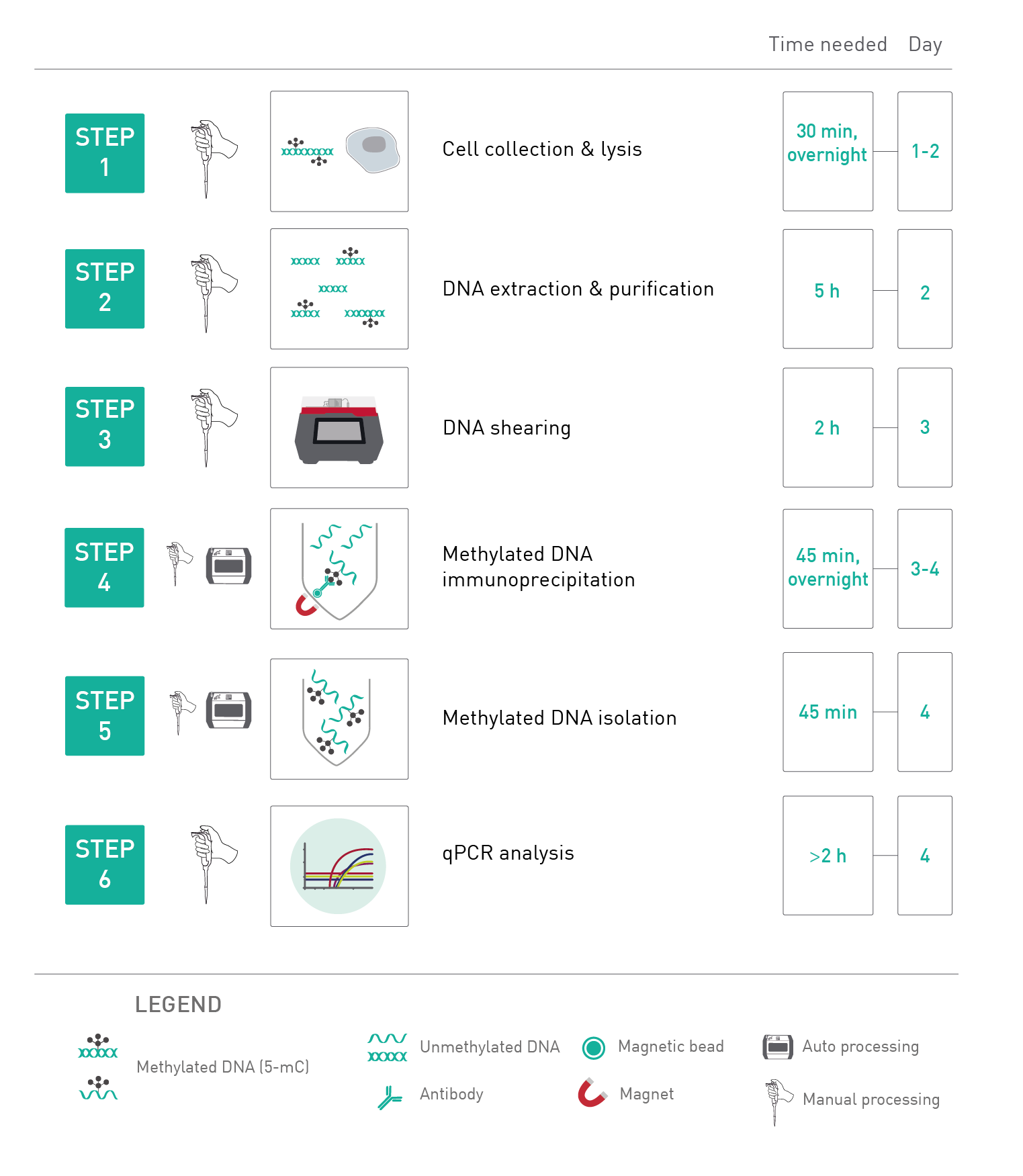
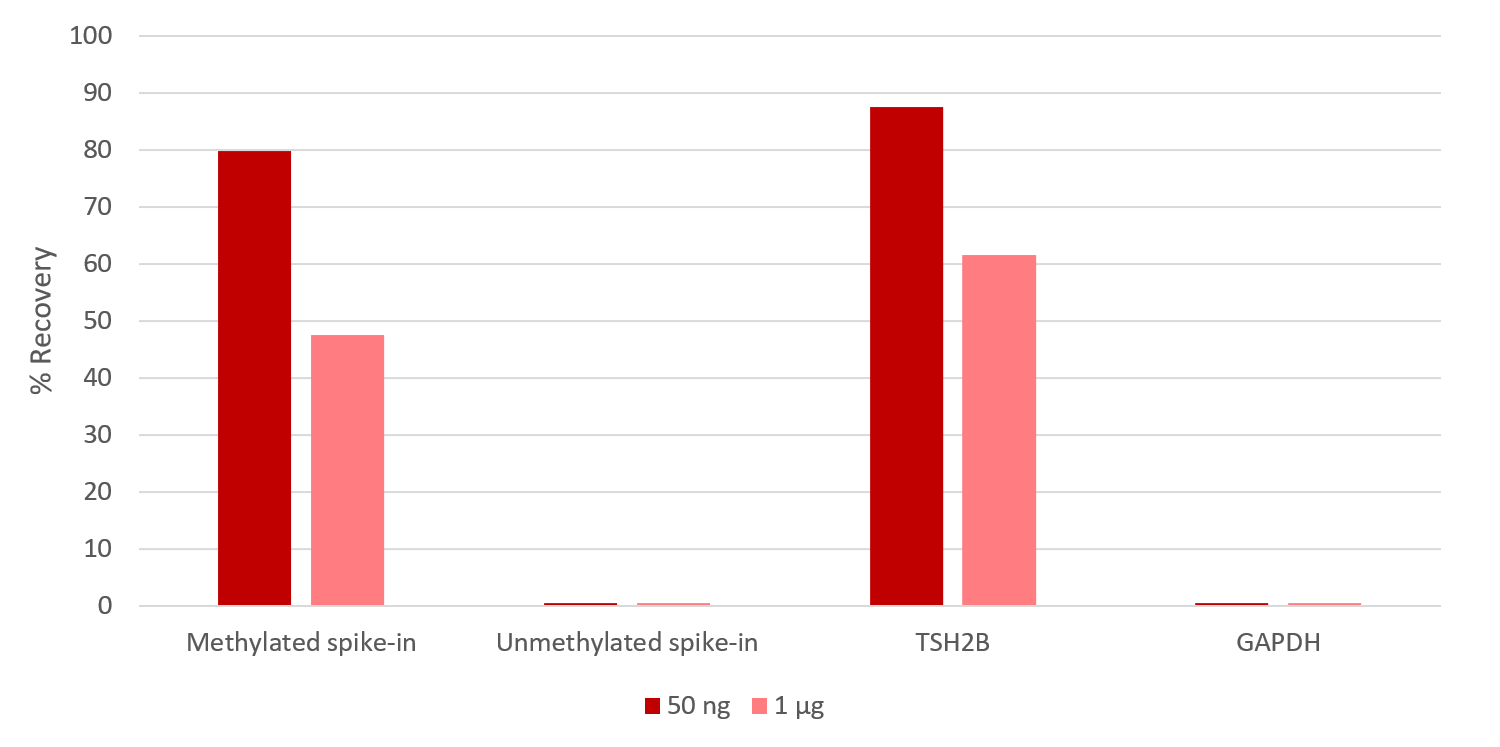
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: MagMeDIP kit (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C02010020). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
HIV Infection as an Independent Factor Accelerating Epigenetic Ageing in Men Treated with Integrase Inhibitors: A Case–Control Study
Bożejko, Mateusz et al.
Abstract
A number of published studies suggest that HIV infection accelerates epigenetic ageing. The main aim of this study was to ascertain if HIV infection is an independent factor leading to DNA hypomethylation and accelerating epigenetic ageing in men successfully treated with integrase inhibitor (INSTI)-based ... |
Cell-free DNA methylation and fragmentomics-based liquid biopsy for accurate esophageal cancer detection
Wang, Jingyun et al.
Background
Cell-free DNA is a promising source of biomarkers for early cancer detection and carries tumor-driven methylation and fragmentation features that have achieved good diagnostic efficacy across various cancers. However, there were no studies that detected both of them for esophageal cancer diagnosis.
... |
Arginine Metabolism Supports De Novo Pyrimidine Biosynthesis to Block DNA Damage and Maintain Epstein-Barr Virus Latency
White, Shaowen et al.
Incompletely understood mechanisms serve to maintain Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latency in most B-cell states, in which viral oncogene(s) are expressed but lytic antigens are repressed. Shortly after EBV’s discovery and even before it was named, early pioneers Werne and Gertrude Henle identified that restriction... |
Analog epigenetic memory revealed by targeted chromatin editing
Palacios, Sebastian et al.
Cells store information by means of chromatin modifications that persist through cell divisions and can hold gene expression silenced over generations. However, how these modifications may maintain other gene expression states has remained unclear. This study shows that chromatin modifications can maintain a wide ... |
Epigenetic responses in Borrelia-infected Ixodes scapularis ticks: Over-expression of euchromatic histone lysine methyltransferase 2 and no change in DNA methylation
MacIntosh, Grace Hadley et al.
Borrelia burgdorferi, a tick-vectored spirochete bacteria best known for causing Lyme disease, has been found to induce physiological and behavioural changes in its tick vector that can increase tick fitness and its ability to transmit the bacteria. The mechanism by which this bacterium modulates these changes r... |
Coupling Immunoprecipitation with Multiplexed Digital PCR for Cell-Free DNA Methylation Detection in Small Plasma Volumes of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer
Truong, Truong T et al.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a major global health challenge, with an increasing incidence of early-onset cases among young adults. Targeted analysis of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylation in blood has emerged as a promising minimally invasive diagnostic approach. While digital PCR (dPCR) offers high sensitivit... |
Caloric restriction prevents inheritance of polycystic ovary syndrome through oocyte-mediated DNA methylation reprogramming
Yue Liu et al.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a prevalent metabolic and reproductive endocrine disorder with strong heritability. However, the independent role of oocytes in mediating this heritability remains unclear. Utilizing in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer and surrogacy, we demonstrated that oocytes ... |
Transgenerational inheritance of diabetes susceptibility in male offspring with maternal androgen exposure
Yuqing, Zhang., et al.
Androgen exposure (AE) poses a profound health threat to women, yet its transgenerational impacts on male descendants remain unclear. Here, employing a large-scale mother-child cohort, we show that maternal hyperandrogenism predisposes sons to β-cell dysfunction. Male offspring mice with prenatal AE exhibited h... |
Histone variant H3.5 in testicular cell differentiation and its interactions with histone chaperones
Patrick Philipp Weil et al.
Testicular cell differentiation is a highly regulated process, essential for male reproductive health. The histone variant H3.5 is apparently a critical player in this intricate orchestra of cell types, but its regulation and function remains poorly understood. To elucidate its role, we fractionized testicular cells... |
Differential methylation of circulating free DNA assessed through cfMeDiP as a new tool for breast cancer diagnosis and detection of BRCA1/2 mutation
Piera Grisolia et al.
Background
Recent studies have highlighted the importance of the cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylation profile in detecting breast cancer (BC) and its different subtypes. We investigated whether plasma cfDNA methylation, using cell-free Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation and High-Throughput Sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq), ma... |
Prediction of brain metastasis development with DNA methylation signatures
Jeffrey A. Zuccato et al.
Brain metastases (BMs) are the most common and among the deadliest brain tumors. Currently, there are no reliable predictors of BM development from primary cancer, which limits early intervention. Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most common BM source and here we obtained 402 tumor and plasma samples from a large c... |
Association between TNF-α, cortisol levels, and exposure to PM10 and PM2.5: a pilot study
Dolcini J. et al.
Purpose
The most harmful atmospheric pollutant for human health is particulate matter (PM). We analyzed the correlation between short-term lag exposure to PM10 and PM2.5, salivary cortisol and TNF-α level, and methylation levels of the TNF-α promoter.
Methods
A pilot study including 20 subjects. Eight... |
Epigenomic signatures of sarcomatoid differentiation to guide the treatment of renal cell carcinoma
Talal El Zarif et al.
Renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation (sRCC) is associated with poor survival and a heightened response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Two major barriers to improving outcomes for sRCC are the limited understanding of its gene regulatory programs and the low diagnostic yield of tumor biopsie... |
Detecting small cell transformation in patients with advanced EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma through epigenomic cfDNA profiling
Talal El Zarif et al.
Purpose: Histologic transformation to small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a mechanism of treatment resistance in patients with advanced oncogene-driven lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) that currently requires histologic review for diagnosis. Herein, we sought to develop an epigenomic cell-free (cf)DNA-based approach to non-i... |
Prostate cancer detection through unbiased capture of methylated cell-free DNA
Ermira Lleshi et al.
Prostate cancer screening using prostate-specific antigen (PSA) has been shown to reduce mortality but with substantial overdiagnosis, leading to unnecessary biopsies. The identification of a highly specific biomarker using liquid biopsies, represents an unmet need in the diagnostic pathway for prostate cancer. In t... |
A Pre-Leukemic DNA Methylation Signature in Healthy Individuals at Higher Risk for Developing Myeloid Malignancy
Zhentang Lao et al.
Purpose: DNA methylation alterations are widespread in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), some of which appear to have evolved independently of somatic mutations in epigenetic regulators. While the presence of somatic mutations in peripheral blood can predict the risk of development of ... |
Neurofibromin 1 controls metabolic balance and Notch-dependent quiescence of murine juvenile myogenic progenitors
Wei X. et al.
Patients affected by neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) frequently show muscle weakness with unknown etiology. Here we show that, in mice, Neurofibromin 1 (Nf1) is not required in muscle fibers, but specifically in early postnatal myogenic progenitors (MPs), where Nf1 loss led to cell cycle exit and differenti... |
Promoter DNA methylation patterns in oral, laryngeal and oropharyngeal anatomical regions are associated with tumor differentiation, nodal involvement and survival
Rivera‑Peña B. et al.
Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) can be used as head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic targets in precision medicine workflows. DNA from 21 HNSCC and 10 healthy oral tissue samples was hybridized to a genome‑wide tiling array to identify DMRs in a discovery cohor... |
Cerebrospinal fluid methylome-based liquid biopsies for accuratemalignant brain neoplasm classification.
Zuccato Jeffrey A et al.
BACKGROUND: Resolving the differential diagnosis between brain metastases (BM), glioblastomas (GBM), and central nervous system lymphomas (CNSL) is an important dilemma for the clinical management of the main three intra-axial brain tumor types. Currently, treatment decisions require invasive diagnostic surgical bio... |
Transgenerational endocrine disruptor effects of cadmium in zebrafish andcontribution of standing epigenetic variation to adaptation.
Pierron F. et al.
Evidence has emerged that environmentally-induced epigenetic changes can have long-lasting effects on gene transcription across generations. These recent findings highlight the need to investigate the transgenerational impacts of pollutants to assess their long term effects on populations. In this study, we investig... |
Differentiation block in acute myeloid leukemia regulated by intronicsequences of FTO
Camera F. et al.
Iroquois transcription factor gene IRX3 is highly expressed in 20–30\% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and contributes to the pathognomonic differentiation block. Intron 8 FTO sequences ∼220kB downstream of IRX3 exhibit histone acetylation, DNA methylation, and contacts with th... |
Epigenetic modifier alpha-ketoglutarate modulates aberrant gene bodymethylation and hydroxymethylation marks in diabetic heart.
Dhat R. et al.
BACKGROUND: Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a leading cause of death in diabetic patients. Hyperglycemic myocardial microenvironment significantly alters chromatin architecture and the transcriptome, resulting in aberrant activation of signaling pathways in a diabetic heart. Epigenetic marks play vital roles in tra... |
Pre-diagnosis plasma cell-free DNA methylome profiling up to sevenyears prior to clinical detection reveals early signatures of breast cancer
Cheng N. et al.
Profiling of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has been well demonstrated to be a potential non-invasive screening tool for early cancer detection. However, limited studies have investigated the detectability of cfDNA methylation markers that are predictive of cancers in asymptomatic individuals. We performed cfDNA methylation ... |
Cell-free multi-omics analysis reveals tumor status-informativesignatures in gastrointestinal cancer patients’ plasma
Tao Y. et al.
During cancer development, host’s tumorigenesis and immune signals are released to and informed by circulating molecules, like cell-free DNA (cfDNA) and RNA (cfRNA) in blood. However, these two kinds of molecules are still not systematically compared in gastrointestinal cancer. Here, we profiled 4 types of cel... |
Methylation and expression of glucocorticoid receptor exon-1 variants andFKBP5 in teenage suicide-completers.
Rizavi H. et al.
A dysregulated hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis has repeatedly been demonstrated to play a fundamental role in psychiatric disorders and suicide, yet the mechanisms underlying this dysregulation are not clear. Decreased expression of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) gene, which is also susceptible to epigen... |
Bridging biological cfDNA features and machine learning approaches.
Moser T. et al.
Liquid biopsies (LBs), particularly using circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), are expected to revolutionize precision oncology and blood-based cancer screening. Recent technological improvements, in combination with the ever-growing understanding of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) biology, are enabling the detection of tumor-speci... |
Gene body DNA hydroxymethylation restricts the magnitude oftranscriptional changes during aging.
Occean J. R. et al.
DNA hydroxymethylation (5hmC) is the most abundant oxidative derivative of DNA methylation (5mC) and is typically enriched at enhancers and gene bodies of transcriptionally active and tissue-specific genes. Although aberrant genomic 5hmC has been implicated in many age-related diseases, the functional role of the mo... |
Neonatal inflammation increases hippocampal KCC2 expression throughmethylation-mediated TGF-β1 downregulation leading to impairedhippocampal cognitive function and synaptic plasticity in adult mice.
Rong J. et al.
The mechanisms by which neonatal inflammation leads to cognitive deficits in adulthood remain poorly understood. Inhibitory GABAergic synaptic transmission plays a vital role in controlling learning, memory and synaptic plasticity. Since early-life inflammation has been reported to adversely affect the GABAergic syn... |
Impact of FecB Mutation on Ovarian DNA Methylome inSmall-Tail Han Sheep.
Xie L. et al.
UNLABELLED: Booroola fecundity (FecB) gene, a mutant of bone morphogenetic protein 1B (BMPR-1B) that was discovered in Booroola Merino, was the first prolificacy gene identified in sheep related to increased ovulation rate and litter size. The mechanism of FecB impact on reproduction is unclear. METHODS: In this stu... |
Consistent DNA Hypomethylations in Prostate Cancer.
Araúzo-Bravo M.J. et al.
With approximately 1.4 million men annually diagnosed with prostate cancer (PCa) worldwide, PCa remains a dreaded threat to life and source of devastating morbidity. In recent decades, a significant decrease in age-specific PCa mortality has been achieved by increasing prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening and i... |
Cell-free DNA methylation-defined prognostic subgroups in small celllung cancer identified by leukocyte methylation subtraction
Ul Haq Sami et al.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) methylome is understudied. Here, we comprehensively profile SCLC using cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq). Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from plasma of 74 SCLC patients pre-treatment and from 20 non-cancer participants, genomic DNA (gDNA) from peri... |
The cell-free DNA methylome captures distinctions between localized andmetastatic prostate tumors.
Chen Sujun et al.
Metastatic prostate cancer remains a major clinical challenge and metastatic lesions are highly heterogeneous and difficult to biopsy. Liquid biopsy provides opportunities to gain insights into the underlying biology. Here, using the highly sensitive enrichment-based sequencing technology, we provide analysis of 60 ... |
A SOX2-engineered epigenetic silencer factor represses the glioblastomagenetic program and restrains tumor development.
Benedetti V. et al.
Current therapies remain unsatisfactory in preventing the recurrence of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), which leads to poor patient survival. By rational engineering of the transcription factor SOX2, a key promoter of GBM malignancy, together with the Kruppel-associated box and DNA methyltransferase3A/L catalytic dom... |
mTORC1 is required for epigenetic silencing during β-cell functionalmaturation.
Ni Qicheng et al.
OBJECTIVE: The mechanistic target of rapamycin comple×1 (mTORC1) is a key molecule that links nutrients, hormones, and growth factors to cell growth/function. Our previous studies have shown that mTORC1 is required for β-cell functional maturation and identity maintenance; however, the underlying mechanis... |
Detection of ovarian cancer using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.
Lu Huaiwu et al.
BACKGROUND: Ovarian cancer (OC) is a highly lethal gynecologic cancer, and it is hard to diagnose at an early stage. Clinically, there are no ovarian cancer-specific markers for early detection. Here, we demonstrate the use of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylomes to detect ovarian cancer, especially the early-stage OC. ... |
A genome-wide screen reveals new regulators of the 2-cell-like cell state
Defossez Pierre-Antoine et al.
In mammals, only the zygote and blastomeres of the early embryo are fully totipotent. This totipotency is mirrored in vitro by mouse "2-cell-like cells" (2CLCs), which appear at low frequency in cultures of Embryonic Stem cells (ESCs). Because totipotency is incompletely understood, we carried out a genomewide CRISP... |
Heat stress during grain filling regulates seed germination throughalterations of DNA methylation in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).
Sakai Yuki et al.
KEY MESSAGE: Alterations in DNA methylation levels of ROS, GA and ABA related gene promoters cause transcriptional changes upon imbibition to induce seed germination in barley seeds exposed to heat stress during grain filling. Environmental changes, especially changes in temperature, during seed development affect g... |
Hexokinase 2 is a transcriptional target and a positive modulator ofAHR signalling.
Watzky M. et al.
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) regulates the expression of numerous genes in response to activation by agonists including xenobiotics. Although it is well appreciated that environmental signals and cell intrinsic features may modulate this transcriptional response, how it is mechanistically achieved remains poo... |
Corticosterone induces discrete epigenetic signatures in the dorsal andventral hippocampus that depend upon sex and genotype: focus on methylatedNr3c1 gene.
Caradonna S. G. et al.
The genomic effects of circulating glucocorticoids are particularly relevant in cortico-limbic structures, which express a high concentration of steroid hormone receptors. To date, no studies have investigated genomic differences in hippocampal subregions, namely the dorsal (dHPC) and ventral (vHPC) hippocampus, in ... |
Methionine Metabolism Controls the B-cell EBV Epigenome andViral Latency
Guo R. et al.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) subverts host epigenetic pathways to switch between viral latency programs, colonize the B-cell compartment and reactivate. Within memory B-cells, the reservoir for lifelong infection, EBV genomic DNA and histone methylation marks restrict gene expression. But, this epigenetic strategy also ... |
Integrating SNPs-based genetic risk factor with blood epigenomicresponse of differentially arsenic-exposed rural subjects revealsdisease-associated signaling pathways.
Rehman Muhammad Yasir Abdur et al.
Arsenic (As) contamination in groundwater is responsible for numerous adverse health outcomes among millions of people. Epigenetic alterations are among the most widely studied mechanisms of As toxicity. To understand how As exposure alters gene expression through epigenetic modifications, a systematic genome-wide s... |
Stella regulates the Development of Female Germline Stem Cells byModulating Chromatin Structure and DNA Methylation.
Hou Changliang et al.
Female germline stem cells (FGSCs) have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into oocytes. , encoded by a maternal effect gene, plays an important role in oogenesis and early embryonic development. However, its function in FGSCs remains unclear. In this study, we showed that CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of p... |
Examining age-dependent DNA methylation patterns and gene expression inthe male and female mouse hippocampus.
Chinn Carlene A et al.
DNA methylation is a well-characterized epigenetic modification involved in numerous molecular and cellular functions. Methylation patterns have also been associated with aging mechanisms. However, how DNA methylation patterns change within key brain regions involved in memory formation in an age- and sex-specific m... |
Therapy-induced DNA methylation inactivates MCT1 and renders tumor cells vulnerable to MCT4 inhibition
Catherine Vander Linden, Cyril Corbet, Estelle Bastien, Ruben Martherus, Céline Guilbaud, Laurenne Petit, Loris Wauthier, Axelle Loriot, Charles De Smet, Olivier Feron
Metabolic plasticity in cancer cells makes use of metabolism-targeting agents very challenging. Drug-induced metabolic rewiring may, however, uncover vulnerabilities that can be exploited. We report that resistance to glycolysis inhibitor 3-bromopyruvate (3-BrPA) arises from DNA methylation in treated cancer cells a... |
Epigenetic Plasticity Enables CNS-Trafficking of EBV-infectedB Lymphocytes
Soldan S. S. et al.
Subpopulations of B-lymphocytes traffic to different sites and organs to provide diverse and tissue-specific functions. Here, we provide evidence that epigenetic differences confer a neuroinvasive phenotype. An EBV+ B cell lymphoma cell line (M14) with low frequency trafficking to the CNS was neuroadapted to generat... |
Dnmt1 has de novo activity targeted to transposable elements
Haggerty C. et al.
DNA methylation plays a critical role during development, particularly in repressing retrotransposons. The mammalian methylation landscape is dependent on the combined activities of the canonical maintenance enzyme Dnmt1 and the de novo Dnmts, 3a and 3b. Here, we demonstrate that Dnmt1 displays de novo methylation a... |
Alterations of DNA Methylation Caused by Cold Plasma Treatment Restore Delayed Germination of Heat-Stressed Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Seeds
Suriyasak, C. et al.
In rice (Oryza sativa L.), seeds exposed to heat stress during grain filling exhibit delayed germination because of DNA methylation levels at promoters of abscisic acid (ABA, a germination-inhibiting hormone) catabolism genes and α-amylase (starchhydrolyzing enzyme) genes, affecting their expression levels. Co... |
Prenatal Stress Leads to the Altered Maturation of Corticostriatal SynapticPlasticity and Related Behavioral Impairments Through EpigeneticModifications of Dopamine D2 Receptor in Mice.
Li, Yingchun and Rong, Jing and Zhong, Haiquan and Liang, Min and Zhu,Chunting and Chang, Fei and Zhou, Rong
Prenatal stress (PRS) had a long-term adverse effect on motor behaviors. Corticostriatal synaptic plasticity, a cellular basis for motor controlling, has been proven to participate in the pathogenesis of many behavior disorders. Based on the reports about the involvement of epigenetic DNA alterations in PRS-induced ... |
Comparative genome-wide methylation analysis of longissimus dorsi musclesin Yorkshire and Wannanhua pigs.
Li, X-J et al.
DNA methylation was one of the earliest discovered epigenetic modifications in vertebrates, and is an important epigenetic mechanism involved in the expression of genes in many biological processes, including muscle growth and development. Its effects on economically important traits are evidenced in reported differ... |
Mechanism of delayed seed germination caused by high temperature duringgrain filling in rice (Oryza sativa L.).
Suriyasak, Chetphilin and Oyama, Yui and Ishida, Toshiaki and Mashiguchi,Kiyoshi and Yamaguchi, Shinjiro and Hamaoka, Norimitsu and Iwaya-Inoue,Mari and Ishibashi, Yushi
High temperature during grain filling considerably reduces yield and quality in rice (Oryza sativa L.); however, how high temperature affects seed germination of the next generation is not yet well understood. Here, we report that seeds from plants exposed to high temperature during the grain filling stage germinate... |
Network integration and modelling of dynamic drug responses at multi-omicslevels.
Selevsek, Nathalie and Caiment, Florian and Nudischer, Ramona and Gmuender,Hans and Agarkova, Irina and Atkinson, Francis L and Bachmann, Ivo andBaier, Vanessa and Barel, Gal and Bauer, Chris and Boerno, Stefan and Bosc,Nicolas and Clayton, Olivia and
Uncovering cellular responses from heterogeneous genomic data is crucial for molecular medicine in particular for drug safety. This can be realized by integrating the molecular activities in networks of interacting proteins. As proof-of-concept we challenge network modeling with time-resolved proteome, transcriptome... |
Frataxin gene editing rescues Friedreich's ataxia pathology in dorsal rootganglia organoid-derived sensory neurons.
Mazzara, PG and Muggeo, S and Luoni, M and Massimino, L and Zaghi, M andValverde, PT and Brusco, S and Marzi, MJ and Palma, C and Colasante, Gand Iannielli, A and Paulis, M and Cordiglieri, C and Giannelli, SG andPodini, P and Gellera, C and Ta
Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA) is an autosomal-recessive neurodegenerative and cardiac disorder which occurs when transcription of the FXN gene is silenced due to an excessive expansion of GAA repeats into its first intron. Herein, we generate dorsal root ganglia organoids (DRG organoids) by in vitro differentiation of ... |
Integrated analysis of DNA methylation profile of HLA-G gene andimaging in coronary heart disease: Pilot study.
Schiano, C and Benincasa, G and Infante, T and Franzese, M and Castaldo, Rand Fiorito, C and Mansueto, G and Grimaldi, V and Della, Valle G andFatone, G and Soricelli, A and Nicoletti, GF and Ruocco, A and Mauro, Cand Salvatore, M and Napoli, C
AIMS: Immune endothelial inflammation, underlying coronary heart disease (CHD) related phenotypes, could provide new insight into the pathobiology of the disease. We investigated DNA methylation level of the unique CpG island of HLA-G gene in CHD patients and evaluated the correlation with cardiac computed tomograph... |
Comparative DNA methylome analysis of estrus ewes reveals the complexregulatory pathways of sheep fecundity.
Miao, X and Luo, Q and Xie, L and Zhao, H and Qin, X
BACKGROUND/AIMS: Sheep are important livestock with variant ovulation rate and fertility. Dorset sheep is a typical breed with low prolificacy, whereas Small Tail Han sheep with FecB mutation (HanBB) have hyperprolificacy. Our previous studies have revealed the gene expression difference between the ovaries from Dor... |
Methylation in pericytes after acute injury promotes chronic kidneydisease.
Chou, YH and Pan, SY and Shao, YH and Shih, HM and Wei, SY andLai, CF and Chiang, WC and Schrimpf, C and Yang, KC and Lai, LC andChen, YM and Chu, TS and Lin, SL
The origin and fate of renal myofibroblasts is not clear after acute kidney injury (AKI). Here, we demonstrate that myofibroblasts were activated from quiescent pericytes (qPericytes) and the cell numbers increased after ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced AKI (IRI-AKI). Myofibroblasts underwent apoptosis during ren... |
Integrated epigenetic biomarkers in circulating cell-free DNA as a robust classifier for pancreatic cancer.
Cao F, Wei A, Hu X, He Y, Zhang J, Xia L, Tu K, Yuan J, Guo Z, Liu H, Xie D, Li A
BACKGROUND: The high lethal rate of pancreatic cancer is partly due to a lack of efficient biomarkers for screening and early diagnosis. We attempted to develop effective and noninvasive methods using 5-methylcytosine (5mC) and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) markers from circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) for the det... |
Detection of renal cell carcinoma using plasma and urine cell-free DNA methylomes.
Nuzzo PV, Berchuck JE, Korthauer K, Spisak S, Nassar AH, Abou Alaiwi S, Chakravarthy A, Shen SY, Bakouny Z, Boccardo F, Steinharter J, Bouchard G, Curran CR, Pan W, Baca SC, Seo JH, Lee GM, Michaelson MD, Chang SL, Waikar SS, Sonpavde G, Irizarry RA, Pome
Improving early cancer detection has the potential to substantially reduce cancer-related mortality. Cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq) is a highly sensitive assay capable of detecting early-stage tumors. We report accurate classification of patients across all ... |
Detection and discrimination of intracranial tumors using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.
Nassiri F, Chakravarthy A, Feng S, Shen SY, Nejad R, Zuccato JA, Voisin MR, Patil V, Horbinski C, Aldape K, Zadeh G, De Carvalho DD
Definitive diagnosis of intracranial tumors relies on tissue specimens obtained by invasive surgery. Noninvasive diagnostic approaches provide an opportunity to avoid surgery and mitigate unnecessary risk to patients. In the present study, we show that DNA-methylation profiles from plasma reveal highly specific sign... |
DNA methylation enzymes and PRC1 restrict B-cell Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein expression.
Guo R, Zhang Y, Teng M, Jiang C, Schineller M, Zhao B, Doench JG, O'Reilly RJ, Cesarman E, Giulino-Roth L, Gewurz BE
To accomplish the remarkable task of lifelong infection, the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) switches between four viral genome latency and lytic programmes to navigate the B-cell compartment and evade immune responses. The transforming programme, consisting of highly immunogenic EBV nuclear antigen (EBNA) and latent membr... |
TET-Mediated Hypermethylation Primes SDH-Deficient Cells for HIF2α-Driven Mesenchymal Transition.
Morin A, Goncalves J, Moog S, Castro-Vega LJ, Job S, Buffet A, Fontenille MJ, Woszczyk J, Gimenez-Roqueplo AP, Letouzé E, Favier J
Loss-of-function mutations in the SDHB subunit of succinate dehydrogenase predispose patients to aggressive tumors characterized by pseudohypoxic and hypermethylator phenotypes. The mechanisms leading to DNA hypermethylation and its contribution to SDH-deficient cancers remain undemonstrated. We examine th... |
Genome-wide DNA Methylation Analysis of Mantle Edge and Mantle Central from Pearl Oyster Pinctada fucata martensii.
Zhang J, Luo S, Gu Z, Deng Y, Jiao Y
DNA methylation is a type of epigenetic modification that alters gene expression without changing the DNA sequence and mediates some cases of phenotypic plasticity. In this study, we identified six DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) genes and two methyl-CpG binding domain protein2 (MBD2) gene from Pinctada fucat... |
Preterm birth is associated with epigenetic programming of transgenerational hypertension in mice.
Dumeige L, Nehlich M, Viengchareun S, Perrot J, Pussard E, Lombès M, Martinerie L
Renal and cardiovascular complications of prematurity are well established, notably the development of hypertension in adulthood. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. Our objective was to investigate the impact of prematurity on the ontogenesis of renal corticosteroid pathways, to e... |
Alteration in global DNA methylation status following preconditioning injury influences axon growth competence of the sensory neurons.
Shin HY, Kim K, Kwon MJ, Oh YJ, Kim EH, Kim HS, Hong CP, Lee JH, Lee K, Kim BG
Preconditioning peripheral nerve injury primes the sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) to acquire axon regeneration competence. Transcription of a large set of regeneration-associated-genes (RAGs) contributes to the enhanced intrinsic axonal regeneration capacity. However, the mechanism underlying the ... |
Lithium treatment reverses irradiation-induced changes in rodent neural progenitors and rescues cognition.
Zanni G, Goto S, Fragopoulou AF, Gaudenzi G, Naidoo V, Di Martino E, Levy G, Dominguez CA, Dethlefsen O, Cedazo-Minguez A, Merino-Serrais P, Stamatakis A, Hermanson O, Blomgren K
Cranial radiotherapy in children has detrimental effects on cognition, mood, and social competence in young cancer survivors. Treatments harnessing hippocampal neurogenesis are currently of great relevance in this context. Lithium, a well-known mood stabilizer, has both neuroprotective, pro-neurogenic as well as ant... |
Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA.
Shen SY, Burgener JM, Bratman SV, De Carvalho DD
Circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) comprises small DNA fragments derived from normal and tumor tissue that are released into the bloodstream. Recently, methylation profiling of cfDNA as a liquid biopsy tool has been gaining prominence due to the presence of tissue-specific markers in cfDNA. We have previously reporte... |
Single-base methylome profiling of the giant kelp Saccharina japonica reveals significant differences in DNA methylation to microalgae and plants.
Fan X, Han W, Teng L, Jiang P, Zhang X, Xu D, Li C, Pellegrini M, Wu C, Wang Y, Kaczurowski MJS, Lin X, Tirichine L, Mock T, Ye N
Brown algae have convergently evolved plant-like body plans and reproductive cycles, which in plants are controlled by differential DNA methylation. Here we provide the first single-base methylome profiles of haploid gametophytes and diploid sporophytes of a multicellular alga. Although only c. 1.4% of cytosines in ... |
Genome-wide methylation in alcohol use disorder subjects: implications for an epigenetic regulation of the cortico-limbic glucocorticoid receptors (NR3C1).
Gatta E, Grayson DR, Auta J, Saudagar V, Dong E, Chen Y, Krishnan HR, Drnevich J, Pandey SC, Guidotti A
Environmental factors, including substance abuse and stress, cause long-lasting changes in the regulation of gene expression in the brain via epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation. We examined genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in the prefrontal cortex (PFC, BA10) of 25 pairs of control and individuals wi... |
DNA methylation of the Tacr2 gene in a CUMS model of depression.
Xiang D, Xiao J, Fu L, Yao L, Wan Q, Xiao L, Zhu F, Wang G, Liu Z
Tacr2, the gene encoding the NK2 receptor, belongs to G protein-coupled receptors. Accumulating evidence has indicated that the tachykinin receptors may contribute to the pathophysiology of depression. During the last decade, some studies have shown that Tacr2 activation is involved in the modulation of emotional pr... |
Epigenetic Alterations in Juvenile Spondyloarthritis Patients: a Preliminary Study of Selected Genes Promoter Methylation and Silencing
Lamot Lovro, Blažeković Antonela, Jerčić Kristina Gotovac, Ivković Tina Catela, Vidović Mandica, Lamot Mirta, Kapitanović Sanja, Borovečki Fran, Harjaček Miroslav
Juvenile spondyloarthritis (jSpA) is a complex disease with both genetic and environmental factors contributing to etiology. Multiple studies have shown that epigenetic mechanisms could link the environment and gene expression and thus provide a potential explanation for external contribution in the pathogenesis of ... |
The methylation pattern of DNA and complex correlations with gene expressions during TuMV infection in Chinese cabbage
J. YU , L.-W. GAO , Y. YANG , C. LIU , R.-J. ZHANG , F.-F. SUN , L.-X. SONG , D. XIAO , T.-K. LIU , X.-L. HOU , and C.-W. ZHANG
Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) is one of the most important economic crops. However, its yield and quality can be severely threatened by Turnip mosaic virus (TuMV). Emerging evidence indicates that epigenetic mechanisms, especially DNA methylation, play an important role in regulating gene expres... |
Epigenetic control of the angiotensin-converting enzyme in endothelial cells during inflammation.
Mudersbach T, Siuda D, Kohlstedt K, Fleming I
The angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) plays a central role in the renin-angiotensin system, which is involved in the regulation of blood pressure. Alterations in ACE expression or activity are associated with various pathological phenotypes, particularly cardiovascular diseases. In human endothelial cells, ACE was... |
Genome-wide DNA methylation profiles in Tibetan and Yorkshire pigs under high-altitude hypoxia.
Zhang B, Ban D, Gou X, Zhang Y, Yang L, Chamba Y, Zhang H
Background: Tibetan pigs, which inhabit the Tibetan Plateau, exhibit distinct phenotypic and physiological characteristics from those of lowland pigs and have adapted well to the extreme conditions at high altitude. However, the genetic and epigenetic mechanisms of hypoxic adaptation in animals remain unclear. Metho... |
Assessment and site-specific manipulation of DNA (hydroxy-)methylation during mouse corticogenesis.
Noack F, Pataskar A, Schneider M, Buchholz F, Tiwari VK, Calegari F
Dynamic changes in DNA (hydroxy-)methylation are fundamental for stem cell differentiation. However, the signature of these epigenetic marks in specific cell types during corticogenesis is unknown. Moreover, site-specific manipulation of cytosine modifications is needed to reveal the significance and function of the... |
DMSO induces drastic changes in human cellular processes and epigenetic landscape in vitro.
Verheijen M, Lienhard M, Schrooders Y, Clayton O, Nudischer R, Boerno S, Timmermann B, Selevsek N, Schlapbach R, Gmuender H, Gotta S, Geraedts J, Herwig R, Kleinjans J, Caiment F
Though clinical trials for medical applications of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) reported toxicity in the 1960s, later, the FDA classified DMSO in the safest solvent category. DMSO became widely used in many biomedical fields and biological effects were overlooked. Meanwhile, biomedical science has evolved towards sensi... |
Evidence of association of circulating epigenetic-sensitive biomarkers with suspected coronary heart disease evaluated by Cardiac Computed Tomography.
Infante T, Forte E, Schiano C, Punzo B, Cademartiri F, Cavaliere C, Salvatore M, Napoli C
Circulating biomarkers available in clinical practice do not allow to stratify patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) prior the onset of a clinically relevant event. We evaluated the methylation status of specific genomic segments and gene expression in peripheral blood of patients undergoing Cardiac Computed To... |
LncRNA Dnmt3aos regulates Dnmt3a expression leading to aberrant DNA methylation in macrophage polarization
Xueqin Li, Yingying Zhang, Mengying Zhang, Xiang Kong, Hui Yang, Min Zhong, Weiya Pei, Yang Xu, Xiaolong Zhu, Tianbing Chen, Jingjing Ye, and Kun
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play key roles in various biological processes. However, the roles of lncRNAs in macrophage polarization remain largely unexplored. In this study, thousands of lncRNAs were identified that are differentially expressed in distinct polarized bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). Among... |
Global distribution of DNA hydroxymethylation and DNA methylation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Wernig-Zorc S, Yadav MP, Kopparapu PK, Bemark M, Kristjansdottir HL, Andersson PO, Kanduri C, Kanduri M
BACKGROUND: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has been a good model system to understand the functional role of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in cancer progression. More recently, an oxidized form of 5-mC, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) has gained lot of attention as a regulatory epigenetic modification with prognostic ... |
Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.
Shen SY, Singhania R, Fehringer G, Chakravarthy A, Roehrl MHA, Chadwick D, Zuzarte PC, Borgida A, Wang TT, Li T, Kis O, Zhao Z, Spreafico A, Medina TDS, Wang Y, Roulois D, Ettayebi I, Chen Z, Chow S, Murphy T, Arruda A, O'Kane GM, Liu J, Mansour M, McPher
The use of liquid biopsies for cancer detection and management is rapidly gaining prominence. Current methods for the detection of circulating tumour DNA involve sequencing somatic mutations using cell-free DNA, but the sensitivity of these methods may be low among patients with early-stage cancer given the limited ... |
Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation to identify genes and pathways associated with male sterility in soybean
Han Shaohuai, Li Yanwei, Li Jiajia, Zhang Hao, Ding Xianlong, He Tingting, Gai Junyi, Yang Shouping
DNA methylation is an epigenetic modification, which is important for gene expression regulation. Although genome-wide DNA methylation studies have been reported in several plant species, the difference in the methylation pattern between the cytoplasmic male sterile (CMS) line and its maintainer in soybean remains u... |
Folic acid supplementation alters the DNA methylation profile and improves insulin resistance in high-fat-diet-fed mice.
Li W, Tang R, Ma F, Ouyang S, Liu Z, Wu J
Folic acid (FA) supplementation may protect from obesity and insulin resistance, the effects and mechanism of FA on chronic high-fat-diet-induced obesity-related metabolic disorders are not well elucidated. We adopted a genome-wide approach to directly examine whether FA supplementation affects the DNA methylation p... |
Embryonic germ cell extracts erase imprinted genes and improve the efficiency of induced pluripotent stem cells.
Hu J, Zhao Q, Feng Y, Li N, Gu Y, Sun R, Duan L, Wu Y, Shan Z, Lei L
Patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have the potential to be useful in the treatment of human diseases. While prior studies have reported multiple methods to generate iPSCs, DNA methylation continues to limit the totipotency and reprogramming efficiency of iPSCs. Here, we first show the competenc... |
Copper induces expression and methylation changes of early development genes in Crassostrea gigas embryos.
Sussarellu R, Lebreton M, Rouxel J, Akcha F, Rivière G
Copper contamination is widespread along coastal areas and exerts adverse effects on marine organisms such as mollusks. In the Pacific oyster, copper induces severe developmental abnormalities during early life stages; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms are largely unknown. This study aims to better unders... |
Aberrant methylated key genes of methyl group metabolism within the molecular etiology of urothelial carcinogenesis.
Erichsen L, Ghanjati F, Beermann A, Poyet C, Hermanns T, Schulz WA, Seifert HH, Wild PJ, Buser L, Kröning A, Braunstein S, Anlauf M, Jankowiak S, Hassan M, Bendhack ML, Araúzo-Bravo MJ, Santourlidis S
Urothelial carcinoma (UC), the most common cancer of the urinary bladder causes severe morbidity and mortality, e.g. about 40.000 deaths in the EU annually, and incurs considerable costs for the health system due to the need for prolonged treatments and long-term monitoring. Extensive aberrant DNA methylation ... |
Integrative omics data analyses of repeated dose toxicity of valproic acid in vitro reveal new mechanisms of steatosis induction
van Breda S.G.J. et al.
Valproic acid (VPA) is a very potent anti-cancer and neuro-protective drug probably by its HDAC inhibiting properties, which may cause steatosis in the liver. The present study investigates the effect of repetitive VPA treatment of primary human hepatocytes (PHH) on whole genome gene expression-, DNA methylation-, a... |
Copper induces expression and methylation changes of early development genes in Crassostrea gigas embryos
Rossana Sussarellu, Morgane Lebreton, Julien Rouxel, Farida Akcha, Guillaume Rivière
Copper contamination is widespread along coastal areas and exerts adverse effects on marine organisms such as mollusks. In the Pacific oyster, copper induces severe developmental abnormalities during early life stages; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms are largely unknown. This study aims to better unders... |
Genome-wide analysis of day/night DNA methylation differences in Populus nigra.
Ding C.J. et al.
DNA methylation is an important mechanism of epigenetic modification. Methylation changes during stress responses and developmental processes have been well studied; however, their role in plant adaptation to the day/night cycle is poorly understood. In this study, we detected global methylation patterns in leaves o... |
Obligatory and facilitative allelic variation in the DNA methylome within common disease-associated loci
Bell C.G. et al.
Integrating epigenetic data with genome-wide association study (GWAS) results can reveal disease mechanisms. The genome sequence itself also shapes the epigenome, with CpG density and transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) strongly encoding the DNA methylome. Therefore, genetic polymorphism impacts on ... |
Epigenetic alterations in TRAMP mice: epigenome DNA methylation profiling using MeDIP-seq.
Li W, Huang Y, Sargsyan D, Khor TO, Guo Y, Shu L, Yang AY, Zhang C, Paredes-Gonzalez X, Verzi M, Hart RP, Kong AN
Purpose: We investigated the genomic DNA methylation profile of prostate cancer in transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) cancer model and to analyze the crosstalk among targeted genes and the related functional pathways. Methods: Prostate DNA samples from 24-week-old TRAMP and C57BL/6 male mice wer... |
Analysis of DNA methylome and transcriptome profiling following Gibberellin A3 (GA3) foliar application in Nicotiana tabacum L.
Manoharlal Raman, Saiprasad G. V. S., Kaikala Vinay, Suresh Kumar R., Kovařík Ales
The present work investigated a comprehensive genome-wide landscape of DNA methylome and its relationship with transcriptome upon gibberellin A3 (GA3) foliar application under practical field conditions in solanaceae model, Nicotiana tabacum L. Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation-Sequencing (MeDIP-Seq) analysis uncov... |
Data on novel DNA methylation changes induced by valproic acid in human hepatocytes
Wolters J. et al.
Valproic acid (VPA) is a widely prescribed antiepileptic drug in the world. Despite its pharmacological importance, it may cause liver toxicity and steatosis. However the exact mechanism of the steatosis formation is unknown. The data presented in this DIB publication is used to further investigate the VPA-induced m... |
Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA Methylation Patterns Induced by Valproic Acid in Human Hepatocytes
Wolters J.E.J. et al.
Valproic acid (VPA) is one of the most widely prescribed antiepileptic drugs in the world. Despite its pharmacological importance, it may cause liver toxicity and steatosis through mitochondrial dysfunction. The aim of this study is to further investigate VPA-induced mechanisms of steatosis by analyzing changes in p... |
Genome methylation and regulatory functions for hypoxic adaptation in Tibetan chicken embryos
Zhang Y. et al.
Tibetan chickens have unique adaptations to the extreme high-altitude environment that they inhabit. Epigenetic DNA methylation affects many biological processes, including hypoxic adaptation; however, the regulatory genes for DNA methylation in hypoxic adaptation remain unknown. In this study, methylated DNA immuno... |
Emerging Role of One-Carbon Metabolism and DNA Methylation Enrichment on δ-Containing GABAA Receptor Expression in the Cerebellum of Subjects with Alcohol Use Disorders (AUD
Gatta E. et al.
Background
Cerebellum is an area of the brain particularly sensitive to the effects of acute and chronic alcohol consumption. Alcohol exposure decreases cerebellar Purkinje cell output by increasing GABA release from Golgi cells onto extrasynaptic α6/δ-containing GABAA receptors located on glutamate... |
Coordinate Regulation of TET2 and EBNA2 Control DNA Methylation State of Latent Epstein-Barr Virus
Lu F. et al.
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) latency and its associated carcinogenesis are regulated by dynamic changes in DNA methylation of both virus and host genomes. We show here that the Ten-Eleven Translocation 2 (TET2) gene, implicated in hydroxymethylation and active DNA demethylation, is a key regulator of EBV latency type DN... |
Intracellular adenosine regulates epigenetic programming in endothelial cells to promote angiogenesis
Xu Y. et al.
The nucleoside adenosine is a potent regulator of vascular homeostasis, but it remains unclear how expression or function of the adenosine-metabolizing enzyme adenosine kinase (ADK) and the intracellular adenosine levels influence angiogenesis. We show here that hypoxia lowered the expression of ADK and increased th... |
Vitamin C induces specific demethylation of H3K9me2 in mouse embryonic stem cells via Kdm3a/b
Kevin T. Ebata, Kathryn Mesh, Shichong Liu, Misha Bilenky, Alexander Fekete, Michael G. Acker, Martin Hirst, Benjamin A. Garcia and Miguel Ramalho-Santos
Background
Histone methylation patterns regulate gene expression and are highly dynamic during development. The erasure of histone methylation is carried out by histone demethylase enzymes. We had previously shown that vitamin C enhances the activity of Tet enzymes in embryonic stem (ES) cells, leading to DNA... |
Dynamics of DNA methylomes underlie oyster development
Riviere G. et al.
DNA methylation is a critical epigenetic regulator of development in mammals and social insects, but its significance in development outside these groups is not understood. Here we investigated the genome-wide dynamics of DNA methylation in a mollusc model, the oyster Crassostrea gigas, from the egg to the completio... |
MeDIP-seq and nCpG analyses illuminate sexually dimorphic methylation of gonadal development genes with high historic methylation in turtle hatchlings with temperature-dependent sex determination
Radhakrishnan S. et al.
Background
DNA methylation alters gene expression but not DNA sequence and mediates some cases of phenotypic plasticity. Temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD) epitomizes phenotypic plasticity where environmental temperature drives embryonic sexual fate, as occurs commonly in turtles. Importantly, the temp... |
Protective vaccination and blood-stage malaria modify DNA methylation of gene promoters in the liver of Balb/c mice.
Al-Quraishy S. et al.
Epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation are increasingly recognized to be critical for vaccination efficacy and outcome of different infectious diseases, but corresponding information is scarcely available for host defense against malaria. In the experimental blood-stage malaria Plasmodium chabaudi, we investi... |
Comparative analysis of MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq and estimation of gene expression changes in a rodent model of schizophrenia
Neary J.L. et al.
We conducted a comparative study of multiplexed affinity enrichment sequence methodologies (MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq) in a rodent model of schizophrenia, induced by in utero methylazoxymethanol acetate (MAM) exposure. We also examined related gene expression changes using a pooled sample approach. MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq... |
Overexpression of LINE-1 Retrotransposons in Autism Brain
Shpyleva S. et al.
Long interspersed nuclear elements-1 (LINE-1 or L1) are mobile DNA sequences that are capable of duplication and insertion (retrotransposition) within the genome. Recently, retrotransposition of L1 was shown to occur within human brain leading to somatic mosaicism in hippocampus and cerebellum. Because unregulated L... |
Integrative "-Omics" Analysis in Primary Human Hepatocytes Unravels Persistent Mechanisms of Cyclosporine A-Induced Cholestasis
Wolters J.E. et al.
Cyclosporine A (CsA) is an undecapeptide with strong immunosuppressant activities and is used a lot after organ transplantation. Furthermore, it may induce cholestasis in the liver. In general, the drug-induced cholestasis (DIC) pathway includes genes involved in the uptake, synthesis, conjugation, and secretion of ... |
Genome-wide DNA promoter methylation and transcriptome analysis in human adipose tissue unravels novel candidate genes for obesity
Keller M. et al.
Objective/methods
DNA methylation plays an important role in obesity and related metabolic complications. We examined genome-wide DNA promoter methylation along with mRNA profiles in paired samples of human subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) and omental visceral adipose tissue (OVAT) from non-obese vs. obese individ... |
Novel regional age-associated DNA methylation changes within human common disease-associated loci
Bell CG et al.
BACKGROUND:
Advancing age progressively impacts on risk and severity of chronic disease. It also modifies the epigenome, with changes in DNA methylation, due to both random drift and variation within specific functional loci.
RESULTS:
In a discovery set of 2238 peripheral-blood genome-wide DNA methylomes aged 1... |
Inheritable Silencing of Endogenous Genes by Hit-and-Run Targeted Epigenetic Editing
Amabile A. et al.
Gene silencing is instrumental to interrogate gene function and holds promise for therapeutic applications. Here, we repurpose the endogenous retroviruses' silencing machinery of embryonic stem cells to stably silence three highly expressed genes in somatic cells by epigenetics. This was achieved by transiently... |
Trichloroethylene-Induced DNA Methylation Changes in Male F344 Rat Liver
Jiang Y. et al.
Trichloroethylene (TCE), a common environmental contaminant, causes hepatocellular carcinoma in mice but not in rats. To understand the mechanisms of the species-specific hepatocarcinogenecity of TCE, we examined the methylation status of DNA in the liver of rats exposed to TCE at 0 or 1000 mg/kg b.w. for 5 days usi... |
Dynamic Interplay between the Transcriptome and Methylome in Response to Oxidative and Alkylating Stress
Deferme L et al.
In recent years, it has been shown that free radicals not only react directly with DNA but also regulate epigenetic processes such as DNA methylation, which may be relevant within the context of, for example, tumorigenesis. However, how these free radicals impact the epigenome remains unclear. We therefore investiga... |
Efficiency of methylated DNA immunoprecipitation bisulphite sequencing for whole-genome DNA methylation analysis
Jeong HM et al.
We compared four common methods for measuring DNA methylation levels and recommended the most efficient method in terms of cost and coverage.
MATERIALS & METHODS:
The DNA methylation status of liver and stomach tissues was profiled using four different methods, whole-genome bisulphite sequencing (WG-BS), targe... |
Aflatoxin B1 induces persistent epigenomic effects in primary human hepatocytes associated with hepatocellular carcinoma
Linda Rieswijka, Sandra M.H. Claessena, Otto Bekersc, Marcel van Herwijnena, Daniël H.J. Theunissena, Danyel G.J. Jennena, Theo M.C.M. de Koka, Jos C.S. Kleinjansa,Simone G.J. van Bredaa
Chronic exposure to aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) has, in certain regions in the world, been strongly associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development. AFB1 is a very potent hepatotoxic and carcinogenic mycotoxin which is frequently reported as a food contaminant. Epigenetic modifications provoked by environmental e... |
Paternal B Vitamin Intake Is a Determinant of Growth, Hepatic Lipid Metabolism and Intestinal Tumor Volume in Female Apc1638N Mouse Offspring
Sabet JA, Park LK, Iyer LK, Tai AK, Koh GY, Pfalzer AC, Parnell LD, Mason JB, Liu Z, Byun AJ, Crott JW
Background
The importance of maternal nutrition to offspring health and risk of disease is well established. Emerging evidence suggests paternal diet may affect offspring health as well.
Objective
In the current study we sought to determine whether modulating pre-conception paternal B vitamin intake alters intest... |
Regulation of miR-200c/141 expression by intergenic DNA-looping and transcriptional read-through
Batista L et al.
The miR-200 family members have been implicated in stress responses and ovarian tumorigenesis. Here, we find that miR-200c/141 transcription is intimately linked to the transcription of the proximal upstream gene PTPN6 (SHP1) in all physiological conditions tested. PTPN6 and miR-200c/141 are transcriptionally co-reg... |
Maternal immune activation induces GAD1 and GAD2 promoter remodeling in the offspring prefrontal cortex
Labouesse MA et al.
Maternal infection during pregnancy increases the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in the offspring. In addition to its influence on other neuronal systems, this early-life environmental adversity has been shown to negatively affect cortical γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) functions in adult life, including imp... |
DNA methylation profiling: comparison of genome-wide sequencing methods and the Infinium Human Methylation 450 Bead Chip
Walker DL, Bhagwate AV, Baheti S, Smalley RL, Hilker CA, Sun Z, Cunningham JM
AIMS:
To compare the performance of four sequence-based and one microarray methods for DNA methylation profiling.
METHODS:
DNA from two cell lines were profiled by reduced representation bisulfite sequencing, methyl capture sequencing (SS-Meth Seq), NimbleGen SeqCapEpi CpGiant(Nimblegen MethSeq), methylated DNA... |
High cortisol in 5-year-old children causes loss of DNA methylation in SINE retrotransposons: a possible role for ZNF263 in stress-related diseases
Nätt D, Johansson I, Faresjö T, Ludvigsson J, Thorsell A
BACKGROUND:
Childhood stress leads to increased risk of many adult diseases, such as major depression and cardiovascular disease. Studies show that adults with experienced childhood stress have specific epigenetic changes, but to understand the pathways that lead to disease, we also need to study the epigenetic l... |
Arterial endothelial methylome: differential DNA methylation in athero-susceptible disturbed flow regions in vivo
Jiang YZ1, Manduchi E2, Stoeckert CJ Jr3, Davies PF
BACKGROUND:
Atherosclerosis is a heterogeneously distributed disease of arteries in which the endothelium plays an important central role. Spatial transcriptome profiling of endothelium in pre-lesional arteries has demonstrated differential phenotypes primed for athero-susceptibility at hemodynamic sites associat... |