How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: MicroChIP DiaPure columns (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C03040001). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
PRC1-mediated H2A.Zub promotes gene expression by preventing H3.1K27me1 incorporation in Arabidopsis
Baile, Fernando et al.
Background: PcG complexes are pivotal in orchestrating the transition from embryonic to vegetative development in plants. However, the mechanisms underlying the gene expression reprogramming that takes place during this developmental transition are still not fully understood. Several studies suggest that incorp... |
Genetic disruption of the baculum compromises the ability of male mice to copulate
Ghione, Caleb R et al.
The baculum, a bone in the penis of many mammal species, shows an astonishing level of morphological divergence between species. Despite hundreds of years of interest, biologists have been unable to directly test its function. The goal of the current study is to uncover molecular details that could allow selecti... |
Extracellular Vesicles From Follicular Fluid in Infertile Women: Size, Morphology and miRNA Content Analysis
Solène Ducarre et al.
The declining birth rates and fertility challenges in Europe have intensified global concerns over rising infertility, particularly among women. This study decisively investigates follicular fluid‐related extracellular vesicles (FF‐EVs) from infertile patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or diminished ovar... |
Trithorax regulates long-term memory in Drosophila through epigenetic maintenance of mushroom body metabolic state and translation capacity
Nicholas Raun et al.
The role of epigenetics and chromatin in the maintenance of postmitotic neuronal cell identities is not well understood. Here, we show that the histone methyltransferase Trithorax (Trx) is required in postmitotic memory neurons of the Drosophila mushroom body (MB) to enable their capacity for long-term mem... |
Integrated multi-omics analysis of PBX1 in mouse adult neural stem- and progenitor cells identifies a transcriptional module that functionally links PBX1 to TCF3/4
Vera Laub et al.
Developmental transcription factors act in networks, but how these networks achieve cell- and tissue specificity is still poorly understood. Here, we explored pre-B cell leukemia homeobox 1 (PBX1) in adult neurogenesis combining genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic approaches. ChIP-seq analysis uncovered PBX1 bind... |
A PRE loop at the dac locus acts as a topological chromatin structure that restricts and specifies enhancer–promoter communication
Denaud S. et al.
Three-dimensional (3D) genome folding has a fundamental role in the regulation of developmental genes by facilitating or constraining chromatin interactions between cis-regulatory elements (CREs). Polycomb response elements (PREs) are a specific kind of CRE involved in the memory of transcriptional states in&nb... |
A multiomic atlas of the aging hippocampus reveals molecular changes in response to environmental enrichment
Perez R. F. at al.
Aging involves the deterioration of organismal function, leading to the emergence of multiple pathologies. Environmental stimuli, including lifestyle, can influence the trajectory of this process and may be used as tools in the pursuit of healthy aging. To evaluate the role of epigenetic mechanisms in this context, ... |
Inflammatory stress-mediated chromatin changes underlie dysfunction in endothelial cells
Liu H. et al.
Inflammatory stresses underlie endothelial dysfunction and contribute to the development of chronic cardiovascular disorders such as atherosclerosis and vascular fibrosis. The initial transcriptional response of endothelial cells to pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha is well established. However, very few ... |
Mutant FUS induces chromatin reorganization in the hippocampus andalters memory processes.
Tzeplaeff L. et al.
Cytoplasmic mislocalization of the nuclear Fused in Sarcoma (FUS) protein is associated to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). Cytoplasmic FUS accumulation is recapitulated in the frontal cortex and spinal cord of heterozygous Fus mice. Yet, the mechanisms linking FUS mislocalizati... |
FXR inhibition may protect from SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducingACE2.
Brevini Teresa et al.
Prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection through the modulation of viral host receptors, such as ACE2, could represent a new chemoprophylactic approach for COVID-19 complementing vaccination. However, the mechanisms controlling ACE2 expression remain elusive. Here, we identify the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) as a direct re... |
Intranasal administration of Acinetobacter lwoffii in a murine model ofasthma induces IL-6-mediated protection associated with cecal microbiotachanges.
Alashkar A. B. et al.
BACKGROUND: Early-life exposure to certain environmental bacteria including Acinetobacter lwoffii (AL) has been implicated in protection from chronic inflammatory diseases including asthma later in life. However, the underlying mechanisms at the immune-microbe interface remain largely unknown. METHODS: The effects o... |
Caffeine intake exerts dual genome-wide effects on hippocampal metabolismand learning-dependent transcription.
Paiva I. et al.
Caffeine is the most widely consumed psychoactive substance in the world. Strikingly, the molecular pathways engaged by its regular consumption remain unclear. We herein addressed the mechanisms associated with habitual (chronic) caffeine consumption in the mouse hippocampus using untargeted orthogonal omics techniq... |
Effects of GSK-J4 on JMJD3 Histone Demethylase in Mouse Prostate Cancer Xenografts
Sanchez A. et al.
Background/aim: Histone methylation status is required to control gene expression. H3K27me3 is an epigenetic tri-methylation modification to histone H3 controlled by the demethylase JMJD3. JMJD3 is dysregulated in a wide range of cancers and has been shown to control the expression of a specific growth-modulato... |
Effects of GSK-J4 on JMJD3 Histone Demethylase in MouseProstate Cancer Xenografts.
Sanchez A. et al.
BACKGROUND/AIM: Histone methylation status is required to control gene expression. H3K27me3 is an epigenetic tri-methylation modification to histone H3 controlled by the demethylase JMJD3. JMJD3 is dysregulated in a wide range of cancers and has been shown to control the expression of a specific growth-modulatory ge... |
Autocrine Vitamin D-signaling switches off pro-inflammatory programsof Th1 cells
Chauss D.et al.
The molecular mechanisms governing orderly shutdown and retraction of CD4+ T helper (Th)1 responses remain poorly understood. Here, we show that complement triggers contraction of Th1 responses by inducing intrinsic expression of the vitamin D (VitD) receptor (VDR) and the VitD-activating enzyme CYP27B1, permitting ... |
Essential role of a ThPOK autoregulatory loop in the maintenance ofmature CD4 T cell identity and function.
Basu Jayati et al.
The transcription factor ThPOK (encoded by the Zbtb7b gene) controls homeostasis and differentiation of mature helper T cells, while opposing their differentiation to CD4 intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) in the intestinal mucosa. Thus CD4 IEL differentiation requires ThPOK transcriptional repression via reactivati... |
The histone modification H3K4me3 is altered at the locus in Alzheimer'sdisease brain.
Smith, Adam et al.
Several epigenome-wide association studies of DNA methylation have highlighted altered DNA methylation in the gene in Alzheimer's disease (AD) brain samples. However, no study has specifically examined histone modifications in the disease. We use chromatin immunoprecipitation-qPCR to quantify tri-methylation at hist... |
Digging Deeper into Breast Cancer Epigenetics: Insights from ChemicalInhibition of Histone Acetyltransferase TIP60 .
Idrissou, Mouhamed and Lebert, Andre and Boisnier, Tiphanie and Sanchez,Anna and Houfaf Khoufaf, Fatma Zohra and Penault-Llorca, Frédérique andBignon, Yves-Jean and Bernard-Gallon, Dominique
Breast cancer is often sporadic due to several factors. Among them, the deregulation of epigenetic proteins may be involved. TIP60 or KAT5 is an acetyltransferase that regulates gene transcription through the chromatin structure. This pleiotropic protein acts in several cellular pathways by acetylating proteins. RNA... |
Delineating the early transcriptional specification of the mammalian trachea and esophagus.
Kuwahara A, Lewis AE, Coombes C, Leung FS, Percharde M, Bush JO
The genome-scale transcriptional programs that specify the mammalian trachea and esophagus are unknown. Though NKX2-1 and SOX2 are hypothesized to be co-repressive master regulators of tracheoesophageal fates, this is untested at a whole transcriptomic scale and their downstream networks remain unidentified. By comb... |
Combinatorial action of NF-Y and TALE at embryonic enhancers defines distinct gene expression programs during zygotic genome activation in zebrafish.
Stanney W, Ladam F, Donaldson IJ, Parsons TJ, Maehr R, Bobola N, Sagerström CG
Animal embryogenesis is initiated by maternal factors, but zygotic genome activation (ZGA) shifts regulatory control to the embryo during blastula stages. ZGA is thought to be mediated by maternally provided transcription factors (TFs), but few such TFs have been identified in vertebrates. Here we report that NF-Y a... |
Whsc1 links pluripotency exit with mesendoderm specification.
Tian TV, Di Stefano B, Stik G, Vila-Casadesús M, Sardina JL, Vidal E, Dasti A, Segura-Morales C, De Andrés-Aguayo L, Gómez A, Goldmann J, Jaenisch R, Graf T
How pluripotent stem cells differentiate into the main germ layers is a key question of developmental biology. Here, we show that the chromatin-related factor Whsc1 (also known as Nsd2 and MMSET) has a dual role in pluripotency exit and germ layer specification of embryonic stem cells. On induction of differentiatio... |
Spatial confinement downsizes the inflammatory response of macrophages.
Jain N, Vogel V
Macrophages respond to chemical/metabolic and physical stimuli, but their effects cannot be readily decoupled in vivo during pro-inflammatory activation. Here, we show that preventing macrophage spreading by spatial confinement, as imposed by micropatterning, microporous substrates or cell crowding, suppresses late ... |
SIRT1-dependent epigenetic regulation of H3 and H4 histone acetylation in human breast cancer
Khaldoun Rifaï et al.
Breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed malignancy in women worldwide. It is well established that the complexity of carcinogenesis involves profound epigenetic deregulations that contribute to the tumorigenesis process. Deregulated H3 and H4 acetylated histone marks are amongst those alterations. Sirtuin-1 (... |
Reciprocal signalling by Notch-Collagen V-CALCR retains muscle stem cells in their niche.
Baghdadi MB, Castel D, Machado L, Fukada SI, Birk DE, Relaix F, Tajbakhsh S, Mourikis P
The cell microenvironment, which is critical for stem cell maintenance, contains both cellular and non-cellular components, including secreted growth factors and the extracellular matrix. Although Notch and other signalling pathways have previously been reported to regulate quiescence of stem cells, the co... |
A new metabolic gene signature in prostate cancer regulated by JMJD3 and EZH2.
Daures M, Idrissou M, Judes G, Rifaï K, Penault-Llorca F, Bignon YJ, Guy L, Bernard-Gallon D
Histone methylation is essential for gene expression control. Trimethylated lysine 27 of histone 3 (H3K27me3) is controlled by the balance between the activities of JMJD3 demethylase and EZH2 methyltransferase. This epigenetic mark has been shown to be deregulated in prostate cancer, and evidence shows H3K27me3 enri... |
Contrasting epigenetic states of heterochromatin in the different types of mouse pluripotent stem cells.
Tosolini M, Brochard V, Adenot P, Chebrout M, Grillo G, Navia V, Beaujean N, Francastel C, Bonnet-Garnier A, Jouneau A
Mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and epiblast stem cells (EpiSCs) represent naive and primed pluripotency states, respectively, and are maintained in vitro by specific signalling pathways. Furthermore, ESCs cultured in serum-free medium with two kinase inhibitors (2i-ESCs) are thought to be the ground naïve pl... |
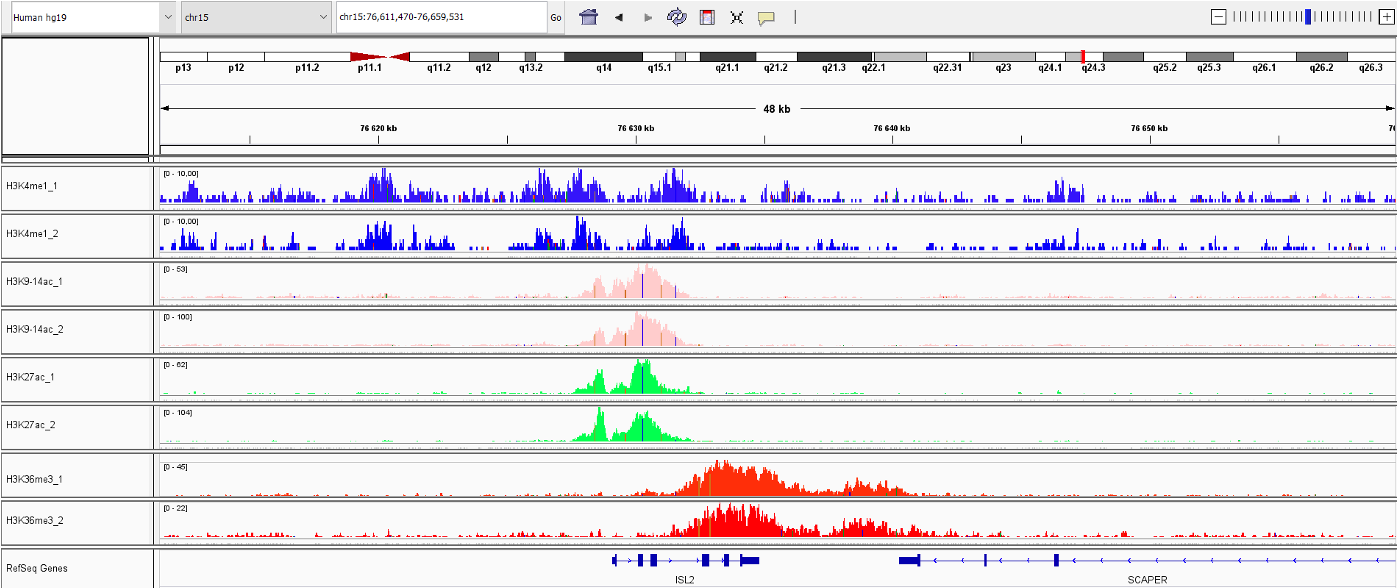
Isl1 mediates mesenchymal expansion in the developing external genitalia via regulation of Bmp4, Fgf10 and Wnt5a
Ching S.T. et al.
Genital malformations are among the most common human birth defects, and both genetic and environmental factors can contribute to these malformations. Development of the external genitalia in mammals relies on complex signaling networks, and disruption of these signaling pathways can lead to genital defects. Islet-1... |
In Situ Fixation Redefines Quiescence and Early Activation of Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells
Machado L. et al.
Summary
State of the art techniques have been developed to isolate and analyze cells from various tissues, aiming to capture their in vivo state. However, the majority of cell isolation protocols involve lengthy mechanical and enzymatic dissociation steps followed by flow cytometry, exposing cells to stres... |
The RPMI-1640 vitamin mixture promotes bovine blastocyst development in vitro and downregulates gene expression of TXNIP with epigenetic modification of associated histones
Ikeda S.et al.
Diverse environmental conditions surrounding preimplantation embryos, including available nutrients, affect their metabolism and development in both short- and long-term manner. Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) is a possible marker for preimplantation stress that is implicated in in vitro fertilization- (IVF)... |
Global analysis of H3K27me3 as an epigenetic marker in prostate cancer progression
Ngollo M. et al.
BACKGROUND:
H3K27me3 histone marks shape the inhibition of gene transcription. In prostate cancer, the deregulation of H3K27me3 marks might play a role in prostate tumor progression.
METHODS:
We investigated genome-wide H3K27me3 histone methylation profile using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and 2X400K p... |
Crebbp loss cooperates with Bcl2 over-expression to promote lymphoma in mice
Idoia García-Ramírez, Saber Tadros, Inés González-Herrero, Alberto Martín-Lorenzo, Guillermo Rodríguez-Hernández, Dalia Moore, Lucía Ruiz-Roca, Oscar Blanco, Diego Alonso-López, Javier De Las Rivas, Keenan Hartert, Romain Duval, David Klinkebiel, Martin B
CREBBP is targeted by inactivating mutations in follicular lymphoma (FL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Here, we provide evidence from transgenic mouse models that Crebbp deletion results in deficits in B-cell development and can cooperate with Bcl2 over-expression to promote B-cell lymphoma. Through tra... |
Aorta macrophage inflammatory and epigenetic changes in a murine model of obstructive sleep apnea: Potential role of CD36.
Cortese R. et al.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) affects 8-10% of the population, is characterized by chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH), and causally associates with cardiovascular morbidities. In CIH-exposed mice, closely mimicking the chronicity of human OSA, increased accumulation and proliferation of pro-inflammatory metabolic M1... |
Loss of Ezh2 synergizes with JAK2-V617F in initiating myeloproliferative neoplasms and promoting myelofibrosis
Shimizu T et al.
Myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) patients frequently show co-occurrence of JAK2-V617F and mutations in epigenetic regulator genes, including EZH2. In this study, we show that JAK2-V617F and loss of Ezh2 in hematopoietic cells contribute synergistically to the development of MPN. The MPN phenotype induced by JAK2-V6... |
Methionine-dependent histone methylation at developmentally important gene loci in mouse preimplantation embryos
Kudo M, Ikeda S, Sugimoto M, Kume S
The involvement of specific nutrients in epigenetic gene regulation is a possible mechanism underlying nutrition-directed phenotypic alteration. However, the involvement of nutrients in gene-specific epigenetic regulation remains poorly understood. Methionine has been received attention as a possible nutrient involv... |