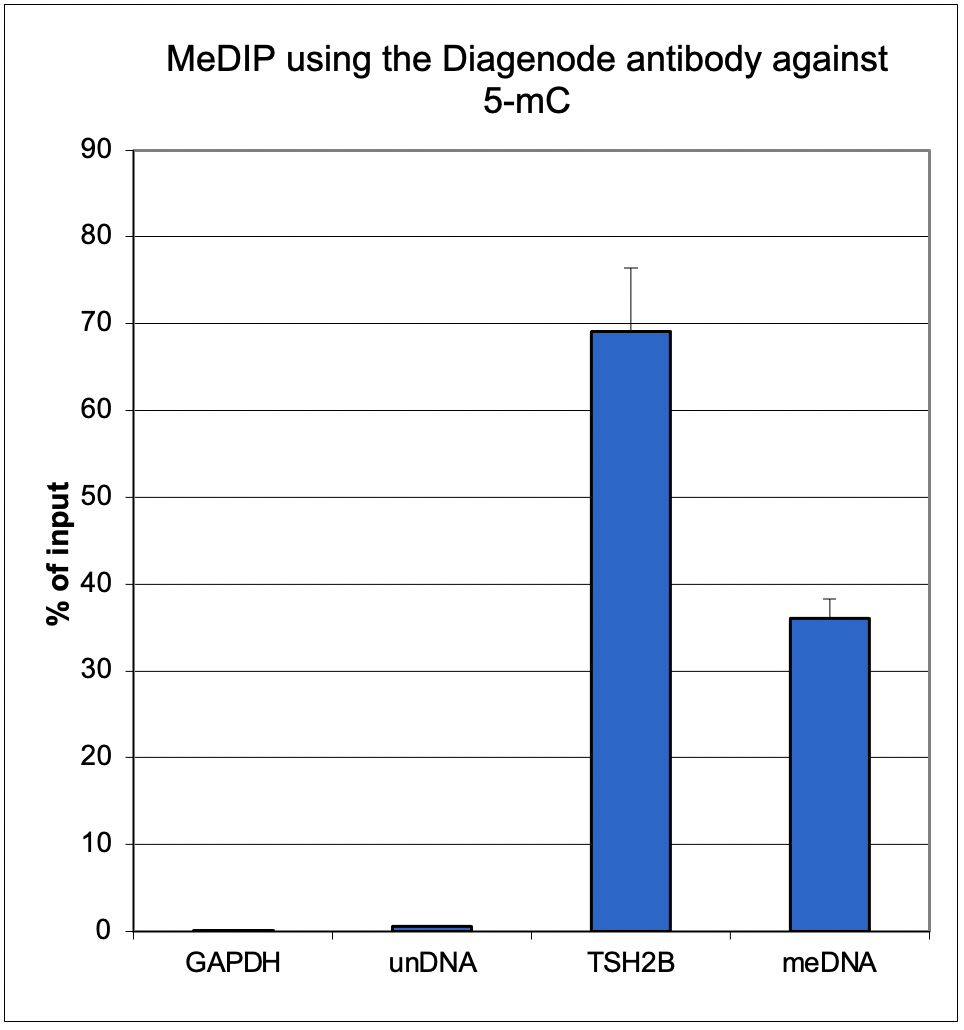
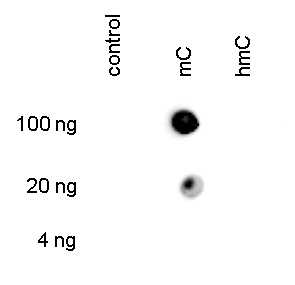
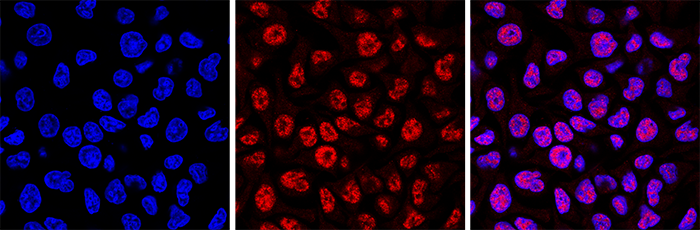
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) monoclonal antibody 33D3 (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15200081-500 Lot# RD-007). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
HIV Infection as an Independent Factor Accelerating Epigenetic Ageing in Men Treated with Integrase Inhibitors: A Case–Control Study
Bożejko, Mateusz et al.
Abstract
A number of published studies suggest that HIV infection accelerates epigenetic ageing. The main aim of this study was to ascertain if HIV infection is an independent factor leading to DNA hypomethylation and accelerating epigenetic ageing in men successfully treated with integrase inhibitor (INSTI)-based ... |
Analog epigenetic memory revealed by targeted chromatin editing
Palacios, Sebastian et al.
Cells store information by means of chromatin modifications that persist through cell divisions and can hold gene expression silenced over generations. However, how these modifications may maintain other gene expression states has remained unclear. This study shows that chromatin modifications can maintain a wide ... |
De novo assembly and delivery of synthetic megabase-scale human DNA into mouse early embryos
Liu, Yue et al.
Epigenetic modifications on natural chromosomes are inherited and maintained in a default state, making it challenging to remove intrinsic marks to study the fundamental principles of their establishment and further influence on transcriptional regulation. In this study, we developed SynNICE, a method for assemb... |
Traditional Chinese Medicine Luo Tong Formula attenuates retinal injury in experimental diabetic retinopathy via modulation of DNA methylation: in vivo experiment integrated with molecular docking, ADMET assessment, and molecular dynamics simulation
Xue, Chongxiang et al.
Background: Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a leading cause of blindness in the adult population. Luo-Tong Formula (LTF), a traditional Chinese medicine prescription, has been frequently employed in the treatment of DR. However, the ability of LTF to prevent retinal injury and disease progression, as well as potential ... |
Epigenetic responses in Borrelia-infected Ixodes scapularis ticks: Over-expression of euchromatic histone lysine methyltransferase 2 and no change in DNA methylation
MacIntosh, Grace Hadley et al.
Borrelia burgdorferi, a tick-vectored spirochete bacteria best known for causing Lyme disease, has been found to induce physiological and behavioural changes in its tick vector that can increase tick fitness and its ability to transmit the bacteria. The mechanism by which this bacterium modulates these changes r... |
Coupling Immunoprecipitation with Multiplexed Digital PCR for Cell-Free DNA Methylation Detection in Small Plasma Volumes of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer
Truong, Truong T et al.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a major global health challenge, with an increasing incidence of early-onset cases among young adults. Targeted analysis of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylation in blood has emerged as a promising minimally invasive diagnostic approach. While digital PCR (dPCR) offers high sensitivit... |
Transgenerational inheritance of diabetes susceptibility in male offspring with maternal androgen exposure
Yuqing, Zhang., et al.
Androgen exposure (AE) poses a profound health threat to women, yet its transgenerational impacts on male descendants remain unclear. Here, employing a large-scale mother-child cohort, we show that maternal hyperandrogenism predisposes sons to β-cell dysfunction. Male offspring mice with prenatal AE exhibited h... |
Elevating RNA m5C methylation provides a promising strategy for crop productivity
Xiaofeng Gu et al.
RNA 5-methylcytidine (m5C) has been identified as a key epi-transcriptomic modification of mRNAs involved in regulating multiple post-transcriptional processes. Here, we found that knockout of the RNA m5C demethylase, OsNOP2, results in elevated m5C levels and positively influences numerous agronomic traits in rice.... |
Exploring the Epigenetic Landscape of Spermatozoa: Impact of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Supplementation on DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation
Elisa Hug et al.
Reproductive success is dependent on gamete integrity, and oxidative stress alters male nuclei, meaning that no DNA repair is possible due to chromatin compaction. The composition of sperm makes it highly sensitive to reactive oxygen species (ROS) but, at the same time, ROS are needed for sperm physiology. Over the ... |
A multidimensional recommendation framework for identifying biological targets to aid the diagnosis and treatment of liver metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer
Feng Qi et al.
The quest to understand the molecular mechanisms of tumour metastasis and identify pivotal biomarkers for cancer therapy is increasing in importance. Single-omics analyses, constrained by their focus on a single biological layer, cannot fully elucidate the complexities of tumour molecular profiles and can thus overl... |
Differential methylation of circulating free DNA assessed through cfMeDiP as a new tool for breast cancer diagnosis and detection of BRCA1/2 mutation
Piera Grisolia et al.
Background
Recent studies have highlighted the importance of the cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylation profile in detecting breast cancer (BC) and its different subtypes. We investigated whether plasma cfDNA methylation, using cell-free Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation and High-Throughput Sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq), ma... |
Prediction of brain metastasis development with DNA methylation signatures
Jeffrey A. Zuccato et al.
Brain metastases (BMs) are the most common and among the deadliest brain tumors. Currently, there are no reliable predictors of BM development from primary cancer, which limits early intervention. Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most common BM source and here we obtained 402 tumor and plasma samples from a large c... |
RNA m5C oxidation by TET2 regulates chromatin state and leukaemogenesis
Zhongyu Zou et al.
Mutation of tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 2 (encoded by TET2) drives myeloid malignancy initiation and progression1,2,3. TET2 deficiency is known to cause a globally opened chromatin state and activation of genes contributing to aberrant haematopoietic stem cell self-renewal4,5. However, the open chromatin obs... |
Differentiation block in acute myeloid leukemia regulated by intronicsequences of FTO
Camera F. et al.
Iroquois transcription factor gene IRX3 is highly expressed in 20–30\% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and contributes to the pathognomonic differentiation block. Intron 8 FTO sequences ∼220kB downstream of IRX3 exhibit histone acetylation, DNA methylation, and contacts with th... |
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase sustains a core epigenetic programthat promotes metastatic colonization in breast cancer.
Couto J.P. et al.
Metastatic colonization of distant organs accounts for over 90% of deaths related to solid cancers, yet the molecular determinants of metastasis remain poorly understood. Here, we unveil a mechanism of colonization in the aggressive basal-like subtype of breast cancer that is driven by the NAD+ metabolic enzyme... |
The Effect of Metformin and Carbohydrate-Controlled Diet onDNA Methylation and Gene Expression in the Endometrium of Womenwith Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
Garcia-Gomez E. et al.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine disease associated with infertility and metabolic disorders in reproductive-aged women. In this study, we evaluated the expression of eight genes related to endometrial function and their DNA methylation levels in the endometrium of PCOS patients and women without the... |
Epigenetic modifier alpha-ketoglutarate modulates aberrant gene bodymethylation and hydroxymethylation marks in diabetic heart.
Dhat R. et al.
BACKGROUND: Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a leading cause of death in diabetic patients. Hyperglycemic myocardial microenvironment significantly alters chromatin architecture and the transcriptome, resulting in aberrant activation of signaling pathways in a diabetic heart. Epigenetic marks play vital roles in tra... |
Integrated analysis from multicentre studies identities RNAmethylation- related lncRNA risk stratification systems for glioma
Huang Fanxuan and Wang Xinyu and Zhong Junzhe and Chen Hao and Song Dan and Xu Tianye and Tian Kaifu and Sun Penggang and Sun Nan and Ma Wenbin and Liu Yuxiang andYu Daohan and Meng Xiangqi and Jiang Chuanlu and Xuan Hanwen and Qian Da an
Gastric cancer (GC) is the fourth leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Due to the lack of effective chemotherapy methods for advanced gastric cancer and poor prognosis, the emergence of immunotherapy has brought new hope to gastric cancer. Further research is needed to improve the response rate to immunotherapy ... |
The RNA m5C Methylase NSUN2 Modulates Corneal EpithelialWound Healing.
Luo G. et al.
PURPOSE: The emerging epitranscriptomics offers insights into the physiopathological roles of various RNA modifications. The RNA methylase NOP2/Sun domain family member 2 (NSUN2) catalyzes 5-methylcytosine (m5C) modification of mRNAs. However, the role of NSUN2 in corneal epithelial wound healing (CEWH) remains unkn... |
Methylation and expression of glucocorticoid receptor exon-1 variants andFKBP5 in teenage suicide-completers.
Rizavi H. et al.
A dysregulated hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis has repeatedly been demonstrated to play a fundamental role in psychiatric disorders and suicide, yet the mechanisms underlying this dysregulation are not clear. Decreased expression of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) gene, which is also susceptible to epigen... |
Bridging biological cfDNA features and machine learning approaches.
Moser T. et al.
Liquid biopsies (LBs), particularly using circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), are expected to revolutionize precision oncology and blood-based cancer screening. Recent technological improvements, in combination with the ever-growing understanding of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) biology, are enabling the detection of tumor-speci... |
Gene body DNA hydroxymethylation restricts the magnitude oftranscriptional changes during aging.
Occean J. R. et al.
DNA hydroxymethylation (5hmC) is the most abundant oxidative derivative of DNA methylation (5mC) and is typically enriched at enhancers and gene bodies of transcriptionally active and tissue-specific genes. Although aberrant genomic 5hmC has been implicated in many age-related diseases, the functional role of the mo... |
Consistent DNA Hypomethylations in Prostate Cancer.
Araúzo-Bravo M.J. et al.
With approximately 1.4 million men annually diagnosed with prostate cancer (PCa) worldwide, PCa remains a dreaded threat to life and source of devastating morbidity. In recent decades, a significant decrease in age-specific PCa mortality has been achieved by increasing prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening and i... |
RNA 5-Methylcytosine Modification Regulates VegetativeDevelopment Associated with H3K27 Trimethylation inArabidopsis.
Zhang D.et al.
Methylating RNA post-transcriptionally is emerging as a significant mechanism of gene regulation in eukaryotes. The crosstalk between RNA methylation and histone modification is critical for chromatin state and gene expression in mammals. However, it is not well understood mechanistically in plants. Here, the author... |
Cardiac epigenetic changes in VEGF signaling genes associates with myocardial microvascular rarefaction in experimental chronic kidney disease.
Eirin Alfonso and Chade Alejandro R
BACKGROUND: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is common in patients with heart failure, and often results in left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD). However, the mechanisms responsible for cardiac damage in CKD-LVDD remain to be elucidated. Epigenetic alterations may impose long-lasting effects on cellular transcr... |
The Arabidopsis APOLO and human UPAT sequence-unrelated longnoncoding RNAs can modulate DNA and histone methylation machineries inplants.
Fonouni-Farde C. et al.
BACKGROUND: RNA-DNA hybrid (R-loop)-associated long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), including the Arabidopsis lncRNA AUXIN-REGULATED PROMOTER LOOP (APOLO), are emerging as important regulators of three-dimensional chromatin conformation and gene transcriptional activity. RESULTS: Here, we show that in addition to the PRC1... |
A genome-wide screen reveals new regulators of the 2-cell-like cell state
Defossez Pierre-Antoine et al.
In mammals, only the zygote and blastomeres of the early embryo are fully totipotent. This totipotency is mirrored in vitro by mouse "2-cell-like cells" (2CLCs), which appear at low frequency in cultures of Embryonic Stem cells (ESCs). Because totipotency is incompletely understood, we carried out a genomewide CRISP... |
NSUN2-mediated RNA mC modification modulates uveal melanoma cellproliferation and migration.
Luo Guangying et al.
RNA 5-methylcytosine (mC) is a widespread post-transcriptional modification involved in diverse biological processes through controlling RNA metabolism. However, its roles in uveal melanoma (UM) remain unknown. Here, we describe the biological roles and regulatory mechanisms of RNA mC in UM. Initially, we identified... |
Global DNA methylation and cellular 5-methylcytosine and H4acetylated patterns in primary and secondary dormant seeds of Capsellabursa-pastoris (L.) Medik. (shepherd's purse).
Gomez-Cabellos Sara et al.
Despite the importance of dormancy and dormancy cycling for plants' fitness and life cycle phenology, a comprehensive characterization of the global and cellular epigenetic patterns across space and time in different seed dormancy states is lacking. Using Capsella bursa-pastoris (L.) Medik. (shepherd's purse) seeds ... |
Stella regulates the Development of Female Germline Stem Cells byModulating Chromatin Structure and DNA Methylation.
Hou Changliang et al.
Female germline stem cells (FGSCs) have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into oocytes. , encoded by a maternal effect gene, plays an important role in oogenesis and early embryonic development. However, its function in FGSCs remains unclear. In this study, we showed that CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of p... |
Highly recurrent epimutations in gastric cancer CpG islandmethylator phenotypes and inflammation
Padmanabhan N. et al.
Background CIMP (CpG island methylator phenotype) is an epigenetic molecular subtype, observed in multiple malignancies and associated with the epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressors. Currently, for most cancers including gastric cancer (GC), mechanisms underlying CIMP remain poorly understood. We sought to disco... |
LINE-1 transcription in round spermatids is associated with accretion of5-carboxylcytosine in their open reading frames
Blythe M. et al.
Chromatin of male and female gametes undergoes a number of reprogramming events during the transition from germ cell to embryonic developmental programs. Although the rearrangement of DNA methylation patterns occurring in the zygote has been extensively characterized, little is known about the dynamics of DNA modifi... |
Sensitive and reproducible cell-free methylome quantification with synthetic spike-in controls
Wilson, S.L. et al.
Background. Cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation-sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq) identifies genomic regions with DNA methylation, using a protocol adapted to work with low-input DNA samples and with cell-free DNA (cfDNA). This method allows for DNA methylation profiling of circulating tumour DNA in cancer patients&... |
Detection of renal cell carcinoma using plasma and urine cell-free DNA methylomes.
Nuzzo PV, Berchuck JE, Korthauer K, Spisak S, Nassar AH, Abou Alaiwi S, Chakravarthy A, Shen SY, Bakouny Z, Boccardo F, Steinharter J, Bouchard G, Curran CR, Pan W, Baca SC, Seo JH, Lee GM, Michaelson MD, Chang SL, Waikar SS, Sonpavde G, Irizarry RA, Pome
Improving early cancer detection has the potential to substantially reduce cancer-related mortality. Cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq) is a highly sensitive assay capable of detecting early-stage tumors. We report accurate classification of patients across all ... |
Detection and discrimination of intracranial tumors using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.
Nassiri F, Chakravarthy A, Feng S, Shen SY, Nejad R, Zuccato JA, Voisin MR, Patil V, Horbinski C, Aldape K, Zadeh G, De Carvalho DD
Definitive diagnosis of intracranial tumors relies on tissue specimens obtained by invasive surgery. Noninvasive diagnostic approaches provide an opportunity to avoid surgery and mitigate unnecessary risk to patients. In the present study, we show that DNA-methylation profiles from plasma reveal highly specific sign... |
AXR1 affects DNA methylation independently of its role in regulatingmeiotic crossover localization.
Christophorou, N and She, W and Long, J and Hurel, A and Beaubiat, S andIdir, Y and Tagliaro-Jahns, M and Chambon, A and Solier, V and Vezon, D andGrelon, M and Feng, X and Bouché, N and Mézard, C
Meiotic crossovers (COs) are important for reshuffling genetic information between homologous chromosomes and they are essential for their correct segregation. COs are unevenly distributed along chromosomes and the underlying mechanisms controlling CO localization are not well understood. We previously showed that m... |
In vitro capture and characterization of embryonic rosette-stage pluripotency between naive and primed states.
Neagu A, van Genderen E, Escudero I, Verwegen L, Kurek D, Lehmann J, Stel J, Dirks RAM, van Mierlo G, Maas A, Eleveld C, Ge Y, den Dekker AT, Brouwer RWW, van IJcken WFJ, Modic M, Drukker M, Jansen JH, Rivron NC, Baart EB, Marks H, Ten Berge D
Following implantation, the naive pluripotent epiblast of the mouse blastocyst generates a rosette, undergoes lumenogenesis and forms the primed pluripotent egg cylinder, which is able to generate the embryonic tissues. How pluripotency progression and morphogenesis are linked and whether intermediate pluripotent st... |
Episo: quantitative estimation of RNA 5-methylcytosine at isoform level by high-throughput sequencing of RNA treated with bisulfite.
Liu J, An Z, Luo J, Li J, Li F, Zhang Z
MOTIVATION: RNA 5-methylcytosine (m5C) is a type of post-transcriptional modification that may be involved in numerous biological processes and tumorigenesis. RNA m5C can be profiled at single-nucleotide resolution by high-throughput sequencing of RNA treated with bisulfite (RNA-BisSeq). However, the exploration of ... |
Intra- and inter-generational changes in the cortical DNA methylome in response to therapeutic intermittent hypoxia in mice.
Belmonte KCD, Harman JC, Lanson NA, Gidday JM
Recent evidence from our lab documents functional resilience to retinal ischemic injury in untreated mice derived from parents exposed to repetitive hypoxic conditioning (RHC) prior to breeding. To begin to understand the epigenetic basis of this intergenerational protection, we used methylated DNA immunoprecipitati... |
Lithium treatment reverses irradiation-induced changes in rodent neural progenitors and rescues cognition.
Zanni G, Goto S, Fragopoulou AF, Gaudenzi G, Naidoo V, Di Martino E, Levy G, Dominguez CA, Dethlefsen O, Cedazo-Minguez A, Merino-Serrais P, Stamatakis A, Hermanson O, Blomgren K
Cranial radiotherapy in children has detrimental effects on cognition, mood, and social competence in young cancer survivors. Treatments harnessing hippocampal neurogenesis are currently of great relevance in this context. Lithium, a well-known mood stabilizer, has both neuroprotective, pro-neurogenic as well as ant... |
Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA.
Shen SY, Burgener JM, Bratman SV, De Carvalho DD
Circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) comprises small DNA fragments derived from normal and tumor tissue that are released into the bloodstream. Recently, methylation profiling of cfDNA as a liquid biopsy tool has been gaining prominence due to the presence of tissue-specific markers in cfDNA. We have previously reporte... |
Silencing of tumor-suppressive NR_023387 in renal cell carcinoma via promoter hypermethylation and HNF4A deficiency.
Zhou H, Guo L, Yao W, Shi R, Yu G, Xu H, Ye Z
Dysregulation of the epigenetic status of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) has been linked to diverse human diseases including human cancers. However, the landscape of the whole-genome methylation profile of lncRNAs and the precise roles of these lncRNAs remain elusive in renal cell carcinoma (RCC). We first examined l... |
Epitranscriptomic Addition of mC to HIV-1 Transcripts Regulates Viral Gene Expression.
Courtney DG, Tsai K, Bogerd HP, Kennedy EM, Law BA, Emery A, Swanstrom R, Holley CL, Cullen BR
How the covalent modification of mRNA ribonucleotides, termed epitranscriptomic modifications, alters mRNA function remains unclear. One issue has been the difficulty of quantifying these modifications. Using purified HIV-1 genomic RNA, we show that this RNA bears more epitranscriptomic modifications than ... |
Aberrant expression of imprinted lncRNA MEG8 causes trophoblast dysfunction and abortion.
Sheng F, Sun N, Ji Y, Ma Y, Ding H, Zhang Q, Yang F, Li W
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a group of noncoding RNAs whose nucleotides are longer than 200 bp. Previous studies have shown that they play an important regulatory role in many developmental processes and biological pathways. However, the contributions of lncRNAs to placental development are largely unkn... |
Defining UHRF1 Domains that Support Maintenance of Human Colon Cancer DNA Methylation and Oncogenic Properties.
Kong X, Chen J, Xie W, Brown SM, Cai Y, Wu K, Fan D, Nie Y, Yegnasubramanian S, Tiedemann RL, Tao Y, Chiu Yen RW, Topper MJ, Zahnow CA, Easwaran H, Rothbart SB, Xia L, Baylin SB
UHRF1 facilitates the establishment and maintenance of DNA methylation patterns in mammalian cells. The establishment domains are defined, including E3 ligase function, but the maintenance domains are poorly characterized. Here, we demonstrate that UHRF1 histone- and hemimethylated DNA binding functions, but not E3 ... |
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Activity and Remodeling of Glycerophosphocholine Lipids Support Cytokine Induction in Response to Fungal Patterns.
Márquez S, Fernández JJ, Mancebo C, Herrero-Sánchez C, Alonso S, Sandoval TA, Rodríguez Prados M, Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Montero O, Fernández N, Sánchez Crespo M
Increased glycolysis parallels immune cell activation, but the role of pyruvate remains largely unexplored. We found that stimulation of dendritic cells with the fungal surrogate zymosan causes decreases of pyruvate, citrate, itaconate, and α-ketoglutarate, while increasing oxaloacetate, succinate, lactate, ox... |
Increased Serine and One-Carbon Pathway Metabolism by PKCλ/ι Deficiency Promotes Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer.
Reina-Campos M, Linares JF, Duran A, Cordes T, L'Hermitte A, Badur MG, Bhangoo MS, Thorson PK, Richards A, Rooslid T, Garcia-Olmo DC, Nam-Cha SY, Salinas-Sanchez AS, Eng K, Beltran H, Scott DA, Metallo CM, Moscat J, Diaz-Meco MT
Increasingly effective therapies targeting the androgen receptor have paradoxically promoted the incidence of neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC), the most lethal subtype of castration-resistant prostate cancer (PCa), for which there is no effective therapy. Here we report that protein kinase C (PKC)λ/&iota... |
Global distribution of DNA hydroxymethylation and DNA methylation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Wernig-Zorc S, Yadav MP, Kopparapu PK, Bemark M, Kristjansdottir HL, Andersson PO, Kanduri C, Kanduri M
BACKGROUND: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has been a good model system to understand the functional role of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in cancer progression. More recently, an oxidized form of 5-mC, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) has gained lot of attention as a regulatory epigenetic modification with prognostic ... |
Transcriptome-Wide Mapping 5-Methylcytosine by mC RNA Immunoprecipitation Followed by Deep Sequencing in Plant.
Gu X, Liang Z
Transcriptome-wide mapping RNA modification is crucial to understand the distribution and function of RNA modifications. Here, we describe a protocol to transcriptome-wide mapping 5-methylcytosine (mC) in plant, by a RNA immunoprecipitation followed by deep sequencing (mC-RIP-seq) approach. The procedure includes RN... |
Sensitivity of pituitary gonadotropes to hyperglycemia leads to epigenetic aberrations and reduced follicle-stimulating hormone levels.
Feldman A, Saleh A, Pnueli L, Qiao S, Shlomi T, Boehm U, Melamed P
The connection between metabolism and reproductive function is well recognized, and we hypothesized that the pituitary gonadotropes, which produce luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), mediate some of the effects directly via insulin-independent glucose transporters, which allow continued gluco... |
Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.
Shen SY, Singhania R, Fehringer G, Chakravarthy A, Roehrl MHA, Chadwick D, Zuzarte PC, Borgida A, Wang TT, Li T, Kis O, Zhao Z, Spreafico A, Medina TDS, Wang Y, Roulois D, Ettayebi I, Chen Z, Chow S, Murphy T, Arruda A, O'Kane GM, Liu J, Mansour M, McPher
The use of liquid biopsies for cancer detection and management is rapidly gaining prominence. Current methods for the detection of circulating tumour DNA involve sequencing somatic mutations using cell-free DNA, but the sensitivity of these methods may be low among patients with early-stage cancer given the limited ... |
Transcription Factors Drive Tet2-Mediated Enhancer Demethylation to Reprogram Cell Fate.
Sardina JL, Collombet S, Tian TV, Gómez A, Di Stefano B, Berenguer C, Brumbaugh J, Stadhouders R, Segura-Morales C, Gut M, Gut IG, Heath S, Aranda S, Di Croce L, Hochedlinger K, Thieffry D, Graf T
Here, we report DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation dynamics at nucleotide resolution using C/EBPα-enhanced reprogramming of B cells into induced pluripotent cells (iPSCs). We observed successive waves of hydroxymethylation at enhancers, concomitant with a decrease in DNA methylation, suggesting active deme... |
Oxidative stress in sperm affects the epigenetic reprogramming in early embryonic development.
Wyck S, Herrera C, Requena CE, Bittner L, Hajkova P, Bollwein H, Santoro R
BACKGROUND: Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced oxidative stress is well known to play a major role in male infertility. Sperm are sensitive to ROS damaging effects because as male germ cells form mature sperm they progressively lose the ability to repair DNA damage. However, how oxidative DNA lesions in sperm aff... |
Integrated analysis of DNA methylation profiling and gene expression profiling identifies novel markers in lung cancer in Xuanwei, China.
Wang J, Duan Y, Meng QH, Gong R, Guo C, Zhao Y, Zhang Y
BACKGROUND: Aberrant DNA methylation occurs frequently in cancer. The aim of this study was to identify novel methylation markers in lung cancer in Xuanwei, China, through integrated genome-wide DNA methylation and gene expression studies. METHODS: Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) and differentially expresse... |
mGlu1 Receptors Monopolize the Synaptic Control of Cerebellar Purkinje Cells by Epigenetically Down-Regulating mGlu5 Receptors.
Notartomaso S, Nakao H, Mascio G, Scarselli P, Cannella M, Zappulla C, Madonna M, Motolese M, Gradini R, Liberatore F, Zonta M, Carmignoto G, Battaglia G, Bruno V, Watanabe M, Aiba A, Nicoletti F
In cerebellar Purkinje cells (PCs) type-1 metabotropic glutamate (mGlu1) receptors play a key role in motor learning and drive the refinement of synaptic innervation during postnatal development. The cognate mGlu5 receptor is absent in mature PCs and shows low expression levels in the adult cerebellar cortex. Here w... |
Determination of the presence of 5-methylcytosine in Paramecium tetraurelia.
Singh A, Vancura A, Woycicki RK, Hogan DJ, Hendrick AG, Nowacki M
5-methylcytosine DNA methylation regulates gene expression and developmental programming in a broad range of eukaryotes. However, its presence and potential roles in ciliates, complex single-celled eukaryotes with germline-somatic genome specialization via nuclear dimorphism, are largely uncharted. While canonical c... |
Structural and mechanistic insights into UHRF1-mediated DNMT1 activation in the maintenance DNA methylation.
Li T, Wang L, Du Y, Xie S, Yang X, Lian F, Zhou Z, Qian C
UHRF1 plays multiple roles in regulating DNMT1-mediated DNA methylation maintenance during DNA replication. The UHRF1 C-terminal RING finger functions as an ubiquitin E3 ligase to establish histone H3 ubiquitination at Lys18 and/or Lys23, which is subsequently recognized by DNMT1 to promote its localization onto rep... |
Epigenetics and early domestication: differences in hypothalamic DNA methylation between red junglefowl divergently selected for high or low fear of humans.
Bélteky J, Agnvall B, Bektic L, Höglund A, Jensen P, Guerrero-Bosagna C
BACKGROUND: Domestication of animals leads to large phenotypic alterations within a short evolutionary time-period. Such alterations are caused by genomic variations, yet the prevalence of modified traits is higher than expected if they were caused only by classical genetics and mutations. Epigenetic mechanisms may ... |
Copper induces expression and methylation changes of early development genes in Crassostrea gigas embryos.
Sussarellu R, Lebreton M, Rouxel J, Akcha F, Rivière G
Copper contamination is widespread along coastal areas and exerts adverse effects on marine organisms such as mollusks. In the Pacific oyster, copper induces severe developmental abnormalities during early life stages; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms are largely unknown. This study aims to better unders... |
Aberrant methylated key genes of methyl group metabolism within the molecular etiology of urothelial carcinogenesis.
Erichsen L, Ghanjati F, Beermann A, Poyet C, Hermanns T, Schulz WA, Seifert HH, Wild PJ, Buser L, Kröning A, Braunstein S, Anlauf M, Jankowiak S, Hassan M, Bendhack ML, Araúzo-Bravo MJ, Santourlidis S
Urothelial carcinoma (UC), the most common cancer of the urinary bladder causes severe morbidity and mortality, e.g. about 40.000 deaths in the EU annually, and incurs considerable costs for the health system due to the need for prolonged treatments and long-term monitoring. Extensive aberrant DNA methylation ... |
Genome-wide analysis of day/night DNA methylation differences in Populus nigra.
Ding C.J. et al.
DNA methylation is an important mechanism of epigenetic modification. Methylation changes during stress responses and developmental processes have been well studied; however, their role in plant adaptation to the day/night cycle is poorly understood. In this study, we detected global methylation patterns in leaves o... |
Obligatory and facilitative allelic variation in the DNA methylome within common disease-associated loci
Bell C.G. et al.
Integrating epigenetic data with genome-wide association study (GWAS) results can reveal disease mechanisms. The genome sequence itself also shapes the epigenome, with CpG density and transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) strongly encoding the DNA methylome. Therefore, genetic polymorphism impacts on ... |
Analysis of DNA methylome and transcriptome profiling following Gibberellin A3 (GA3) foliar application in Nicotiana tabacum L.
Manoharlal Raman, Saiprasad G. V. S., Kaikala Vinay, Suresh Kumar R., Kovařík Ales
The present work investigated a comprehensive genome-wide landscape of DNA methylome and its relationship with transcriptome upon gibberellin A3 (GA3) foliar application under practical field conditions in solanaceae model, Nicotiana tabacum L. Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation-Sequencing (MeDIP-Seq) analysis uncov... |
5-Methylcytosine RNA Methylation in Arabidopsis Thaliana
Cui X. et al.
5-Methylcytosine (m5C) is a well-characterized DNA modification, and is also predominantly reported in abundant non-coding RNAs in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. However, the distribution and biological functions of m5C in plant mRNAs remain largely unknown. Here, we report transcriptome-wide profiling of RNA m5C ... |
Maternal obesity programs increased leptin gene expression in rat male offspring via epigenetic modifications in a depot-specific manner
Lecoutre S. et al.
OBJECTIVE:
According to the Developmental Origin of Health and Disease (DOHaD) concept, maternal obesity and accelerated growth in neonates predispose offspring to white adipose tissue (WAT) accumulation. In rodents, adipogenesis mainly develops during lactation. The mechanisms underlying the phenomenon known as ... |
Increased 5-hydroxymethylation levels in the hippocampus of rat extinguished from cocaine self-administration
Sadakierska-Chudy A. et al.
Drug craving and relapse risk during abstinence from cocaine are thought to be caused by persistent changes in transcription and chromatin regulation. Although several brain regions are involved in these processes, the hippocampus seems to play an important role in context-evoked craving and drug-seeking behavior. O... |
The RNA helicase DHX9 establishes nucleolar heterochromatin, and this activity is required for embryonic stem cell differentiation
Leone S. et al.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been implicated in the regulation of chromatin conformation and epigenetic patterns. lncRNA expression levels are widely taken as an indicator for functional properties. However, the role of RNA processing in modulating distinct features of the same lncRNA is less understood. The ... |
Pramel7 mediates ground-state pluripotency through proteasomal-epigenetic combined pathways.
Graf U. et al.
Naive pluripotency is established in preimplantation epiblast. Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) represent the immortalization of naive pluripotency. 2i culture has optimized this state, leading to a gene signature and DNA hypomethylation closely comparable to preimplantation epiblast, the developmental ground state. Here... |
CHD4 Has Oncogenic Functions in Initiating and Maintaining Epigenetic Suppression of Multiple Tumor Suppressor Genes
Xia L. et al.
An oncogenic role for CHD4, a NuRD component, is defined for initiating and supporting tumor suppressor gene (TSG) silencing in human colorectal cancer. CHD4 recruits repressive chromatin proteins to sites of DNA damage repair, including DNA methyltransferases where it imposes de novo DNA methylation. At TSGs, CHD4 ... |
Critical threshold levels of DNA methyltransferase 1 are required to maintain DNA methylation across the genome in human cancer cells.
Cai Y. et al.
Reversing DNA methylation abnormalities and associated gene silencing, through inhibiting DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) is an important potential cancer therapy paradigm. Maximizing this potential requires defining precisely how these enzymes maintain genome-wide, cancer-specific DNA methylation. To date, there is ... |
Regulation of DNA demethylation by the XPC DNA repair complex in somatic and pluripotent stem cells.
Ho J.J. et al.
Faithful resetting of the epigenetic memory of a somatic cell to a pluripotent state during cellular reprogramming requires DNA methylation to silence somatic gene expression and dynamic DNA demethylation to activate pluripotency gene transcription. The removal of methylated cytosines requires the base excision repa... |
Epigenetic regulation of RELN and GAD1 in the frontal cortex (FC) of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) subjects
Zhubi A. et al.
Both Reelin (RELN) and glutamate decarboxylase 67 (GAD1) have been implicated in the pathophysiology of Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). We have previously shown that both mRNAs are reduced in the cerebella (CB) of ASD subjects through a mechanism that involves increases in the amounts of MECP2 binding to the corres... |
Intergenerational Transmission of Enhanced Seizure Susceptibility after Febrile Seizures
Wu D. et al.
Environmental exposure early in development plays a role in susceptibility to disease in later life. Here, we demonstrate that prolonged febrile seizures induced by exposure of rat pups to a hyperthermic environment enhance seizure susceptibility not only in these hyperthermia-treated rats but also in their future o... |
Pharmacological inhibition of DNA methyltransferase 1 promotes neuronal differentiation from rodent and human nasal olfactory stem/progenitor cell cultures
Franco I. et al.
Nasal olfactory stem and neural progenitor cells (NOS/PCs) are considered possible tools for regenerative stem cell therapies in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurogenesis is a complex process regulated by extrinsic and intrinsic signals that include DNA-methylation and other chromatin modifications that could be expe... |
Distinct 5-methylcytosine profiles in poly(A) RNA from mouse embryonic stem cells and brain
Amort T. et al.
Background
Recent work has identified and mapped a range of posttranscriptional modifications in mRNA, including methylation of the N6 and N1 positions in adenine, pseudouridylation, and methylation of carbon 5 in cytosine (m5C). However, knowledge about the prevalence and transcriptome-wide distribution of m5C i... |
Novel regional age-associated DNA methylation changes within human common disease-associated loci
Bell CG et al.
BACKGROUND:
Advancing age progressively impacts on risk and severity of chronic disease. It also modifies the epigenome, with changes in DNA methylation, due to both random drift and variation within specific functional loci.
RESULTS:
In a discovery set of 2238 peripheral-blood genome-wide DNA methylomes aged 1... |
5-hydroxymethylcytosine marks postmitotic neural cells in the adult and developing vertebrate central nervous system
Diotel N et al.
The epigenetic mark 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) is a cytosine modification that is abundant in the central nervous system of mammals and which results from 5-methylcytosine oxidation by TET enzymes. Such a mark is suggested to play key roles in the regulation of chromatin structure and gene expression. However, i... |
Regulation of the DNA Methylation Landscape in Human Somatic Cell Reprogramming by the miR-29 Family
Hysolli E et al.
Reprogramming to pluripotency after overexpression of OCT4, SOX2, KLF4, and MYC is accompanied by global genomic and epigenomic changes. Histone modification and DNA methylation states in induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have been shown to be highly similar to embryonic stem cells (ESCs). However, epigenetic d... |
Genome-Wide DNA Methylation in Mixed Ancestry Individuals with Diabetes and Prediabetes from South Africa
Matsha TE et al.
Aims. To conduct a genome-wide DNA methylation in individuals with type 2 diabetes, individuals with prediabetes, and control mixed ancestry individuals from South Africa. Methods. We used peripheral blood to perform genome-wide DNA methylation analysis in 3 individuals with screen detected diabetes, 3 individuals w... |
Dnmt2/Trdmt1 as Mediator of RNA Polymerase II Transcriptional Activity in Cardiac Growth
Ghanbarian H et al.
Dnmt2/Trdmt1 is a methyltransferase, which has been shown to methylate tRNAs. Deficient mutants were reported to exhibit various, seemingly unrelated, defects in development and RNA-mediated epigenetic heredity. Here we report a role in a distinct developmental regulation effected by a noncoding RNA. We show that Dn... |
Epigenetic inactivation of the CpG demethylase TET1 as a DNA methylation feedback loop in human cancers
Li L et al.
Promoter CpG methylation is a fundamental regulatory process of gene expression. TET proteins are active CpG demethylases converting 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, with loss of 5 hmC as an epigenetic hallmark of cancers, indicating critical roles of TET proteins in epigenetic tumorigenesis. Thro... |
Biochemical reconstitution of TET1–TDG–BER-dependent active DNA demethylation reveals a highly coordinated mechanism
Weber AR, Krawczyk C, Robertson AB, Kuśnierczyk A, Vågbø CB, Schuermann D, Klungland A, Schär P
Cytosine methylation in CpG dinucleotides is an epigenetic DNA modification dynamically established and maintained by DNA methyltransferases and demethylases. Molecular mechanisms of active DNA demethylation began to surface only recently with the discovery of the 5-methylcytosine (5mC)-directed hydroxylase and base... |
Hydroxymethylation of microRNA-365-3p Regulates Nociceptive Behaviors via Kcnh2
Pan Z, Zhang M, Ma T, Xue Z-Y, Li G-F, Hao L-Y, Zhu L-J, Li Y-Q, Ding H-L, Cao J-L
DNA 5-hydroxylmethylcytosine (5hmC) catalyzed by ten-eleven translocation methylcytosine dioxygenase (TET) occurs abundantly in neurons of mammals. However, the in vivo causal link between TET dysregulation and nociceptive modulation has not been established. Here, we found that spinal TET1 and TET3 were significant... |
Biochemical reconstitution of TET1-TDG-BER-dependent active DNA demethylation reveals a highly coordinated mechanism
Weber AR et al.
Cytosine methylation in CpG dinucleotides is an epigenetic DNA modification dynamically established and maintained by DNA methyltransferases and demethylases. Molecular mechanisms of active DNA demethylation began to surface only recently with the discovery of the 5-methylcytosine (5mC)-directed hydroxylase and base... |
Genome-wide DNA methylation profile of developing deciduous tooth germ in miniature pigs
Su Y, Fan Z, Wu X, Li Y, Wang F, Zhang C, Wang J, Du J, Wang S
BACKGROUND:
DNA methylation is an important epigenetic modification critical to the regulation of gene expression during development. To date, little is known about the role of DNA methylation in tooth development in large animal models. Thus, we carried out a comparative genomic analysis of genome-wide DNA methy... |
Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation Analysis of Mammalian Endogenous Retroviruses.
Rebollo R, Mager DL
Endogenous retroviruses are repetitive sequences found abundantly in mammalian genomes which are capable of modulating host gene expression. Nevertheless, most endogenous retrovirus copies are under tight epigenetic control via histone-repressive modifications and DNA methylation. Here we describe a common method us... |
The dual specificity phosphatase 2 gene is hypermethylated in human cancer and regulated by epigenetic mechanisms
Tanja Haag, Antje M. Richter, Martin B. Schneider, Adriana P. Jiménez and Reinhard H. Dammann
Dual specificity phosphatases are a class of tumor-associated proteins involved in the negative regulation of the MAP kinase pathway. Downregulation of the dual specificity phosphatase 2 (DUSP2) has been reported in cancer. Epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressor genes by abnormal promoter methylation is ... |
Role of Growth Arrest and DNA Damage-Inducible, Beta in Alcohol-Drinking Behaviors
Gavin DP, Kusumo H, Zhang H, Guidotti A, Pandey SC
BACKGROUND:
The contribution of epigenetic factors, such as histone acetylation and DNA methylation, to the regulation of alcohol-drinking behavior has been increasingly recognized over the last several years. GADD45b is a protein demonstrated to be involved in DNA demethylation at neurotrophic factor gene promoter... |
Protocol for Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) Analysis
Karpova NN et al.
DNA methylation is a fundamental epigenetic mechanism for silencing gene expression by either modifying chromatin structure to a repressive state or interfering with the transcription factors’ binding. DNA methylation primarily occurs at the position C5 of a cytosine ring mainly in the context of CpG dinucleot... |
De novo DNA methylation drives 5hmC accumulation in mouse zygotes
Amouroux R, Nashun B, Shirane K, Nakagawa S, Hill PW, D'Souza Z, Nakayama M, Matsuda M, Turp A, Ndjetehe E, Encheva V, Kudo NR, Koseki H, Sasaki H, Hajkova P
Zygotic epigenetic reprogramming entails genome-wide DNA demethylation that is accompanied by Tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 3 (Tet3)-driven oxidation of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC; refs ,,,). Here we demonstrate using detailed immunofluorescence analysis and ultrasensitive LC-MS-ba... |
DNA methylation profiling: comparison of genome-wide sequencing methods and the Infinium Human Methylation 450 Bead Chip
Walker DL, Bhagwate AV, Baheti S, Smalley RL, Hilker CA, Sun Z, Cunningham JM
AIMS:
To compare the performance of four sequence-based and one microarray methods for DNA methylation profiling.
METHODS:
DNA from two cell lines were profiled by reduced representation bisulfite sequencing, methyl capture sequencing (SS-Meth Seq), NimbleGen SeqCapEpi CpGiant(Nimblegen MethSeq), methylated DNA... |
Oxidative DNA damage in mouse sperm chromosomes: Size matters.
Kocer A et al.
Normal embryo and foetal development as well as the health of the progeny are mostly dependent on gamete nuclear integrity. In the present study, in order to characterize more precisely oxidative DNA damage in mouse sperm we used two mouse models that display high levels of sperm oxidative DNA damage, a common alter... |
Evidence for Epigenetic Regulation of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines, Interleukin-12 and Interferon Gamma, in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from PTSD Patients
Marpe Bam, Xiaoming Yang, Juhua Zhou, Jay P. Ginsberg, Quinne Leyden, Prakash S. Nagarkatti, Mitzi Nagarkatti
While Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is associated with immune dysfunction, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Studies suggest a role for involvement of epigenetic mechanisms and microRNAs (miRNAs). Here, we examined genome-wide histone and DNA methylation in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBM... |
Immunohistochemical Detection of Oxidized Forms of 5-Methylcytosine in Embryonic and Adult Brain Tissue
Abakir A et al.
DNA methylation (5-methylcytosine, 5mC) is a major epigenetic modification of the eukaryotic genome associated with gene repression. Ten-eleven translocation proteins (Tet1/2/3) can oxidize 5mC to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5fC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC). Recent studies demonstrate that 5h... |
Gadd45b and N-methyl-D-aspartate induced DNA demethylation in postmitotic neurons.
Gavin DP, Kusumo H, Sharma RP, Guizzetti M, Guidotti A, Pandey SC.
AIM: In nondividing neurons examine the role of Gadd45b in active 5-methylcytosine (5MC) and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5HMC) removal at a gene promoter highly implicated in mental illnesses and cognition, Bdnf.
MATERIALS & METHODS: Mouse primary cortical neuronal cultures with and without Gadd45b siRNA transfect... |
Active human nucleolar organizer regions are interspersed with inactive rDNA repeats in normal and tumor cells.
Zillner K, Komatsu J, Filarsky K, Kalepu R, Bensimon A, Németh A
AIM:
The synthesis of rRNA is a key determinant of normal and malignant cell growth and subject to epigenetic regulation. Yet, the epigenomic features of rDNA arrays clustered in nucleolar organizer regions are largely unknown. We set out to explore for the first time how DNA methylation is distributed on individ... |
Reinforcement of STAT3 activity reprogrammes human embryonic stem cells to naive-like pluripotency.
Chen H, Aksoy I, Gonnot F, Osteil P, Aubry M, Hamela C, Rognard C, Hochard A, Voisin S, Fontaine E, Mure M, Afanassieff M, Cleroux E, Guibert S, Chen J, Vallot C, Acloque H, Genthon C, Donnadieu C, De Vos J, Sanlaville D, Guérin JF, Weber M, Stanton LW, R
Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF)/STAT3 signalling is a hallmark of naive pluripotency in rodent pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), whereas fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-2 and activin/nodal signalling is required to sustain self-renewal of human PSCs in a condition referred to as the primed state. It is unknown why LIF/... |
Targeted disruption of DNMT1, DNMT3A and DNMT3B in human embryonic stem cells.
Liao J, Karnik R, Gu H, Ziller MJ, Clement K, Tsankov AM, Akopian V, Gifford CA, Donaghey J, Galonska C, Pop R, Reyon D, Tsai SQ, Mallard W, Joung JK, Rinn JL, Gnirke A, Meissner A
DNA methylation is a key epigenetic modification involved in regulating gene expression and maintaining genomic integrity. Here we inactivated all three catalytically active DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) in human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) using CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing to further investigate the roles and genom... |
Characterization of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma methylome identifies aberrant disruption of key signaling pathways and methylated tumor suppressor genes.
Li L, Zhang Y, Fan Y, Sun K, Su X, Du Z, Tsao SW, Loh TK, Sun H, Chan AT, Zeng YX, Chan WY, Chan FK, Tao Q
Aims: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a common tumor consistently associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection and prevalent in South China, including Hong Kong, and southeast Asia. Current genomic sequencing studies found only rare mutations in NPC, indicating its critical epigenetic etiology, while no epigenome ... |
CpG signalling, H2A.Z/H3 acetylation and microRNA-mediated deferred self-attenuation orchestrate foetal NOS3 expression.
Postberg J, Kanders M, Forcob S, Willems R, Orth V, Hensel KO, Weil PP, Wirth S, Jenke AC
BACKGROUND: An adverse intrauterine environment leads to permanent physiological changes including vascular tone regulation, potentially influencing the risk for adult vascular diseases. We therefore aimed to monitor responsive NOS3 expression in human umbilical artery endothelial cells (HUAEC) and to study the unde... |
Acute Depletion Redefines the Division of Labor among DNA Methyltransferases in Methylating the Human Genome.
Tiedemann RL, Putiri EL, Lee JH, Hlady RA, Kashiwagi K, Ordog T, Zhang Z, Liu C, Choi JH, Robertson KD
Global patterns of DNA methylation, mediated by the DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), are disrupted in all cancers by mechanisms that remain largely unknown, hampering their development as therapeutic targets. Combinatorial acute depletion of all DNMTs in a pluripotent human tumor cell line, followed by epigenome and ... |
A B-cell targeting virus disrupts potentially protective genomic methylation patterns in lymphoid tissue by increasing global 5-hydroxmethylcytosine levels
Ciccone NA, Mwangi W, Ruzov A, Smith LP, Butter C, Nair V
The mechanisms by which viruses modulate the immune system include changes in host genomic methylation. 5-hydroxmethylcytosine (5hmC) is the catalytic product of the Tet (Ten-11 translocation) family of enzymes and may serve as an intermediate of DNA demethylation. Recent reports suggest that 5hmC may confer consequ... |
Spontaneous sleep-wake cycle and sleep deprivation differently induce Bdnf1, Bdnf4 and Bdnf9a DNA methylation and transcripts levels in the basal forebrain and frontal cortex in rats.
Ventskovska O, Porkka-Heiskanen T, Karpova NN
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Bdnf) regulates neuronal plasticity, slow wave activity and sleep homeostasis. Environmental stimuli control Bdnf expression through epigenetic mechanisms, but there are no data on epigenetic regulation of Bdnf by sleep or sleep deprivation. Here we investigated whether 5-methylcyt... |
Transient accumulation of 5-carboxylcytosine indicates involvement of active demethylation in lineage specification of neural stem cells.
Wheldon LM, Abakir A, Ferjentsik Z, Dudnakova T, Strohbuecker S, Christie D, Dai N, Guan S, Foster JM, Corrêa IR, Loose M, Dixon JE, Sottile V, Johnson AD, Ruzov A
5-Methylcytosine (5mC) is an epigenetic modification involved in regulation of gene activity during differentiation. Tet dioxygenases oxidize 5mC to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5fC), and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC). Both 5fC and 5caC can be excised from DNA by thymine-DNA glycosylase (TDG) follow... |
Long-term parental methamphetamine exposure of mice influences behavior and hippocampal DNA methylation of the offspring.
Itzhak Y, Ergui I, Young JI
The high rate of methamphetamine (METH) abuse among young adults and women of childbearing age makes it imperative to determine the long-term effects of METH exposure on the offspring. We hypothesized that parental METH exposure modulates offspring behavior by disrupting epigenetic programming of gene expression in ... |
Alterations of epigenetic signatures in hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α deficient mouse liver determined by improved ChIP-qPCR and (h)MeDIP-qPCR assays.
Zhang Q, Lei X, Lu H
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α) is a liver-enriched transcription factor essential for liver development and function. In hepatocytes, HNF4α regulates a large number of genes important for nutrient/xenobiotic metabolism and cell differentiation and proliferation. Currently, little is known about the epigenetic ... |
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ regulates genes involved in insulin/insulin-like growth factor signaling and lipid metabolism during adipogenesis through functionally distinct enhancer classes.
Oger F, Dubois-Chevalier J, Gheeraert C, Avner S, Durand E, Froguel P, Salbert G, Staels B, Lefebvre P, Eeckhoute J
The nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) is a transcription factor whose expression is induced during adipogenesis and that is required for the acquisition and control of mature adipocyte functions. Indeed, PPAR induces the expression of genes involved in lipid synthesis and storage thr... |
Global DNA methylation screening of liver in piperonyl butoxide-treated mice in a two-stage hepatocarcinogenesis model.
Yafune A, Kawai M, Itahashi M, Kimura M, Nakane F, Mitsumori K, Shibutani M
Disruptive epigenetic gene control has been shown to be involved in carcinogenesis. To identify key molecules in piperonyl butoxide (PBO)-induced hepatocarcinogenesis, we searched hypermethylated genes using CpG island (CGI) microarrays in non-neoplastic liver cells as a source of proliferative lesions at 25 weeks a... |
Genome-wide screening identifies Plasmodium chabaudi-induced modifications of DNA methylation status of Tlr1 and Tlr6 gene promoters in liver, but not spleen, of female C57BL/6 mice.
Al-Quraishy S, Dkhil MA, Abdel-Baki AA, Delic D, Santourlidis S, Wunderlich F
Epigenetic reprogramming of host genes via DNA methylation is increasingly recognized as critical for the outcome of diverse infectious diseases, but information for malaria is not yet available. Here, we investigate the effect of blood-stage malaria of Plasmodium chabaudi on the DNA methylation status of host gene ... |
Characterization of the DNA methylome and its interindividual variation in human peripheral blood monocytes.
Shen H, Qiu C, Li J, Tian Q, Deng HW
AIM: Peripheral blood monocytes (PBMs) play multiple and critical roles in the immune response, and abnormalities in PBMs have been linked to a variety of human disorders. However, the DNA methylation landscape in PBMs is largely unknown. In this study, we characterized epigenome-wide DNA methylation profiles in pur... |
Multivalent histone engagement by the linked tandem Tudor and PHD domains of UHRF1 is required for the epigenetic inheritance of DNA methylation.
Rothbart SB, Dickson BM, Ong MS, Krajewski K, Houliston S, Kireev DB, Arrowsmith CH, Strahl BD
Histone post-translational modifications regulate chromatin structure and function largely through interactions with effector proteins that often contain multiple histone-binding domains. While significant progress has been made characterizing individual effector domains, the role of paired domains and how they func... |
Transcriptome-wide mapping of 5-methylcytidine RNA modifications in bacteria, archaea, and yeast reveals m5C within archaeal mRNAs.
Edelheit S, Schwartz S, Mumbach MR, Wurtzel O, Sorek R
The presence of 5-methylcytidine (m(5)C) in tRNA and rRNA molecules of a wide variety of organisms was first observed more than 40 years ago. However, detection of this modification was limited to specific, abundant, RNA species, due to the usage of low-throughput methods. To obtain a high resolution, systematic, an... |
Methyl donor supplementation blocks the adverse effects of maternal high fat diet on offspring physiology.
Carlin J, George R, Reyes TM
Maternal consumption of a high fat diet during pregnancy increases the offspring risk for obesity. Using a mouse model, we have previously shown that maternal consumption of a high fat (60%) diet leads to global and gene specific decreases in DNA methylation in the brain of the offspring. The present experiments wer... |
Naive pluripotency is associated with global DNA hypomethylation.
Leitch HG, McEwen KR, Turp A, Encheva V, Carroll T, Grabole N, Mansfield W, Nashun B, Knezovich JG, Smith A, Surani MA, Hajkova P
Naive pluripotent embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and embryonic germ cells (EGCs) are derived from the preimplantation epiblast and primordial germ cells (PGCs), respectively. We investigated whether differences exist between ESCs and EGCs, in view of their distinct developmental origins. PGCs are programmed to undergo ... |
DNA methylation analysis in the intestinal epithelium-effect of cell separation on gene expression and methylation profile.
Jenke AC, Postberg J, Raine T, Nayak KM, Molitor M, Wirth S, Kaser A, Parkes M, Heuschkel RB, Orth V, Zilbauer M
BACKGROUND: Epigenetic signatures are highly cell type specific. Separation of distinct cell populations is therefore desirable for all epigenetic studies. However, to date little information is available on whether separation protocols might influence epigenetic and/or gene expression signatures and hence might be ... |
Association of UHRF1 with methylated H3K9 directs the maintenance of DNA methylation.
Rothbart SB, Krajewski K, Nady N, Tempel W, Xue S, Badeaux AI, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Martinez JY, Bedford MT, Fuchs SM, Arrowsmith CH, Strahl BD
A fundamental challenge in mammalian biology has been the elucidation of mechanisms linking DNA methylation and histone post-translational modifications. Human UHRF1 (ubiquitin-like PHD and RING finger domain-containing 1) has multiple domains that bind chromatin, and it is implicated genetically in the maintenance ... |
Histone acetylation and DNA demethylation of T-cells result in an anaplastic large cell lymphoma-like phenotype.
Joosten M, Seitz V, Zimmermann K, Sommerfeld A, Berg E, Lenze D, Leser U, Stein H, Hummel M
Background. A characteristic feature of anaplastic large cell lymphoma is the significant repression of the T-cell expression program despite its T-cell origin. The reasons for this down-regulation of T-cell phenotype are still unknown. Design and Methods. To elucidate whether epigenetic mechanisms are responsible f... |
Growth Arrest and DNA-Damage-Inducible, Beta (GADD45b)-Mediated DNA Demethylation in Major Psychosis.
Gavin DP, Sharma RP, Chase KA, Matrisciano F, Dong E, Guidotti A
Aberrant neocortical DNA methylation has been suggested to be a pathophysiological contributor to psychotic disorders. Recently, a growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, beta (GADD45b) protein-coordinated DNA demethylation pathway, utilizing cytidine deaminases and thymidine glycosylases, has been identified in the... |
Epigenetic silencing mediated through activated PI3K/AKT signaling in breast cancer.
Zuo T, Liu TM, Lan X, Weng YI, Shen R, Gu F, Huang YW, Liyanarachchi S, Deatherage DE, Hsu PY, Taslim C, Ramaswamy B, Shapiro CL, Lin HJ, Cheng AS, Jin VX, Huang TH
Trimethylation of histone 3 lysine 27 (H3K27me3) is a critical epigenetic mark for the maintenance of gene silencing. Additional accumulation of DNA methylation in target loci is thought to cooperatively support this epigenetic silencing during tumorigenesis. However, molecular mechanisms underlying the complex inte... |
Estrogen-mediated epigenetic repression of large chromosomal regions through DNA looping.
Hsu PY, Hsu HK, Singer GA, Yan PS, Rodriguez BA, Liu JC, Weng YI, Deatherage DE, Chen Z, Pereira JS, Lopez R, Russo J, Wang Q, Lamartiniere CA, Nephew KP, Huang TH
The current concept of epigenetic repression is based on one repressor unit corresponding to one silent gene. This notion, however, cannot adequately explain concurrent silencing of multiple loci observed in large chromosome regions. The long-range epigenetic silencing (LRES) can be a frequent occurrence throughout ... |
Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) from Low Amounts of Cells.
Borgel J, Guibert S, Weber M.
Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) is an immunocapturing approach for unbiased enrichment of DNA that is methylated on cytosines. The principle is that genomic DNA is randomly sheared by sonication and immunoprecipitated with an antibody that specifically recognizes 5-methylcytidine (5mC), which can be combi... |