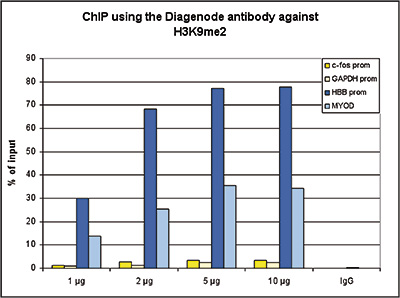
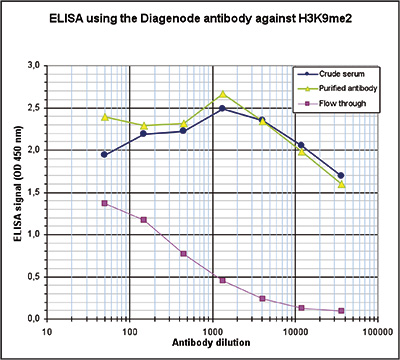
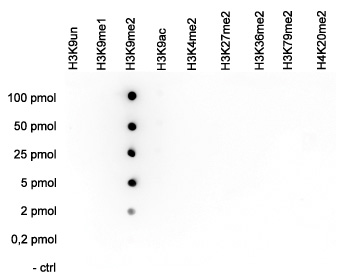
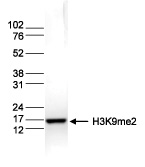
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K9me2 Antibody (sample size) (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410060-10 Lot# A90-0042). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
H3K9 methylation patterns during somatic embryogenic competenceexpression in tamarillo (Solanum betaceum Cav.)
Cordeiro D. et al.
The capacity to regenerate is intrinsic to plants and is the basis of natural asexual propagation and artificial cloning. Despite there are different ways of plant regeneration, they all require a change in cell fate and pluripotency reacquisition, in particular somatic embryogenesis. The mechanisms underlying somat... |
Heterocycle-containing tranylcypromine derivatives endowed with highanti-LSD1 activity.
Fioravanti R. et al.
As regioisomers/bioisosteres of , a 4-phenylbenzamide tranylcypromine (TCP) derivative previously disclosed by us, we report here the synthesis and biological evaluation of some (hetero)arylbenzoylamino TCP derivatives -, in which the 4-phenyl moiety of was shifted at the benzamide C3 position or replaced by 2- or 3... |
Gene bookmarking by the heat shock transcription factor programs theinsulin-like signaling pathway.
Das Srijit et al.
Maternal stress can have long-lasting epigenetic effects on offspring. To examine how epigenetic changes are triggered by stress, we examined the effects of activating the universal stress-responsive heat shock transcription factor HSF-1 in the germline of Caenorhabditis elegans. We show that, when activated in germ... |
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 and KRYPTONITE regulate pathogen-inducedprogrammed cell death in Arabidopsis.
Dvořák Tomaštíková E. et al.
The Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) is well-known for its role in controlling developmental transitions by suppressing the premature expression of key developmental regulators. Previous work revealed that PRC2 also controls the onset of senescence, a form of developmental programmed cell death (PCD) in plants. ... |
Germline activity of the heat shock factor HSF-1 programs theinsulin-receptor daf-2 in C. elegans
Das, S. et al.
The mechanisms by which maternal stress alters offspring phenotypes remain poorly understood. Here we report that the heat shock transcription factor HSF-1, activated in the C. elegans maternal germline upon stress, epigenetically programs the insulin-like receptor daf-2 by increasing repressive H3K9me2 levels throu... |
Formation of the CenH3-Deficient Holocentromere in Lepidoptera AvoidsActive Chromatin.
Senaratne, Aruni P and Muller, Héloïse and Fryer, Kelsey A and Kawamoto,Munetaka and Katsuma, Susumu and Drinnenberg, Ines A
Despite the essentiality for faithful chromosome segregation, centromere architectures are diverse among eukaryotes and embody two main configurations: mono- and holocentromeres, referring, respectively, to localized or unrestricted distribution of centromeric activity. Of the two, some holocentromeres offer the cur... |
The hypomethylation of imprinted genes in IVF/ICSI placenta samples is associated with concomitant changes in histone modifications.
Choux C, Petazzi P, Sanchez-Delgado M, Hernandez Mora JR, Monteagudo A, Sagot P, Monk D, Fauque P
Although more and more children are born by Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART), ART safety has not fully been demonstrated. Notably, ART could disturb the delicate step of implantation, and trigger placenta-related adverse outcomes with potential long-term effects, through disrupted epigenetic regulation. We h... |
An optimised Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) method for starchy leaves of Nicotiana benthamiana to study histone modifications of an allotetraploid plant
Buddhini Ranawaka, Milos Tanurdzic, Peter Waterhouse, Fatima Naim
All flowering plants have evolved through multiple rounds of polyploidy throughout the evolutionary process. Intergenomic interactions between subgenomes in polyploid plants are predicted to induce chromatin modifications such as histone modifications to regulate expression of gene homoeologs. Nicotiana benthamiana ... |
The hypomethylation of imprinted genes in IVF/ICSI placenta samplesis associated with concomitant changes in histone modifications.
Choux C. et al.
Although more and more children are born by Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART), ART safety has not fully been demonstrated. Notably, ART could disturb the delicate step of implantation, and trigger placenta-related adverse outcomes with potential long-term effects, through disrupted epigenetic regulation. We h... |
Ectopic application of the repressive histone modification H3K9me2 establishes post-zygotic reproductive isolation in Arabidopsis thaliana
Jiang H. et al.
Hybrid seed lethality as a consequence of interspecies or interploidy hybridizations is a major mechanism of reproductive isolation in plants. This mechanism is manifested in the endosperm, a dosage-sensitive tissue supporting embryo growth. Deregulated expression of imprinted genes such as ADMETOS (ADM) underpin th... |
Inhibition of Histone H3K9 Methylation by BIX-01294 Promotes Stress-Induced Microspore Totipotency and Enhances Embryogenesis Initiation
Berenguer E. et al.
Microspore embryogenesis is a process of cell reprogramming, totipotency acquisition and embryogenesis initiation, induced in vitro by stress treatments and widely used in plant breeding for rapid production of doubled-haploids, but its regulating mechanisms are still largely unknown. Increasing evidence has reveale... |
Microinjection of Antibodies Targeting the Lamin A/C Histone-Binding Site Blocks Mitotic Entry and Reveals Separate Chromatin Interactions with HP1, CenpB and PML.
Dixon C.R. et al.
Lamins form a scaffold lining the nucleus that binds chromatin and contributes to spatial genome organization; however, due to the many other functions of lamins, studies knocking out or altering the lamin polymer cannot clearly distinguish between direct and indirect effects. To overcome this obstacle, we specifica... |
H3K23me1 is an evolutionarily conserved histone modification associated with CG DNA methylation in Arabidopsis
Trejo-Arellano M.S. et al.
Amino-terminal tails of histones are targets for diverse post-translational modifications whose combinatorial action may constitute a code that will be read and interpreted by cellular proteins to define particular transcriptional states. Here, we describe monomethylation of histone H3 lysine 23 (H3K23me1) as a hist... |
Genome-wide analyses of four major histone modifications in Arabidopsis hybrids at the germinating seed stage
Zhu A. et al.
Background
Hybrid vigour (heterosis) has been used for decades in cropping agriculture, especially in the production of maize and rice, because hybrid varieties exceed their parents in plant biomass and seed yield. The molecular basis of hybrid vigour is not fully understood. Previous studies have suggested that ... |
Applying the INTACT method to purify endosperm nuclei and to generate parental-specific epigenome profiles.
Moreno-Romero J. et al.
The early endosperm tissue of dicot species is very difficult to isolate by manual dissection. This protocol details how to apply the INTACT (isolation of nuclei tagged in specific cell types) system for isolating early endosperm nuclei of Arabidopsis at high purity and how to generate parental-specific epigenome pr... |
Heterochromatic histone modifications at transposons in Xenopus tropicalis embryos
van Kruijsbergen I. et al.
Transposable elements are parasitic genomic elements that can be deleterious for host gene function and genome integrity. Heterochromatic histone modifications are involved in the repression of transposons. However, it remains unknown how these histone modifications mark different types of transposons during embryon... |
Fumarate is an epigenetic modifier that elicits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Sciacovelli M et al.
Mutations of the tricarboxylic acid cycle enzyme fumarate hydratase cause hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer1. Fumarate hydratase-deficient renal cancers are highly aggressive and metastasize even when small, leading to a very poor clinical outcome2. Fumarate, a small molecule metabolite that accumulate... |
Normal stroma suppresses cancer cell proliferation via mechanosensitive regulation of JMJD1a-mediated transcription
Kaukonen R et al.
Tissue homeostasis is dependent on the controlled localization of specific cell types and the correct composition of the extracellular stroma. While the role of the cancer stroma in tumour progression has been well characterized, the specific contribution of the matrix itself is unknown. Furthermore, the mechanisms ... |
Parental epigenetic asymmetry of PRC2-mediated histone modifications in the Arabidopsis endosperm
Moreno-Romero J et al.
Parental genomes in the endosperm are marked by differential DNA methylation and are therefore epigenetically distinct. This epigenetic asymmetry is established in the gametes and maintained after fertilization by unknown mechanisms. In this manuscript, we have addressed the key question whether parentally inherited... |
The histone demethylase JMJD2A/KDM4A links ribosomal RNA transcription to nutrients and growth factors availability
Salifou K, Ray S, Verrier L, Aguirrebengoa M, Trouche D, Panov KI, Vandromme M
The interplay between methylation and demethylation of histone lysine residues is an essential component of gene expression regulation and there is considerable interest in elucidating the roles of proteins involved. Here we report that histone demethylase KDM4A/JMJD2A, which is involved in the regulation of cell pr... |
Embryonic transcription is controlled by maternally defined chromatin state
Hontelez S et al.
Histone-modifying enzymes are required for cell identity and lineage commitment, however little is known about the regulatory origins of the epigenome during embryonic development. Here we generate a comprehensive set of epigenome reference maps, which we use to determine the extent to which maternal factors shape c... |
The histone demethylase enzyme KDM3A is a key estrogen receptor regulator in breast cancer.
Wade MA, Jones D, Wilson L, Stockley J, Coffey K, Robson CN, Gaughan L
Endocrine therapy has successfully been used to treat estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer, but this invariably fails with cancers becoming refractory to treatment. Emerging evidence has suggested that fluctuations in ER co-regulatory protein expression may facilitate resistance to therapy and be involved i... |
Polycomb binding precedes early-life stress responsive DNA methylation at the Avp enhancer.
Murgatroyd C, Spengler D
Early-life stress (ELS) in mice causes sustained hypomethylation at the downstream Avp enhancer, subsequent overexpression of hypothalamic Avp and increased stress responsivity. The sequence of events leading to Avp enhancer methylation is presently unknown. Here, we used an embryonic stem cell-derived model of hypo... |
Lamin A/C-promoter interactions specify chromatin state-dependent transcription outcomes.
Lund E, Oldenburg AR, Delbarre E, Freberg CT, Duband-Goulet I, Eskeland R, Buendia B, Collas P
The nuclear lamina is implicated in the organization of the eukaryotic nucleus. Association of nuclear lamins with the genome occurs through large chromatin domains including mostly, but not exclusively, repressed genes. How lamin interactions with regulatory elements modulate gene expression in different cellular c... |
Long range epigenetic silencing is a trans-species mechanism that results in cancer specific deregulation by overriding the chromatin domains of normal cells.
Forn M, Muñoz M, Tauriello DV, Merlos-Suárez A, Rodilla V, Bigas A, Batlle E, Jordà M, Peinado MA
DNA methylation and chromatin remodeling are frequently implicated in the silencing of genes involved in carcinogenesis. Long Range Epigenetic Silencing (LRES) is a mechanism of gene inactivation that affects multiple contiguous CpG islands and has been described in different human cancer types. However, it is unkno... |
AGRONOMICS1: a new resource for Arabidopsis transcriptome profiling.
Rehrauer H, Aquino C, Gruissem W, Henz SR, Hilson P, Laubinger S, Naouar N, Patrignani A, Rombauts S, Shu H, Van de Peer Y, Vuylsteke M, Weigel D, Zeller G, Hennig L
Transcriptome profiling has become a routine tool in biology. For Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), the Affymetrix ATH1 expression array is most commonly used, but it lacks about one-third of all annotated genes present in the reference strain. An alternative are tiling arrays, but previous designs have not allowe... |