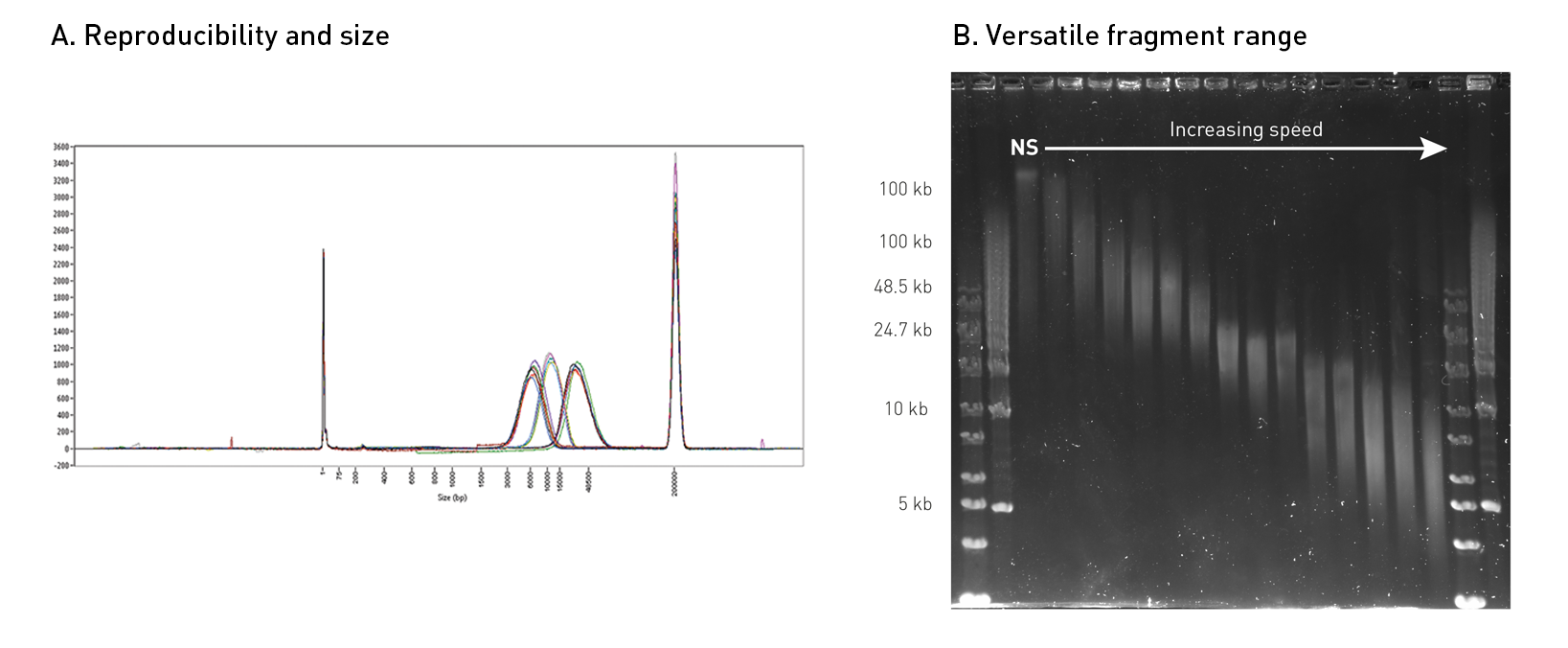
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: Megaruptor® 3 (Hologic Diagenode Cat# B06010003). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
High-quality genome sequence of five Antarctic actinomycetes: Micromonospora ureilytica DSM 120150, Nocardiopsis akebiae DSM 120151, Streptomyces fildesensis DSM 41987T, Streptomyces hypolithicus DSM 41950T and Streptomyces albidoflavus DSM 120149
Tarazona Janampa, Ulrike et al.
Micromonospora ureilytica DSM 120150, Nocardiopsis akebiae DSM 120151, Streptomyces fildesensis DSM 41987T, Streptomyces hypolithicus DSM 41950T and Streptomyces albidoflavus DSM 120149 are five Antarctic strains. Here, we present the high-quality genome sequences of... |
Using the linear references from the pangenome to discover missing autism variants
Sui, Yang et al.
To better understand large-effect pathogenic variation associated with autism, we generated long-read sequencing (LRS) data to construct phased and near-complete genome assemblies (average contig N50 = 43 Mbp, QV = 56) for 189 individuals from 51 families with unsolved cases. We applied r... |
Genomic Validation of PERV‐C‐Free Pigs to Support Xenotransplantation
Benjamin, Neal R et al.
Porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERVs) are present in the germ lines of domesticated pigs (Sus scrofa) and related suids. There are three types of PERVs, PERV‐A, ‐B, and ‐C, which differ in their host range. PERV‐A and ‐B can infect human and porcine cells, while PERV‐C only infects porcine cells. PERV‐A and ‐B are... |
Structural variations in evolutionary novel genomic regions: new insights into neurodevelopmental disorders by long-read DNA Sequencing
Rincic, Martina et al.
Background
Neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) are highly diverse conditions often associated with genetic abnormalities. However, a large number of NDD cases remain undiagnosed despite thorough genetic testing using short-read sequencing and chromosomal microarray analysis. Emerging evidence indicates that struc... |
Targeted sequencing and iterative assembly of near-complete genomes
Gamaarachchi, Hasindu et al.
Complete telomere-to-telomere diploid genome assemblies have long posed significant challenges due to the intricate architecture of genomes. In diploid organisms, separating the two parental haplotypes becomes particularly difficult, especially amid highly repetitive sequences, centromeres, and telomeres. Traditiona... |
Deep Intronic SVA_E Insertion Identified as the Most Common Pathogenic Variant Associated With Canavan Disease
Dominguez Gonzalez, Carlos A et al.
Background and objectives: Canavan disease (CD) is a neurodegenerative disorder in which biallelic pathogenic variants in ASPA result in spongiform degeneration of the cerebral white matter, leading to progressive and irreversible motor and cognitive decline. Despite comprehensive genetic testing, man... |
Phased genome assemblies and pangenome graphs of human populations of Japan and Saudi Arabia
Kulmanov, Maxat et al.
The selection of a reference sequence in genome analysis is critical, as it serves as the foundation for all downstream analyses. Recently, the pangenome graph has been proposed as a data model that incorporates haplotypes from multiple individuals. Here we present JaSaPaGe, a pangenome graph reference for Saudi... |
A draft UAE-based Arab pangenome reference
Nassir, Nasna et al.
Pangenomes provide a robust and comprehensive portrayal of genetic diversity in humans, but Arab populations remain underrepresented. We present a preliminary UAE-based Arab Pangenome Reference (UPR) utilizing 53 individuals of diverse Arab ethnicities residing in the United Arab Emirates. We assembled nuclear a... |
Near-complete Middle Eastern genomes refine autozygosity and enhance disease-causing and population-specific variant discovery
Ghorbani, Mohammadmersad et al.
Advances in long-read sequencing have enabled routine complete assembly of human genomes, but much remains to be done to represent broader populations and show impact on disease-gene discovery. Here, we report highly accurate, near-complete and phased genomes from six Middle Eastern (ME) family trios (n = 18) wi... |
Complete sequencing of ape genomes
Yoo, D., et al.
The most dynamic and repetitive regions of great ape genomes have traditionally been excluded from comparative studies1,2,3. Consequently, our understanding of the evolution of our species is incomplete. Here we present haplotype-resolved reference genomes and comparative analyses of six ape species: chimpanzee,... |
Centromeric transposable elements and epigenetic status drive karyotypic variation in the eastern hoolock gibbon
Hartley, Gabrielle A et al.
Great apes have maintained a stable karyotype with few large-scale rearrangements; in contrast, gibbons have undergone a high rate of chromosomal rearrangements coincident with rapid centromere turnover. Here, we characterize fully assembled centromeres in the eastern hoolock gibbon, Hoolock leuconedys (HLE), findin... |
Conservation of dichromatin organization along regional centromeres
Dubocanin, Danilo et al.
The attachment of the kinetochore to the centromere is essential for genome maintenance, yet the highly repetitive nature of satellite regional centromeres limits our understanding of their chromatin organization. We demonstrate that single-molecule chromatin fiber sequencing (Fiber-seq) can uniquely co-resolve kine... |
Human de novo mutation rates from a four-generation pedigree reference
Porubsky, David et al.
Understanding the human de novo mutation (DNM) rate requires complete sequence information1. Here using five complementary short-read and long-read sequencing technologies, we phased and assembled more than 95% of each diploid human genome in a four-generation, twenty-eight-member family (CEPH 1463). We estimate 98-... |
The Utah NeoSeq Project: a collaborative multidisciplinary program to facilitate genomic diagnostics in the neonatal intensive care unit
Malone Jenkins, Sabrina et al.
Rapid genomic diagnostics in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit represents a paradigm shift in medicine with increasing evidence of the utility of early diagnosis, impacting management. The goal of the Utah NeoSeq Project was to implement and evaluate a multidisciplinary and longitudinal rapid sequencing program while... |
Cellulophaga algicola alginate lyase and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Psl glycoside hydrolase inhibit biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa CF2843 on three-dimensional aggregates of lung epithelial cells
Neetu, Pal S, et al.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic pathogen that produces a biofilm containing the polysaccharides, alginate, Psl, and Pel, and causes chronic lung infection in cystic fibrosis patients. Others and we have previously explored the use of alginate lyases in inhibiting P. aeruginosa biofilm for... |
Bat genomes illuminate adaptations to viral tolerance and disease resistance
Morales, A.E., Dong, Y., Brown, T. et al.
Zoonoses are infectious diseases transmitted from animals to humans. Bats have been suggested to harbour more zoonotic viruses than any other mammalian order1. Infections in bats are largely asymptomatic2,3, indicating limited tissue-damaging inflammation and immunopathology. To investigate the genomic basis of dise... |
Single chromatin fiber profiling and nucleosome position mapping in the human brain
Peter. Cyril J et al.
We apply a single-molecule chromatin fiber sequencing (Fiber-seq) protocol designed for amplification-free cell-type-specific mapping of the regulatory architecture at nucleosome resolution along extended ∼10-kb chromatin fibers to neuronal and non-neuronal nuclei sorted from human brain tissue. Specificall... |
The genome sequence of the Elbow-stripe Grass-veneer, Agriphilageniculea (Haworth, 1811)
Boyes Douglas and Hammond James
We present a genome assembly from an individual female Agriphila geniculea (the Elbow-stripe Grass-veneer; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Crambidae). The genome sequence is 781.6 megabases in span. Most of the assembly is scaffolded into 30 chromosomal pseudomolecules, including the Z and W sex chromosomes. The m... |
The genome sequence of the Turnip Sawfly, Athalia rosae(Linnaeus, 1758)
Crowley Liam M. and Broad Gavin R. and Green Andrew
We present a genome assembly from an individual female Athalia rosae (the Turnip Sawfly; Arhropoda; Insecta; Hymenoptera; Athaliidae). The genome sequence is 172 megabases in span. Most of the assembly is scaffolded into eight chromosomal pseudomolecules. The mitochondrial genome has also been assembled and is 16.3 ... |
A high-quality, haplotype-phased genome reconstruction reveals unexpectedhaplotype diversity in a pearl oyster.
Takeuchi Takeshi et al.
Homologous chromosomes in the diploid genome are thought to contain equivalent genetic information, but this common concept has not been fully verified in animal genomes with high heterozygosity. Here we report a near-complete, haplotype-phased, genome assembly of the pearl oyster, Pinctada fucata, using hi-fidelity... |
Complete Genome Sequence of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus DM065,Isolated from the Human Oral Cavity.
Park Do-Young et al.
The 3.0-Mb complete genome of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus strain DM065, which was isolated from the oral cavity of healthy volunteers in South Korea, was sequenced using a combination of PacBio and Illumina technologies. The genome consists of one circular chromosome and two plasmids and lacks antimicrobial resista... |
The genome sequence of the malaria mosquito, Anopheles funestus,Giles, 1900
Ayala Diego et al.
We present a genome assembly from an individual female Anopheles funestus (the malaria mosquito; Arthropoda; Insecta; Diptera; Culicidae). The genome sequence is 251 megabases in span. The majority of the assembly is scaffolded into three chromosomal pseudomolecules with the X sex chromosome assembled. The complete ... |
Semi-automated assembly of high-quality diploid human reference genomes.
Jarvis Erich D et al.
The current human reference genome, GRCh38, represents over 20 years of effort to generate a high-quality assembly, which has benefitted society. However, it still has many gaps and errors, and does not represent a biological genome as it is a blend of multiple individuals. Recently, a high-quality telomere-to-telom... |
Integration of Hi-C with short and long-read genome sequencingreveals the structure of germline rearranged genomes.
Schöpflin R.et al.
Structural variants are a common cause of disease and contribute to a large extent to inter-individual variability, but their detection and interpretation remain a challenge. Here, we investigate 11 individuals with complex genomic rearrangements including germline chromothripsis by combining short- and long-read ge... |
The genome sequence of the orange-tip butterfly, Anthocharis cardamines(Linnaeus, 1758)
Ebdon S. et al.
We present a genome assembly from an individual female Anthocharis cardamines (the orange-tip; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Pieridae). The genome sequence is 360 megabases in span. The majority (99.74\%) of the assembly is scaffolded into 31 chromosomal pseudomolecules, with the W and Z sex chromosomes assemble... |
The genome sequence of the satellite, Eupsilia transversa (Hufnagel,1766)
Crowley L. et al.
We present a genome assembly from an individual female Eupsilia transversa (the satellite; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). The genome sequence is 467 megabases in span. The entire assembly (100\%) is scaffolded into 32 chromosomal pseudomolecules with the W and Z sex chromosomes assembled. The complete... |
The genome sequence of the common yellow swallowtail, Papilio machaon(Linnaeus, 1758)
Lohse K. et al.
We present a genome assembly from an individual female Papilio machaon (the common yellow swallowtail; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Papilionidae). The genome sequence is 252 megabases in span. The majority of the assembly (99.97\%) is scaffolded into 31 chromosomal pseudomolecules with the W and Z sex chromosom... |
The genome sequence of the Arran brown, Erebia ligea (Linnaeus,1758)
Lohse K. et al.
We present a genome assembly from an individual male Erebia ligea (Arran brown; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Nymphalidae). The genome sequence is 506 megabases in span. The majority (99.92\%) of the assembly is scaffolded into 29 chromosomal pseudomolecules, with the Z sex chromosome assembled. The complete mit... |
Complete Genome Sequence of Strain DM083 Isolated from HumanTongue Coating.
Park Do-Young et al.
We isolated Lactiplantibacillus plantarum DM083 from the human tongue coating to establish a strain library for oral probiotics. It has a single circular 3,197,299 bp chromosome with a guanine-cytosine (GC) content of 44.6\% without plasmids. Importantly, the genome is devoid of the antimicrobial resistance gene, sa... |
The genome sequence of the yellow-legged clearwing, Synanthedonvespiformis (Linnaeus, 1761)
Boyes Douglas and Lees David
We present a genome assembly from an individual male Synanthedon vespiformis (the yellow-legged clearwing; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Sesiidae). The genome sequence is 287 megabases in span. Of the assembly, 100\% is scaffolded into 31 chromosomal pseudomolecules with the Z sex chromosome assembled. The compl... |
The genome sequence of the pale mottled willow, Caradrina clavipalpis(Scopoli, 1763)
Boyes Douglas and Boyes Clare
We present a genome assembly from an individual male Caradrina clavipalpis (pale mottled willow; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). The genome sequence is 474 megabases in span. The entire assembly (100\%) is scaffolded into 31 chromosomal pseudomolecules with the Z sex chromosome assembled. The complete ... |
The genome sequence of the smoky wainscot, Mythimna impura (Hubner,1808)
Boyes Douglas and Gibbs Melanie
We present a genome assembly from an individual female Mythimna impura (smoky wainscot; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). The genome sequence is 949 megabases in span. The majority of the assembly (98.39\%) is scaffolded into 32 chromosomal pseudomolecules with the W and Z sex chromosomes assembled. The ... |
Comparative analyses of Theobroma cacao and T. grandiflorummitogenomes reveal conserved gene content embedded within complex andplastic structures.
de Abreu Vinicius A C et al.
Unlike the chloroplast genomes (ptDNA), the plant mitochondrial genomes (mtDNA) are much more plastic in structure and size but maintain a conserved and essential gene set related to oxidative phosphorylation. Moreover, the plant mitochondrial genes and mtDNA are good markers for phylogenetic, evolutive, and compara... |
The genome sequence of the wall brown, Lasiommata megera (Linnaeus,1767)
Lohse Konrad and Wright Charlotte
We present a genome assembly from an individual female Lasiommata megera (the wall brown; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Nymphalidae). The genome sequence is 488 megabases in span. The majority of the assembly (99.97\%) is scaffolded into 30 chromosomal pseudomolecules with the W and Z sex chromosomes assembled. ... |
The genome sequence of the sallow kitten, Furcula furcula (Clerck,1759)
Boyes Douglas et al.
We present a genome assembly from an individual male Furcula furcula (the sallow kitten; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Notodontidae). The genome sequence is 736 megabases in span. The entire assembly (100\%) is scaffolded into 29 chromosomal pseudomolecules, with the Z sex chromosome assembled. The complete mito... |
The genome sequence of the peacock moth, Macaria notata (Linnaeus,1758)
Boyes Douglas et al.
We present a genome assembly from an individual male Macaria notata (the peacock moth; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Geometridae). The genome sequence is 394 megabases in span. The majority of the assembly (99.98\%) is scaffolded into 29 chromosomal pseudomolecules with the Z sex chromosome assembled. The comple... |
Plant species-specific basecaller improves actual accuracy of nanoporesequencing
Ferguson Scott et al.
Long-read sequencing platforms offered by Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) allow native DNA containing epigenetic modifications to be directly sequenced, but can be limited by lower per-base accuracies. A key step post-sequencing is basecalling, the process of converting raw electrical signals produced by the sequ... |
The chromosome-level genome of Gypsophila paniculata reveals themolecular mechanism of floral development and ethylene insensitivity
Fan Li et al.
Gypsophila paniculata, belonging to the Caryophyllaceae of the Caryophyllales, is one of the worldwide famous cut flowers. It is commonly used as dried flowers, whereas the underlying mechanism of flower senescence has not yet been addressed. Here, we present a chromosome-scale genome assembly for G. paniculata with... |
The leaf beetle Chelymorpha alternans propagates a plant pathogen inexchange for pupal protection.
Berasategui Aileen et al.
Many insects rely on microbial protection in the early stages of their development. However, in contrast to symbiont-mediated defense of eggs and young instars, the role of microbes in safeguarding pupae remains relatively unexplored, despite the susceptibility of the immobile stage to antagonistic challenges. Here,... |
The genome sequence of the hawthorn shieldbug, Acanthosomahaemorrhoidale (Linnaeus, 1758)
Crowley Liam M. and Mulley John
We present a genome assembly from an individual male Acanthosoma haemorrhoidale (hawthorn shieldbug; Arthropoda; Insecta; Hemiptera; Acanthosomatidae). The genome sequence is 866 megabases in span. The majority of the assembly (99.98\%) is scaffolded into 7 chromosomal pseudomolecules with the X and Y sex chromosome... |
The genome sequence of the dun-bar pinion, Cosmia trapezina(Linnaeus, 1758)
Boyes Douglas et al.
We present a genome assembly from an individual male Cosmia trapezina (dun-bar pinion; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). The genome sequence is 825 megabases in span. The majority of the assembly (99.87\%) is scaffolded into 32 chromosomal pseudomolecules with the Z chromosome assembled. The complete mit... |
Equilibrated evolution of the mixed auto-/allopolyploidhaplotype-resolved genome of the invasive hexaploid Prussian carp.
Kuhl Heiner et al.
Understanding genome evolution of polyploids requires dissection of their often highly similar subgenomes and haplotypes. Polyploid animal genome assemblies so far restricted homologous chromosomes to a 'collapsed' representation. Here, we sequenced the genome of the asexual Prussian carp, which is a close relative ... |
Haplotype-resolved Chinese male genome assembly based on high-fidelitysequencing
Yang X. et al.
The advantages of both the length and accuracy of high-fidelity (HiFi) reads enable chromosome-scale haplotype-resolved genome assembly. In this study, we sequenced a cell line named HJ, established from a Chinese Han male individual by using HiFi and Hi-C. We assembled two high-quality haplotypes of the HJ genome (... |
Complete Genome Sequence of Herpes Simplex Virus 2 StrainG.
Chang Weizhong et al.
Herpes simplex virus type (HSV-2) is a common causative agent of genital tract infections. Moreover, HSV-2 and HIV infection can mutually increase the risk of acquiring another virus infection. Due to the high GC content and highly repetitive regions in HSV-2 genomes, only the genomes of four strains have been compl... |
The genome sequence of a stonefly, Nemurella pictetii Klapalek, 1900
Macadam Craig et al.
We present a genome assembly from an individual male Nemurella pictetii (Arthropoda; Insecta; Plecoptera; Nemouridae). The genome sequence is 257 megabases in span. The majority of the assembly (99.79\%) is scaffolded into 12 chromosomal pseudomolecules, with the X sex chromosome assembled. The X chromosome was foun... |
The genome sequence of the furry-claspered furrow bee, Lasioglossumlativentre (Schenck, 1853)
Falk Steven and Monks Joseph
We present a genome assembly from an individual male Lasioglossum lativentre (the furry-claspered furrow bee; Arthropoda; Insecta; Hymenoptera; Halictidae). The genome sequence is 479 megabases in span. The majority of the assembly (75.22\%) is scaffolded into 14 chromosomal pseudomolecules. The mitochondrial genome... |
Improved chromosome-level genome assembly of the Glanville fritillarybutterfly () integrating Pacific Biosciences long reads and ahigh-density linkage map
Smolander Olli-Pekka et al.
Abstract Background The Glanville fritillary (Melitaea cinxia) butterfly is a model system for metapopulation dynamics research in fragmented landscapes. Here, we provide a chromosome-level assembly of the butterfly's genome produced from Pacific Biosciences sequencing of a pool of males, combined with a linkage map... |
The genome sequence of a parasitoid wasp, Forster, 1771.
Broad Gavin
We present a genome assembly from an individual female (Arthropoda; Insecta; Hymenoptera; Ichneumonidae). The genome sequence is 315 megabases in span. The majority of the assembly (82.64\%) is scaffolded into 12 chromosomal pseudomolecules. Gene annotation of this assembly on Ensembl has identified 10,622 protein c... |
The genome sequence of the brimstone moth, Opisthograptis luteolata(Linnaeus, 1758)
Boyes Douglas and Phillips Dominic
We present a genome assembly from an individual male (the brimstone moth; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Geometridae). The genome sequence is 363 megabases in span. The majority of the assembly (99.99\%) is scaffolded into 31 chromosomal pseudomolecules with the Z sex chromosome assembled. The complete mitochondr... |
The genome sequence of Gymnosoma rotundatum (Linnaeus, 1758), aparasitoid ladybird fly
Smith Matthew
We present a genome assembly from an individual male (Arthropoda; Insecta; Diptera; Tachinidae). The genome sequence is 779 megabases in span. The majority of the assembly (97.07\%) is scaffolded into six chromosomal pseudomolecules, with the X sex chromosome assembled. |
Reference genome assembly of the big berry Manzanita (Arctostaphylosglauca).
Huang Yi et al.
Arctostaphylos (Ericaceae) species, commonly known as manzanitas, are an invaluable fire-adapted chaparral clade in the California Floristic Province (CFP), a world biodiversity hotspot on the west coast of North America. This diverse woody genus includes many rare and/or endangered taxa, and the genus plays essenti... |
Establishing community reference samples, data and call sets forbenchmarking cancer mutation detection using whole-genome sequencing.
Fang Li Tai et al.
The lack of samples for generating standardized DNA datasets for setting up a sequencing pipeline or benchmarking the performance of different algorithms limits the implementation and uptake of cancer genomics. Here, we describe reference call sets obtained from paired tumor-normal genomic DNA (gDNA) samples derived... |
De novo genome assembly of the marine teleost, bluefin trevally (Caranxmelampygus).
Pickett, Brandon D and Glass, Jessica R and Ridge, PerryG and Kauwe, John S K
The bluefin trevally, Caranx melampygus, also known as the bluefin kingfish or bluefin jack, is known for its remarkable, bright-blue fins. This marine teleost is a widely prized sportfish, but few resources have been devoted to the genomics and conservation of this species because it is not targeted by large-scale ... |
Targeted long-read sequencing identifies missing disease-causingvariation.
Miller Danny E et al.
Despite widespread clinical genetic testing, many individuals with suspected genetic conditions lack a precise diagnosis, limiting their opportunity to take advantage of state-of-the-art treatments. In some cases, testing reveals difficult-to-evaluate structural differences, candidate variants that do not fully expl... |
Evidence of an epidemic spread of KPC-producing in Czech hospitals
Kraftova Lucie et al.
The aim of the present study is to describe the ongoing spread of the KPC-producing strains, which is evolving to an epidemic in Czech hospitals. During the period of 2018–2019, a total of 108 KPC-producing Enterobacterales were recovered from 20 hospitals. Analysis of long-read sequencing data revealed the pr... |
Familial thrombocytopenia due to a complex structural variant resulting ina WAC-ANKRD26 fusion transcript.
Wahlster, Lara and Verboon, Jeffrey M and Ludwig, Leif S and Black, Susan Cand Luo, Wendy and Garg, Kopal and Voit, Richard A and Collins, Ryan L andGarimella, Kiran and Costello, Maura and Chao, Katherine R and Goodrich,Julia K and DiTroia, Stephanie
Advances in genome sequencing have resulted in the identification of the causes for numerous rare diseases. However, many cases remain unsolved with standard molecular analyses. We describe a family presenting with a phenotype resembling inherited thrombocytopenia 2 (THC2). THC2 is generally caused by single nucleot... |
PCIP-seq: simultaneous sequencing of integrated viral genomes and theirinsertion sites with long reads.
Artesi, M. et al.
The integration of a viral genome into the host genome has a major impact on the trajectory of the infected cell. Integration location and variation within the associated viral genome can influence both clonal expansion and persistence of infected cells. Methods based on short-read sequencing can identify viral inse... |
Complete vertebrate mitogenomes reveal widespread repeats and geneduplications.
Formenti G. et al.
BACKGROUND: Modern sequencing technologies should make the assembly of the relatively small mitochondrial genomes an easy undertaking. However, few tools exist that address mitochondrial assembly directly. RESULTS: As part of the Vertebrate Genomes Project (VGP) we develop mitoVGP, a fully automated pipeline for sim... |
Comparison of long read sequencing technologies in interrogating bacteriaand fly genomes.
Tvedte, Eric S and Gasser, Mark and Sparklin, Benjamin C and Michalski,Jane and Hjelmen, Carl E and Johnston, J Spencer and Zhao, Xuechu andBromley, Robin and Tallon, Luke J and Sadzewicz, Lisa and Rasko, David Aand Hotopp, Julie C Dunning
The newest generation of DNA sequencing technology is highlighted by the ability to generate sequence reads hundreds of kilobases in length. Pacific Biosciences (PacBio) and Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) have pioneered competitive long read platforms, with more recent work focused on improving sequencing throug... |
A single nucleotide polymorphism variant located in the cis-regulatoryregion of the ABCG2 gene is associated with mallard egg colour.
Liu H. et al.
Avian egg coloration is shaped by natural selection, but its genetic basis remains unclear. Here, we used genome-wide association analysis and identity by descent to finely map green egg colour to a 179-kb region of Chr4 based on the resequencing of 352 ducks (Anas platyrhynchos) from a segregating population result... |
Chromosome-scale genome assembly provides insights into the evolution andflavor synthesis of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims).
Xia Z. et al.
Passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) is an economically valuable fruit that is cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. Here, we report an ~1341.7 Mb chromosome-scale genome assembly of passion fruit, with 98.91\% (~1327.18 Mb) of the assembly assigned to nine pseudochromosomes. T... |
Rapid and ongoing evolution of repetitive sequence structures in humancentromeres.
Suzuki Y. et al.
Our understanding of centromere sequence variation across human populations is limited by its extremely long nested repeat structures called higher-order repeats that are challenging to sequence. Here, we analyzed chromosomes 11, 17, and X using long-read sequencing data for 36 individuals from diverse populations i... |
Efficient hybrid de novo assembly of human genomes with WENGAN.
Di Genova A. et al.
Generating accurate genome assemblies of large, repeat-rich human genomes has proved difficult using only long, error-prone reads, and most human genomes assembled from long reads add accurate short reads to polish the consensus sequence. Here we report an algorithm for hybrid assembly, WENGAN, that provides very hi... |
Complete Genome Sequence of sp. Strain Nx66, Isolated from WatersContaminated with Petrochemicals in El Saf-Saf Valley, Algeria.
Chéraiti, Nardjess and Plewniak, Frédéric and Tighidet, Salima andSayeh, Amalia and Gil, Lisa and Malherbe, Ludivine and Memmi, Yosr andZilliox, Laurence and Vandecasteele, Céline and Boyer, Pierre andLopez-Roques, Céline and Jaulhac, Benoît and Bensou
sp. strain Nx66 was isolated from waters contaminated by petrochemical effluents collected in Algeria. Its genome was sequenced using Illumina MiSeq (2 × 150-bp read pairs) and Oxford Nanopore (long reads) technologies and was assembled using Unicycler. It is composed of one chromosome of 3.42 Mb and on... |
Contrasting signatures of genomic divergence during sympatric speciation.
Kautt, Andreas F and Kratochwil, Claudius F and Nater, Alexander andMachado-Schiaffino, Gonzalo and Olave, Melisa and Henning, Frederico andTorres-Dowdall, Julián and Härer, Andreas and Hulsey, C Darrin andFranchini, Paolo and Pippel, Martin and Myers,
The transition from 'well-marked varieties' of a single species into 'well-defined species'-especially in the absence of geographic barriers to gene flow (sympatric speciation)-has puzzled evolutionary biologists ever since Darwin. Gene flow counteracts the buildup of genome-wide differentiation, which is a hallmark... |
Genome structure and content of the rice root-knot nematode ().
Phan, Ngan Thi and Orjuela, Julie and Danchin, Etienne G J and Klopp,Christophe and Perfus-Barbeoch, Laetitia and Kozlowski, Djampa K andKoutsovoulos, Georgios D and Lopez-Roques, Céline and Bouchez, Olivier andZahm, Margot and Besnard, Guillaume and B
Discovered in the 1960s, is a root-knot nematode species considered as a major threat to rice production. Yet, its origin, genomic structure, and intraspecific diversity are poorly understood. So far, such studies have been limited by the unavailability of a sufficiently complete and well-assembled genome. In this s... |
Repeat expansions confer WRN dependence in microsatellite-unstablecancers.
van Wietmarschen, Niek and Sridharan, Sriram and Nathan, William J andTubbs, Anthony and Chan, Edmond M and Callen, Elsa and Wu, Wei and Belinky,Frida and Tripathi, Veenu and Wong, Nancy and Foster, Kyla and Noorbakhsh,Javad and Garimella, Kiran and Cr
The RecQ DNA helicase WRN is a synthetic lethal target for cancer cells with microsatellite instability (MSI), a form of genetic hypermutability that arises from impaired mismatch repair. Depletion of WRN induces widespread DNA double-strand breaks in MSI cells, leading to cell cycle arrest and/or apoptosis. However... |
Breakpoint mapping of a t(9;22;12) chronic myeloid leukaemia patient withe14a3 BCR-ABL1 transcript using Nanopore sequencing.
Zhao, Hu and Chen, Yuan and Shen, Chanjuan and Li, Lingshu and Li, Qingzhaoand Tan, Kui and Huang, Huang and Hu, Guoyu
BACKGROUND: The genetic changes in chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) have been well established, although challenges persist in cases with rare fusion transcripts or complex variant translocations. Here, we present a CML patient with e14a3 BCR-ABL1 transcript and t(9;22;12) variant Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome. METHOD... |
Interruption of an MSH4 homolog blocks meiosis in metaphase I andeliminates spore formation in Pleurotus ostreatus.
Lavrijssen, Brian and Baars, Johan P and Lugones, Luis G and Scholtmeijer,Karin and Sedaghat Telgerd, Narges and Sonnenberg, Anton S M and van Peer,Arend F
Pleurotus ostreatus, one of the most widely cultivated edible mushrooms, produces high numbers of spores causing severe respiratory health problems for people, clogging of filters and spoilage of produce. A non-sporulating commercial variety (SPOPPO) has been successfully introduced into the market in 2006. This var... |