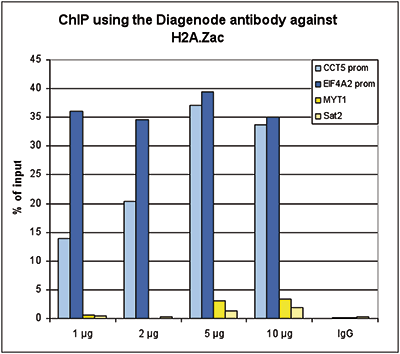
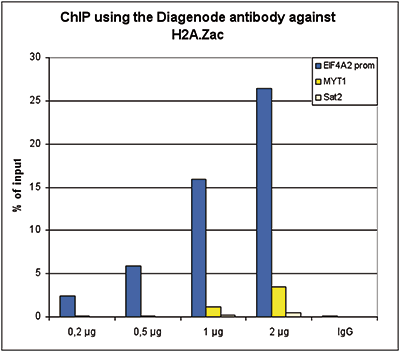
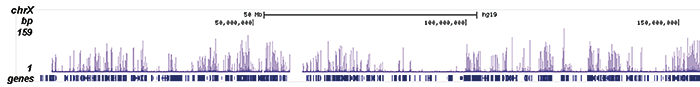
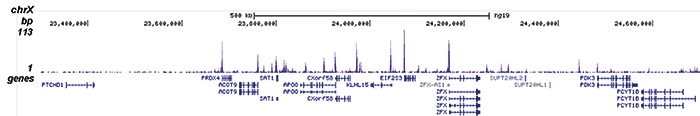
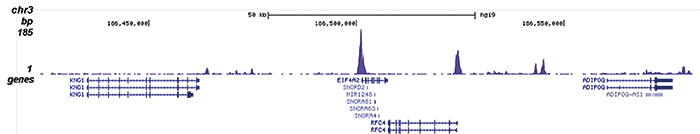
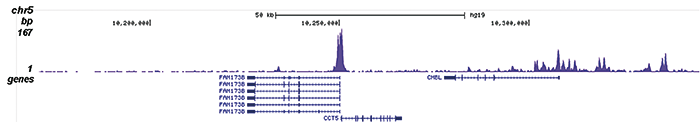
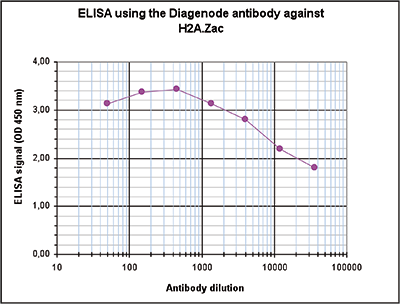
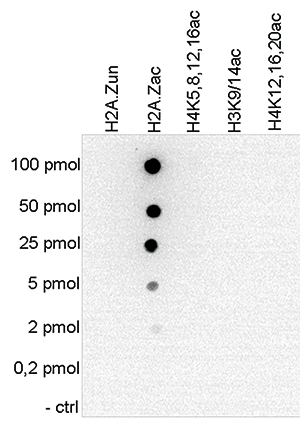
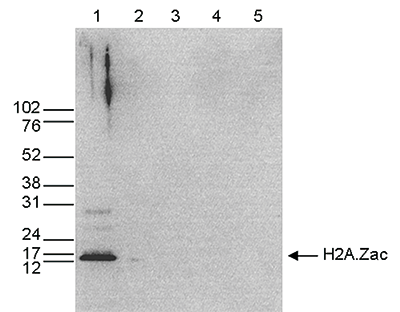
Histones are the main constituents of the protein part of chromosomes of eukaryotic cells. They are rich in the amino acids arginine and lysine and have been greatly conserved during evolution. Histones pack the DNA into tight masses of chromatin. Two core histones of each class H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 assemble and are wrapped by 146 base pairs of DNA to form one octameric nucleosome. Histone tails undergo numerous post-translational modifications, which either directly or indirectly alter chromatin structure to facilitate transcriptional activation or repression or other nuclear processes. In addition to the genetic code, combinations of the different histone modifications reveal the so-called “histone code”. Histone methylation and demethylation is dynamically regulated by respectively histone methyl transferases and histone demethylases. Acetylation of the histone H2A variant H2A.Z is associated with the promoters of active genes.