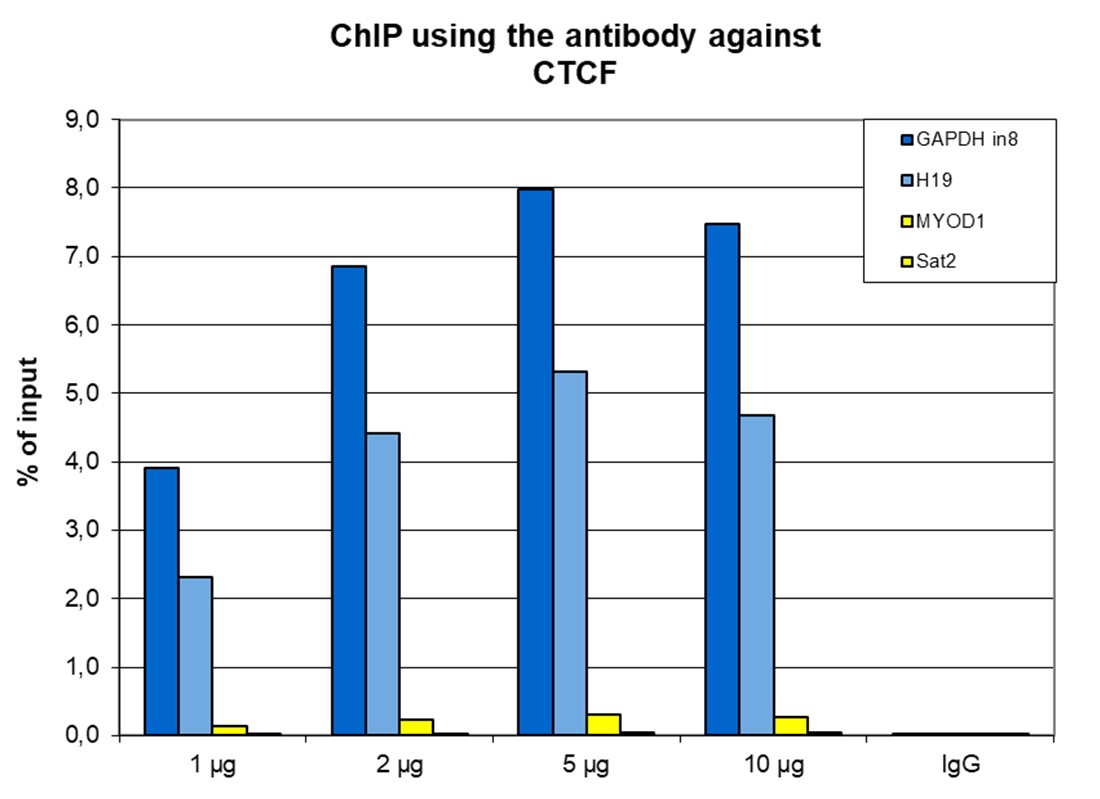
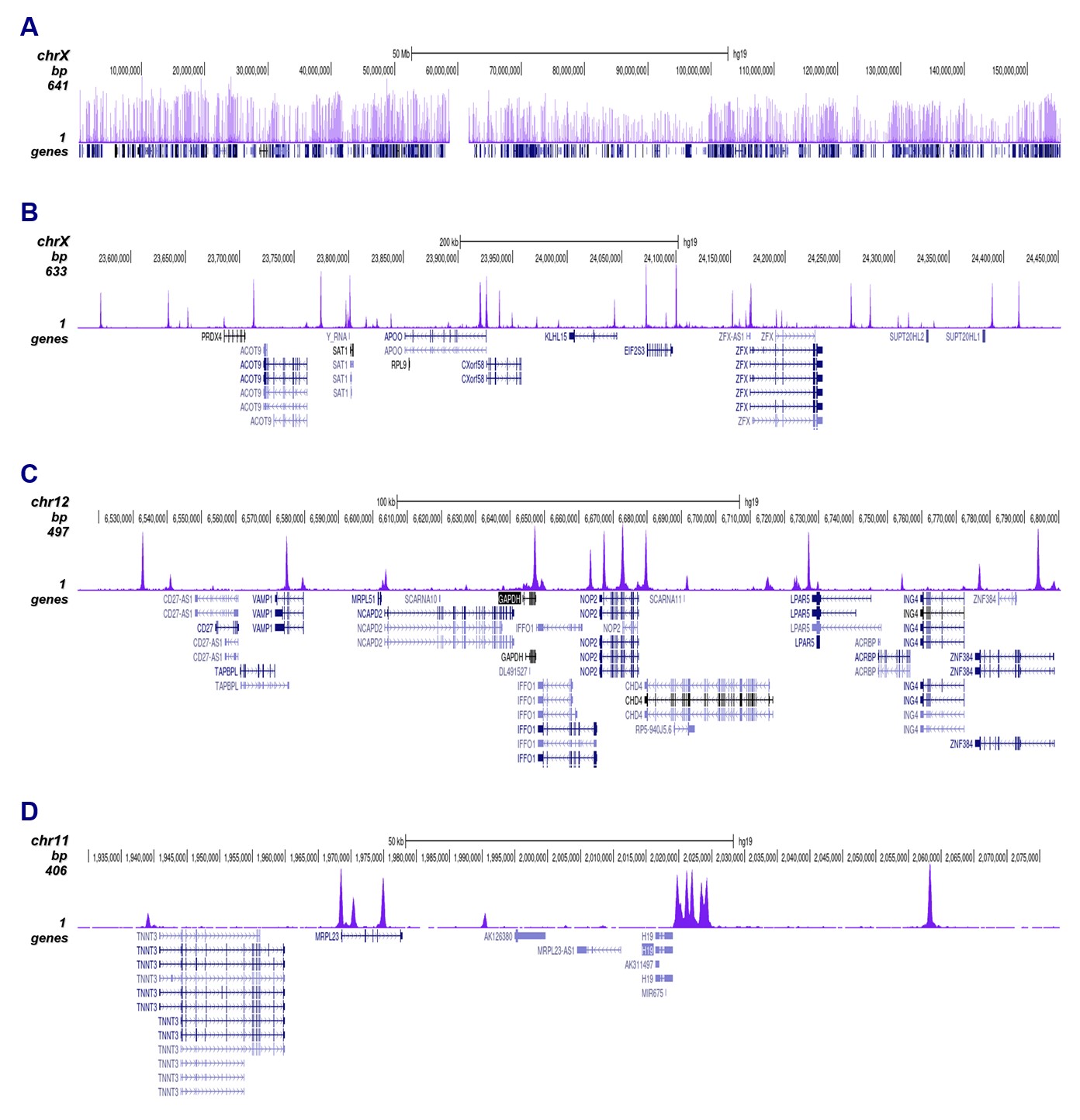
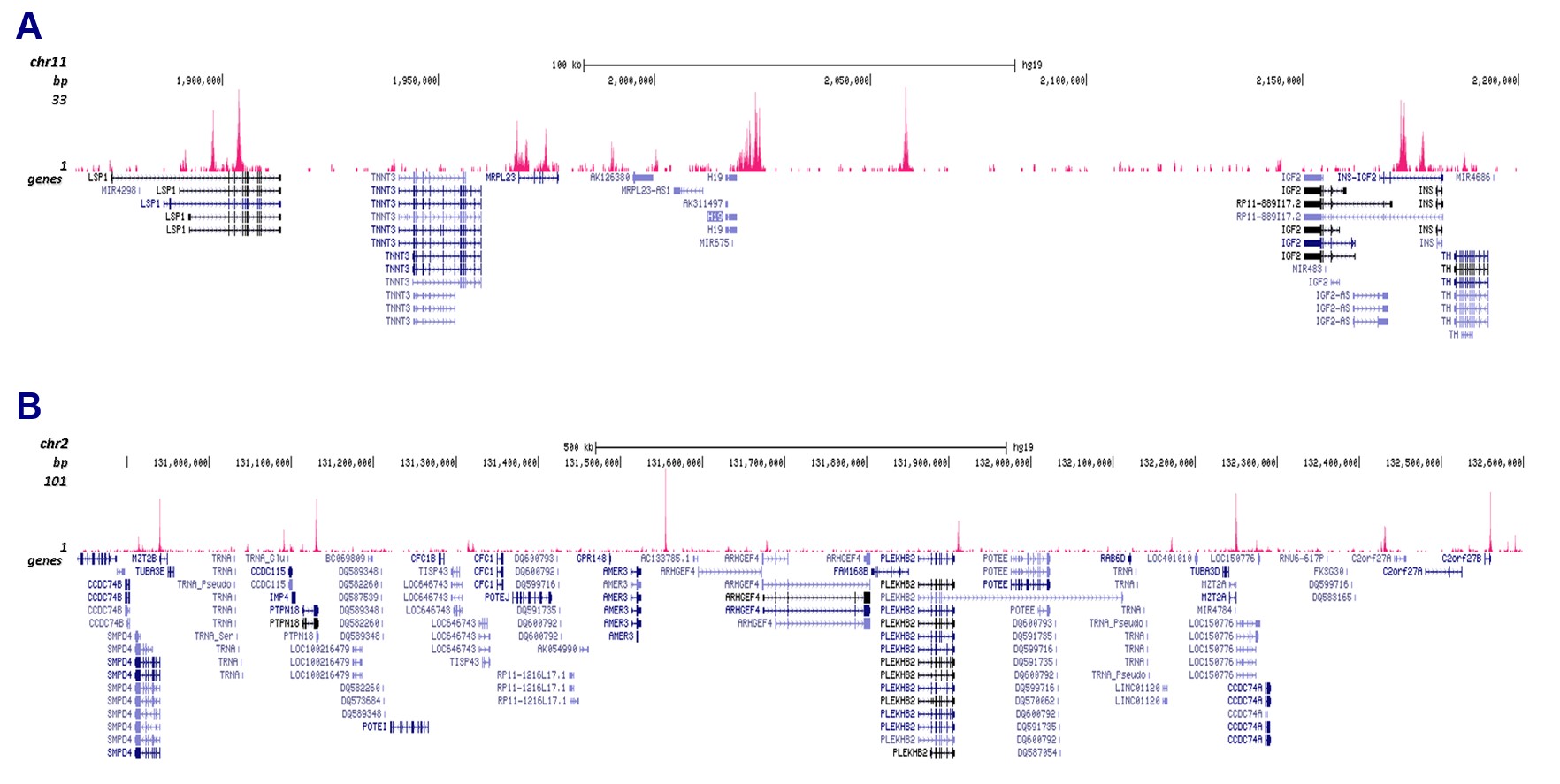
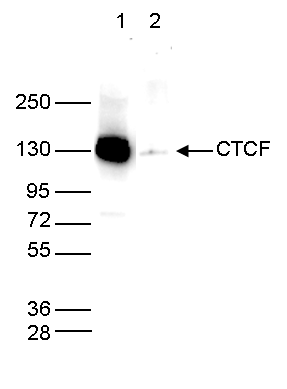
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: CTCF polyclonal antibody (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410210 Lot# A2355P). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Motif distribution and DNA methylation underlie distinct Cdx2 binding during development and homeostasis
Alireza Lorzadeh et al.
Transcription factors guide tissue development by binding to developmental stage-specific targets and establishing an appropriate enhancer landscape. In turn, DNA and chromatin modifications direct the genomic binding of transcription factors. However, how transcription factors navigate chromatin features to selecti... |
Systematic prioritization of functional variants and effector genes underlying colorectal cancer risk
Law P.J. et al.
Genome-wide association studies of colorectal cancer (CRC) have identified 170 autosomal risk loci. However, for most of these, the functional variants and their target genes are unknown. Here, we perform statistical fine-mapping incorporating tissue-specific epigenetic annotations and massively parallel reporter as... |
DeSUMOylation of chromatin-bound proteins limits the rapidtranscriptional reprogramming induced by daunorubicin in acute myeloidleukemias.
Boulanger M. et al.
Genotoxicants have been used for decades as front-line therapies against cancer on the basis of their DNA-damaging actions. However, some of their non-DNA-damaging effects are also instrumental for killing dividing cells. We report here that the anthracycline Daunorubicin (DNR), one of the main drugs used to treat A... |
RNA polymerase II CTD is dispensable for transcription and requiredfor termination in human cells.
Yahia Y. et al.
The largest subunit of RNA polymerase (Pol) II harbors an evolutionarily conserved C-terminal domain (CTD), composed of heptapeptide repeats, central to the transcriptional process. Here, we analyze the transcriptional phenotypes of a CTD-Δ5 mutant that carries a large CTD truncation in human cells. Our... |
In skeletal muscle and neural crest cells, SMCHD1 regulates biologicalpathways relevant for Bosma syndrome and facioscapulohumeral dystrophyphenotype.
Laberthonnière C. et al.
Many genetic syndromes are linked to mutations in genes encoding factors that guide chromatin organization. Among them, several distinct rare genetic diseases are linked to mutations in SMCHD1 that encodes the structural maintenance of chromosomes flexible hinge domain containing 1 chromatin-associated factor. In hu... |
Vitamin D Receptor Cross-talk with p63 Signaling PromotesEpidermal Cell Fate.
Oda Y. et al.
The vitamin D receptor with its ligand 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D (1,25D) regulates epidermal stem cell fate, such that VDR removal from Krt14 expressing keratinocytes delays re-epithelialization of epidermis after wound injury in mice. In this study we deleted Vdr from Lrig1 expressing stem cells in the isthmus of th... |
Hypomethylation and overexpression of Th17-associated genes is ahallmark of intestinal CD4+ lymphocytes in Crohn's disease.
Sun Z. et al.
BACKGROUND: The development of Crohn's disease (CD) involves immune cell signaling pathways regulated by epigenetic modifications. Aberrant DNA methylation has been identified in peripheral blood and bulk intestinal tissue from CD patients. However, the DNA methylome of disease-associated intestinal CD4 + lymphocyte... |
Low affinity CTCF binding drives transcriptional regulation whereashigh affinity binding encompasses architectural functions
Marina-Zárate E. et al.
CTCF is a DNA-binding protein which plays critical roles in chromatin structure organization and transcriptional regulation; however, little is known about the functional determinants of different CTCF-binding sites (CBS). Using a conditional mouse model, we have identified one set of CBSs that are lost upon CTCF de... |
Epigenetic regulation of plastin 3 expression by the macrosatelliteDXZ4 and the transcriptional regulator CHD4.
Strathmann E. A. et al.
Dysregulated Plastin 3 (PLS3) levels associate with a wide range of skeletal and neuromuscular disorders and the most common types of solid and hematopoietic cancer. Most importantly, PLS3 overexpression protects against spinal muscular atrophy. Despite its crucial role in F-actin dynamics in healthy cells and its i... |
Auxin-inducible degron 2 system deciphers functions of CTCF domains intranscriptional regulation.
Hyle J. et al.
BACKGROUND: CTCF is a well-established chromatin architectural protein that also plays various roles in transcriptional regulation. While CTCF biology has been extensively studied, how the domains of CTCF function to regulate transcription remains unknown. Additionally, the original auxin-inducible degron 1 (AID1) s... |
DNA dioxygenases Tet2/3 regulate gene promoter accessibility andchromatin topology in lineage-specific loci to control epithelialdifferentiation.
Chen G-D et al.
Execution of lineage-specific differentiation programs requires tight coordination between many regulators including Ten-eleven translocation (TET) family enzymes, catalyzing 5-methylcytosine oxidation in DNA. Here, by using --driven ablation of genes in skin epithelial cells, we demonstrate that ablation of results... |
K27M in canonical and noncanonical H3 variants occurs in distinctoligodendroglial cell lineages in brain midline gliomas.
Jessa Selin et al.
Canonical (H3.1/H3.2) and noncanonical (H3.3) histone 3 K27M-mutant gliomas have unique spatiotemporal distributions, partner alterations and molecular profiles. The contribution of the cell of origin to these differences has been challenging to uncouple from the oncogenic reprogramming induced by the mutation. Here... |
Identification of genomic binding sites and direct target genes for thetranscription factor DDIT3/CHOP.
Osman A. et al.
DDIT3 is a tightly regulated basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor and key regulator in cellular stress responses. It is involved in a variety of pathological conditions and may cause cell cycle block and apoptosis. It is also implicated in differentiation of some specialized cell types and as an oncogene... |
The telomeric protein TERF2/TRF2 impairs HMGB1-driven autophagy.
Iachettini S.et al.
TERF2/TRF2 is a pleiotropic telomeric protein that plays a crucial role in tumor formation and progression through several telomere-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Here, we uncovered a novel function for this protein in regulating the macroautophagic/autophagic process upon different stimuli. By using both bi... |
Embryonic heat conditioning in chicks induces transgenerationalheat/immunological resilience via methylation on regulatory elements.
Rosenberg Tali et al.
The question of whether behavioral traits are heritable is under debate. An obstacle in demonstrating transgenerational inheritance in mammals originates from the maternal environment's effect on offspring phenotype. Here, we used in ovo embryonic heat conditioning (EHC) of first-generation chicks, demonstrating her... |
TRF2 cooperates with CTCF for controlling the oncomiR-193b-3p incolorectal cancer.
Dinami R. et al.
The Telomeric Repeat binding Factor 2 (TRF2), a key protein involved in telomere integrity, is over-expressed in several human cancers and promotes tumor formation and progression. Recently, TRF2 has been also found outside telomeres where it can affect gene expression. Here we provide evidence that TRF2 is able to ... |
Variation in PU.1 binding and chromatin looping at neutrophil enhancersinfluences autoimmune disease susceptibility
Watt S. et al.
Neutrophils play fundamental roles in innate inflammatory response, shape adaptive immunity1, and have been identified as a potentially causal cell type underpinning genetic associations with immune system traits and diseases2,3 The majority of these variants are non-coding and the underlying mechanisms are not full... |
ATRX regulates glial identity and the tumor microenvironment inIDH-mutant glioma
Babikir, Husam and Wang, Lin and Shamardani, Karin andCatalan, Francisca and Sudhir, Sweta and Aghi, Manish K. andRaleigh, David R. and Phillips, Joanna J. and Diaz, AaronA.
Background Recent single-cell transcriptomic studies report that IDH-mutant gliomas share a common hierarchy of cellular phenotypes, independent of genetic subtype. However, the genetic differences between IDH-mutant glioma subtypes are prognostic, predictive of response to chemotherapy, and correlate with distinct ... |
Phase separation drives aberrant chromatin looping and cancerdevelopment.
Ahn JH et al.
The development of cancer is intimately associated with genetic abnormalities that target proteins with intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs). In human haematological malignancies, recurrent chromosomal translocation of nucleoporin (NUP98 or NUP214) generates an aberrant chimera that invariably retains the nucleop... |
Genetic perturbation of PU.1 binding and chromatin looping at neutrophilenhancers associates with autoimmune disease.
Watt, Stephen et al.
Neutrophils play fundamental roles in innate immune response, shape adaptive immunity, and are a potentially causal cell type underpinning genetic associations with immune system traits and diseases. Here, we profile the binding of myeloid master regulator PU.1 in primary neutrophils across nearly a hundred voluntee... |
Fra-1 regulates its target genes via binding to remote enhancers withoutexerting major control on chromatin architecture in triple negative breastcancers.
Bejjani, Fabienne and Tolza, Claire and Boulanger, Mathias and Downes,Damien and Romero, Raphaël and Maqbool, Muhammad Ahmad and Zine ElAabidine, Amal and Andrau, Jean-Christophe and Lebre, Sophie and Brehelin,Laurent and Parrinello, Hughes and Rohmer,
The ubiquitous family of dimeric transcription factors AP-1 is made up of Fos and Jun family proteins. It has long been thought to operate principally at gene promoters and how it controls transcription is still ill-understood. The Fos family protein Fra-1 is overexpressed in triple negative breast cancers (TNBCs) w... |
Functional annotations of three domestic animal genomes provide vitalresources for comparative and agricultural research.
Kern C. et al.
Gene regulatory elements are central drivers of phenotypic variation and thus of critical importance towards understanding the genetics of complex traits. The Functional Annotation of Animal Genomes consortium was formed to collaboratively annotate the functional elements in animal genomes, starting with domesticate... |
STAG proteins promote cohesin ring loading at R-loops
Porter, H. et al.
Most studies of cohesin function consider the Stromalin Antigen (STAG/SA) proteins as core complex members given their ubiquitous interaction with the cohesin ring. Here, we provide functional data to support the notion that the SA subunit is not a mere passenger in this structure, but instead plays a key role in co... |
Environmental enrichment induces epigenomic and genome organization changesrelevant for cognitive function
Espeso-Gil, S. et al.
In early development, the environment triggers mnemonic epigenomic programs resulting in memory and learning experiences to confer cognitive phenotypes into adulthood. To uncover how environmental stimulation impacts the epigenome and genome organization, we used the paradigm of environmental enrichment (EE) in youn... |
Postoperative abdominal sepsis induces selective and persistent changes inCTCF binding within the MHC-II region of human monocytes.
Siegler B. et al.
BACKGROUND: Postoperative abdominal infections belong to the most common triggers of sepsis and septic shock in intensive care units worldwide. While monocytes play a central role in mediating the initial host response to infections, sepsis-induced immune dysregulation is characterized by a defective antigen present... |
Histone H3.3G34-Mutant Interneuron Progenitors Co-opt PDGFRA for Gliomagenesis.
Chen C. et al.
Histone H3.3 glycine 34 to arginine/valine (G34R/V) mutations drive deadly gliomas and show exquisite regional and temporal specificity, suggesting a developmental context permissive to their effects. Here we show that 50\% of G34R/V tumors (n = 95) bear activating PDGFRA mutations that display strong selection... |
Integrative Omics Analyses Reveal Epigenetic Memory in Diabetic Renal CellsRegulating Genes Associated With Kidney Dysfunction.
Bansal, A and Balasubramanian, S and Dhawan, S and Leung, A and Chen, Z andNatarajan, R
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a major complication of diabetes and the leading cause of end-stage renal failure. Epigenetics has been associated with metabolic memory, in which prior periods of hyperglycemia enhance the future risk of developing DKD despite subsequent glycemic control. To understand the mechanist... |
Preformed chromatin topology assists transcriptional robustness of during limb development.
Paliou C, Guckelberger P, Schöpflin R, Heinrich V, Esposito A, Chiariello AM, Bianco S, Annunziatella C, Helmuth J, Haas S, Jerković I, Brieske N, Wittler L, Timmermann B, Nicodemi M, Vingron M, Mundlos S, Andrey G
Long-range gene regulation involves physical proximity between enhancers and promoters to generate precise patterns of gene expression in space and time. However, in some cases, proximity coincides with gene activation, whereas, in others, preformed topologies already exist before activation. In this study, we inves... |
High-throughput ChIPmentation: freely scalable, single day ChIPseq data generation from very low cell-numbers.
Gustafsson C, De Paepe A, Schmidl C, Månsson R
BACKGROUND: Chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled to sequencing (ChIP-seq) is widely used to map histone modifications and transcription factor binding on a genome-wide level. RESULTS: We present high-throughput ChIPmentation (HT-ChIPmentation) that eliminates the need for DNA purification prior to library amplifica... |
DNA methylation signatures follow preformed chromatin compartments in cardiac myocytes
Nothjunge S. et al.
Storage of chromatin in restricted nuclear space requires dense packing while ensuring DNA accessibility. Thus, different layers of chromatin organization and epigenetic control mechanisms exist. Genome-wide chromatin interaction maps revealed large interaction domains (TADs) and higher order A and B compartments, r... |
High Resolution Mapping of Chromatin Conformation in Cardiac Myocytes Reveals Structural Remodeling of the Epigenome in Heart Failure
Rosa-Garrido M. et al.
Background -Cardiovascular disease is associated with epigenomic changes in the heart, however the endogenous structure of cardiac myocyte chromatin has never been determined. Methods -To investigate the mechanisms of epigenomic function in the heart, genome-wide chromatin conformation capture (Hi-C) and DNA sequenc... |
Platelet function is modified by common sequence variation in megakaryocyte super enhancers
Petersen R. et al.
Linking non-coding genetic variants associated with the risk of diseases or disease-relevant traits to target genes is a crucial step to realize GWAS potential in the introduction of precision medicine. Here we set out to determine the mechanisms underpinning variant association with platelet quantitative traits usi... |
Loss of cohesin complex components STAG2 or STAG3 confers resistance to BRAF inhibition in melanoma
Shen CH et al.
The protein kinase B-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase (BRAF) is an oncogenic driver and therapeutic target in melanoma. Inhibitors of BRAF (BRAFi) have shown high response rates and extended survival in patients with melanoma who bear tumors that express mutations encoding BRAF proteins mutant at Val600, ... |
BET protein inhibition sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomidetreatment by attenuating MGMT expression
Tancredi A. et al.
Bromodomain and extra-terminal tail (BET) proteins have been identified as potential epigenetic targets in cancer, including glioblastoma. These epigenetic modifiers link the histone code to gene transcription that can be disrupted with small molecule BET inhibitors (BETi). With the aim of developing rational combin... |