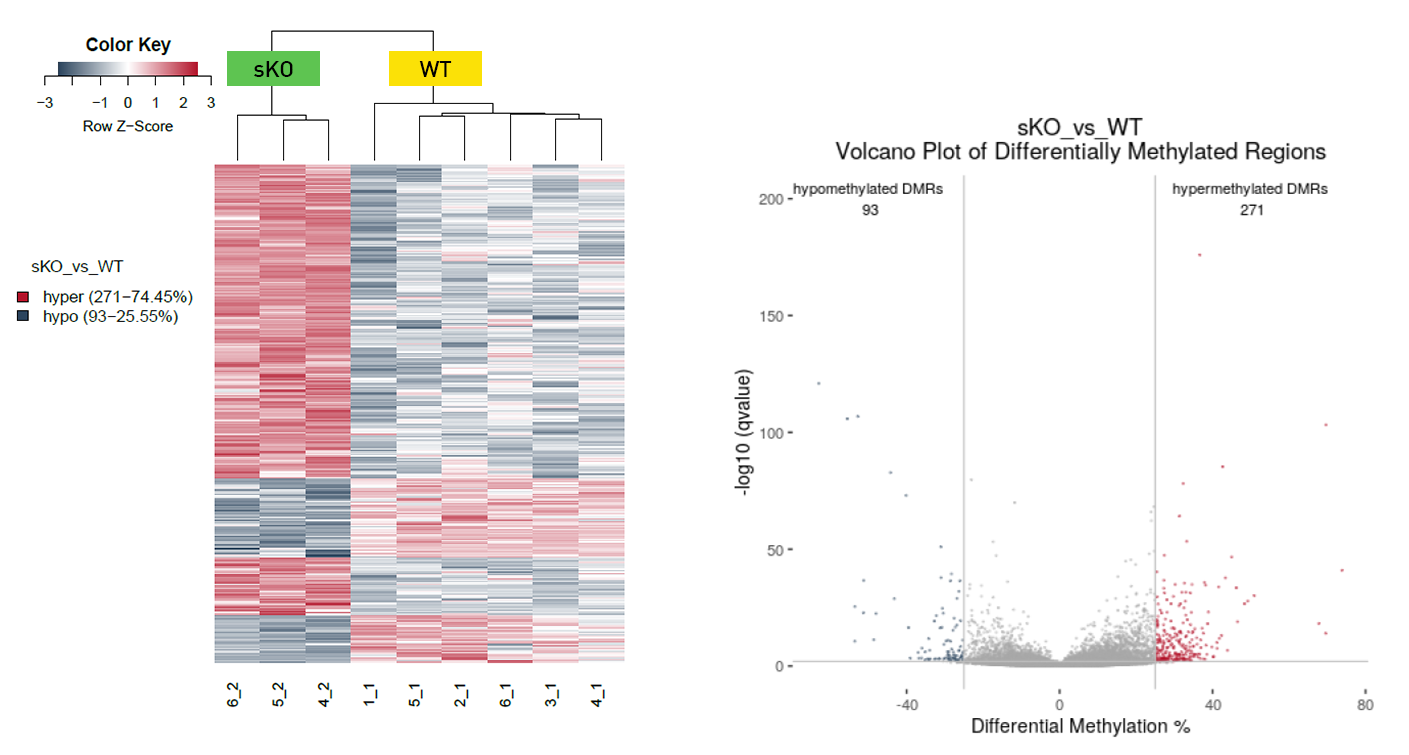
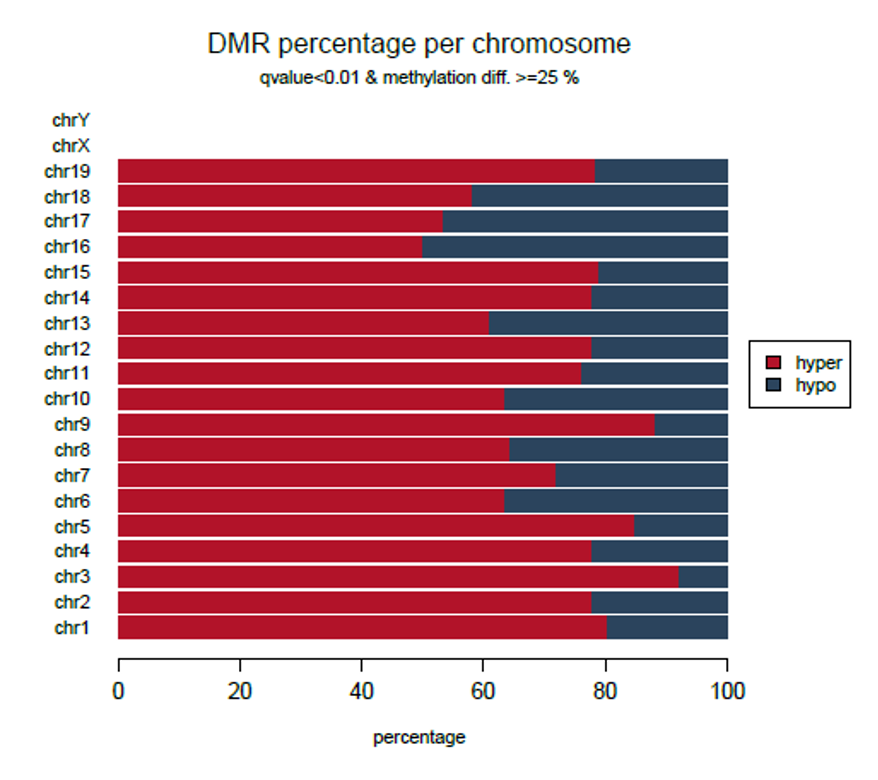
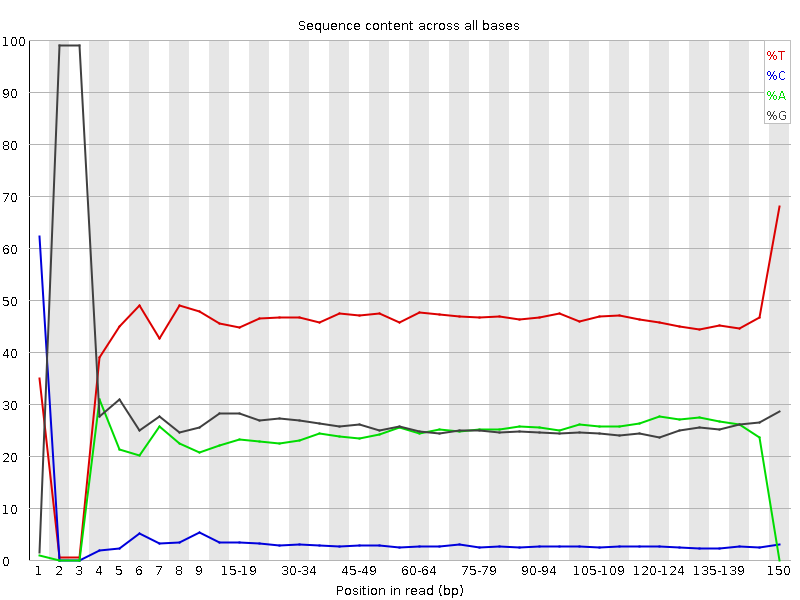
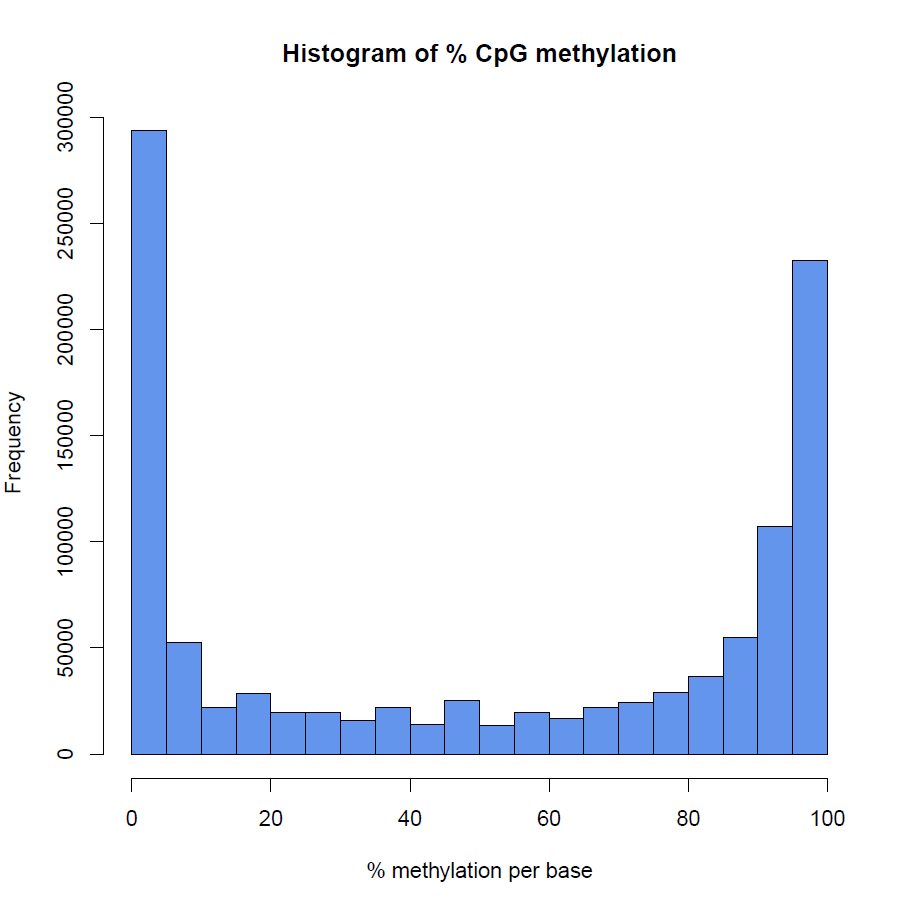
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: Premium RRBS kit V2
RRBS for low DNA amounts and accurate analysis (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C02030036). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
SIRT1 mediates brain metabolic and developmental consequences of methionine synthase deficiency in inborn errors of cobalamin metabolism
Matmat, Karim et al.
Inborn errors of vitamin B12 metabolism (IECM) resulting from impaired methionine synthase (MTR) activity cause severe cognitive and neurological deficits that remain unresponsive to conventional B12 supplementation. Using a brain-specific Mtr knockout mouse model, we identify the NAD+-dependent deacetylase SIRT1 as... |
DNA methylation dynamics associated with visual system remodeling during flatfish metamorphosis
Guerrero-Peña, Laura et al.
Background: Flatfish metamorphosis involves dramatic tissue remodeling, including the migration of one eye to the opposite side of the body, enabling the transition from pelagic to benthic life. While this process requires precise transcriptional regulation, the role of epigenetic mechanisms remains poorly unde... |
Stage-specific transcriptomic and DNA methylation responses to triploidy in European sea bass embryos and larvae
Beato, S et al.
Background: Polyploidy, the condition of having more than two chromosome sets, is relatively common in plants but rare in animals, largely due to reproductive challenges associated with altered chromosome numbers. In fish, however, polyploidy occurs naturally in several species, and triploidy can be artificiall... |
Multigenerational temperature effects on paternal epigenetic inheritance in European sea bass
Sánchez-Baizán, Núria et al.
Environmental changes can induce epigenetic modifications, influencing gene expression, phenotype, and species adaptation. This study investigates how temperature affects genome-wide DNA methylation patterns, particularly in genes crucial for sex development and whether these modifications can be transmitted acros... |
Developmental modulation of schizophrenia risk gene methylation in offspring exhibiting cognitive deficits following maternal immune activation
Woods, Rebecca M et al.
Maternal infection during pregnancy has been shown in epidemiological studies to increase the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders, like schizophrenia, in the developing fetus. Epigenetic mechanisms are thought to play a crucial role in linking maternal immune activation (MIA) to a higher risk of schizophrenia i... |
Recurrent spontaneous miscarriages from sperm after ABVD chemotherapy in a patient with Hodgkin’s lymphoma: sperm DNA and methylation profiling
Lecuyer, Gwendoline et al.
Lymphomas represent one of the most common malignant diseases in young men and an important issue is how treatments will affect their reproductive health. It has been hypothesized that chemotherapies, similarly to environmental chemicals, may alter the spermatogenic epigenome. Here, we report the genomic and epigeno... |
Epigenetic regulation of visual system remodeling during flatfish metamorphosis: DNA methylation dynamics in ocular migration and visual adaptation
Laura Guerrero-Peña et al.
Flatfish metamorphosis is characterized by extensive tissue remodeling, associated with a transition from pelagic to benthic lifestyle, being the migration of one eye the most dramatic change. Epigenetic mechanisms exert a pivotal role in developmental programs. This study investigates the DNA methylation profiles o... |
Epigenetic Regulation During Flatfish 2 Metamorphosis: Integrative Omics 3 Analysis of DNA Methylation and Gene 4 Expression in Turbot Brain
Laura Guerrero-Peña et al.
The regulation of gene expression plays a pivotal role in the complex metamorphic process of flatfishes, which oversees the dynamic alterations that occur during their transition from a pelagic to a benthic way of life. Flatfish metamorphosis is characterized by substantial modifications in both form and function, w... |
Mission SpaceX CRS-19 RRRM-1 space flight induced skin genomic plasticity via an epigenetic trigger
Kanhaiya Singh et al.
Highlights
Exposure to space environment causes genome-wide adaptive epigenetic changes
Space-exposure adaptive genome-wide changes are only seen in select “responder” mice
In space, genome-wide epigenetic changes mark induction of genomic plasticity
Genome-wide hypomethylation in... |
Multi-omics characterization of chronic social defeat stress recall-activated engram nuclei in Arc-GFP mice
Monika Chanu Chongtham et al.
Susceptibility to chronic social stressors often results in the development of mental health disorders including major depressive and anxiety disorders. In contrast, some individuals remain resilient even after repeated stress exposure. Understanding the molecular drivers behind these divergent phenotypic outcomes i... |
Pesticide-induced transgenerational alterations of genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in the pancreas of Xenopus tropicalis correlate with metabolic phenotypes
Roza M. et al.
The unsustainable use of manmade chemicals poses significant threats to biodiversity and human health. Emerging evidence highlights the potential of certain chemicals to cause transgenerational impacts on metabolic health. Here, we investigate male transmitted epigenetic transgenerational effects of the anti-androge... |
Triphenyl Phosphate Alters Methyltransferase Expression and Induces Genome-Wide Aberrant DNA Methylation in Zebrafish Larvae
Negi C.K. et al.
Emerging environmental contaminants, organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs), pose significant threats to ecosystems and human health. Despite numerous studies reporting the toxic effects of OPFRs, research on their epigenetic alterations remains limited. In this study, we investigated the effects of exposure to 2-... |
Differential DNA methylation in iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons: a step forward on the role of SNORD116 microdeletion in the pathophysiology of addictive behavior in Prader-Willi syndrome
Salles J. et al.
Introduction
A microdeletion including the SNORD116 gene (SNORD116 MD) has been shown to drive the Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) features. PWS is a neurodevelopmental disorder clinically characterized by endocrine impairment, intellectual disability and psychiatric symptoms such as a lack of emotional ... |
Long-term effects of myo-inositol on traumatic brain injury: Epigenomic and transcriptomic studies
Oganezovi N. et al.
Background and purpose
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) and its consequences remain great challenges for neurology. Consequences of TBI are associated with various alterations in the brain but little is known about long-term changes of epigenetic DNA methylation patterns. Moreover, nothing is known about potential trea... |
DNA methylome, R-loop and clinical exome profiling of patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Feró, O. et al.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a fatal neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the death of motor neurons, the aetiology of which is essentially unknown. Here, we present an integrative epigenomic study in blood samples from seven clinically characterised sporadic ALS patients to elucidate molecular fact... |
Gestational Caloric Restriction Alters Adipose Tissue Methylome and Offspring’s Metabolic Profile in a Swine Model
Mas-Pares B. et al.
Limited nutrient supply to the fetus results in physiologic and metabolic adaptations that have unfavorable consequences in the offspring. In a swine animal model, we aimed to study the effects of gestational caloric restriction and early postnatal metformin administration on offspring’s adipose tissue epigene... |
Diagnostic Algorithm to Subclassify Atypical Spitzoid Tumors in Low and High Risk According to Their Methylation Status
Gonzales-Munoz J.F. et al.
Current diagnostic algorithms are insufficient for the optimal clinical and therapeutic management of cutaneous spitzoid tumors, particularly atypical spitzoid tumors (AST). Therefore, it is crucial to identify new markers that allow for reliable and reproducible diagnostic assessment and can also be used as a predi... |
Knockout of TRDMT1 methyltransferase affects DNA methylome inglioblastoma cells.
Zabek T. et al.
Purpose: We have previously shown that TRDMT1 methyltransferase is a regulator of chemotherapy-associated responses in glioblastoma cells. Despite the fact that glioblastoma, a common and malignant brain tumor, is widely characterized in terms of genetic and epigenetic markers, there are no data on TRDMT1-relat... |
Sperm DNA methylation is predominantly stable in mice offspring bornafter transplantation of long-term cultured spermatogonial stem cells.
Serrano J. B.et al.
BACKGROUND: Spermatogonial stem cell transplantation (SSCT) is proposed as a fertility therapy for childhood cancer survivors. SSCT starts with cryopreserving a testicular biopsy prior to gonadotoxic treatments such as cancer treatments. When the childhood cancer survivor reaches adulthood and desires biological chi... |
DNA methylation changes from primary cultures through senescence-bypassin Syrian hamster fetal cells initially exposed to benzo[a]pyrene.
Desaulniers D. et al.
Current chemical testing strategies are limited in their ability to detect non-genotoxic carcinogens (NGTxC). Epigenetic anomalies develop during carcinogenesis regardless of whether the molecular initiating event is associated with genotoxic (GTxC) or NGTxC events; therefore, epigenetic markers may be harnessed to ... |
Myelodysplastic Syndrome associated TET2 mutations affect NK cellfunction and genome methylation.
Boy M. et al.
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are clonal hematopoietic disorders, representing high risk of progression to acute myeloid leukaemia, and frequently associated to somatic mutations, notably in the epigenetic regulator TET2. Natural Killer (NK) cells play a role in the anti-leukemic immune response via their cytolyti... |
Epigenetics and stroke: role of DNA methylation and effect of aging onblood-brain barrier recovery.
Phillips C. et al.
Incomplete recovery of blood-brain barrier (BBB) function contributes to stroke outcomes. How the BBB recovers after stroke remains largely unknown. Emerging evidence suggests that epigenetic factors play a significant role in regulating post-stroke BBB recovery. This study aimed to evaluate the epigenetic and trans... |
Development of DNA methylation-based epigenetic age predictors inloblolly pine (Pinus taeda).
Gardner S. T. et al.
Biological ageing is connected to life history variation across ecological scales and informs a basic understanding of age-related declines in organismal function. Altered DNA methylation dynamics are a conserved aspect of biological ageing and have recently been modelled to predict chronological age among vertebrat... |
Molecular toxicity study on glyphosate, Roundup MON 52276 and alow-dose pesticide mixture administered to adult Female rats for 90 days
Mesnage Robin and Antoniou Michael N.
We describe a comprehensive repository describing a collection of data from a range of studies investigating the molecular mechanisms of toxicity of glyphosate, the glyphosate-based herbicide commercial formulation Roundup, and a mixture of glyphosate and 5 other most frequently used pesticides (azoxystrobin, boscal... |
Differential methylation patterns in lean and obese non-alcoholicsteatohepatitis-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hymel Emma et al.
BACKGROUND: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease affects about 24\% of the world's population and may progress to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). While more common in those that are obese, NASH-HCC can develop in lean individuals. The mechanisms by which HCC develops a... |
Altered DNA methylation in estrogen-responsive repetitive sequences ofspermatozoa of infertile men with shortened anogenital distance.
Stenz L. et al.
BACKGROUND: It has been suggested that antenatal exposure to environmental endocrine disruptors is responsible for adverse trends in male reproductive health, including male infertility, impaired semen quality, cryptorchidism and testicular cancer, a condition known as testicular dysgenesis syndrome. Anogenital dist... |
Epigenetic Alterations of Repeated Relapses in Patient-matchedChildhood Ependymomas.
Zhao Sibo et al.
Recurrence is frequent in pediatric ependymoma (EPN). Our longitudinal integrated analysis of 30 patient-matched repeated relapses (3.67 ± 1.76 times) over 13 years (5.8 ± 3.8) reveals stable molecular subtypes (RELA and PFA) and convergent DNA methylation reprogramming duri... |
Epigenetic Suppression of the IL-7 Pathway in ProgressiveGlioblastoma.
Tompa M. et al.
BACKGROUND: Immune evasion in glioblastoma (GBM) shields cancer cells from cytotoxic immune response. METHODS: We investigated CpG methylation in promoters, genes, and pathways in 22 pairs of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sequential (FFPE) GBM using restricted resolution bisulfite sequencing (RRBS) and bioinforma... |
DNA methylation may affect beef tenderness through signal transduction inBos indicus.
de Souza M. M. et al.
BACKGROUND: Beef tenderness is a complex trait of economic importance for the beef industry. Understanding the epigenetic mechanisms underlying this trait may help improve the accuracy of breeding programs. However, little is known about epigenetic effects on Bos taurus muscle and their implications in tenderness, a... |
Folic Acid Treatment Directly Influences the Genetic andEpigenetic Regulation along with the Associated CellularMaintenance Processes of HT-29 and SW480 Colorectal CancerCell Lines.
Zsigrai S. et al.
Folic acid (FA) is a synthetic form of vitamin B9, generally used as a nutritional supplement and an adjunctive medication in cancer therapy. FA is involved in genetic and epigenetic regulation; therefore, it has a dual modulatory role in established neoplasms. We aimed to investigate the effect of short-term (72 h)... |
Complex regulatory role of DNA methylation in caste- and age-specificexpression of a termite
Harrison Mark C. et al.
The reproductive castes of eusocial insects are often characterised by extreme lifespans and reproductive output, indicating an absence of the fecundity/longevity trade-off. The role of DNA methylation in the regulation of caste- and age-specific gene expression in eusocial insects is controversial. While some studi... |
When left does not seem right: epigenetic and bioelectric differencesbetween left- and right-sided breast cancer.
Sofía, Masuelli and Sebastián, Real and Emanuel, Campoy andBranham, María Teresita and Marzese, Diego Matías andMatthew, Salomon and De Blas, Gerardo and Rodolfo, Arias andMichael, Levin and María, Roqué
BACKGROUND: During embryogenesis lateral symmetry is broken, giving rise to Left/Right (L/R) breast tissues with distinct identity. L/R-sided breast tumors exhibit consistently-biased incidence, gene expression, and DNA methylation. We postulate that a differential L/R tumor-microenvironment crosstalk generates diff... |
Comparative Toxicogenomics of Glyphosate and Roundup Herbicidesby Mammalian Stem Cell-Based Genotoxicity Assays andMolecular Profiling in Sprague-Dawley Rats.
Mesnage R. et al.
Whether glyphosate-based herbicides (GBHs) are more potent than glyphosate alone at activating cellular mechanisms, which drive carcinogenesis remain controversial. As GBHs are more cytotoxic than glyphosate, we reasoned they may also be more capable of activating carcinogenic pathways. We tested this hypothesis by ... |
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and MEG3 controls hypoxia-inducedexpression of serum response factor (SRF) and SRF-dependent genes inpulmonary smooth muscle cell.
Kitagawa A. et al.
Although hypoxia induces aberrant gene expression and dedifferentiation of smooth muscle cells (SMCs), mechanisms that alter dedifferentiation gene expression by hypoxia remain unclear. Therefore, we aimed to gain insight into the hypoxia-controlled gene expression in SMCs. We conducted studies using SMCs cultured i... |
The ETS transcription factor ERF controls the exit from the naïve pluripotent state in a MAPK-dependent manner
Maria Vega-Sendino et. al.
The naïve epiblast transitions to a pluripotent primed state during embryo implantation. Despite the relevance of the FGF pathway during this period, little is known about the downstream effectors regulating this signaling. Here, we examined the molecular mechanisms coordinating the naïve to primed transit... |
Adaptive Convergence of Methylomes Reveals Epigenetic Driversand Boosters of Repeated Relapses in Patient-matched ChildhoodEpendymomas and Identifies Targets for Anti-RecurrenceTherapies
Zhao S. et al.
Ependymoma (EPN) is the third most common brain tumor in children and frequently recurs. Here, we report an integrated longitudinal analysis of epigenetic, genetic and tumorigenic changes in 30 patient-matched repeated relapses obtained from 10 pediatric patients to understand the mechanism of recurrences. Genome-wi... |
Genome-Wide Epigenomic Analyses in Patients With Nociceptive and Neuropathic Chronic Pain Subtypes Reveals Alterations in Methylation of Genes Involved in the Neuro-Musculoskeletal System
Stenz et al
Nociceptive pain involves the activation of nociceptors without damage to the nervous system, whereas neuropathic pain is related to an alteration in the central or peripheral nervous system. Chronic pain itself and the transition from acute to chronic pain may be epigenetically controlled. In this cross-sectional s... |
Genome-wide epigenomic analyses in patients with nociceptive andneuropathic chronic pain subtypes reveals alterations in methylation ofgenes involved in the neuro-musculoskeletal system.
Stenz Ludwig et al.
Nociceptive pain involves the activation of nociceptors without damage to the nervous system, whereas neuropathic pain is related to an alteration in the central or peripheral nervous system. Chronic pain itself and the transition from acute to chronic pain may be epigenetically controlled. In this cross-sectional s... |
Biobehavioral organization shapes the immune epigenome in infant rhesusMacaques (Macaca mulatta).
Baxter A. et al.
How individuals respond to and cope with stress is linked with their health and well-being. It is presumed that early stress responsiveness helps shape the health of the developing organism, but the relationship between stress responsiveness and early immune function during development is not well-known. We hypothes... |
Environmental enrichment preserves a young DNA methylation landscape in the aged mouse hippocampus
Sara Zocher, Rupert W. Overall, Mathias Lesche, Andreas Dahl & Gerd Kempermann
The decline of brain function during aging is associated with epigenetic changes, including DNA methylation. Lifestyle interventions can improve brain function during aging, but their influence on age-related epigenetic changes is unknown. Using genome-wide DNA methylation sequencing, we here show that experiencing ... |
Riluzole Administration to Rats with Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia Leads to Loss of DNA Methylation in Neuronal Genes
Luca Pagliaroli, Abel Fothi, Ester Nespoli, Istvan Liko, Borbala Veto, Piroska Devay, Flora Szeri, Bastian Hengerer, Csaba Barta, Tamas Aranyi
Dyskinesias are characterized by abnormal repetitive involuntary movements due to dysfunctional neuronal activity. Although levodopa-induced dyskinesia, characterized by tic-like abnormal involuntary movements, has no clinical treatment for Parkinson’s disease patients, animal studies indicate that Riluzole, w... |
Environmental enrichment preserves a young DNA methylation landscape inthe aged mouse hippocampus
Zocher S. et al.
The decline of brain function during aging is associated with epigenetic changes, including DNA methylation. Lifestyle interventions can improve brain function during aging, but their influence on age-related epigenetic changes is unknown. Using genome-wide DNA methylation sequencing, we here show that experiencing ... |
Pathophysiological adaptations of resistance arteries in rat offspringexposed in utero to maternal obesity is associated with sex-specificepigenetic alterations.
Payen Cyrielle et al.
BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES: Maternal obesity impacts vascular functions linked to metabolic disorders in offspring, leading to cardiovascular diseases during adulthood. Even if the relation between prenatal conditioning of cardiovascular diseases by maternal obesity and vascular function begins to be documented, little i... |
Multi-omics phenotyping of the gut-liver axis reveals metabolicperturbations from a low-dose pesticide mixture in rats.
Mesnage, Robin et al.
Health effects of pesticides are not always accurately detected using the current battery of regulatory toxicity tests. We compared standard histopathology and serum biochemistry measures and multi-omics analyses in a subchronic toxicity test of a mixture of six pesticides frequently detected in foodstuffs (azoxystr... |
Muscle allele-specific expression QTLs may affect meat quality traitsin Bos indicus.
Bruscadin J.J. et al.
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) located in transcript sequences showing allele-specific expression (ASE SNPs) were previously identified in the Longissimus thoracis muscle of a Nelore (Bos indicus) population consisting of 190 steers. Given that the allele-specific expression pattern may result from cis-regul... |
The insecticide permethrin induces transgenerational behavioral changeslinked to transcriptomic and epigenetic alterations in zebrafish (Daniorerio).
Blanc, Mélanie et al.
The pyrethroid insecticide permethrin is widely used for agricultural and domestic purposes. Previous data indicated that it acts as a developmental neurotoxicant and can induce transgenerational effects in non-target organisms. However, associated underlying mechanisms remain unclear. The aim of this study was to i... |
The aging DNA methylome reveals environment-by-aging interactions in amodel teleost
Bertucci, E. M. et al.
The rate at which individuals age underlies variation in life history and attendant health and disease trajectories. Age specific patterning of the DNA methylome (“epigenetic aging”) is strongly correlated with chronological age in humans and can be modeled to produce epigenetic age predictors. However, ... |
Perturbed DNA methylation by sustained overexpression of Gadd45b induces chromatin disorganization, DNA strand breaks and dopaminergic neurondeath in mice
Ravel-Godreuil, C. et al.
Heterochromatin disorganization is a key hallmark of aging and DNA methylation state is currently the main molecular predictor of chronological age. The most frequent neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson disease and Alzheimer’s disease are age-related but how the aging process and chromatin alterations ar... |
The Identification of a Novel Fucosidosis-Associated Mutation: A Case of a5-Year-Old Polish Girl with Two Additional Rare Chromosomal Aberrations andAffected DNA Methylation Patterns.
Domin A. et al.
Fucosidosis is a rare neurodegenerative autosomal recessive disorder, which manifests as progressive neurological and psychomotor deterioration, growth retardation, skin and skeletal abnormalities, intellectual disability and coarsening of facial features. It is caused by biallelic mutations in encoding the α-... |
Developmental cannabidiol exposure increases anxiety and modifiesgenome-wide brain DNA methylation in adult female mice.
Wanner N. M. et al.
BACKGROUND: Use of cannabidiol (CBD), the primary non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis, has recently risen dramatically, while relatively little is known about the underlying molecular mechanisms of its effects. Previous work indicates that direct CBD exposure strongly impacts the brain, with anxiolytic, anti... |
Hepatic transcriptome and DNA methylation patterns following perinataland chronic BPS exposure in male mice.
Brulport A. et al.
BACKGROUND: Bisphenol S (BPS) is a common bisphenol A (BPA) substitute, since BPA is virtually banned worldwide. However, BPS and BPA have both endocrine disrupting properties. Their effects appear mostly in adulthood following perinatal exposures. The objective of the present study was to investigate the impact of ... |
Integrative Analysis of Glucometabolic Traits, Adipose Tissue DNA Methylation and Gene Expression Identifies Epigenetic Regulatory Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance and Obesity in African Americans
Neeraj K. Sharma, Mary E. Comeau, Dennis Montoya, Matteo Pellegrini, Timothy D. Howard, Carl D. Langefeld, Swapan K. Das
Decline in insulin sensitivity due to dysfunction of adipose tissue (AT) is one of the earliest pathogenic events in Type 2 Diabetes. We hypothesize that differential DNA methylation (DNAm) controls insulin sensitivity and obesity by modulating transcript expression in AT. Integrating AT DNAm profiles with transcrip... |
DNA CpG methylation in sequential glioblastoma specimens.
Kraboth, Z and Galik, B and Tompa, M and Kajtar, B and Urban, P andGyenesei, A and Miseta, A and Kalman, B
PURPOSE: Glioblastoma is the most aggressive form of brain tumors. A better understanding of the molecular mechanisms leading to its evolution is essential for the development of treatments more effective than the available modalities. Here, we aim to identify molecular drivers of glioblastoma development and recurr... |
Early Life Exposure to Environmentally Relevant Levels of Endocrine Disruptors Drive Multigenerational and Transgenerational Epigenetic Changes in a Fish Model
Major Kaley M., DeCourten Bethany M., Li Jie, Britton Monica, Settles Matthew L., Mehinto Alvine C., Connon Richard E., Brander Susanne M.
The inland silverside, Menidia beryllina, is a euryhaline fish and a model organism in ecotoxicology. We previously showed that exposure to picomolar (ng/L) levels of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) can cause a variety of effects in M. beryllina, from changes in gene expression to phenotypic alterations. Here ... |
Chronic cannabidiol alters genome-wide DNA methylation in adult mouse hippocampus: epigenetic implications for psychiatric disease.
Wanner NM, Colwell M, Drown C, Faulk C
Cannabidiol (CBD) is the primary non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis (Cannabis sativa) and an increasingly popular dietary supplement as a result of widespread availability of CBD-containing products. CBD is FDA-approved for the treatment of epilepsy and exhibits anxiolytic, antipsychotic, prosocial, and oth... |
Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b-Decommissioned Fetal Enhancers are Linked to Kidney Disease
Guan Y, Liu H, Ma Z, Li SY, Park J, Sheng X, Susztak K
BACKGROUND: Cytosine methylation is an epigenetic mark that dictates cell fate and response to stimuli. The timing and establishment of methylation logic during kidney development remains unknown. DNA methyltransferase 3a and 3b are the enzymes capable of establishing methylation. METHODS: We generated mice with gen... |
Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients, Both Newly Diagnosed and Methotrexate Treated, Show More DNA Methylation Differences in CD4+ Memory Than in CD4+ Naïve T Cells
Guderud Kari, Sunde Line H., Flåm Siri T., Mæhlen Marthe T., Mjaavatten Maria D., Lillegraven Siri, Aga Anna-Birgitte, Evenrød Ida M., Norli Ellen S., Andreassen Bettina K., Franzenburg Sören, Franke Andre, Haavardsholm Espen A., Rayner Simon, Gervin Kris
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes pain and swelling of multiple joints in the body. The underlying disease mechanisms are believed to involve a complex interplay between common genetic and environmental factors. The heritability of RA has been estimated to be ~50% for anti-citrull... |
Obesogen effect of bisphenol S alters mRNA expression and DNA methylation profiling in male mouse liver
Brulport Axelle, Vaiman Daniel, Chagnon Marie-Christine, Le Corre Ludovic
Environmental pollution is increasingly considered an important factor involved in the obesity incidence. Endocrine disruptors (EDs) are important actors in the concept of DOHaD (Developmental Origins of Health and Disease), where epigenetic mechanisms play crucial roles. Bisphenol A (BPA), a monomer used in the man... |
Mitochondrial stress triggers a pro-survival response through epigenetic modifications of nuclear DNA.
Mayorga L, Salassa BN, Marzese DM, Loos MA, Eiroa HD, Lubieniecki F, García Samartino C, Romano PS, Roqué M
Mitochondrial dysfunction represents an important cellular stressor and when intense and persistent cells must unleash an adaptive response to prevent their extinction. Furthermore, mitochondria can induce nuclear transcriptional changes and DNA methylation can modulate cellular responses to stress. We hypothesized ... |
Differential DNA methylation of potassium channel KCa3.1 and immune signalling pathways is associated with infant immune responses following BCG vaccination.
Hasso-Agopsowicz M, Scriba TJ, Hanekom WA, Dockrell HM, Smith SG
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is the only licensed vaccine for tuberculosis (TB) and induces highly variable protection against pulmonary disease in different countries. We hypothesised that DNA methylation is one of the molecular mechanisms driving variability in BCG-induced immune responses. DNA methylatio... |
In Situ Fixation Redefines Quiescence and Early Activation of Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells
Machado L. et al.
Summary
State of the art techniques have been developed to isolate and analyze cells from various tissues, aiming to capture their in vivo state. However, the majority of cell isolation protocols involve lengthy mechanical and enzymatic dissociation steps followed by flow cytometry, exposing cells to stres... |
DNMT3B overexpression contributes to aberrant DNA methylation and MYC-driven tumor maintenance in T-ALL and Burkitt’s lymphoma
Poole et al.
Aberrant DNA methylation is a hallmark of cancer. However, our understanding of how tumor cell-specific DNA methylation patterns are established and maintained is limited. Here, we report that in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) and Burkitt’s lymphoma the MYC oncogene causes overexpression of DNA me... |
DNA methylation and alcohol use disorders: Progress and challenges
Zhang H. and Gelernter J.
Background and Objectives
Risk for alcohol use disorders (AUDs) is influenced by gene–environment interactions. Environmental factors can affect gene expression through epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation. This review outlines the findings regarding the association of DNA methylation and AUDs.
... |
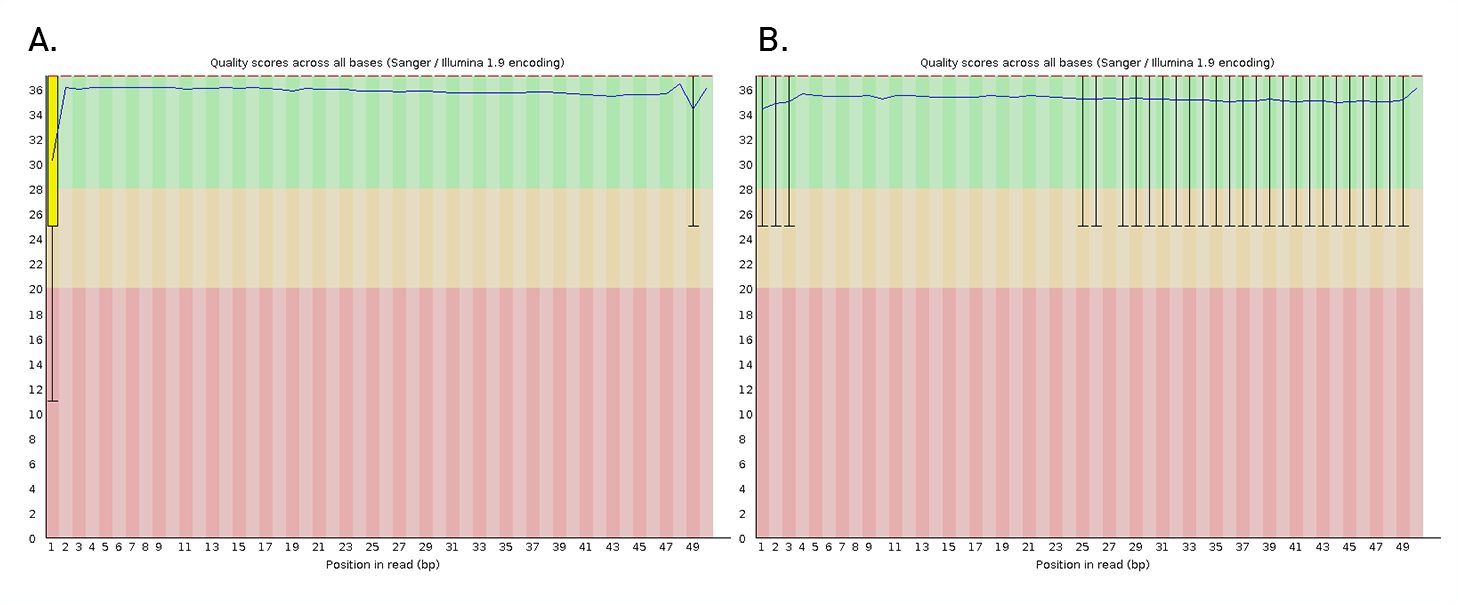
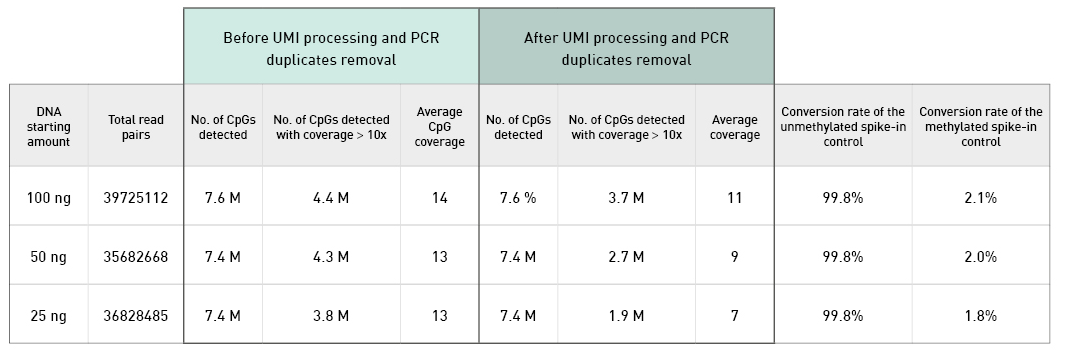
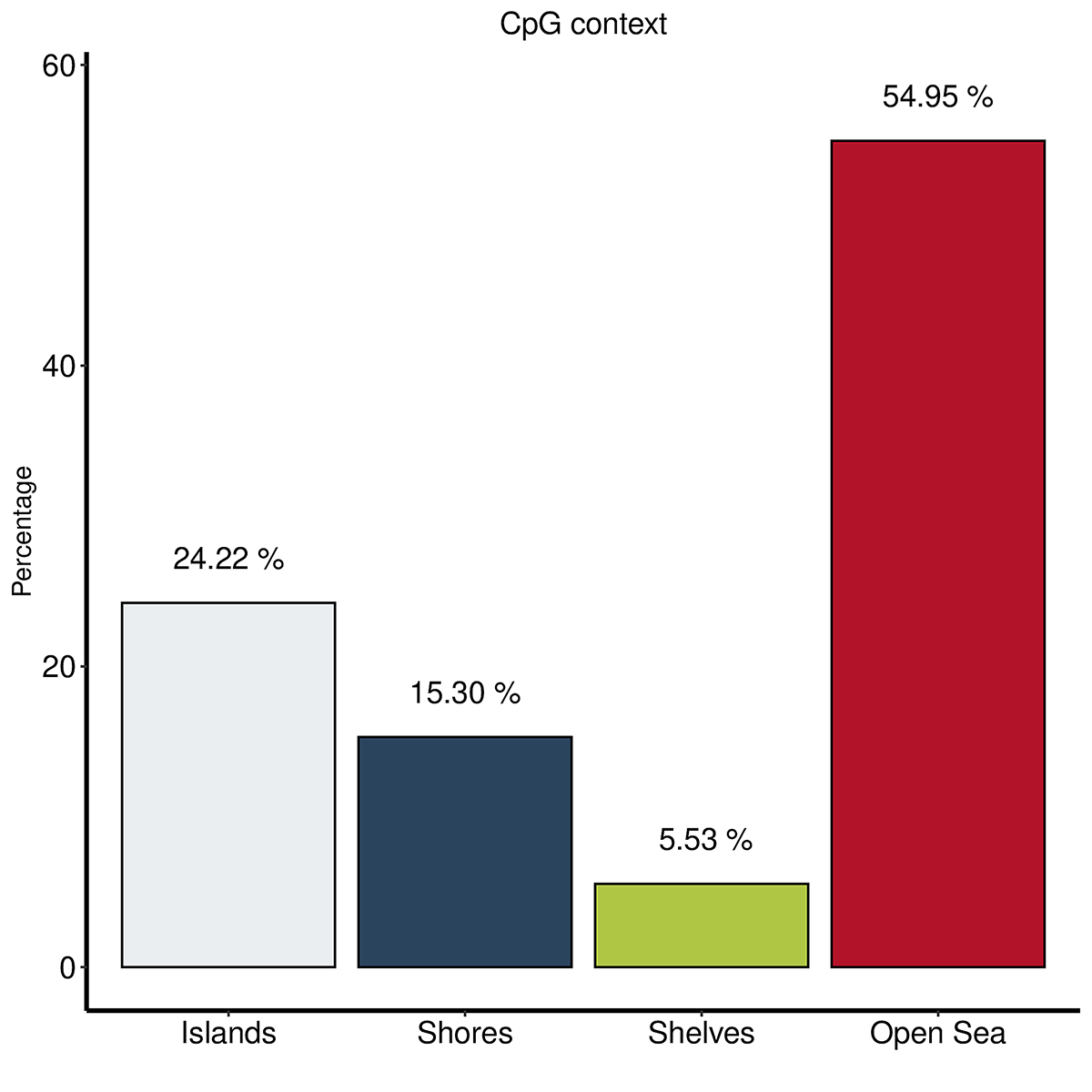
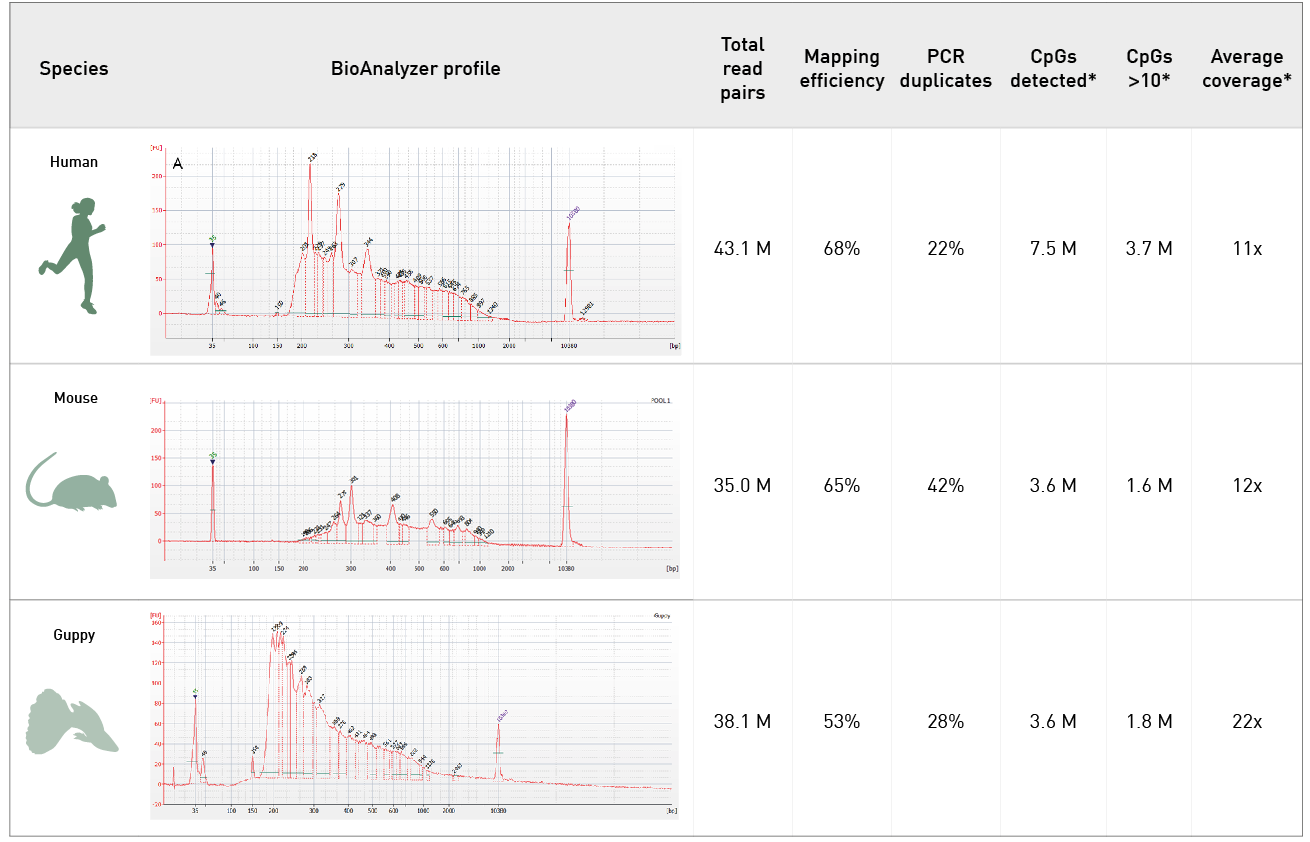
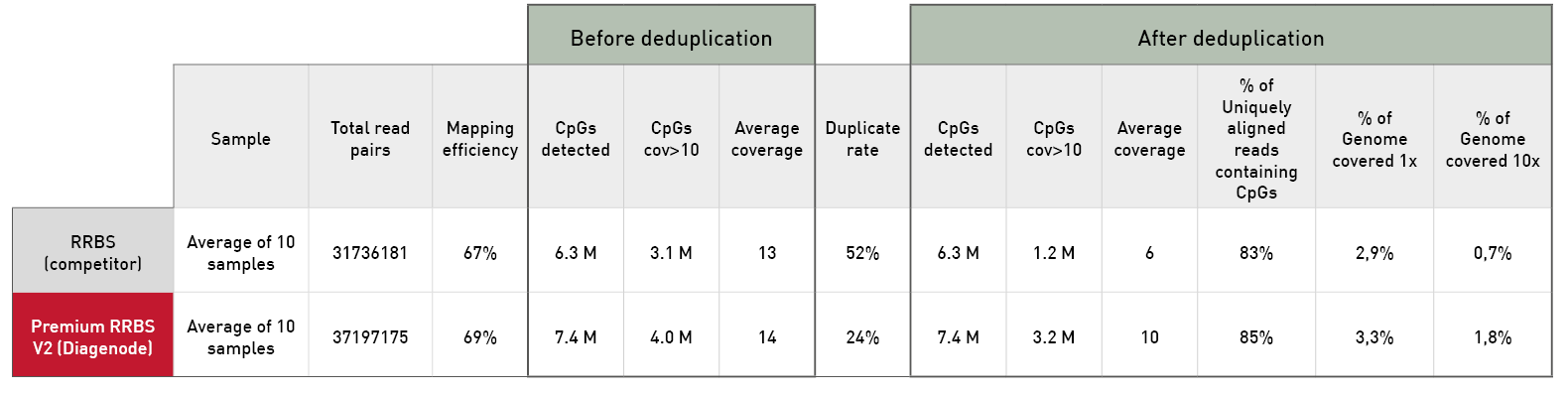
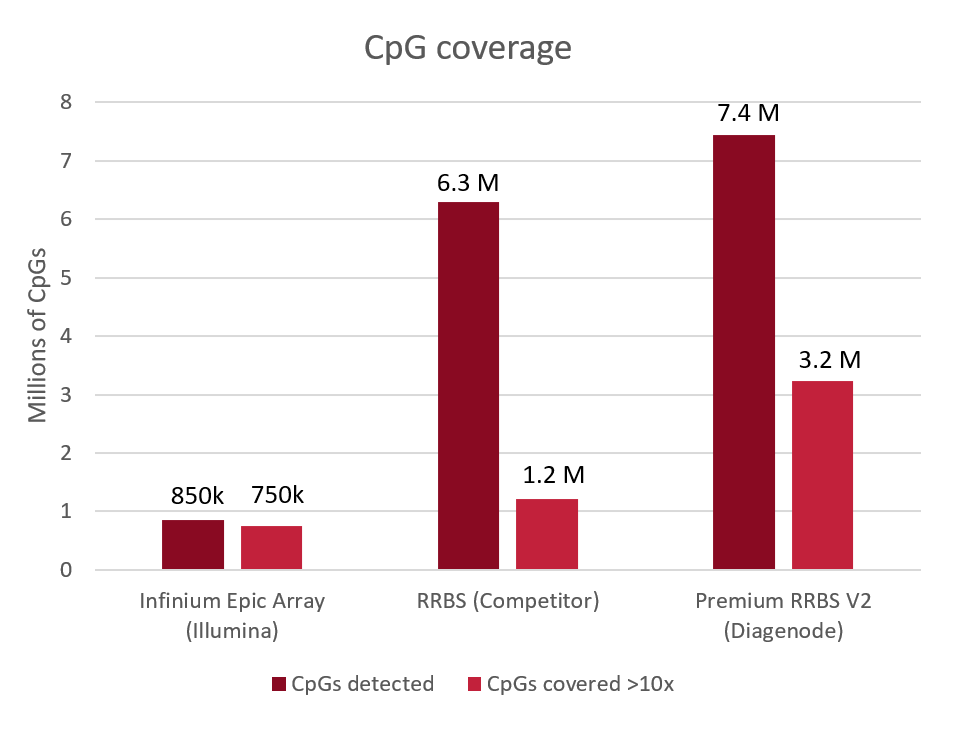
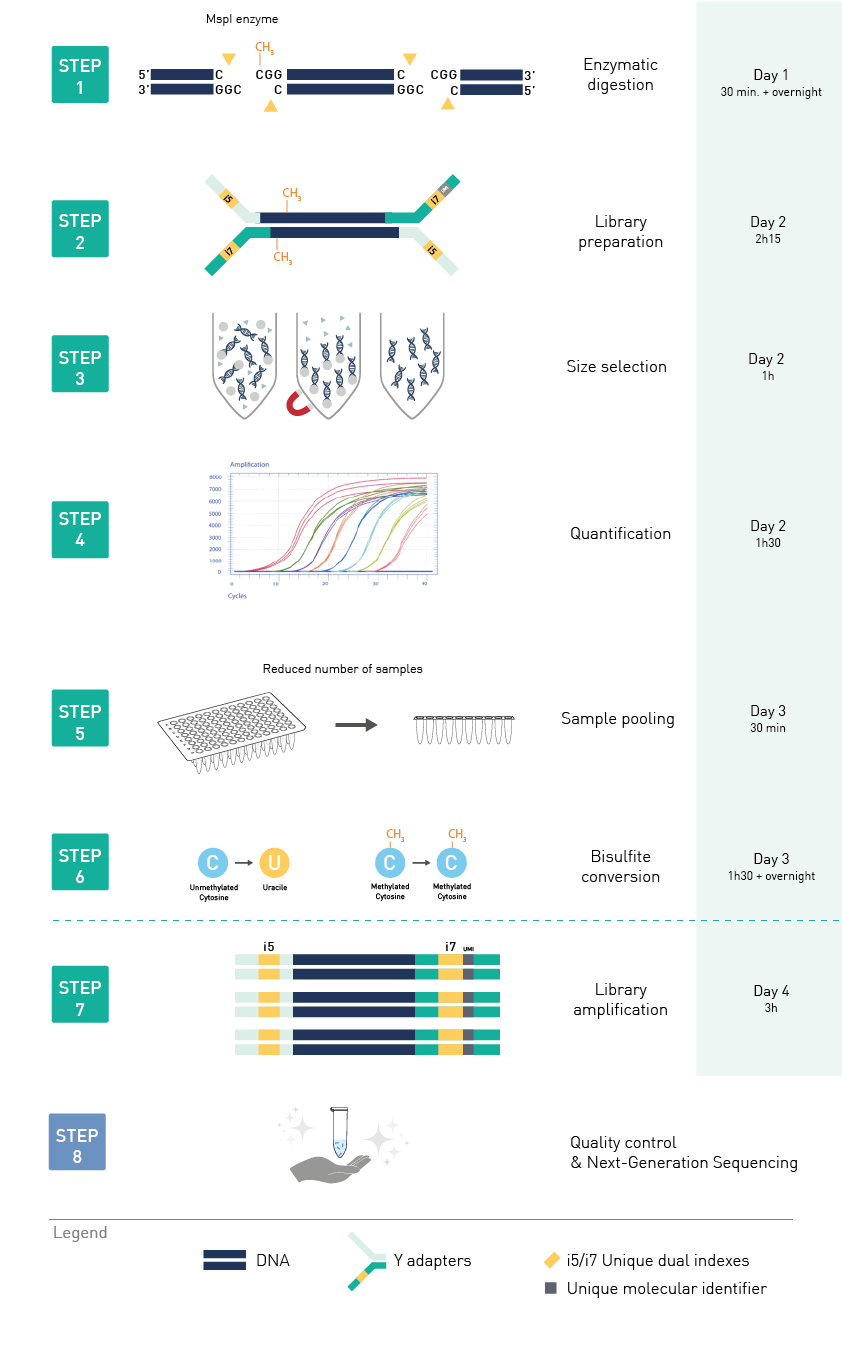
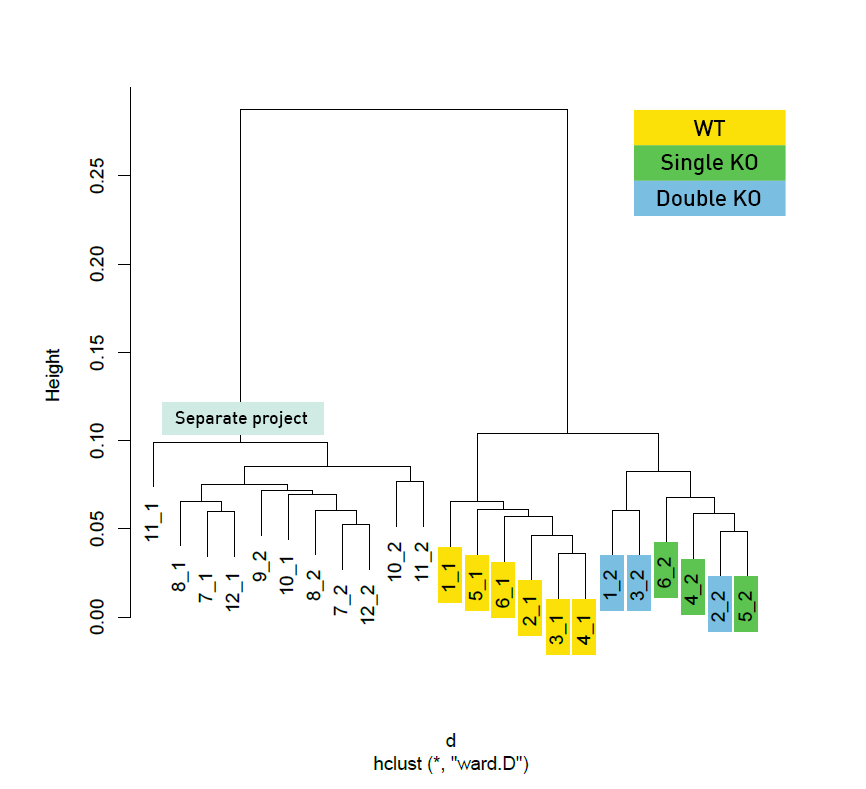
Diagenode® Premium RRBS technology: cost-effective DNA methylation mapping with superior coverage
Anne-Clémence Veillard, Paul Datlinger, Miklos Laczik, Sharon Squazzo & Christoph Bock
Reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS) enables genome-scale DNA methylation analysis in any vertebrate species. The assay benefits from the practical advantages of bisulfite sequencing while avoiding the cost of whole-genome sequencing. The Diagenode Premium RRBS kit makes this technology widely availabl... |