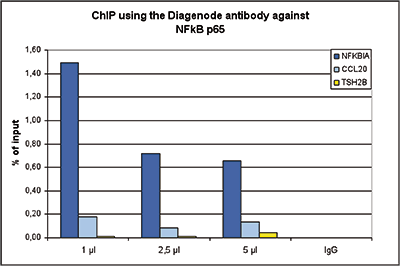
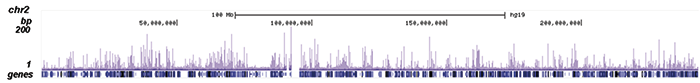
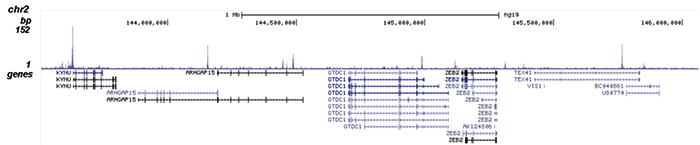
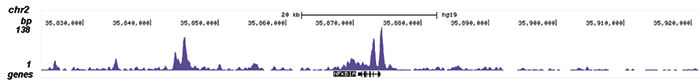
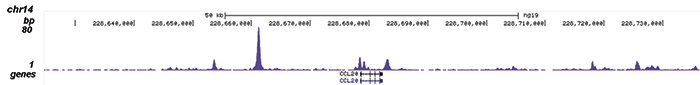
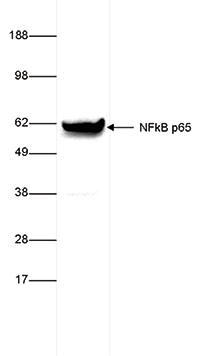
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: NFKB p65 Antibody (sample size) (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15310256-20 Lot# 24468). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Teamwork of clustered low-affinity κB sites and accessory factors regulates transcriptional strength of NF-κB RelA dimers
Shahabi, Shandy et al.
Non-consensus binding sites of transcription factors (TFs) are often observed within the regulatory elements of genes; however, their effect on transcriptional strength is unclear. Within the promoters and enhancers of NF-κB-responsive genes, we identified clusters of non-consensus κB DNA sites, many... |
Constitutive expression of the transcriptional co-activator IκBζ promotes melanoma growth and immunotherapy resistance
Kolb, Antonia et al.
IκBζ, a rather unknown co-regulator of NF-κB, can either activate or repress a subset of NF-κB target genes. While its role as an inducibly expressed, transcriptional regulator of cytokines and chemokines in immune cells is established, IκBζ's function in solid cancer remains un... |
Peroxiredoxin 1-Toll-like receptor 4-p65 axis inhibits receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand-mediated osteoclast differentiation
Jisu Park et al.
Peroxiredoxin 1 (PRDX1), an intracellular antioxidant enzyme, has emerged as a regulator of inflammatory responses via Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling. Despite this, the mechanistic details of the PRDX1-TLR4 axis and its impact on osteoclast differentiation remain elusive. Here, we show that PRDX1 suppresses R... |
PBRM1-deficient PBAF complexes target aberrant genomic loci to activatethe NF-κB pathway in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Yao X. et al.
PBRM1 encodes an accessory subunit of the PBAF SWI/SNF chromatin remodeller, and the inactivation of PBRM1 is a frequent event in kidney cancer. However, the impact of PBRM1 loss on chromatin remodelling is not well examined. Here we show that, in VHL-deficient renal tumours, PBRM1 deficiency results in ectopic PBAF... |
Vitamin C enhances NF-κB-driven epigenomic reprogramming andboosts the immunogenic properties of dendritic cells.
Morante-Palacios O. et al.
Dendritic cells (DCs), the most potent antigen-presenting cells, are necessary for effective activation of naïve T cells. DCs' immunological properties are modulated in response to various stimuli. Active DNA demethylation is crucial for DC differentiation and function. Vitamin C, a known cofactor of ten-eleven... |
The CDK4/6-EZH2 pathway is a potential therapeutic target for psoriasis.
Müller A, Dickmanns A, Resch C, Schäkel K, Hailfinger S, Dobbelstein M, Schulze-Osthoff K, Kramer D
Psoriasis is a frequent inflammatory skin disease characterized by keratinocyte hyperproliferation and a disease-related infiltration of immune cells. Here, we identified a novel pro-inflammatory signaling pathway driven by the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) 4 and 6 and the methyltransferase EZH2 as a valid target f... |
AP-1 activity induced by co-stimulation is required for chromatin opening during T cell activation.
Yukawa M, Jagannathan S, Vallabh S, Kartashov AV, Chen X, Weirauch MT, Barski A
Activation of T cells is dependent on the organized and timely opening and closing of chromatin. Herein, we identify AP-1 as the transcription factor that directs most of this remodeling. Chromatin accessibility profiling showed quick opening of closed chromatin in naive T cells within 5 h of activation. These newly... |
RRAD, IL4I1, CDKN1A, and SERPINE1 genes are potentially co-regulated by NF-κB and p53 transcription factors in cells exposed to high doses of ionizing radiation.
Szołtysek K, Janus P, Zając G, Stokowy T, Walaszczyk A, Widłak W, Wojtaś B, Gielniewski B, Cockell S, Perkins ND, Kimmel M, Widlak P
BACKGROUND: The cellular response to ionizing radiation involves activation of p53-dependent pathways and activation of the atypical NF-κB pathway. The crosstalk between these two transcriptional networks include (co)regulation of common gene targets. Here we looked for novel genes potentially (co)regulated by... |
Pro-inflammatory cytokine and high doses of ionizing radiation have similar effects on the expression of NF-kappaB-dependent genes.
Janus P, Szołtysek K, Zając G, Stokowy T, Walaszczyk A, Widłak W, Wojtaś B, Gielniewski B, Iwanaszko M, Braun R, Cockell S, Perkins ND, Kimmel M, Widlak P
The NF-κB transcription factors are activated via diverse molecular mechanisms in response to various types of stimuli. A plethora of functions associated with specific sets of target genes could be regulated differentially by this factor, affecting cellular response to stress including an anticancer treatment... |