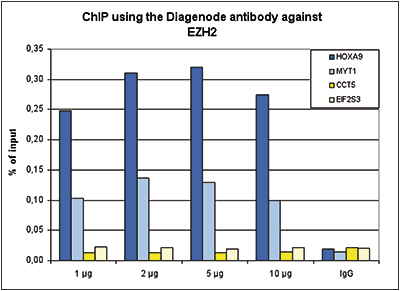
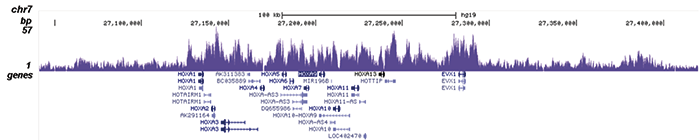
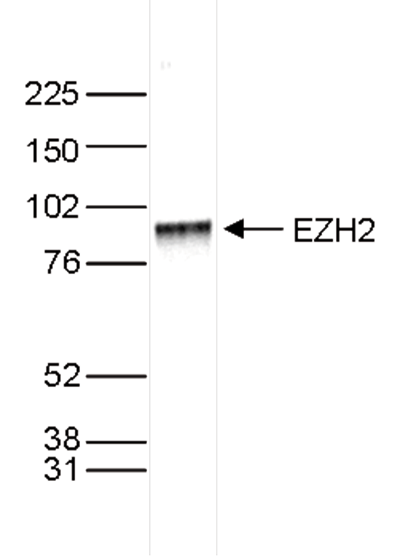
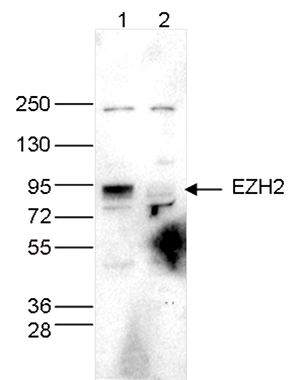
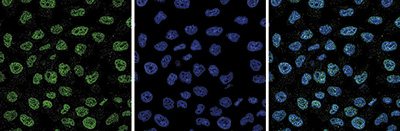
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: EZH2 Antibody (sample size) (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410039-10 Lot# 003). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Accelerated epigenetic aging in Huntington’s disease involves polycomb repressive complex 1
Baptiste Brulé et al.
Loss of epigenetic information during physiological aging compromises cellular identity, leading to de-repression of developmental genes. Here, we assessed the epigenomic landscape of vulnerable neurons in two reference mouse models of Huntington neurodegenerative disease (HD), using cell-type-specific multi-omics, ... |
Master corepressor inactivation through multivalent SLiM-induced polymerization mediated by the oncogene suppressor RAI2
Goradia N. et al.
While the elucidation of regulatory mechanisms of folded proteins is facilitated due to their amenability to high-resolution structural characterization, investigation of these mechanisms in disordered proteins is more challenging due to their structural heterogeneity, which can be captured by a variety of biophysic... |
Master corepressor inactivation through multivalent SLiM-induced polymerization mediated by the oncogene suppressor RAI2
Nishit Goradia et al.
While the elucidation of regulatory mechanisms of folded proteins is facilitated due to their amenability to high-resolution structural characterization, investigation of these mechanisms in disordered proteins is more challenging due to their structural heterogeneity, which can be captured by a variety of biophysic... |
The SAM domain-containing protein 1 (SAMD1) acts as a repressivechromatin regulator at unmethylated CpG islands
Stielow B. et al.
CpG islands (CGIs) are key regulatory DNA elements at most promoters, but how they influence the chromatin status and transcription remains elusive. Here, we identify and characterize SAMD1 (SAM domain-containing protein 1) as an unmethylated CGI-binding protein. SAMD1 has an atypical winged-helix domain that direct... |
EZH2 and KDM6B Expressions Are Associated with Specific EpigeneticSignatures during EMT in Non Small Cell Lung Carcinomas.
Lachat C. et al.
The role of Epigenetics in Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) has recently emerged. Two epigenetic enzymes with paradoxical roles have previously been associated to EMT, EZH2 (Enhancer of Zeste 2 Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) Subunit), a lysine methyltranserase able to add the H3K27me3 mark, and the hist... |
The CDK4/6-EZH2 pathway is a potential therapeutic target for psoriasis.
Müller A, Dickmanns A, Resch C, Schäkel K, Hailfinger S, Dobbelstein M, Schulze-Osthoff K, Kramer D
Psoriasis is a frequent inflammatory skin disease characterized by keratinocyte hyperproliferation and a disease-related infiltration of immune cells. Here, we identified a novel pro-inflammatory signaling pathway driven by the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) 4 and 6 and the methyltransferase EZH2 as a valid target f... |
The Inhibition of the Histone Methyltransferase EZH2 by DZNEP or SiRNA Demonstrates Its Involvement in MGMT, TRA2A, RPS6KA2, and U2AF1 Gene Regulation in Prostate Cancer.
El Ouardi D, Idrissou M, Sanchez A, Penault-Llorca F, Bignon YJ, Guy L, Bernard-Gallon D
In France, prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men (Bray et al., 2018). Previously, our team has reported the involvement of epigenetic factors in prostate cancer (Ngollo et al., 2014, 2017). The histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) is a repressive mark that induces chromatin compaction and thus ge... |
R-Loops Enhance Polycomb Repression at a Subset of Developmental Regulator Genes.
Skourti-Stathaki K, Torlai Triglia E, Warburton M, Voigt P, Bird A, Pombo A
R-loops are three-stranded nucleic acid structures that form during transcription, especially over unmethylated CpG-rich promoters of active genes. In mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs), CpG-rich developmental regulator genes are repressed by the Polycomb complexes PRC1 and PRC2. Here, we show that R-loops form at a... |
Ezh2 controls development of natural killer T cells, which cause spontaneous asthma-like pathology.
Tumes D, Hirahara K, Papadopoulos M, Shinoda K, Onodera A, Kumagai J, Yip KH, Pant H, Kokubo K, Kiuchi M, Aoki A, Obata-Ninomiya K, Tokoyoda K, Endo Y, Kimura MY, Nakayama T
BACKGROUND: Natural killer T (NKT) cells express a T-cell receptor that recognizes endogenous and environmental glycolipid antigens. Several subsets of NKT cells have been identified, including IFN-γ-producing NKT1 cells, IL-4-producing NKT2 cells, and IL-17-producing NKT17 cells. However, little is known... |
Multi-axial self-organization properties of mouse embryonic stem cells into gastruloids.
Beccari L, Moris N, Girgin M, Turner DA, Baillie-Johnson P, Cossy AC, Lutolf MP, Duboule D, Arias AM
The emergence of multiple axes is an essential element in the establishment of the mammalian body plan. This process takes place shortly after implantation of the embryo within the uterus and relies on the activity of gene regulatory networks that coordinate transcription in space and time. Whereas genetic approache... |
MTF2 recruits Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 by helical-shape-selective DNA binding.
Perino M, van Mierlo G, Karemaker ID, van Genesen S, Vermeulen M, Marks H, van Heeringen SJ, Veenstra GJC
ABSTACT: Polycomb-mediated repression of gene expression is essential for development, with a pivotal role played by trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27me3), which is deposited by Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2). The mechanism by which PRC2 is recruited to target genes has remained largely elusive, pa... |
A new metabolic gene signature in prostate cancer regulated by JMJD3 and EZH2.
Daures M, Idrissou M, Judes G, Rifaï K, Penault-Llorca F, Bignon YJ, Guy L, Bernard-Gallon D
Histone methylation is essential for gene expression control. Trimethylated lysine 27 of histone 3 (H3K27me3) is controlled by the balance between the activities of JMJD3 demethylase and EZH2 methyltransferase. This epigenetic mark has been shown to be deregulated in prostate cancer, and evidence shows H3K27me3 enri... |
STAT5BN642H is a driver mutation for T cell neoplasia
Pham H.T.T. et al.
STAT5B is often mutated in hematopoietic malignancies. The most frequent STAT5B mutation, Asp642His (N642H), has been found in over 90 leukemia and lymphoma patients. Here, we used the Vav1 promoter to generate transgenic mouse models that expressed either human STAT5B or STAT5BN642H in the hematopoietic compartment... |
EZH2 Histone Methyltransferase and JMJD3 Histone Demethylase Implications in Prostate Cancer
Idrissou M. et al.
|
Menin regulates Inhbb expression through an Akt/Ezh2-mediated H3K27 histone modification
Gherardi S. et al.
Although Men1 is a well-known tumour suppressor gene, little is known about the functions of Menin, the protein it encodes for. Since few years, numerous publications support a major role of Menin in the control of epigenetics gene regulation. While Menin interaction with MLL complex favours transcriptional activati... |
Praja1 E3 ubiquitin ligase promotes skeletal myogenesis through degradation of EZH2 upon p38α activation
Consalvi S. et al.
Polycomb proteins are critical chromatin modifiers that regulate stem cell differentiation via transcriptional repression. In skeletal muscle progenitors Enhancer of zeste homologue 2 (EZH2), the catalytic subunit of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2), contributes to maintain the chromatin of muscle genes in a rep... |
H3K4 acetylation, H3K9 acetylation and H3K27 methylation in breast tumor molecular subtypes
Judes G et al.
AIM:
Here, we investigated how the St Gallen breast molecular subtypes displayed distinct histone H3 profiles.
PATIENTS & METHODS:
192 breast tumors divided into five St Gallen molecular subtypes (luminal A, luminal B HER2-, luminal B HER2+, HER2+ and basal-like) were evaluated for their histone H3 modifica... |
Premalignant SOX2 overexpression in the fallopian tubes of ovarian cancer patients: Discovery and validation studies
Hellner K et al.
Current screening methods for ovarian cancer can only detect advanced disease. Earlier detection has proved difficult because the molecular precursors involved in the natural history of the disease are unknown. To identify early driver mutations in ovarian cancer cells, we used dense whole genome sequencing of micro... |
The dynamic interactome and genomic targets of Polycomb complexes during stem-cell differentiation
Kloet S.L. et al.
Although the core subunits of Polycomb group (PcG) complexes are well characterized, little is known about the dynamics of these protein complexes during cellular differentiation. We used quantitative interaction proteomics and genome-wide profiling to study PcG proteins in mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and neur... |
MicroRNAs of the miR-290-295 Family Maintain Bivalency in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
Graham B et al.
Numerous developmentally regulated genes in mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are marked by both active (H3K4me3)- and polycomb group (PcG)-mediated repressive (H3K27me3) histone modifications. This bivalent state is thought to be important for transcriptional poising, but the mechanisms that regulate bivalent genes... |
BRCA1 positively regulates FOXO3 expression by restricting FOXO3 gene methylation and epigenetic silencing through targeting EZH2 in breast cancer
C Gong, S Yao, A R Gomes, E P S Man, H J Lee, G Gong, S Chang, S-B Kim, K Fujino, S-W Kim, S K Park, J W Lee, M H Lee, KOHBRA study group, U S Khoo and E W-F Lam
BRCA1 mutation or depletion correlates with basal-like phenotype and poor prognosis in breast cancer but the underlying reason remains elusive. RNA and protein analysis of a panel of breast cancer cell lines revealed that BRCA1 deficiency is associated with downregulation of the expression of the pleiotropic tumour ... |
The JMJD3 Histone Demethylase and the EZH2 Histone Methyltransferase in Prostate Cancer
Daures M, Ngollo M, Judes G, Rifaï K, Kemeny JL, Penault-Llorca F, Bignon YJ, Guy L, Bernard-Gallon D
Prostate cancer is themost common cancer in men. It has been clearly established that genetic and epigenetic alterations of histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) are common events in prostate cancer. This mark is deregulated in prostate cancer (Ngollo et al., 2014). Furthermore, H3K27me3 levels are determine... |
Spatial Interplay between Polycomb and Trithorax Complexes Controls Transcriptional Activity in T Lymphocytes
Onodera A, Tumes DJ, Watanabe Y, Hirahara K, Kaneda A, Sugiyama F, Suzuki Y, Nakayama T
Trithorax group (TrxG) and Polycomb group (PcG) proteins are two mutually antagonistic chromatin modifying complexes, however, how they together mediate transcriptional counter-regulation remains unknown. Genome-wide analysis revealed that binding of Ezh2 and menin, central members of the PcG and TrxG complexes, res... |
Loss of EZH2 results in precocious mammary gland development and activation of STAT5-dependent genes
Yoo KH, Oh S, Kang K, Hensel T, Robinson GW, Hennighausen L
Establishment and differentiation of mammary alveoli during pregnancy are controlled by prolactin through the transcription factors STAT5A and STAT5B (STAT5), which also regulate temporal activation of mammary signature genes. This study addressed the question whether the methyltransferase and transcriptional co-act... |
Polycomb repressive complex PRC1 spatially constrains the mouse embryonic stem cell genome
Schoenfelder S et al.
The Polycomb repressive complexes PRC1 and PRC2 maintain embryonic stem cell (ESC) pluripotency by silencing lineage-specifying developmental regulator genes. Emerging evidence suggests that Polycomb complexes act through controlling spatial genome organization. We show that PRC1 functions as a master regulator of m... |
H19 lncRNA controls gene expression of the Imprinted Gene Network by recruiting MBD1.
Monnier P, Martinet C, Pontis J, Stancheva I, Ait-Si-Ali S, Dandolo L
The H19 gene controls the expression of several genes within the Imprinted Gene Network (IGN), involved in growth control of the embryo. However, the underlying mechanisms of this control remain elusive. Here, we identified the methyl-CpG-binding domain protein 1 MBD1 as a physical and functional partner of the H19 ... |
A key role for EZH2 in epigenetic silencing of HOX genes in mantle cell lymphoma.
Kanduri M, Sander B, Ntoufa S, Papakonstantinou N, Sutton LA, Stamatopoulos K, Kanduri C, Rosenquist R
The chromatin modifier EZH2 is overexpressed and associated with inferior outcome in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). Recently, we demonstrated preferential DNA methylation of HOX genes in MCL compared with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), despite these genes not being expressed in either entity. Since EZH2 has been s... |
Histone lysine trimethylation or acetylation can be modulated by phytoestrogen, estrogen or anti-HDAC in breast cancer cell lines.
Dagdemir A, Durif J, Ngollo M, Bignon YJ, Bernard-Gallon D
AIM: The isoflavones genistein, daidzein and equol (daidzein metabolite) have been reported to interact with epigenetic modifications, specifically hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes. The objective of this study was to analyze and understand the mechanisms by which phytoestrogens act on chromatin in breast c... |
Dynamic Changes in Ezh2 Gene Occupancy Underlie Its Involvement in Neural Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Differentiation towards Oligodendrocytes
Sher F, Boddeke E, Olah M, Copray S
Background: The polycomb group protein Ezh2 is an epigenetic repressor of transcription originally found to prevent untimely differentiation of pluripotent embryonic stem cells. We previously demonstrated that Ezh2 is also expressed in multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs). We showed that Ezh2 expression is downregul... |
RYBP-PRC1 Complexes Mediate H2A Ubiquitylation at Polycomb Target Sites Independently of PRC2 and H3K27me3.
Tavares L, Dimitrova E, Oxley D, Webster J, Poot R, Demmers J, Bezstarosti K, Taylor S, Ura H, Koide H, Wutz A, Vidal M, Elderkin S, Brockdorff N
Polycomb-repressive complex 1 (PRC1) has a central role in the regulation of heritable gene silencing during differentiation and development. PRC1 recruitment is generally attributed to interaction of the chromodomain of the core protein Polycomb with trimethyl histone H3K27 (H3K27me3), catalyzed by a second complex... |
PcG complexes set the stage for epigenetic inheritance of gene silencing in early S phase before replication.
Lanzuolo C, Lo Sardo F, Diamantini A, Orlando V
Polycomb group (PcG) proteins are part of a conserved cell memory system that conveys epigenetic inheritance of silenced transcriptional states through cell division. Despite the considerable amount of information about PcG mechanisms controlling gene silencing, how PcG proteins maintain repressive chromatin during ... |
Silencing of Kruppel-like factor 2 by the histone methyltransferase EZH2 in human cancer.
Taniguchi H, Jacinto FV, Villanueva A, Fernandez AF, Yamamoto H, Carmona FJ, Puertas S, Marquez VE, Shinomura Y, Imai K, Esteller M
The Kruppel-like factor (KLF) proteins are multitasked transcriptional regulators with an expanding tumor suppressor function. KLF2 is one of the prominent members of the family because of its diminished expression in malignancies and its growth-inhibitory, pro-apoptotic and anti-angiogenic roles. In this study, we ... |
Enhancer of Zeste 2 (EZH2) is up-regulated in malignant gliomas and in glioma stem-like cells.
Orzan F, Pellegatta S, Poliani PL, Pisati F, Caldera V, Menghi F, Kapetis D, Marras C, Schiffer D, Finocchiaro G
AIMS: Proteins of the Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) are epigenetic gene silencers and are involved in tumour development. Their oncogenic function might be associated with their role in stem cell maintenance. The histone methyltransferase Enhancer of Zeste 2 (EZH2) is a key member of PRC2 function: we have in... |
Promoter-exon relationship of H3 lysine 9, 27, 36 and 79 methylation on pluripotency-associated genes.
Barrand S, Andersen IS, Collas P
Evidence links pluripotency to a gene regulatory network organized by the transcription factors Oct4, Nanog and Sox2. Expression of these genes is controlled by epigenetic modifications on regulatory regions. However, little is known on profiles of trimethylated H3 lysine residues on coding regions of these genes in... |
The Polycomb group protein EZH2 directly controls DNA methylation.
Viré E, Brenner C, Deplus R, Blanchon L, Fraga M, Didelot C, Morey L, Van Eynde A, Bernard D, Vanderwinden JM, Bollen M, Esteller M, Di Croce L, de Launoit Y, Fuks F
The establishment and maintenance of epigenetic gene silencing is fundamental to cell determination and function. The essential epigenetic systems involved in heritable repression of gene activity are the Polycomb group (PcG) proteins and the DNA methylation systems. Here we show that the corresponding silencing pat... |