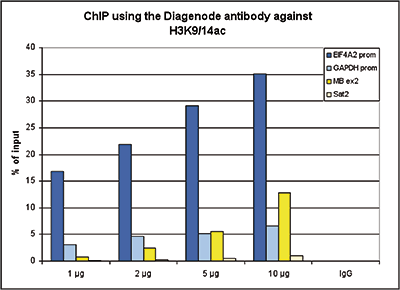
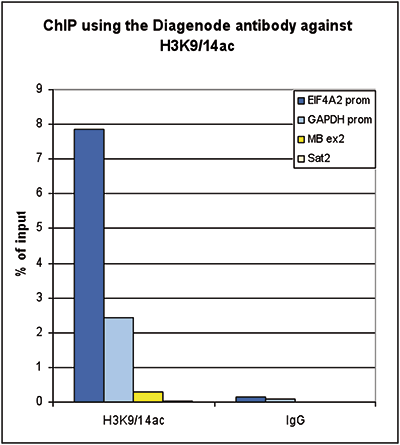
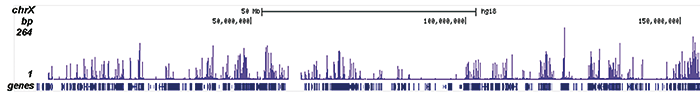
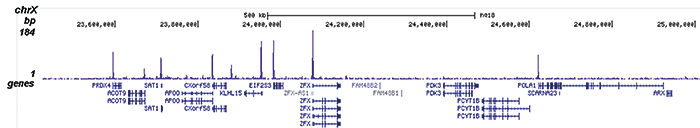
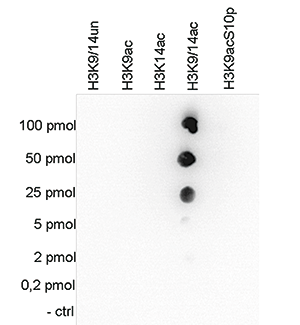
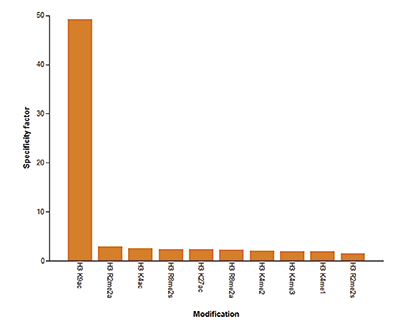
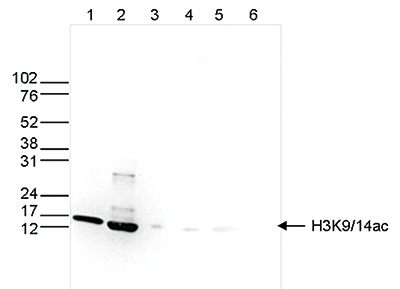
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K9/14ac Antibody (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410200 Lot# A1756D). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
The circadian clock CRY1 regulates pluripotent stem cell identity andsomatic cell reprogramming.
Sato S. et al.
Distinct metabolic conditions rewire circadian-clock-controlled signaling pathways leading to the de novo construction of signal transduction networks. However, it remains unclear whether metabolic hallmarks unique to pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) are connected to clock functions. Reprogramming somatic cells to a pl... |
Caffeine intake exerts dual genome-wide effects on hippocampal metabolismand learning-dependent transcription.
Paiva I. et al.
Caffeine is the most widely consumed psychoactive substance in the world. Strikingly, the molecular pathways engaged by its regular consumption remain unclear. We herein addressed the mechanisms associated with habitual (chronic) caffeine consumption in the mouse hippocampus using untargeted orthogonal omics techniq... |
Chemokine switch regulated by TGF-β1 in cancer-associated fibroblastsubsets determines the efficacy of chemo-immunotherapy.
Vienot A. et al.
Combining immunogenic cell death-inducing chemotherapies and PD-1 blockade can generate remarkable tumor responses. It is now well established that TGF-β1 signaling is a major component of treatment resistance and contributes to the cancer-related immunosuppressive microenvironment. However, whether TGF-β1... |
S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine hydrolase links methionine metabolism to thecircadian clock and chromatin remodeling.
Greco C. M. et al.
Circadian gene expression driven by transcription activators CLOCK and BMAL1 is intimately associated with dynamic chromatin remodeling. However, how cellular metabolism directs circadian chromatin remodeling is virtually unexplored. We report that the S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) hydrolyzing enzyme adenosylhomocyst... |
Homer1a Undergoes Bimodal Transcriptional Regulation by CREB and the Circadian Clock.
Sato S, Bunney BG, Vawter MP, Bunney WE, Sassone-Corsi P
Accumulating evidence points to a significant link between disrupted circadian rhythms and neuronal disfunctions, though the molecular mechanisms underlying this connection are virtually unexplored. The transcript Homer1a, an immediate early gene related to postsynaptic signaling, has been demonstrated to exhibit ro... |
The TGF-β profibrotic cascade targets ecto-5'-nucleotidase gene in proximal tubule epithelial cells and is a traceable marker of progressive diabetic kidney disease.
Cappelli C, Tellez A, Jara C, Alarcón S, Torres A, Mendoza P, Podestá L, Flores C, Quezada C, Oyarzún C, Martín RS
Progressive diabetic nephropathy (DN) and loss of renal function correlate with kidney fibrosis. Crosstalk between TGF-β and adenosinergic signaling contributes to the phenotypic transition of cells and to renal fibrosis in DN models. We evaluated the role of TGF-β on NT5E gene expression coding for the ec... |
Targeting Macrophage Histone H3 Modification as a Leishmania Strategy to Dampen the NF-κB/NLRP3-Mediated Inflammatory Response.
Lecoeur H, Prina E, Rosazza T, Kokou K, N'Diaye P, Aulner N, Varet H, Bussotti G, Xing Y, Milon G, Weil R, Meng G, Späth GF
Aberrant macrophage activation during intracellular infection generates immunopathologies that can cause severe human morbidity. A better understanding of immune subversion strategies and macrophage phenotypic and functional responses is necessary to design host-directed intervention strategies. Here, we uncover a f... |
Nucleome Dynamics during Retinal Development.
Norrie JL, Lupo MS, Xu B, Al Diri I, Valentine M, Putnam D, Griffiths L, Zhang J, Johnson D, Easton J, Shao Y, Honnell V, Frase S, Miller S, Stewart V, Zhou X, Chen X, Dyer MA
More than 8,000 genes are turned on or off as progenitor cells produce the 7 classes of retinal cell types during development. Thousands of enhancers are also active in the developing retinae, many having features of cell- and developmental stage-specific activity. We studied dynamic changes in the 3D chromatin land... |
Acetate Promotes T Cell Effector Function during Glucose Restriction.
Qiu J, Villa M, Sanin DE, Buck MD, O'Sullivan D, Ching R, Matsushita M, Grzes KM, Winkler F, Chang CH, Curtis JD, Kyle RL, Van Teijlingen Bakker N, Corrado M, Haessler F, Alfei F, Edwards-Hicks J, Maggi LB, Zehn D, Egawa T, Bengsch B, Klein Geltink RI, Je
Competition for nutrients like glucose can metabolically restrict T cells and contribute to their hyporesponsiveness during cancer. Metabolic adaptation to the surrounding microenvironment is therefore key for maintaining appropriate cell function. For instance, cancer cells use acetate as a substrate alternati... |
Dissecting the role of H3K27 acetylation and methylation in PRC2 mediated control of cellular identity.
Lavarone E, Barbieri CM, Pasini D
The Polycomb repressive complexes PRC1 and PRC2 act non-redundantly at target genes to maintain transcriptional programs and ensure cellular identity. PRC2 methylates lysine 27 on histone H3 (H3K27me), while PRC1 mono-ubiquitinates histone H2A at lysine 119 (H2Aub1). Here we present engineered mouse embryonic stem c... |
Distinct Circadian Signatures in Liver and Gut Clocks Revealed by Ketogenic Diet
Tognini P. et al.
The circadian clock orchestrates rhythms in physiology and behavior, allowing organismal adaptation to daily environmental changes. While food intake profoundly influences diurnal rhythms in the liver, how nutritional challenges are differentially interpreted by distinct tissue-specific clocks remains poorly explore... |
Circadian Reprogramming in the Liver Identifies Metabolic Pathways of Aging
Sato S. et al.
The process of aging and circadian rhythms are intimately intertwined, but how peripheral clocks involved in metabolic homeostasis contribute to aging remains unknown. Importantly, caloric restriction (CR) extends lifespan in several organisms and rewires circadian metabolism. Using young versus old mice, fed ad lib... |
The Dynamic Epigenetic Landscape of the Retina During Development, Reprogramming, and Tumorigenesis.
Aldiri I. et al.
In the developing retina, multipotent neural progenitors undergo unidirectional differentiation in a precise spatiotemporal order. Here we profile the epigenetic and transcriptional changes that occur during retinogenesis in mice and humans. Although some progenitor genes and cell cycle genes were epigenetically sil... |
Nitric oxide modulates histone acetylation at stress genes by inhibition of histone deacetylases
Mengel A. et al.
Histone acetylation, which is an important mechanism to regulate gene expression, is controlled by the opposing action of histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs). In animals, several HDACs are subjected to regulation by nitric oxide (NO), in plants however, it is unknown whether NO affects... |
H3.3 demarcates GC-rich coding and subtelomeric regions and serves as potential memory mark for virulence gene expression in Plasmodium falciparum
Fraschka SA et al.
Histones, by packaging and organizing the DNA into chromatin, serve as essential building blocks for eukaryotic life. The basic structure of the chromatin is established by four canonical histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4), while histone variants are more commonly utilized to alter the properties of specific chromatin d... |
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay for the Identification of Arabidopsis Protein-DNA Interactions In Vivo
Komar DN, Mouriz A, Jarillo JA, Piñeiro M
Intricate gene regulatory networks orchestrate biological processes and developmental transitions in plants. Selective transcriptional activation and silencing of genes mediate the response of plants to environmental signals and developmental cues. Therefore, insights into the mechanisms that control plant gene expr... |
NAD(+)-SIRT1 control of H3K4 trimethylation through circadian deacetylation of MLL1.
Aguilar-Arnal L, Katada S, Orozco-Solis R, Sassone-Corsi P
The circadian clock controls the transcription of hundreds of genes through specific chromatin-remodeling events. The histone methyltransferase mixed-lineage leukemia 1 (MLL1) coordinates recruitment of CLOCK-BMAL1 activator complexes to chromatin, an event associated with cyclic trimethylation of histone H3 Lys4 (H... |