- Universal compatiblity with a wide variety of plant species
- Optimized and complete kit for start-to-finish plant ChIP
- Validated for the high throughput IP-Star® Automated System
Successful ChIP-seq experiments for a variety of plants
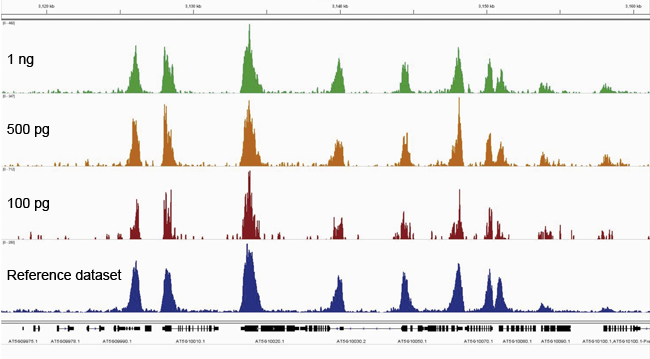
Figure 1. ChIP-seq was performed on Arabidopsis thaliana (Col-0) seedlings using our Premium H3K4me3 ChIP-seq grade antibody. Libraries were prepared with our MicroPlex Library Preparation™ kit from 1 ng (green), 500 pg (orange) and 100 pg (red) IP'd DNA and sequenced on an Illumina® HiSeq 2500. The enrichment in blue represents a public dataset (NCBI GEO Dataset GSM1193621) that we used as an external reference. Enrichments along a wide region of chromosome 5 are uniform regardless of the starting material amount for the preparation of the library.
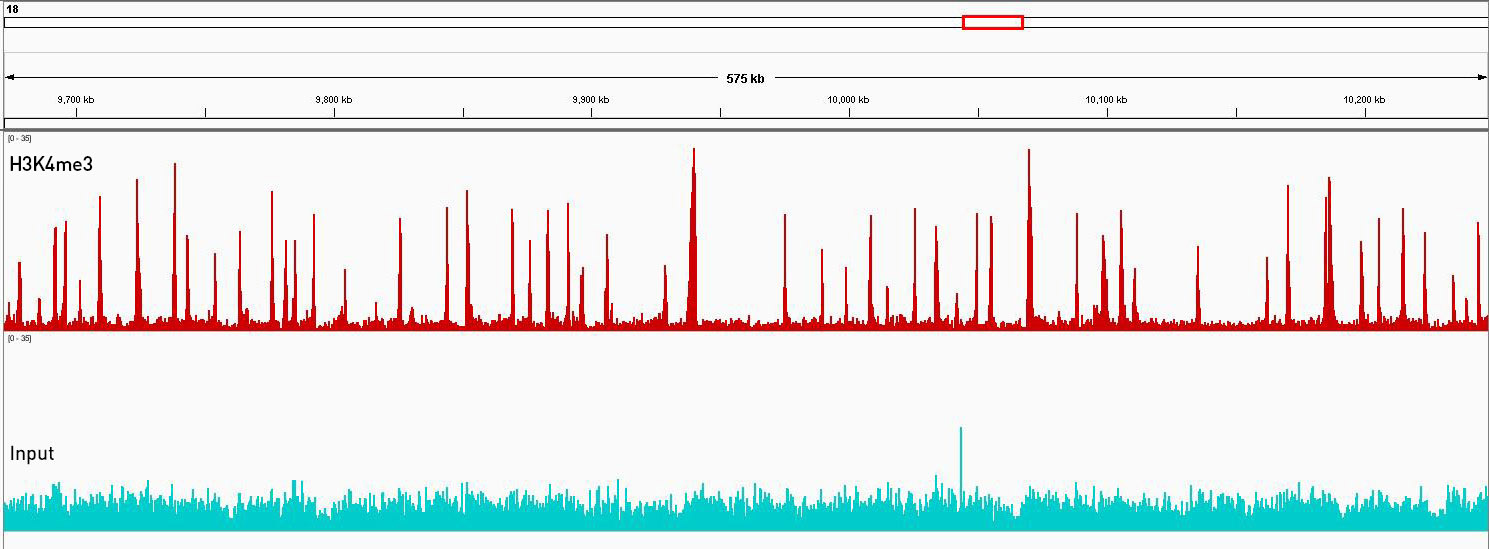
Figure 3. ChIP-seq was performed on Populus trichocarpa stem differenciating xylem using the Premium H3K4me3 ChIP-seq grade antibody. Libraries were prepared with the MicroPlex Library Preparation™ kit from 1 ng of immunoprecipitated DNA using the Universal Plant ChIP-seq kit and 1 ng of Input and sequenced on an Illumina® HiSeq 2500. The enrichment in green represents the input and is considered as the background enrichment. The profile in red represents enrichments along a wide region of scaffold 18. Using the same scale, the peaks of the immunoprecipitated samples are significantly higher than those of the input, indicating a successful ChIP-seq experiment.
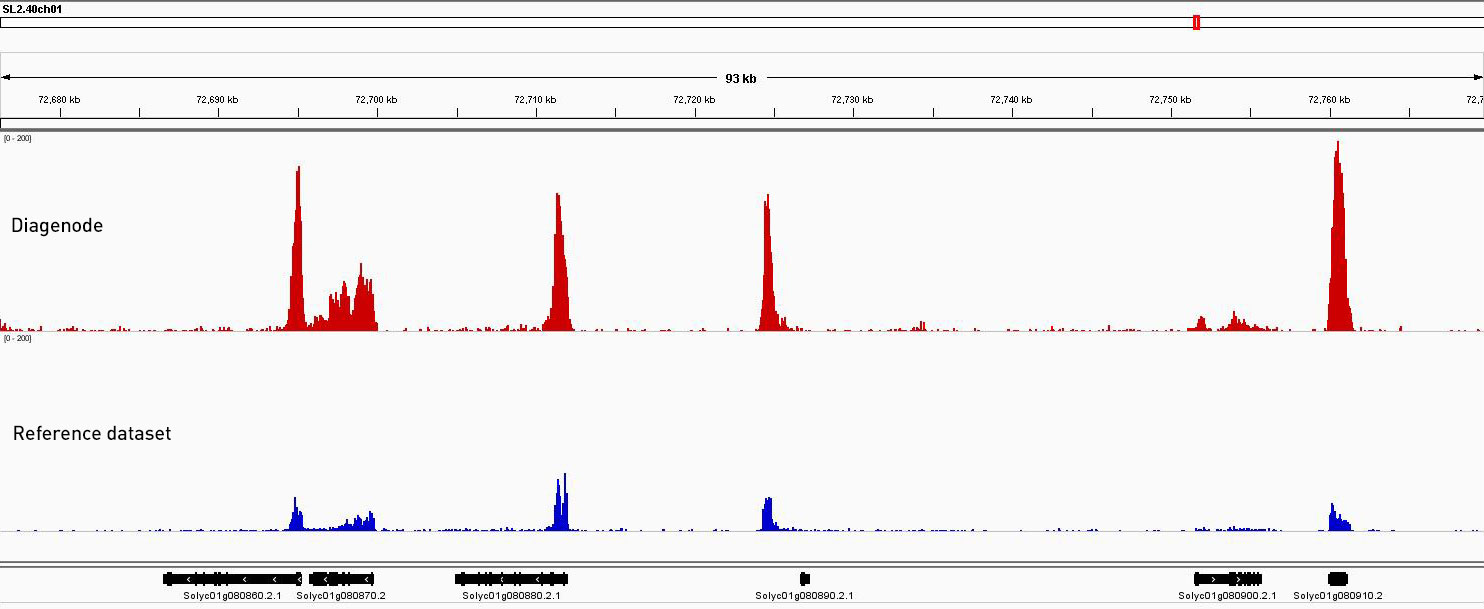
Figure 2. ChIP-seq was performed on Solanum lycopersicum cv. Micro-Tom young leaves using our Premium H3K4me3 ChIP-seq grade antibody. Librairies were prepared with our MicroPlex Librairy Preparation™ kit from 750 pg of immunoprecipitated DNA using the Universal Plant ChIP-seq kit (red) and sequenced on an Illumina® HiSeq 2500. The enrichment in blue represents a dataset obtained from Nguyen et al. 2014 that we used as an external reference. Enrichments are higher and consistent with the reference data along a wide region of chromosome 1.
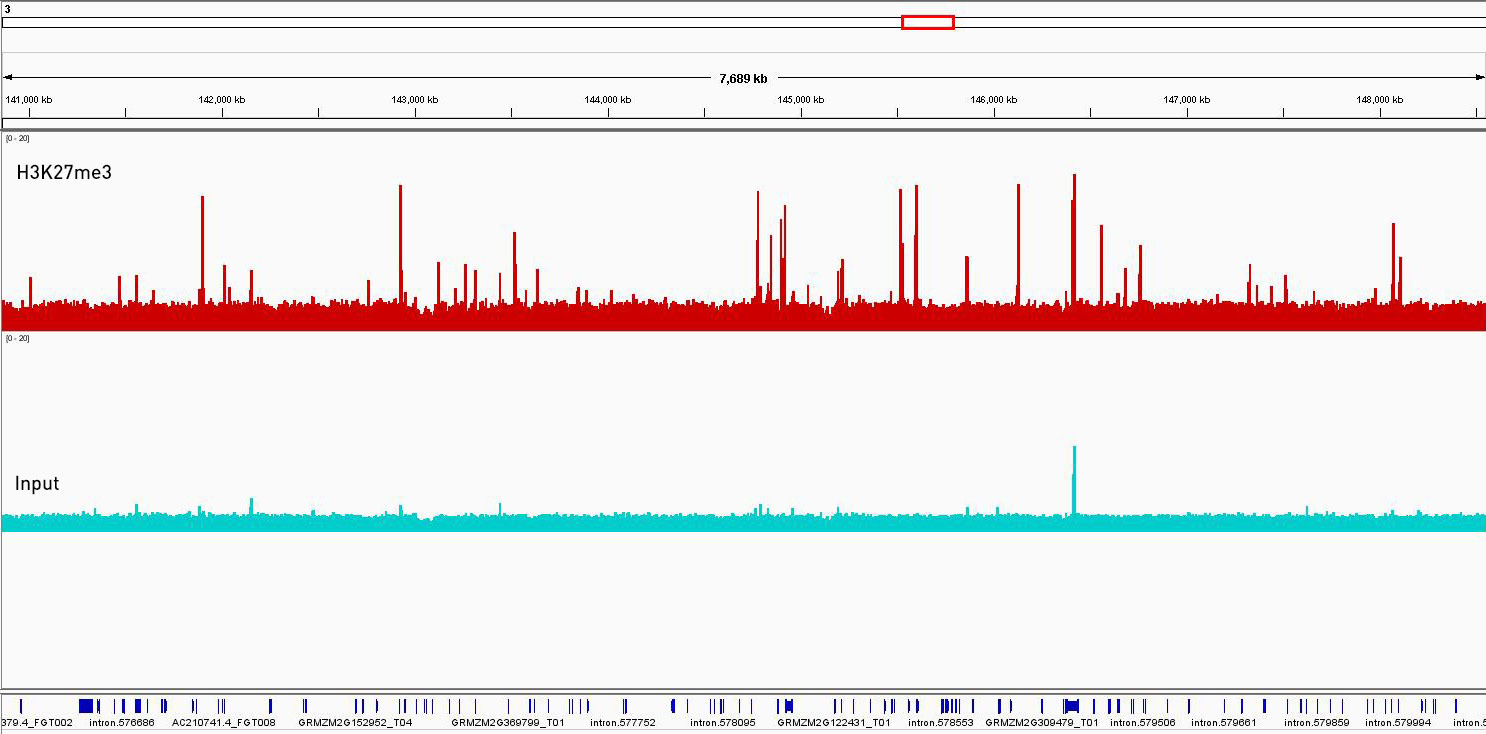
Figure 4. ChIP-seq was performed on Zea mays cv. B73 inner stem using our Premium H3K27me3 ChIP-seq grade antibody. Librairies were prepared with our MicroPlex Librairy Preparation™ kit from 1 ng of immunoprecipitated DNA using the Universal Plant ChIP-seq kit and 1 ng of Input and sequenced on an Illumina® HiSeq 2500. The enrichment in green represents the Input and is considered as the background enrichment. The enrichment in red represents enrichments along a wide region of chromosome 3. Using the same scale, the peaks of the immunoprecipitated sample are significantly higher than those of the input, indicating a successful ChIP-seq experiment.

